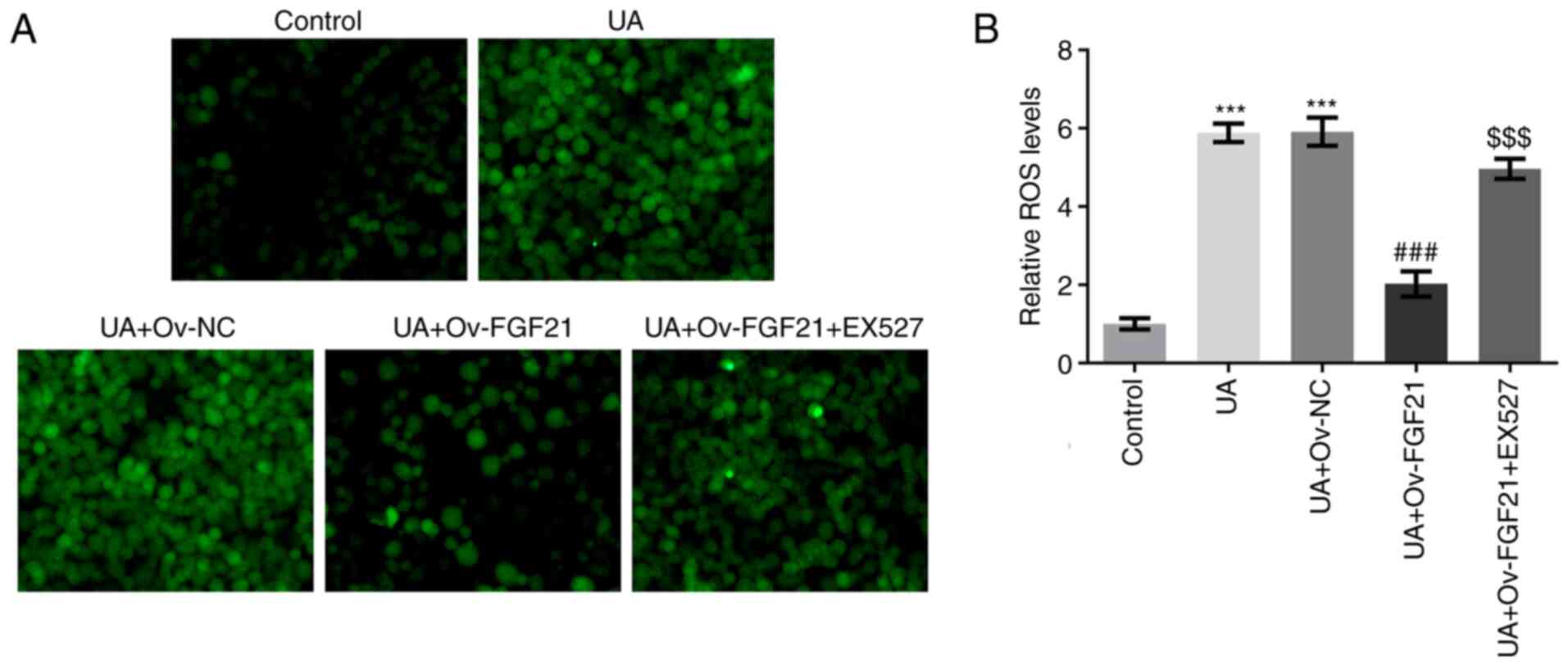
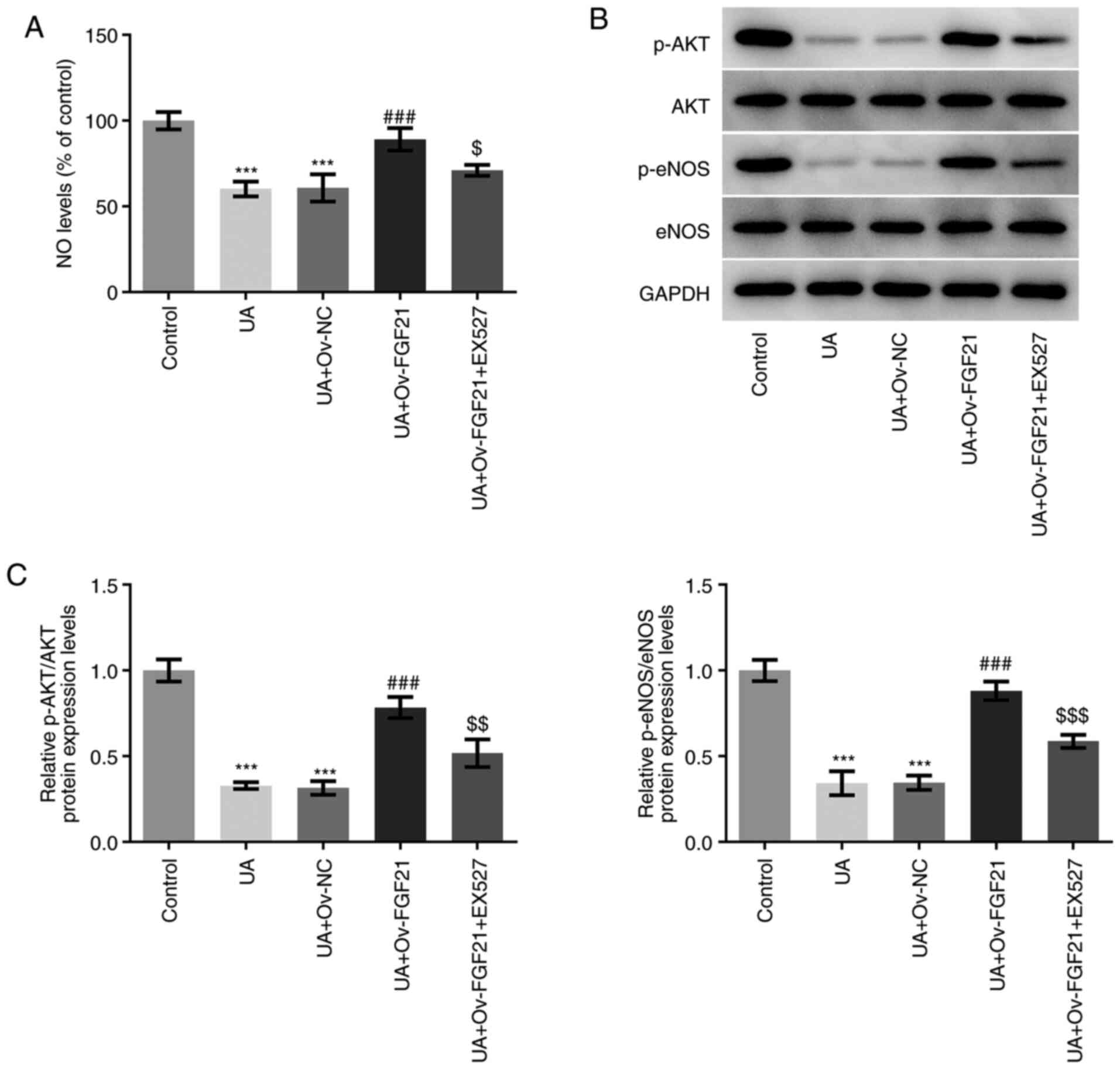
|
1
|
Yang X, Gu J, Lv H, Li H, Cheng Y, Liu Y
and Jiang Y: Uric acid induced inflammatory responses in
endothelial cells via up-regulating(pro)renin receptor. Biomed
Pharmacother. 109:1163–1170. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ramirez-Sandoval JC and Madero M:
Treatment of hyperuricemia in chronic kidney disease. Contrib
Nephrol. 192:135–146. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ng G, Chau EM and Shi Y: Recent
developments in immune activation by uric acid crystals. Arch
Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 58:273–277. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Stodle GS, Silva GB, Tangeras LH, Gierman
LM, Nervik I, Dahlberg UE, Sun C, Aune MH, Thomsen LCV, Bjørge L
and Iversen AC: Placental inflammation in pre-eclampsia by Nod-like
receptor protein (NLRP)3 inflammasome activation in trophoblasts.
Clin Exp Immunol. 193:84–94. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhang S, Wang Y, Cheng J, Huangfu N, Zhao
R, Xu Z, Zhang F, Zheng W and Zhang D: Hyperuricemia and
cardiovascular disease. Curr Pharm Des. 25:700–709. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Johnson RJ, Bakris GL, Borghi C, Chonchol
MB, Feldman D, Lanaspa MA, Merriman TR, Moe OW, Mount DB, Sanchez
Lozada LG, et al: Hyperuricemia, acute and chronic kidney disease,
hypertension, and cardiovascular disease: Report of a scientific
workshop organized by the national kidney foundation. Am J Kidney
Dis. 71:851–865. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Choi YJ, Yoon Y, Lee KY, Hien TT, Kang KW,
Kim KC, Lee J, Lee MY, Lee SM, Kang DH and Lee BH: Uric acid
induces endothelial dysfunction by vascular insulin resistance
associated with the impairment of nitric oxide synthesis. FASEB J.
28:3197–3204. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Assadi F: Allopurinol enhances the blood
pressure lowering effect of enalapril in children with
hyperuricemic essential hypertension. J Nephrol. 27:51–56. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Alonge KM, Meares GP and Hillgartner FB:
Glucagon and insulin cooperatively stimulate fibroblast growth
factor 21 gene transcription by increasing the expression of
activating transcription factor 4. J Biol Chem. 292:5239–5252.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Brahma MK, Adam RC, Pollak NM, Jaeger D,
Zierler KA, Pöcher N, Schreiber R, Romauch M, Moustafa T, Eder S,
et al: Fibroblast growth factor 21 is induced upon cardiac stress
and alters cardiac lipid homeostasis. J Lipid Res. 55:2229–2241.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yan X, Gou Z, Li Y, Wang Y, Zhu J, Xu G
and Zhang Q: Fibroblast growth factor 21 inhibits atherosclerosis
in apoE-/- mice by ameliorating Fas-mediated apoptosis. Lipids
Health Dis. 17:2032018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen JJ, Tao J, Zhang XL, Xia LZ, Zeng JF,
Zhang H, Wei DH, Lv YC, Li GH and Wang Z: Inhibition of the
ox-LDL-induced pyroptosis by FGF21 of human umbilical vein
endothelial cells through the TET2-UQCRC1-ROS pathway. DNA Cell
Biol. 39:661–670. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Guo D, Xiao L, Hu H, Liu M, Yang L and Lin
X: FGF21 protects human umbilical vein endothelial cells against
high glucose-induced apoptosis via PI3K/Akt/Fox3a signaling
pathway. J Diabetes Complications. 32:729–736. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen S, Chen D, Yang H, Wang X, Wang J and
Xu C: Uric acid induced hepatocytes lipid accumulation through
regulation of miR-149-5p/FGF21 axis. BMC Gastroenterol. 20:392020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu ZH, Zhang Y, Wang X, Fan XF, Zhang Y,
Li X, Gong YS and Han LP: SIRT1 activation attenuates cardiac
fibrosis by endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition. Biomed
Pharmacother. 118:1092272019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wu X, Pan C, Chen R, Zhang S, Zhai Y and
Guo H: BML-111 attenuates high glucose-induced inflammation,
oxidative stress and reduces extracellular matrix accumulation via
targeting Nrf2 in rat glomerular mesangial cells. Int
Immunopharmacol. 79:1061082020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Aranda A, Sequedo L, Tolosa L, Quintas G,
Burello E, Castell JV and Gombau L: Dichloro-dihydro-fluorescein
diacetate (DCFH-DA) assay: A quantitative method for oxidative
stress assessment of nanoparticle-treated cells. Toxicol In Vitro.
27:954–963. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu HD, Li W, Chen ZR, Hu YC, Zhang DD,
Shen W, Zhou ML, Zhu L and Hang CH: Expression of the NLRP3
inflammasome in cerebral cortex after traumatic brain injury in a
rat model. Neurochem Res. 38:2072–2083. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li L, Zhang Y and Zeng C: Update on the
epidemiology, genetics, and therapeutic options of hyperuricemia.
Am J Transl Res. 12:3167–3181. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
George C and Minter DA: Hyperuricemia.
StatPearls (Internet). StatPearls Publishing; Treasure Island, FL:
2021
|
|
22
|
Hong Q, Wang L, Huang Z, Feng Z, Cui S, Fu
B, Cai G, Chen X and Wu D: High concentrations of uric acid and
angiotensin II act additively to produce endothelial injury.
Mediators Inflamm. 2020:83876542020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yang B, Li S, Zhu J, Huang S, Zhang A, Jia
Z, Ding G and Zhang Y: miR-214 protects against uric acid-induced
endothelial cell apoptosis. Front Med (Lausanne). 7:4112020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Durnwald C, Mele L, Landon MB, Varner MW,
Casey BM, Reddy UM, Wapner RJ, Rouse DJ, Tita ATN, Thorp JM Jr, et
al: Fibroblast growth factor 21 and metabolic dysfunction in women
with a prior glucose-intolerant pregnancy. Am J Perinatol.
38:1380–1385. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lee SY, Burns SF, Ng KKC, Stensel DJ,
Zhong L, Tan FHY, Chia KL, Fam KD, Yap MMC, Yeo KP, et al:
Fibroblast growth factor 21 mediates the associations between
exercise, aging, and glucose regulation. Med Sci Sports Exerc.
52:370–380. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wu L, Qian L, Zhang L, Zhang J, Zhou J, Li
Y, Hou X, Fang Q, Li H and Jia W: Fibroblast growth factor 21 is
related to atherosclerosis independent of nonalcoholic fatty liver
disease and predicts atherosclerotic cardiovascular events. J Am
Heart Assoc. 9:e0152262020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Osman A, El-Gamal H, Pasha M, Zeidan A,
Korashy HM, Abdelsalam SS, Hasan M, Benameur T and Agouni A:
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress-generated extracellular vesicles
(microparticles) self-perpetuate ER stress and mediate endothelial
cell dysfunction independently of cell survival. Front Cardiovasc
Med. 7:5847912020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Guo Y, Guo R, Su Y, Fu J, Wang S, Kong Y,
Wu C, Wang J, Tan C, Mo C and Zhao B: The PERK/eIF2alpha/ATF4/CHOP
pathway plays a role in regulating monocrotaline-induced
endoplasmic reticulum stress in rat liver. Res Vet Sci.
130:237–239. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li S, Zhu Z, Xue M, Yi X, Liang J, Niu C,
Chen G, Shen Y, Zhang H, Zheng J, et al: Fibroblast growth factor
21 protects the heart from angiotensin II-induced cardiac
hypertrophy and dysfunction via SIRT1. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol
Basis Dis. 1865:1241–1252. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liu X, Wang Y, Hou L, Xiong Y and Zhao S:
Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) promotes formation of aerobic
myofibers via the FGF21-SIRT1-AMPK-PGC1α pathway. J Cell Physiol.
232:1893–1906. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li W, Cao T, Luo C, Cai J, Zhou X, Xiao X
and Liu S: Crosstalk between ER stress, NLRP3 inflammasome, and
inflammation. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 104:6129–6140. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zeng Z, Zheng Q, Chen J, Tan X, Li Q, Ding
L, Zhang R and Lin X: FGF21 mitigates atherosclerosis via
inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated vascular endothelial
cells pyroptosis. Exp Cell Res. 393:1121082020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|