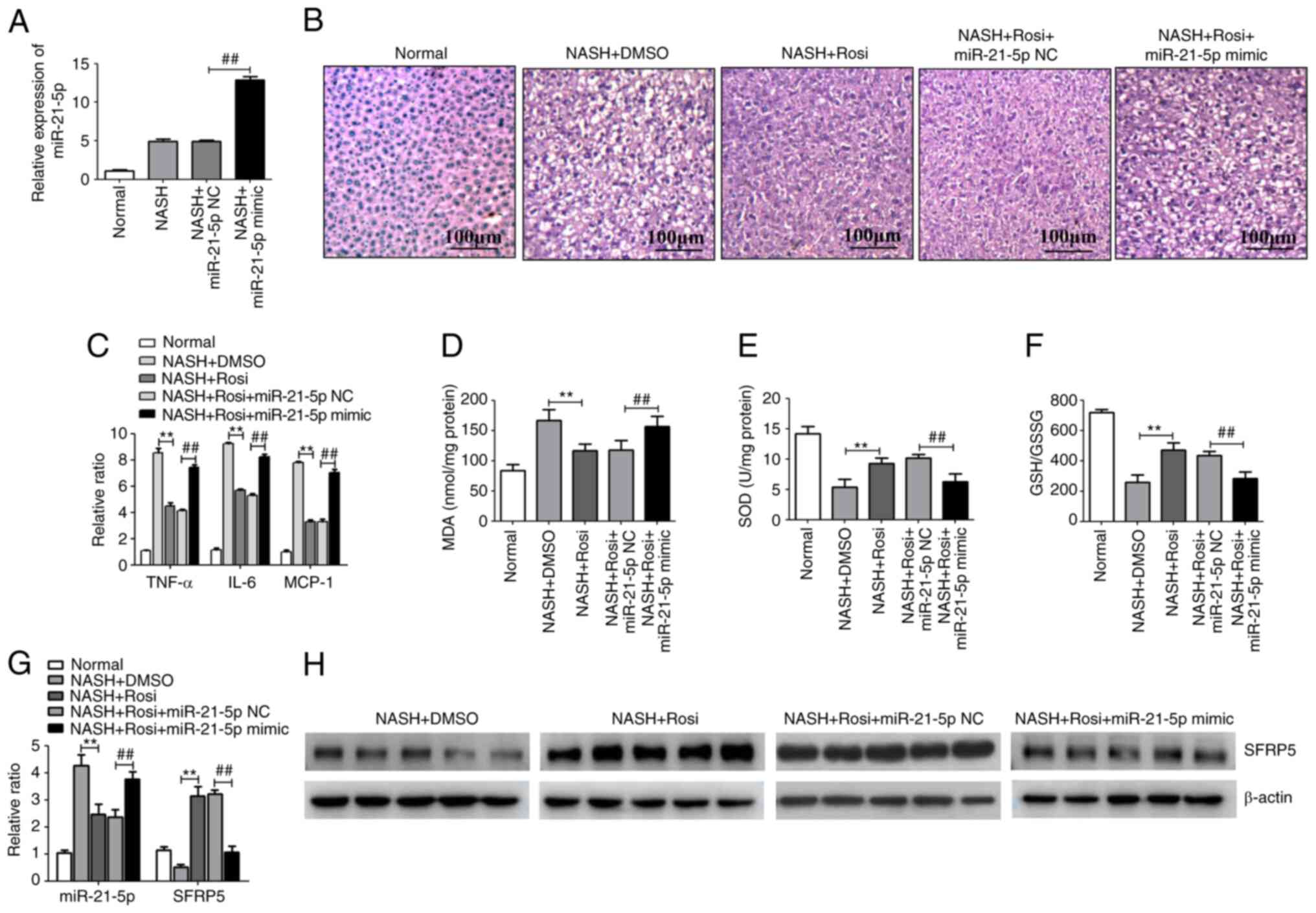
|
1
|
Younossi ZM, Koenig AB, Abdelatif D, Fazel
Y, Henry L and Wymer M: Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty
liver disease-meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence,
and outcomes. Hepatology. 64:73–84. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sanyal AJ: Past, present and future
perspectives in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nat Rev
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 16:377–386. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jain MR, Giri SR, Bhoi B, Trivedi C, Rath
A, Rathod R, Ranvir R, Kadam S, Patel H, Swain P, et al: Dual PPAR
α/γ agonist saroglitazar improves liver histopathology and
biochemistry in experimental NASH models. Liver Int. 38:1084–1094.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhong X and Liu H: Honokiol attenuates
diet-induced non-alcoholic steatohepatitis by regulating macrophage
polarization through activating peroxisome proliferator-activated
receptor gamma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 33:524–532. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Choudhary NS, Kumar N and Duseja A:
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors and their agonists in
nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 9:731–739.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Skat-Rordam J, Ipsen DH, Lykkesfeldt J and
Tveden-Nyborg P: A role of peroxisome proliferator-activated
receptor γ in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Basic Clin
Pharmacol Toxicol. 124:528–537. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ahn J, Lee H, Jung CH and Ha T: Lycopene
inhibits hepatic steatosis via microRNA-21-induced downregulation
of fatty acid-binding protein 7 in mice fed a high-fat diet. Mol
Nutr Food Res. 56:1665–1674. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wei J, Feng L, Li Z, Xu G and Fan X:
MicroRNA-21 activates hepatic stellate cells via PTEN/Akt
signaling. Biomed Pharmacother. 67:387–392. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Dattaroy D, Pourhoseini S, Das S, Alhasson
F, Seth RK, Nagarkatti M, Michelotti GA, Diehl AM and Chatterjee S:
Micro-RNA 21 inhibition of SMAD7 enhances fibrogenesis via
leptin-mediated NADPH oxidase in experimental and human
nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver
Physiol. 308:G298–G312. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Loyer X, Paradis V, Henique C, Vion AC,
Colnot N, Guerin CL, Devue C, On S, Scetbun J, Romain M, et al:
Liver microRNA-21 is overexpressed in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis
and contributes to the disease in experimental models by inhibiting
PPARα expression. Gut. 65:1882–1894. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ouchi N, Higuchi A, Ohashi K, Oshima Y,
Gokce N, Shibata R, Akasaki Y, Shimono A and Walsh K: Sfrp5 is an
anti-inflammatory adipokine that modulates metabolic dysfunction in
obesity. Science. 329:454–457. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li Y, Rankin SA, Sinner D, Kenny AP, Krieg
PA and Zorn AM: Sfrp5 coordinates foregut specification and
morphogenesis by antagonizing both canonical and noncanonical Wnt11
signaling. Genes. 22:3050–3063. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gutierrez-Vidal R, Vega-Badillo J,
Reyes-Fermin LM, Hernandez-Perez HA, Sanchez-Munoz F, Lopez-Alvarez
GS, Larrieta-Carrasco E, Fernandez-Silva I, Mendez-Sanchez N, Tovar
AR, et al: SFRP5 hepatic expression is associated with
non-alcoholic liver disease in morbidly obese women. Ann Hepatol.
14:666–674. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen L, Zhao X, Liang G, Sun J, Lin Z, Hu
R, Chen P, Zhang Z, Zhou L and Li Y: Recombinant SFRP5 protein
significantly alleviated intrahepatic inflammation of nonalcoholic
steatohepatitis. Nutr Metab (Lond). 14:562017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Rinkiko S, Pang XC, Yuan ZW, Chen SY, Zhu
YZ and Xie Y: Combinational applicaton of silybin and tangeretin
attenuates the progression of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH)
in mice via modulating lipid metabolism. Pharmacol Res.
151:1045192020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang K, Liu CY, Zhou LY, Wang JX, Wang M,
Zhao B, Zhao WK, Xu Sh, Fan LH, Zhang XJ, et al: APF lncRNA
regulates autophagy and myocardial infarction by targeting
miR-188-3p. Nat Commun. 6:67792015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang K, Long B, Zhou LY, Liu F, Zhou QY,
Liu CY, Fan YY and Li PF: CARL lncRNA inhibits anoxia-induced
mitochondrial fission and apoptosis in cardiomyocytes by impairing
miR-539-dependent PHB2 downregulation. Nat Commun. 5:35962014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
National Research Council (US) Committee
for the Update of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory
Animals, . Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, 8th
edition. National Academies Press (US); Washington, DC: 2011
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hu C, Liu D, Zhang Y, Lou G, Huang G, Chen
B, Shen X, Gao M, Gong W, Zhou P, et al: LXRα-mediated
downregulation of FOXM1 suppresses the proliferation of
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncogene. 33:2888–2897. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhong D, Yan Z, Zeng YJ, Gao M, Wu GZ, Hu
CJ, Huang G and He FT: MicroRNA-613 represses lipogenesis in HepG2
cells by downregulating LXRα. Lipids Health Dis. 12:322013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Liang W, Menke AL, Driessen A, Koek GH,
Lindeman JH, Stoop R, Havekes LM, Kleemann R and van den Hoek AM:
Establishment of a general NAFLD scoring system for rodent models
and comparison to human liver pathology. PLoS One. 9:e1159222014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Takahashi Y and Fukusato T: Histopathology
of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/nonalcoholic steatohepatitis.
World J Gastroenterol. 20:15539–15548. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Itoh M, Ogawa Y and Suganami T: Chronic
inflammation as a molecular basis of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis:
Role of macrophages and fibroblasts in the liver. Nagoya J Med Sci.
82:391–397. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Smeuninx B, Boslem E and Febbraio MA:
Current and future treatments in the fight against non-alcoholic
fatty liver disease. Cancers (Basel). 28:17142020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Ore A and Akinloye OA: Oxidative stress
and antioxidant biomarkers in clinical and experimental models of
non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Medicina (Kaunas). 55:262019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Penvose A, Keenan JL, Bray D, Ramlall V
and Siggers T: Comprehensive study of nuclear receptor DNA binding
provides a revised framework for understanding receptor
specificity. Nat Commun. 10:25142019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
He L and Hannon GJ: MicroRNAs: Small RNAs
with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet. 5:522–531. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Paik JM, Golabi P, Younossi Y, Mishra A
and Younossi ZM: Changes in the global burden of chronic liver
diseases from 2012 to 2017: The growing impact of NAFLD.
Hepatology. 72:1605–1616. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hong F, Xu P and Zhai Y: The opportunities
and challenges of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors
ligands in clinical drug discovery and development. Int J Mol Sci.
19:21892018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhu Y, Alvares K, Huang Q, Rao MS and
Reddy JK: Cloning of a new member of the peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor gene family from mouse liver. J
Biol Chem. 268:26817–26820. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Soccio RE, Chen ER and Lazar MA:
Thiazolidinediones and the promise of insulin sensitization in type
diabetes. Cell Metab. 20:573–591. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wu HM, Ni XX, Xu QY, Wang Q, Li XY and Hua
J: Regulation of lipid-induced macrophage polarization through
modulating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma
activity a ects hepatic lipid metabolism via a Toll-like receptor
4/NF-B signaling pathway. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 35:1998–2008.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Nan YM, Fu N, Wu WJ, Liang BL, Wang RQ,
Zhao SX, Zhao JM and Yu J: Rosiglitazone prevents nutritional
fibrosis and steatohepatitis in mice. Scand J Gastroenterol.
44:358–365. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Neuschwander-Tetri BA, Brunt EM, Wehmeier
KR, Oliver D and Bacon BR: Improved nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
after 48 weeks of treatment with the PPAR-gamma ligand
rosiglitazone. Hepatology. 38:1008–1017. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ratziu V, Giral P, Jacqueminet S,
Charlotte F, Hartemann-Heurtier A, Serfaty L, Podevin P, Lacorte
JM, Bernhardt C, Bruckert E, et al: Rosiglitazone for nonalcoholic
steatohepatitis: one-year results of the randomized
placebo-controlled fatty liver improvement with rosiglitazone
therapy (FLIRT) trial. Gastroenterology. 135:100–110. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Berlie HD, Kalus JS and Jaber LA:
Thiazolidinediones and the risk of edema: A meta-analysis. Diabetes
Res Clin Pract. 76:279–289. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Singh S, Loke YK and Furberg CD:
Thiazolidinediones and heart failure: A teleo-analysis. Diabetes
Care. 30:2148–2153. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Loke YK, Kwok CS and Singh S: Comparative
cardiovascular effects of thiazolidinediones: Systematic review and
meta-analysis of observational studies. BMJ. 342:d13092011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Liu J, Xiao Y, Wu X, Jiang L, Yang S, Ding
Z, Fang Z, Hua H, Kirby MS and Shou J: A circulating microRNA
signature as noninvasive diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for
nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. BMC Genomics. 19:1882018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Becker PP, Rau M, Schmitt J, Malsch
C..Hammer C, Bantel H, Mullhaupt B and Geier A: Performance of
serum microRNAs −122, −192 and −21 as biomarkers in patients with
non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. PLoS One. 10:e01426612015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Rodrigues PM, Afonso MB, Simao AL,
Carvalho CC, Trindade A, Duarte A, Borralho PM, Machado MV,
Cortez-Pinto H, Rodrigues CM and Castro RE: miR-21-5p ablation and
obeticholic acid ameliorate nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in mice.
Cell Death Dis. 8:e27482017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Nicole W and Kay-Dietrich W: The role of
PPARs in disease. Cells. 9:23672020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Ji H, Wang H, Zhang F, Li X, Xiang L and
Aiguo S: PPARγ agonist pioglitazone inhibits microglia inflammation
by blocking p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling
pathways. Inflamm Res. 59:921–929. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Wang D, Shi L, Xin W, Xu J, Xu J, Li Q, Xu
Z, Wang J, Wang G, Yao W, et al: Activation of PPARg inhibits
pro-inflammatory cytokines production by upregulation of miR-124 in
vitro and in vivo. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 486:726–731. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Qiu Y, Yang J, Bian S, Guozhu C and Yu J:
PPARγ suppresses the proliferation of cardiac myxoma cells through
downregulation of MEF2D in a miR-122-dependent manner. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 474:560–565. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Liu W, Ji Y, Chu H, Wang M, Yang B and Yin
C: SFRP5 mediates downregulation of the wnt5a/caveolin-1/JNK
signaling pathway. J Endocrinol. 247:263–272. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zou DP, Chen YM, Zhang LZ, Yuan XH, Zhang
YJ, Inggawati A, Nguyet PT, Gao TW and Chen J: SFRP5 inhibits
melanin synthesis of melanocytes in vitiligo by suppressing the
Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Genes Dis. 8:677–688. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Tong S, Ji Q, Du Y, Zhu X, Zhu C and Zhou
Y: Sfrp5/Wnt pathway: A protective regulatory system in
atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. J Interferon Cytokine Res.
39:472–482. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Zeng J, Hu J, Lian Y, Jiang Y and Chen B:
SFRP5 is a target gene transcriptionally regulated by PPARγ in
3T3-L1 adipocytes. Gene. 641:190–195. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|