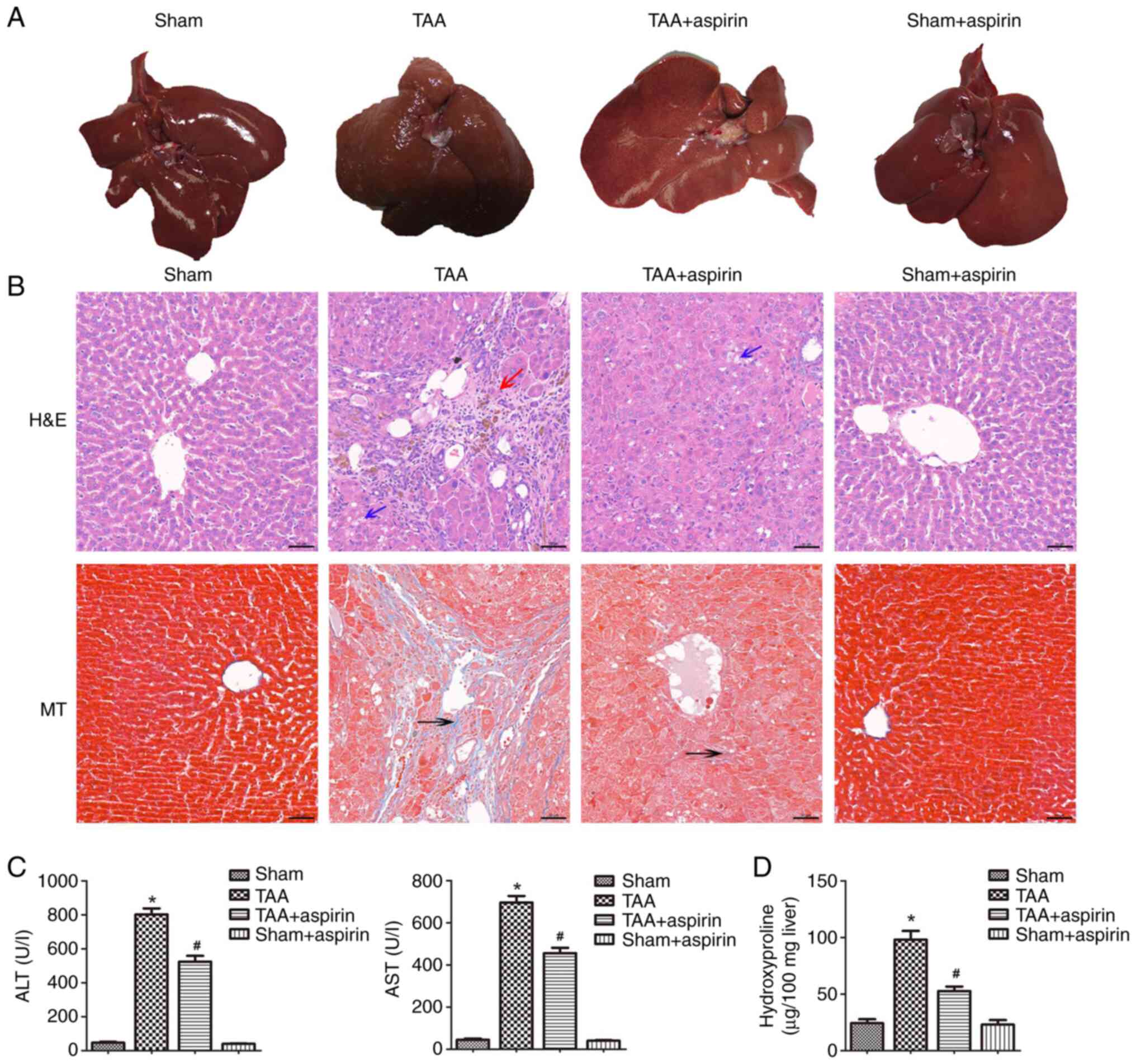
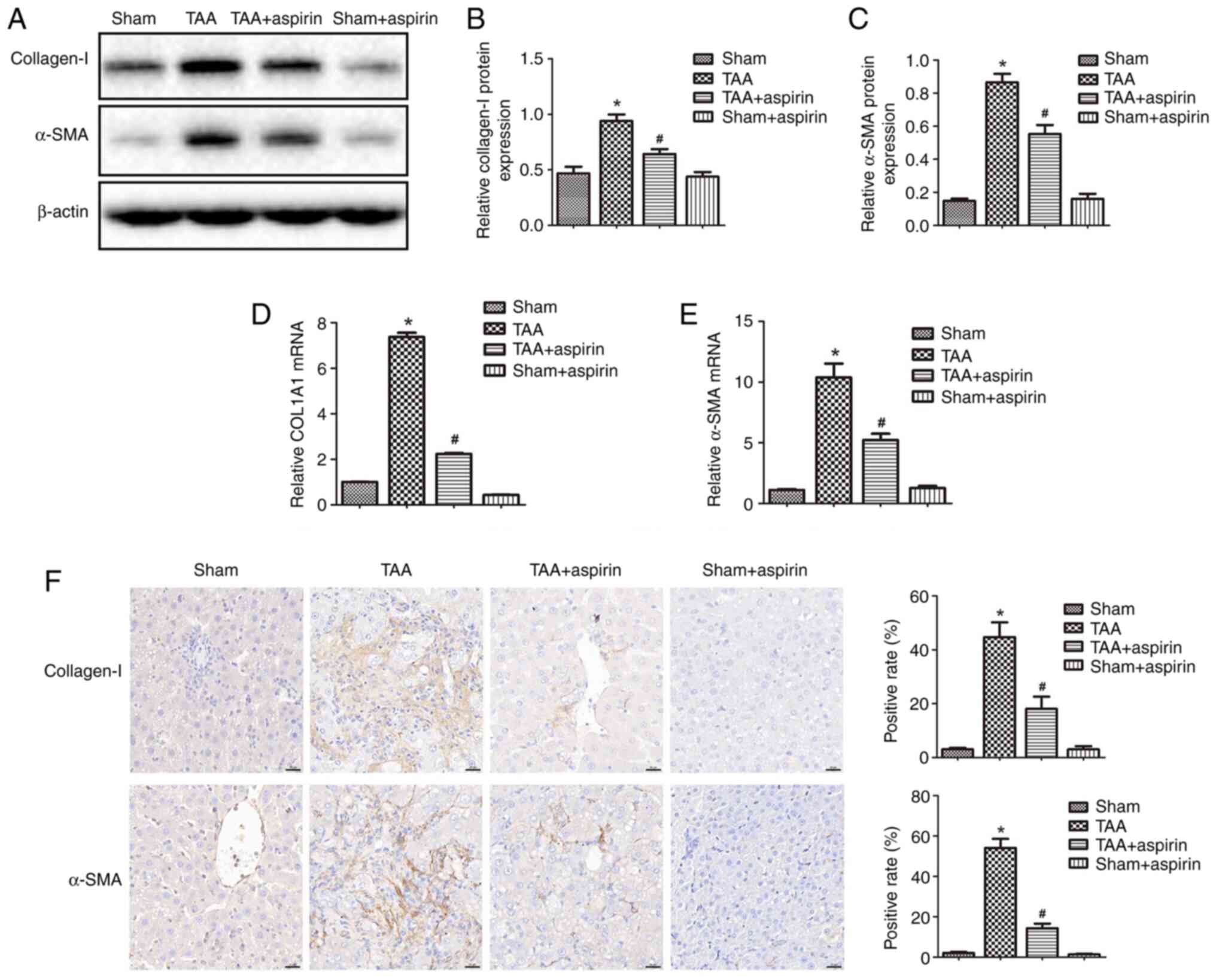
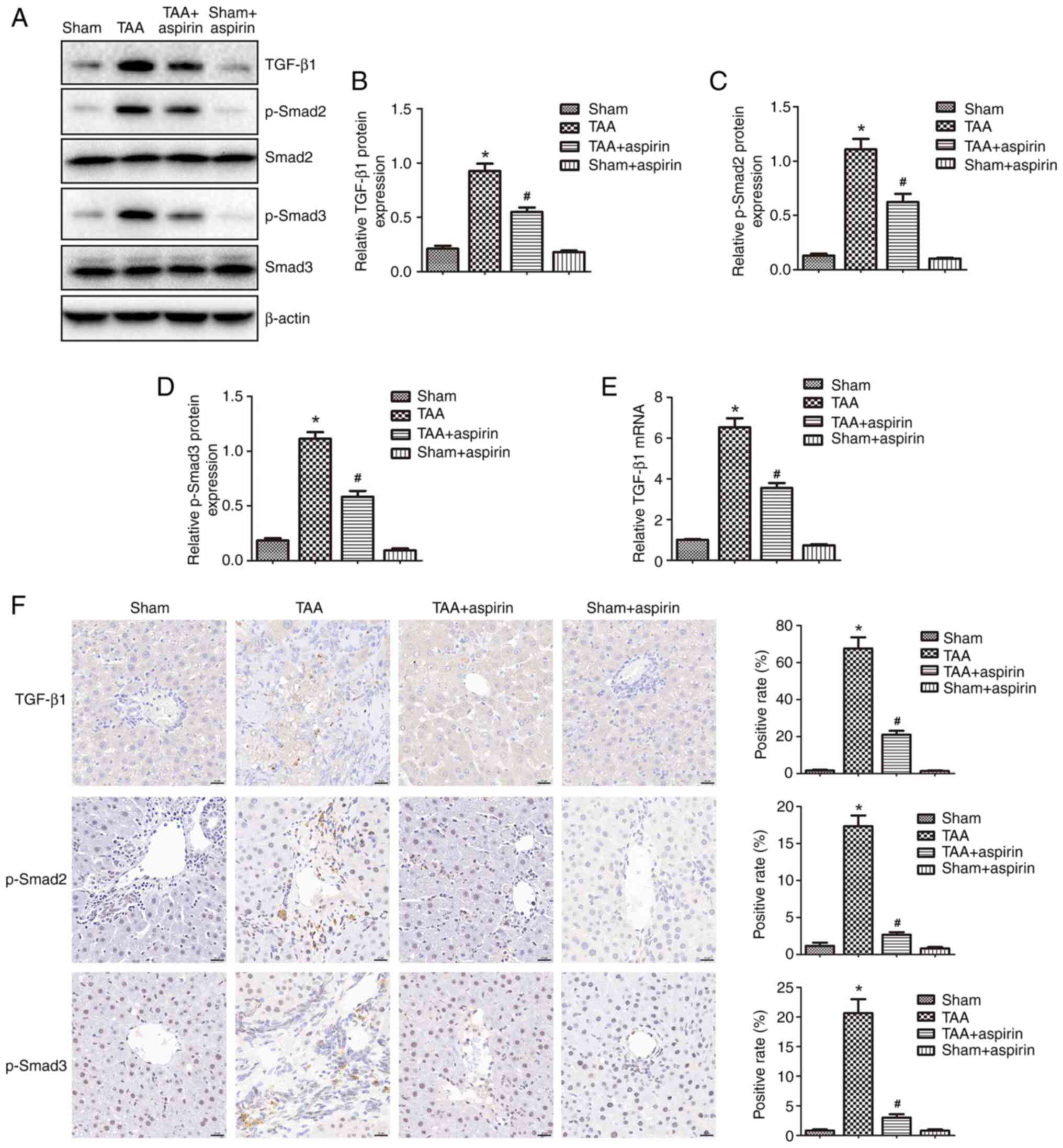
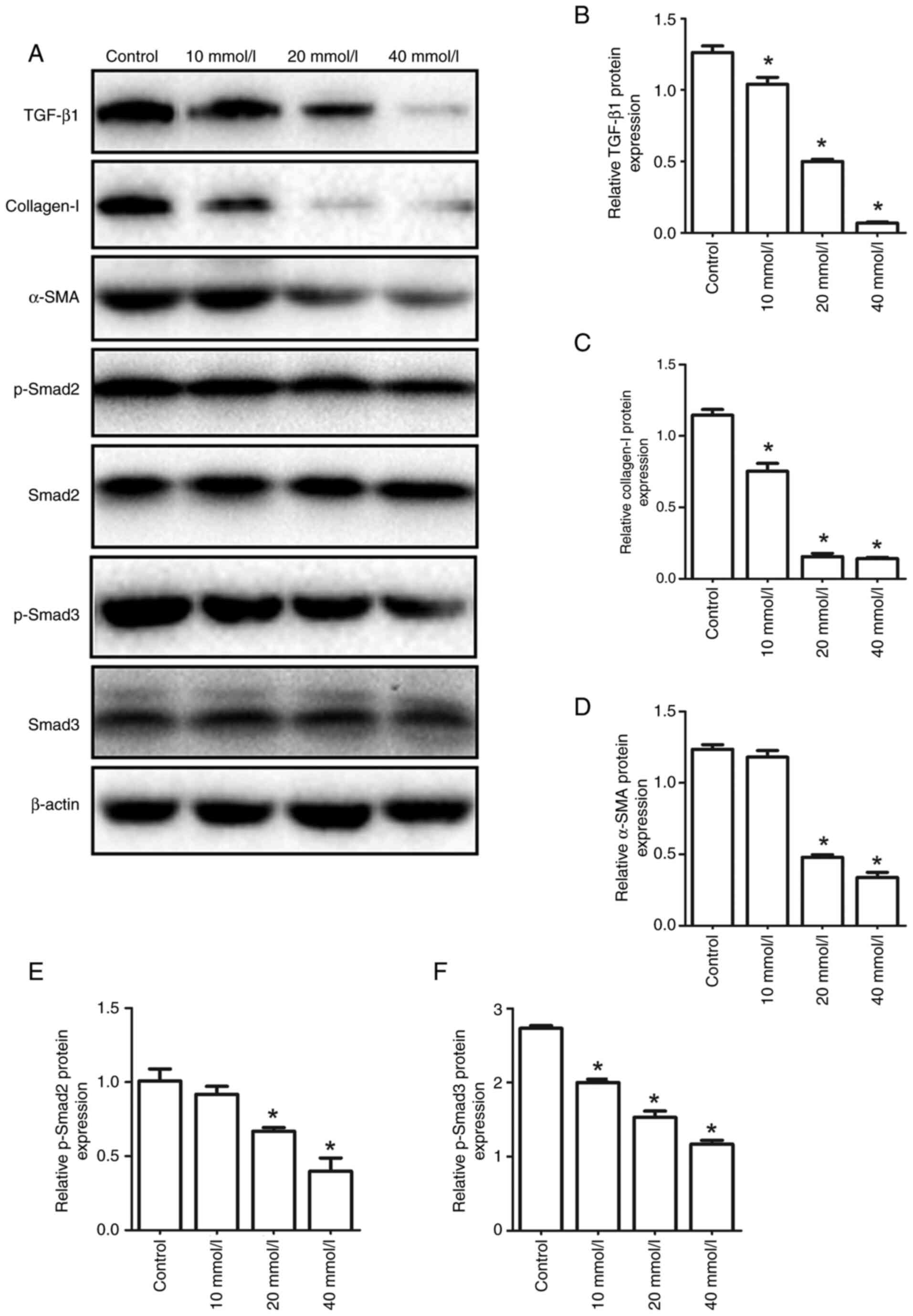
|
1
|
Friedman SL: Liver fibrosis-from bench to
bedside. J Hepatol. 38 (Suppl 1):S38–S53. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Friedman SL: Seminars in medicine of the
Beth Israel Hospital, Boston. The cellular basis of hepatic
fibrosis. Mechanisms and treatment strategies. N Engl J Med.
328:1828–1835. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kisseleva T and Brenner DA: Role of
hepatic stellate cells in fibrogenesis and the reversal of
fibrosis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 22 (Suppl 1):S73–S78. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Friedman SL: Evolving challenges in
hepatic fibrosis. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 7:425–436. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Szabo G and Bala S: Alcoholic liver
disease and the gut-liver axis. World J Gastroenterol.
16:1321–1329. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang D, Hao X, Xu L, Cui J, Xue L and
Tian Z: Intestinal flora imbalance promotes alcohol-induced liver
fibrosis by the TGFβ/smad signaling pathway in mice. Oncol Lett.
14:4511–4516. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yang Y, Kim B, Park YK, Koo SI and Lee JY:
Astaxanthin prevents TGFβ1-induced pro-fibrogenic gene expression
by inhibiting Smad3 activation in hepatic stellate cells. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1850:178–185. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liu Q, Duan ZP, Ha DK, Bengmark S,
Kurtovic J and Riordan SM: Synbiotic modulation of gut flora:
Effect on minimal hepatic encephalopathy in patients with
cirrhosis. Hepatology. 39:1441–1449. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Vonkeman HE and van de Laar MA:
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: Adverse effects and their
prevention. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 39:294–312. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Berk M, Woods RL, Nelson MR, Shah RC, Reid
CM, Storey E, Fitzgerald S, Lockery JE, Wolfe R, Mohebbi M, et al:
Effect of aspirin vs. placebo on the prevention of depression in
older people: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiatry.
77:1012–1020. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Antman EM: Evaluating the cardiovascular
safety of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Circulation.
135:2062–2072. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Henry WS, Laszewski T, Tsang T, Beca F,
Beck AH, McAllister SS and Toker A: Aspirin suppresses growth in
PI3K-mutant breast cancer by activating AMPK and inhibiting mTORC1
Signaling. Cancer Res. 77:790–801. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gray RT, Coleman HG, Hughes C, Murray LJ
and Cardwell CR: Low-dose aspirin use and survival in colorectal
cancer: Results from a population-based cohort study. BMC Cancer.
18:2282018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jiang ZG, Feldbrügge L, Tapper EB, Popov
Y, Ghaziani T, Afdhal N, Robson SC and Mukamal KJ: Aspirin use is
associated with lower indices of liver fibrosis among adults in the
United States. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 43:734–743. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li CJ, Yang ZH, Shi XL and Liu DL: Effects
of aspirin and enoxaparin in a rat model of liver fibrosis. World J
Gastroenterol. 23:6412–6419. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu Y, Nong L, Jia Y, Tan A, Duan L, Lu Y
and Zhao J: Aspirin alleviates hepatic fibrosis by suppressing
hepatic stellate cells activation via the TLR4/NF-κB pathway. Aging
(Albany NY). 12:6058–6066. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang W, Chen XP, Zhang WG, Zhang F, Xiang
S, Dong HH and Zhang L: Hepatic non-parenchymal cells and
extracellular matrix participate in oval cell-mediated liver
regeneration. World J Gastroenterol. 15:552–560. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dranoff JA and Wells RG: Portal
fibroblasts: Underappreciated mediators of biliary fibrosis.
Hepatology. 51:1438–1444. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sherman M and Klein A: AASLD single-topic
research conference on hepatocellular carcinoma: Conference
proceedings. Hepatology. 40:1465–1473. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yanguas SC, Cogliati B, Willebrords J,
Maes M, Colle I, van den Bossche B, de Oliveira C, Andraus W, Alves
VAF, Leclercq I and Vinken M: Experimental models of liver
fibrosis. Arch Toxicol. 90:1025–1048. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dai N, Zou Y, Zhu L, Wang HF and Dai MG:
Antioxidant properties of proanthocyanidins attenuate carbon
tetrachloride (CCl4)-induced steatosis and liver injury in rats via
CYP2E1 regulation. J Med Food. 17:663–669. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Li S, Zheng X, Zhang X, Yu H, Han B, Lv Y,
Liu Y, Wang X and Zhang Z: Exploring the liver fibrosis induced by
deltamethrin exposure in quails and elucidating the protective
mechanism of resveratrol. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 207:1115012021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Simon TG, Henson J, Osganian S, Masia R,
Chan AT, Chung RT and Corey KE: Daily aspirin use associated with
reduced risk for fibrosis progression in patients with nonalcoholic
fatty liver disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol.
17:2776–2784.e2774. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jiao W, Bai M, Yin H, Liu J, Sun J, Su X,
Zeng H and Wen J: Therapeutic effects of an inhibitor of
thioredoxin reductase on liver fibrosis by inhibiting the
transforming growth factor-β1/smads pathway. Front Mol Biosci.
8:6901702021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhangdi HJ, Su SB, Wang F, Liang ZY, Yan
YD, Qin SY and Jiang HX: Crosstalk network among multiple
inflammatory mediators in liver fibrosis. World J Gastroenterol.
25:4835–4849. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cai X, Li Z, Zhang Q, Qu Y, Xu M, Wan X
and Lu L: CXCL6-EGFR-induced Kupffer cells secrete TGF-β1 promoting
hepatic stellate cell activation via the SMAD2/BRD4/C-MYC/EZH2
pathway in liver fibrosis. J Cell Mol Med. 22:5050–5061. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wree A, Holtmann TM, Inzaugarat ME and
Feldstein AE: Novel drivers of the inflammatory response in liver
injury and fibrosis. Semin Liver Dis. 39:275–282. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chávez E, Castro-Sánchez L, Shibayama M,
Tsutsumi V, Salazar EP, Moreno MG and Muriel P: Effects of acetyl
salycilic acid and ibuprofen in chronic liver damage induced by
CCl4. J Appl Toxicol. 32:51–59. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shek FW and Benyon RC: How can
transforming growth factor beta be targeted usefully to combat
liver fibrosis? Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 16:123–126. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Liu N, Feng J, Lu X, Yao Z, Liu Q, Lv Y,
Han Y, Deng J and Zhou Y: Isorhamnetin inhibits liver fibrosis by
reducing autophagy and inhibiting extracellular matrix formation
via the TGF-β1/smad3 and TGF-β1/p38 MAPK pathways. Mediators
Inflamm. 2019:61750912019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Achyut BR and Yang L: Transforming growth
factor-β in the gastrointestinal and hepatic tumor
microenvironment. Gastroenterology. 141:1167–1178. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ahamed J and Laurence J: Role of
platelet-derived transforming growth factor-β1 and reactive oxygen
species in radiation-induced organ fibrosis. Antioxid Redox Signal.
27:977–988. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Meng XM, Nikolic-Paterson DJ and Lan HY:
TGF-β: The master regulator of fibrosis. Nat Rev Nephrol.
12:325–338. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Mao Y, Zhang S, Yu F, Li H, Guo C and Fan
X: Ghrelin attenuates liver fibrosis through regulation of TGF-β1
expression and autophagy. Int J Mol Sci. 16:21911–21930. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Liu X, Hu H and Yin JQ: Therapeutic
strategies against TGF-beta signaling pathway in hepatic fibrosis.
Liver Int. 26:8–22. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang Y, Zhao L, Jiao FZ, Zhang WB, Chen Q
and Gong ZJ: Histone deacetylase inhibitor suberoylanilide
hydroxamic acid alleviates liver fibrosis by suppressing the
transforming growth factor-β1 signal pathway. Hepatobiliary
Pancreat Dis Int. 17:423–429. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lin H, Ying Y, Wang YY, Wang G, Jiang SS,
Huang D, Luo L, Chen YG, Gerstenfeld LC and Luo Z: AMPK
downregulates ALK2 via increasing the interaction between Smurf1
and Smad6, leading to inhibition of osteogenic differentiation.
Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 1864:2369–2377. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|