|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J and
Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 61:69–90.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
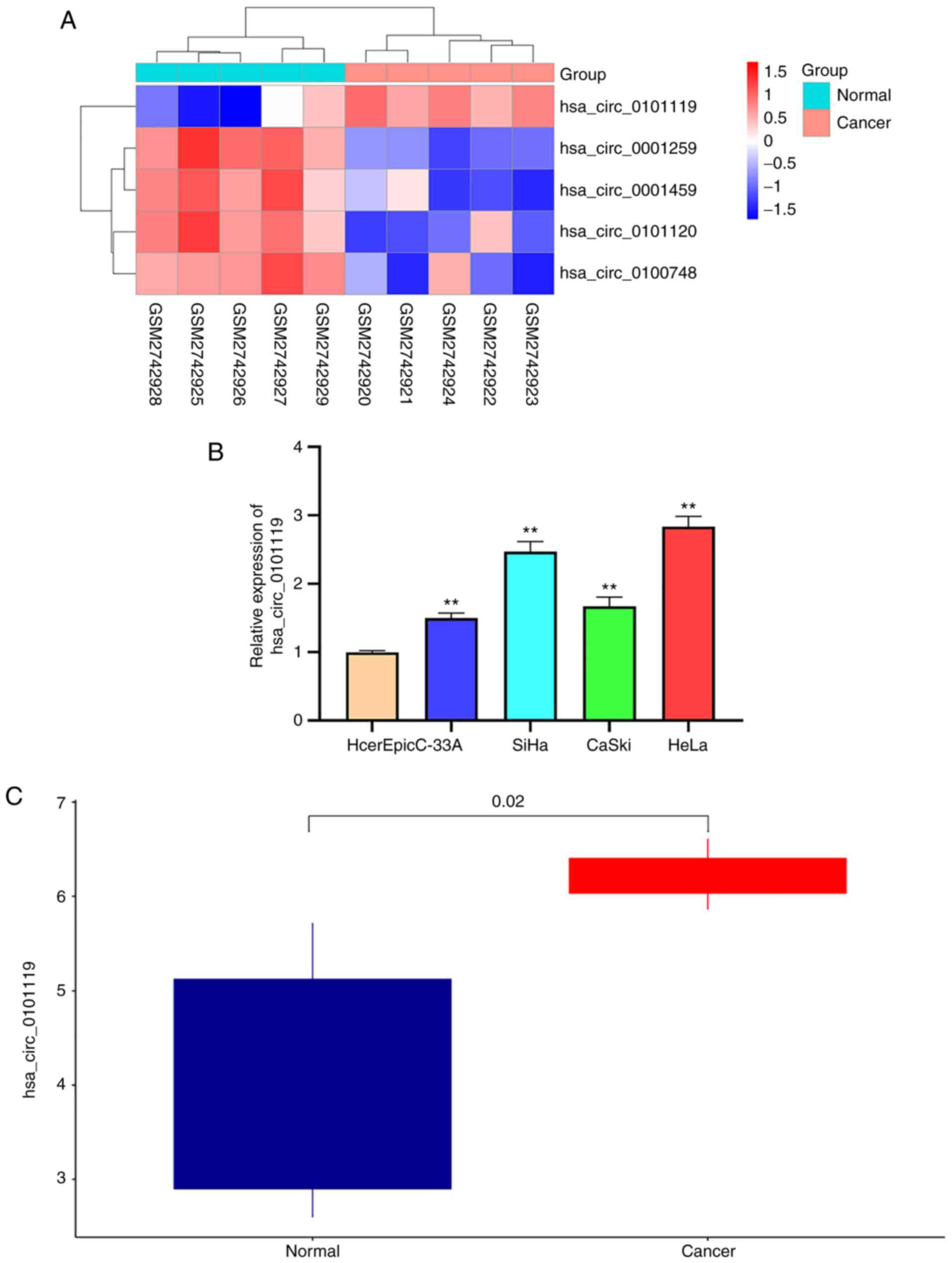
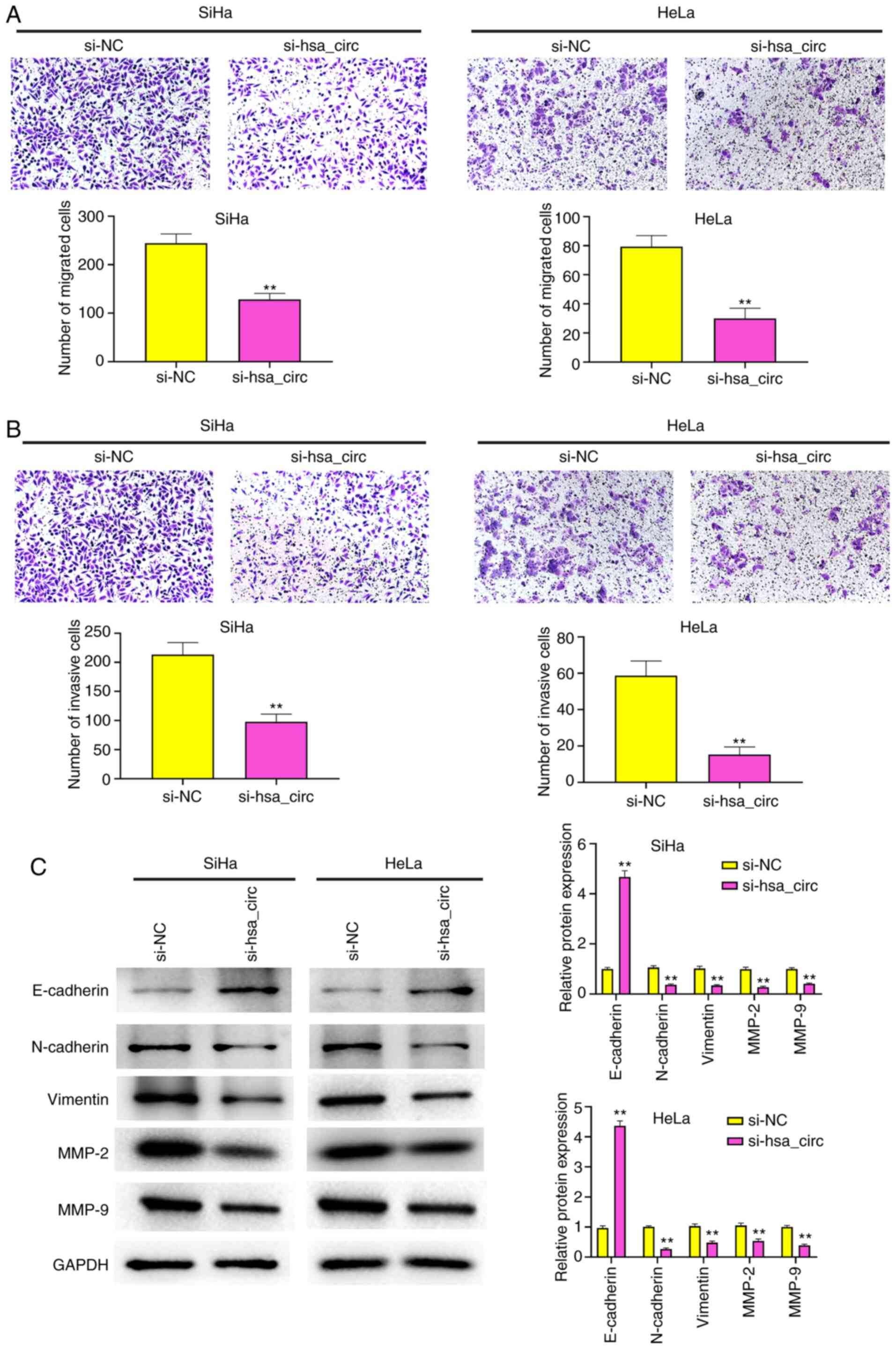
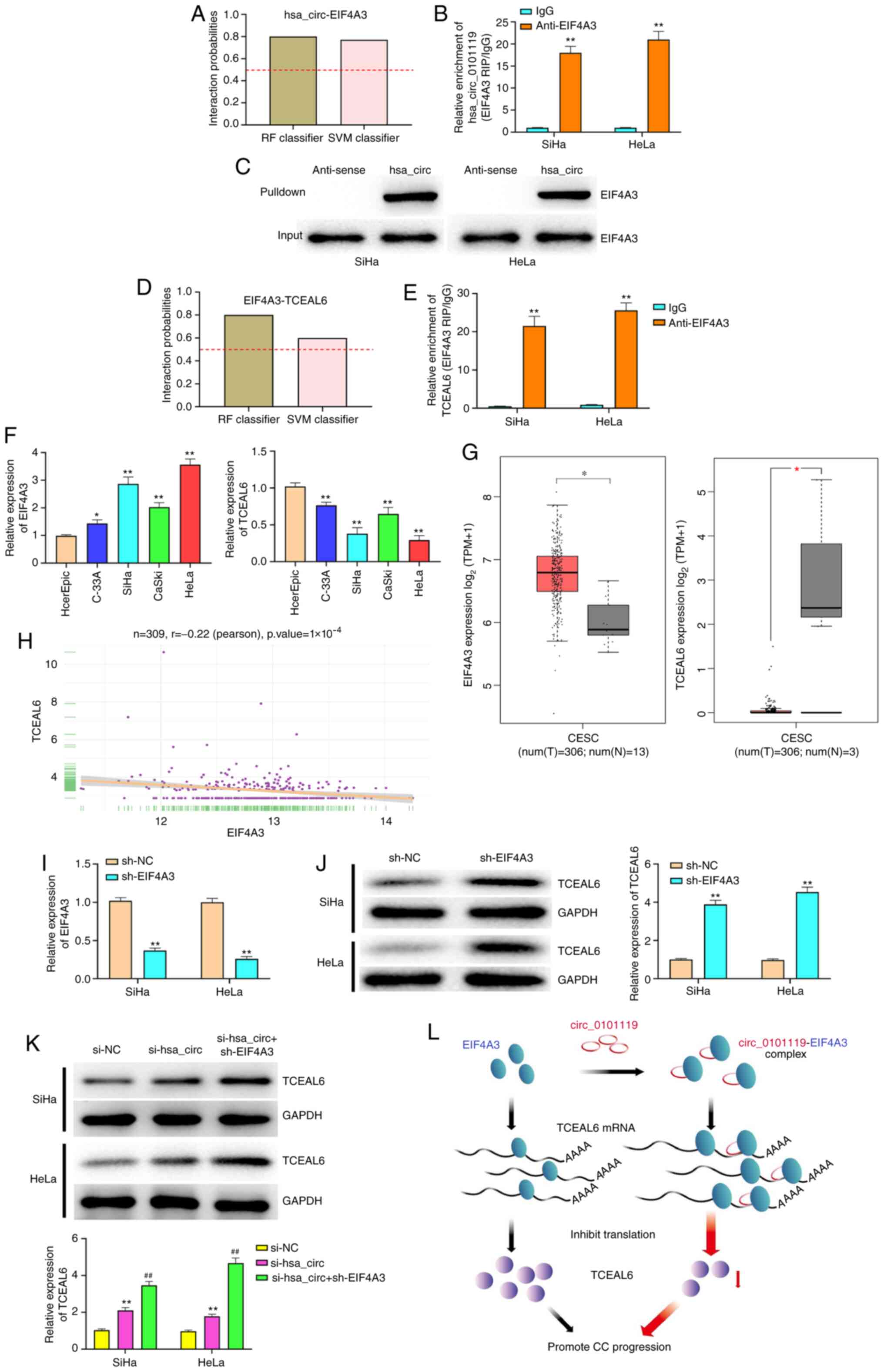
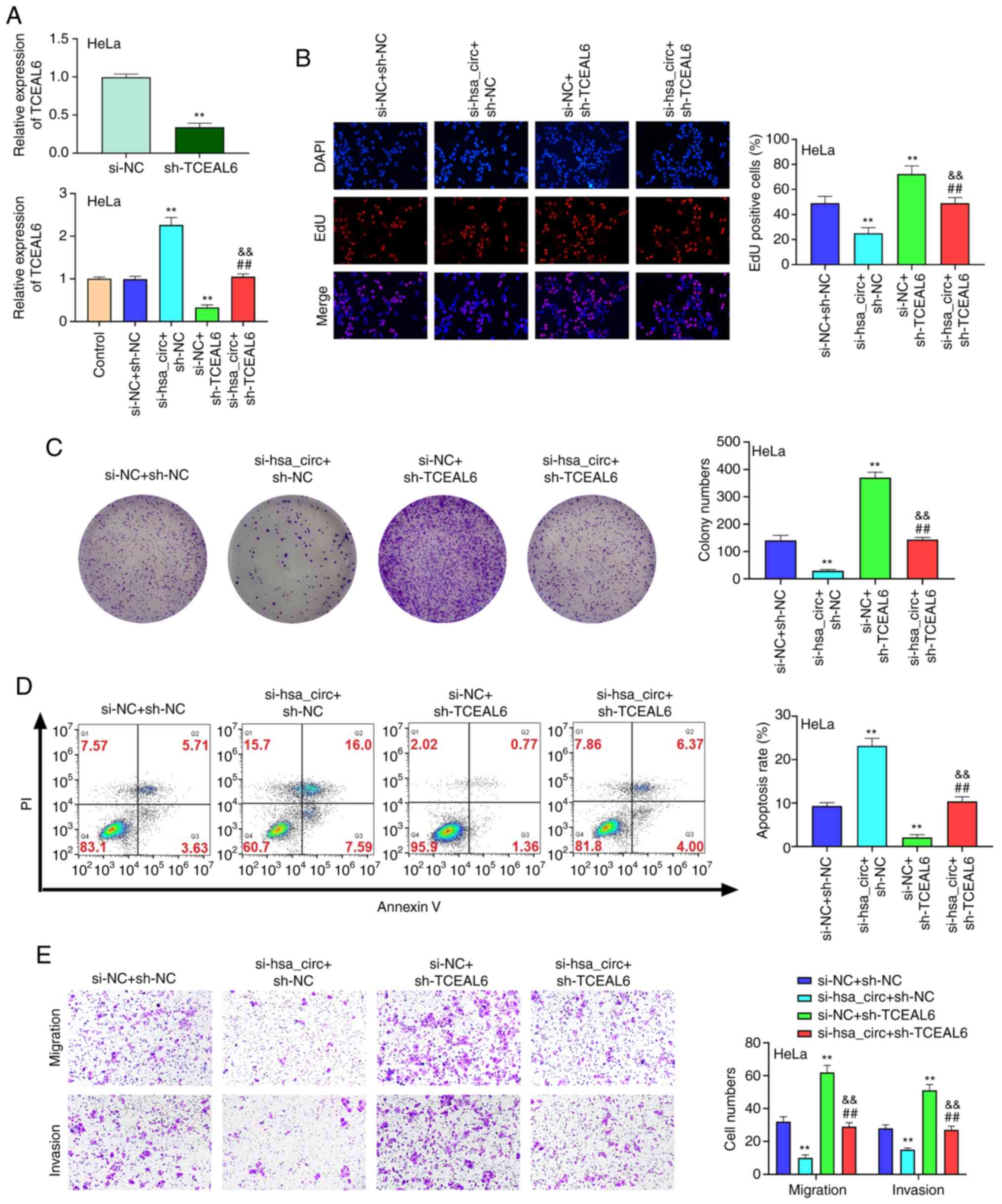
statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 69:7–34. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kessler TA: Cervical cancer: Prevention
and early detection. Semin Oncol Nurs. 33:172–183. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wright JD, Chen L, Tergas AI, Burke WM,
Hou JY, Neugut AI, Ananth CV and Hershman DL: Population-level
trends in relative survival for cervical cancer. Am J Obstet
Gynecol. 213:670.e1–e7. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hentze MW and Preiss T: Circular RNAs:
Splicing's enigma variations. EMBO J. 32:923–925. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Han B, Chao J and Yao H: Circular RNA and
its mechanisms in disease: From the bench to the clinic. Pharmacol
Ther. 187:31–44. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Salzman J: Circular RNA expression: Its
potential regulation and function. Trends Genet. 32:309–316. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ebbesen KK, Kjems J and Hansen TB:
Circular RNAs: Identification, biogenesis and function. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1859:163–168. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cai H, Zhang P, Xu M, Yan L, Liu N and Wu
X: Circular RNA hsa_circ_0000263 participates in cervical cancer
development by regulating target gene of miR-150-5p. J Cell
Physiol. 234:11391–11400. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ou R, Lv J, Zhang Q, Lin F, Zhu L, Huang
F, Li X, Li T, Zhao L, Ren Y and Xu Y: circAMOTL1 Motivates AMOTL1
expression to facilitate cervical cancer growth. Mol Ther Nucleic
Acids. 19:50–60. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang YM, Huang LM, Li DR, Shao JH, Xiong
SL, Wang CM and Lu SM: Hsa_circ_0101996 combined with
hsa_circ_0101119 in peripheral whole blood can serve as the
potential biomarkers for human cervical squamous cell carcinoma.
Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 10:11924–11931. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mao Y, Zhang L and Li Y: circEIF4G2
modulates the malignant features of cervical cancer via the
miR-218/HOXA1 pathway. Mol Med Rep. 19:3714–3722. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Song T, Xu A, Zhang Z, Gao F, Zhao L, Chen
X, Gao J and Kong X: CircRNA hsa_circRNA_101996 increases cervical
cancer proliferation and invasion through activating TPX2
expression by restraining miR-8075. J Cell Physiol.
234:14296–14305. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jeck WR and Sharpless NE: Detecting and
characterizing circular RNAs. Nat Biotechnol. 32:453–461. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
He JH, Li YG, Han ZP, Zhou JB, Chen WM, Lv
YB, He ML, Zuo JD and Zheng L: The CircRNA-ACAP2/Hsa-miR-21-5p/
tiam1 regulatory feedback circuit affects the proliferation,
migration, and invasion of colon cancer SW480 cells. Cell Physiol
Biochem. 49:1539–1550. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chaichian S, Shafabakhsh R, Mirhashemi SM,
Moazzami B and Asemi Z: Circular RNAs: A novel biomarker for
cervical cancer. J Cell Physiol. 235:718–724. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hauer C, Curk T, Anders S, Schwarzl T,
Alleaume AM, Sieber J, Hollerer I, Bhuvanagiri M, Huber W, Hentze
MW and Kulozik AE: Improved binding site assignment by
high-resolution mapping of RNA-protein interactions using iCLIP.
Nat Commun. 6:79212015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lin Y, Zhang J, Cai J, Liang R, Chen G,
Qin G, Han X, Yuan C, Liu Z, Li Y, et al: Systematic analysis of
gene expression alteration and co-expression network of eukaryotic
initiation factor 4A-3 in CANcer. J Cancer. 9:4568–4577. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yeh CH and Shatkin AJ: A HeLa-cell-encoded
p21 is homologous to transcription elongation factor SII. Gene.
143:285–287. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yeh CH and Shatkin AJ: Down-regulation of
rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat promoter activity by a hela
cell basic protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 91:11002–11006. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Pillutla RC, Shimamoto A, Furuichi Y and
Shatkin AJ: Genomic structure and chromosomal localization of
TCEAL1, a human gene encoding the nuclear phosphoprotein p21/SIIR.
Genomics. 56:217–220. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Huang CY, Chen YM, Zhao JJ, Chen YB, Jiang
SS, Yan SM, Zhao BW, Pan K, Wang DD, Lv L, et al: Decreased
expression of transcription elongation factor A-like 7 is
associated with gastric adenocarcinoma prognosis. PLoS One.
8:e546712013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Orhan C, Bulut P, Dalay N, Ersen E and
Buyru N: Downregulation of TCEAL7 expression induces CCND1
expression in non-small cell lung cancer. Mol Biol Rep.
46:5251–5256. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chien J, Staub J, Avula R, Zhang H, Liu W,
Hartmann LC, Kaufmann SH, Smith DI and Shridhar V: Epigenetic
silencing of TCEAL7 (Bex4) in ovarian cancer. Oncogene.
24:5089–5100. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Biewenga P, Buist MR, Moerland PD, Ver
Loren van Themaat E, van Kampen AH, ten Kate FJ and Baas F: Gene
expression in early stage cervical cancer. Gynecol Oncol.
108:520–526. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jiao J, Zhang T, Jiao X, Huang T, Zhao L,
Ma D and Cui B: hsa_circ_0000745 promotes cervical cancer by
increasing cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. J Cell
Physiol. 235:1287–1295. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Roomi MW, Monterrey JC, Kalinovsky T, Rath
M and Niedzwiecki A: Inhibition of invasion and MMPs by a nutrient
mixture in human cancer cell lines: A correlation study. Ex Oncol.
32:243–248. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Qureshi R, Arora H and Rizvi MA: EMT in
cervical cancer: Its role in tumour progression and response to
therapy. Cancer Lett. 356:321–331. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J,
Lortet-Tieulent J and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA
Cancer J Clin. 65:87–108. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Denny L: Cervical cancer: Prevention and
treatment. Discov Med. 14:125–131. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Dragomir M and Calin GA: Circular RNAs in
cancer-lessons learned from microRNAs. Front Oncol. 8:1792018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Li M, Ding W, Sun T, Tariq MA, Xu T, Li P
and Wang J: Biogenesis of circular RNAs and their roles in
cardiovascular development and pathology. FEBS J. 285:220–232.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zong L, Sun Q, Zhang H, Chen Z, Deng Y, Li
D and Zhang L: Increased expression of circRNA_102231 in lung
cancer and its clinical significance. Biomed Pharmacother.
102:639–644. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhang J, Zhao X, Zheng X and Li F:
Circular RNA hsa_circ_0023404 exerts an oncogenic role in cervical
cancer through regulating miR-136/TFCP2/YAP pathway. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 501:428–433. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Hu C, Wang Y, Li A, Zhang J, Xue F and Zhu
L: Overexpressed circ_0067934 acts as an oncogene to facilitate
cervical cancer progression via the miR-545/EIF3C axis. J Cell
Physiol. 234:9225–9232. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang J, Li H and Liang Z: circ-MYBL2
serves as a sponge for miR-361-3p promoting cervical cancer cells
proliferation and invasion. Onco Targets Ther. 12:9957–9964. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Chen R, Mao L, Shi R, Wang W and Cheng J:
circRNA MYLK accelerates cervical cancer via Up-Regulation of RHEB
and activation of mTOR signaling. Cancer Manag Res. 12:3611–3621.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wang Y, Wang L, Wang W and Guo X:
Overexpression of circular RNA hsa_circ_0001038 promotes cervical
cancer cell progression by acting as a ceRNA for miR-337-3p to
regulate cyclin-M3 and metastasis-associated in colon cancer 1
expression. Gene. 733:1442732020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Panda AC, Abdelmohsen K, Martindale JL, Di
Germanio C, Yang X, Grammatikakis I, Noh JH, Zhang Y, Lehrmann E,
Dudekula DB, et al: Novel RNA-binding activity of MYF5 enhances
Ccnd1/Cyclin D1 mRNA translation during myogenesis. Nucleic Acids
Res. 44:2393–2408. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Mazloomian A, Araki S, Ohori M, El-Naggar
AM, Yap D, Bashashati A, Nakao S, Sorensen PH, Nakanishi A, Shah S
and Aparicio S: Pharmacological systems analysis defines EIF4A3
functions in cell-cycle and RNA stress granule formation. Commun
Biol. 2:1652019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zheng X, Huang M, Xing L, Yang R, Wang X,
Jiang R, Zhang L and Chen J: The circRNA circSEPT9 mediated by E2F1
and EIF4A3 facilitates the carcinogenesis and development of
triple-negative breast cancer. Mol Cancer. 19:732020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Xu B, Yang N, Liu Y, Kong P, Han M and Li
B: Circ_cse1l Inhibits Colorectal Cancer Proliferation by Binding
to eIF4A3. Med Sci Monit. 26:e9238762020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Sun HD, Xu ZP, Sun ZQ, Zhu B, Wang Q, Zhou
J, Jin H, Zhao A, Tang WW and Cao XF: Down-regulation of circPVRL3
promotes the proliferation and migration of gastric cancer cells.
Sci Rep. 8:101112018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Tang W, Wang D, Shao L, Liu X, Zheng J,
Xue Y, Ruan X, Yang C, Liu L, Ma J, et al: LINC00680 and TTN-AS1
stabilized by EIF4A3 promoted malignant biological behaviors of
glioblastoma cells. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 19:905–921. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Shibuya T, Tange TØ, Sonenberg N and Moore
MJ: eIF4AIII binds spliced mRNA in the exon junction complex and is
essential for nonsense-mediated decay. Nat Struct Mol Biol.
11:346–351. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|