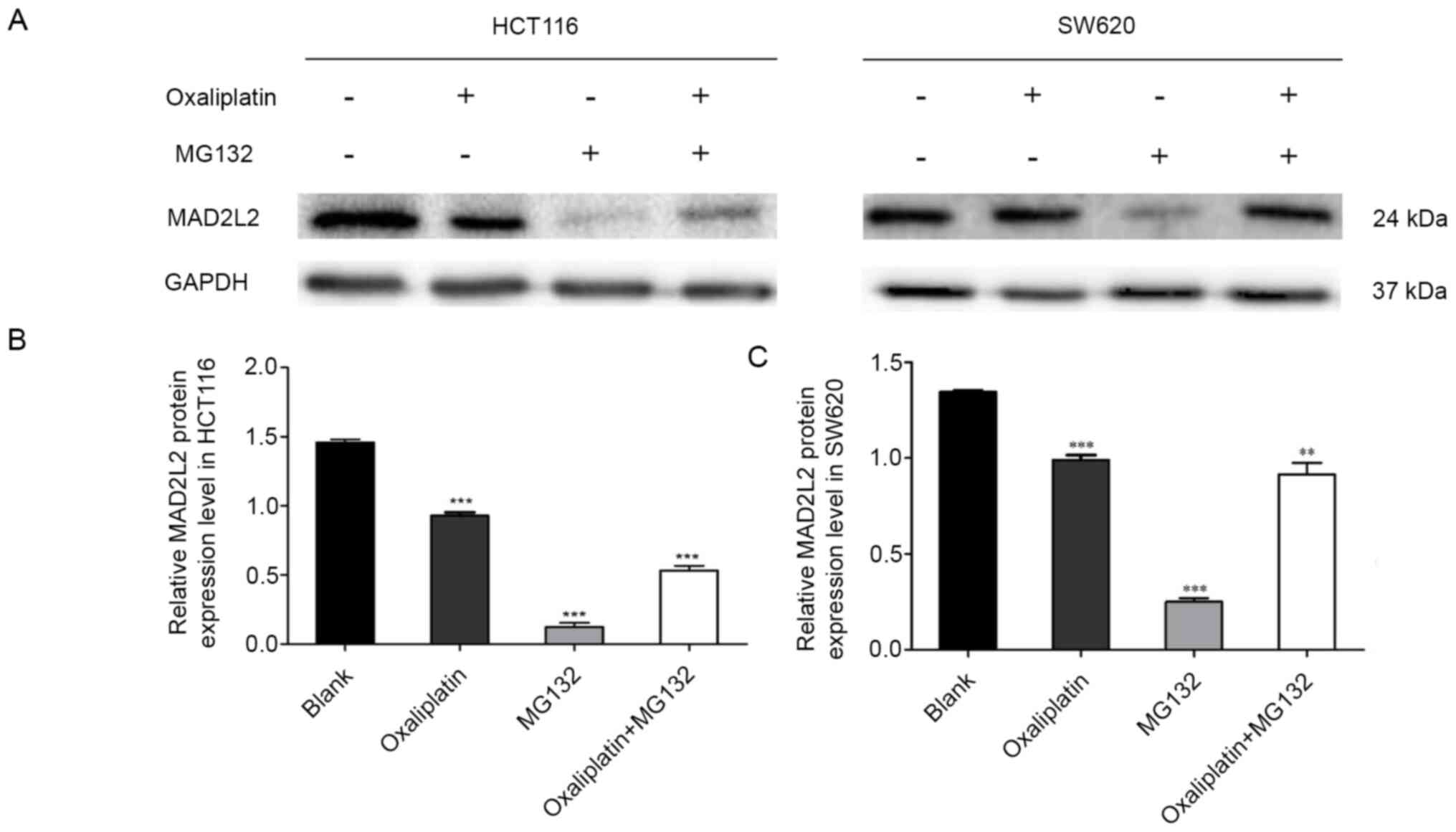
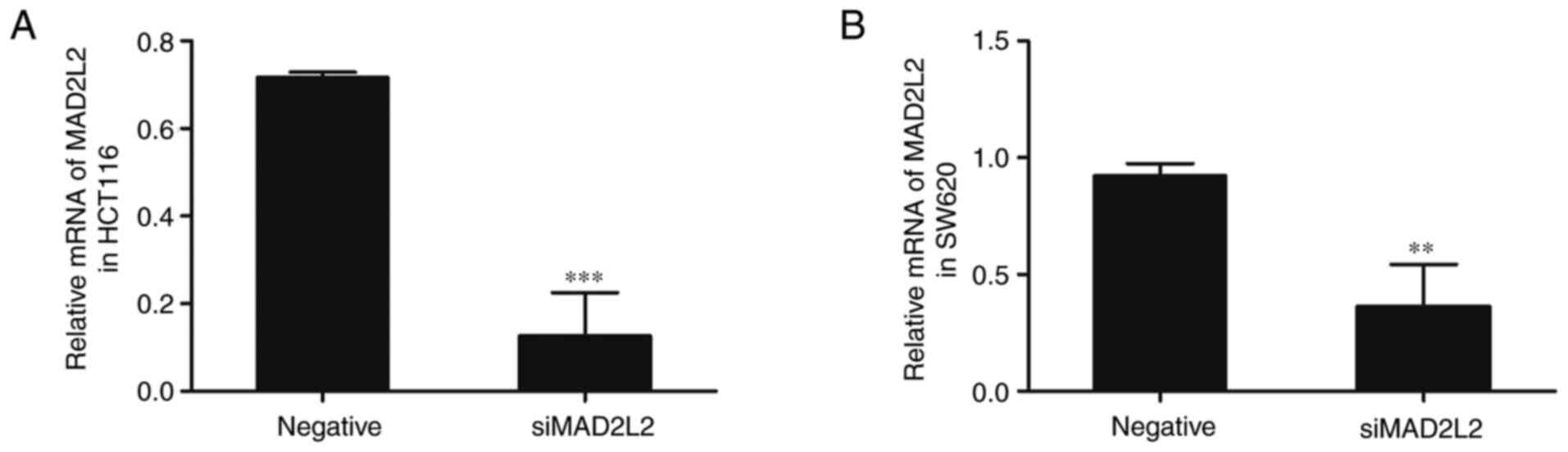
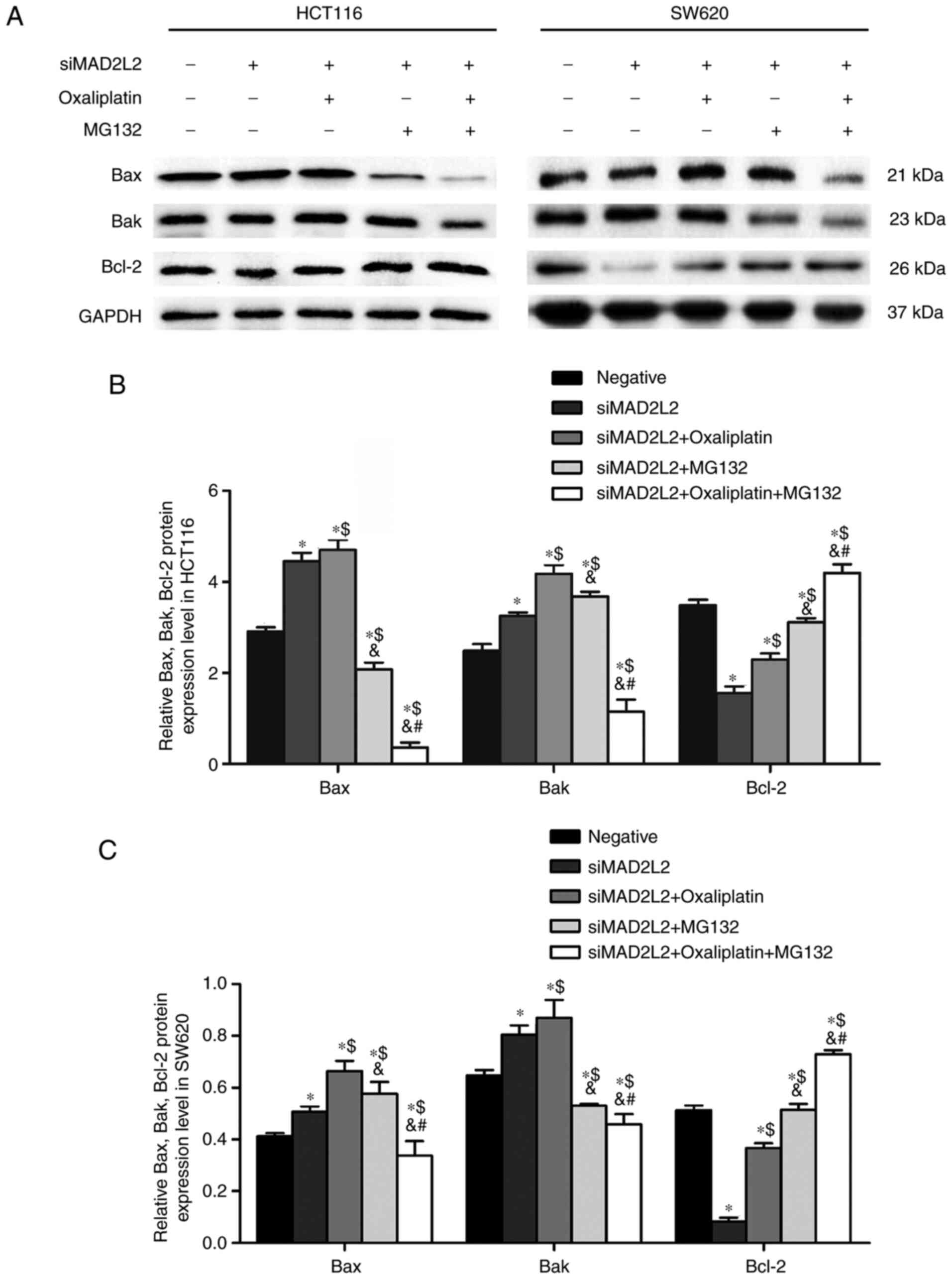
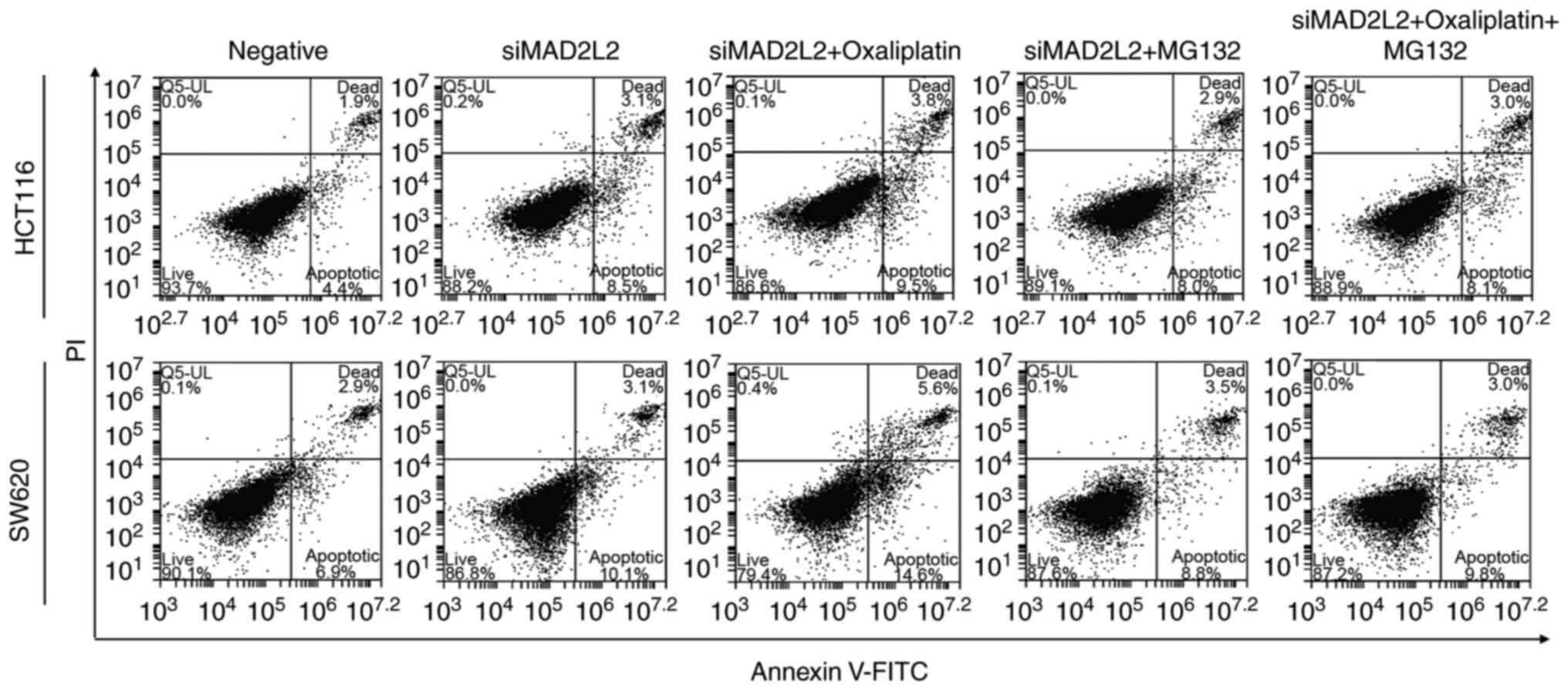
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 70:7–30. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Crowley LC, Marfell BJ and Waterhouse NJ:
Detection of DNA fragmentation in apoptotic cells by TUNEL. Cold
Spring Harb Protoc. 20162016.
|
|
3
|
Zhou J, Zheng R, Zhang S, Zeng H, Wang S,
Chen R, Sun K, Li M, Gu J, Zhuang G and Wei W: Colorectal cancer
burden and trends: Comparison between China and major burden
countries in the world. Chin J Cancer Res. 33:1–10. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
National Health Commission Of The People's
Republic Of China, . National guidelines for diagnosis and
treatment of colorectal cancer 2020 in China (English version).
Chin J Cancer Res. 32:415–445. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sharma G, Anghore D, Khare R and Rawal RK:
Oxaliplatin for colorectal cancer therapy: A review. Clin Cancer
Drugs. 5:13–27. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Brown A, Kumar S and Tchounwou PB:
Cisplatin-based chemotherapy of human cancers. J Cancer Sci Ther.
11:972019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
McQuade RM, Stojanovska V, Bornstein JC
and Nurgali K: Colorectal cancer chemotherapy: The evolution of
treatment and new approaches. Curr Med Chemistry. 24:1537–1557.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sigel A, Riddell IA, Lippard SJ, Sigel H,
Freisinger E and Sigel RKO: Cisplatin and oxaliplatin: Our current
understanding of their actions. 1–42. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ma X, Tang TS and Guo C: Regulation of
translesion DNA synthesis in mammalian cells. Environ Mol Mutagen.
61:680–692. 2020. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Shanbhag V, Sachdev S, Flores JA, Modak MJ
and Singh K: Family A and B DNA polymerases in cancer:
Opportunities for therapeutic interventions. Biology (Basel).
7:52018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sharma S, Shah NA, Joiner AM, Roberts KH
and Canman CE: DNA polymerase zeta is a major determinant of
resistance to platinum-based chemotherapeutic agents. Mol
Pharmacol. 81:778–787. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jiang HG, Chen P, Su JY, Wu M, Qian H,
Wang Y and Li J: Knockdown of REV3 synergizes with ATR inhibition
to promote apoptosis induced by cisplatin in lung cancer cells. J
Cell Physiol. 232:3433–3443. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Malik R, Kopylov M, Gomez-Llorente Y, Jain
R, Johnson RE, Prakash L, Prakash S, Ubarretxena-Belandia I and
Aggarwal AK: Structure and mechanism of B-family DNA polymerase
zeta specialized for translesion DNA synthesis. Nat Struct Mol
Biol. 27:913–924. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Washington MT and Gildenberg MS: Structure
of DNA polymerase ζ: Capturing the getaway driver. Nat Struct Mol
Biol. 27:1–2. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Suzuki T, Sassa A, Gruz P, Gupta RC,
Johnson F, Adachi N and Nohmi T: Error-prone bypass patch by a
low-fidelity variant of DNA polymerase zeta in human cells. DNA
Repair (Amst). 100:1030522021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gaczynska M and Osmulski PA: Targeting
protein-protein interactions in the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway.
Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol. 110:123–165. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bi W, Zhu L, Zeng Z, Jing X, Liang Y, Guo
L, Shi Q, Xu A and Tao E: Investigations into the role of 26S
proteasome non-ATPase regulatory subunit 13 in neuroinflammation.
Neuroimmunomodulation. 21:331–337. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bard JAM, Goodall EA, Greene ER, Jonsson
E, Dong KC and Martin A: Structure and function of the 26S
proteasome. Ann Rev Biochem. 87:697–724. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chen X, Htet ZM, Lopez-Alfonzo E, Martin A
and Walters KJ: Proteasome interaction with ubiquitinated
substrates: From mechanisms to therapies. FEBS J. Nov 19–2020.(Epub
ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tu Y, Chen C, Pan J, Xu J, Zhou ZG and
Wang CY: The Ubiquitin Proteasome Pathway (UPP) in the regulation
of cell cycle control and DNA damage repair and its implication in
tumorigenesis. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 5:726–738. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sakai W, Yuasa-Sunagawa M, Kusakabe M,
Kishimoto A, Matsui T, Kaneko Y, Akagi JI, Huyghe N, Ikura M, Ikura
T, et al: Functional impacts of the ubiquitin-proteasome system on
DNA damage recognition in global genome nucleotide excision repair.
Sci Rep. 10:197042020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ramadan K and Meerang M:
Degradation-linked ubiquitin signal and proteasome are integral
components of DNA double strand break repair: New perspectives for
anti-cancer therapy. FEBS Lett. 585:2868–2875. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Rizzo AA, Vassel FM, Chatterjee N, D'Souza
S, Li Y, Hao B, Hemann MT, Walker GC and Korzhnev DM: Rev7
dimerization is important for assembly and function of the
Rev1/Polζ translesion synthesis complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
115:E8191–E8200. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Feng L, Wei W, Heng Z, Yantao H and Chunbo
W: Knockdown of REV7 inhibits breast cancer cell migration and
invasion. Oncol Res. 24:315–325. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Rosenberg SC and Corbett KD: The
multifaceted roles of the HORMA domain in cellular signaling. J
Cell Biol. 211:745–755. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hara K, Taharazako S, Ikeda M, Fujita H,
Mikami Y, Kikuchi S, Hishiki A, Yokoyama H, Ishikawa Y, Kanno SI,
et al: Dynamic feature of mitotic arrest deficient 2-like protein 2
(MAD2L2) and structural basis for its interaction with chromosome
alignment-maintaining phosphoprotein (CAMP). J Biol Chem.
292:17658–17667. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Sanders MA, Haynes B, Nangia-Makker P,
Polin LA and Shekhar MP: Pharmacological targeting of RAD6
enzyme-mediated translesion synthesis overcomes resistance to
platinum-based drugs. J Biol Chemistry. 292:10347–10363. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jantrapirom S, Piccolo LL, Pruksakorn D,
Potikanond S and Nimlamool W: Ubiquilin networking in cancers.
Cancers. 12:1206–1586. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Leestemaker Y and Ovaa H: Tools to
investigate the ubiquitin proteasome system. Drug discovery today.
Technologies. 26:25–31. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wehmer M, Rudack T, Beck F, Aufderheide A,
Pfeifer G, Plitzko JM, Förster F, Schulten K, Baumeister W and
Sakata E: Structural insights into the functional cycle of the
ATPase module of the 26S proteasome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
114:1305–1310. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Rizzo AA and Korzhnev DM: The Rev1-Polζ
translesion synthesis mutasome: Structure, interactions and
inhibition. Enzymes. 45:139–181. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Fernandes E, Fonseca TG, Carriço T, Mestre
N, Tavares Á and Bebianno MJ: Cytotoxic responses of the anticancer
drug cyclophosphamide in the mussel Mytilus galloprovincialis and
comparative sensitivity with human cells lines. Chemosphere.
261:1276782020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kanao R and Masutani C: Regulation of DNA
damage tolerance in mammalian cells by post-translational
modifications of PCNA. Mutat Res. 803-805:82–88. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lau WCY, Li Y, Zhang Q and Huen MSY:
Molecular architecture of the Ub-PCNA/Pol η complex bound to DNA.
Sci Rep. 5:157592015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Quinet A, Lerner LK, Martins DJ and Menck
CFM: Filling gaps in translesion DNA synthesis in human cells.
Mutat Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen. 836:127–142. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
An H, Yang L, Wang C, Gan Z, Gu H, Zhang
T, Huang X, Liu Y, Li Y, Chang SJ, et al: Interactome analysis
reveals a novel role for RAD6 in the regulation of proteasome
activity and localization in response to DNA damage. Mol Cell Biol.
37:e00419–e00416. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Masuda Y and Masutani C: Spatiotemporal
regulation of PCNA ubiquitination in damage tolerance pathways.
Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 54:418–442. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|