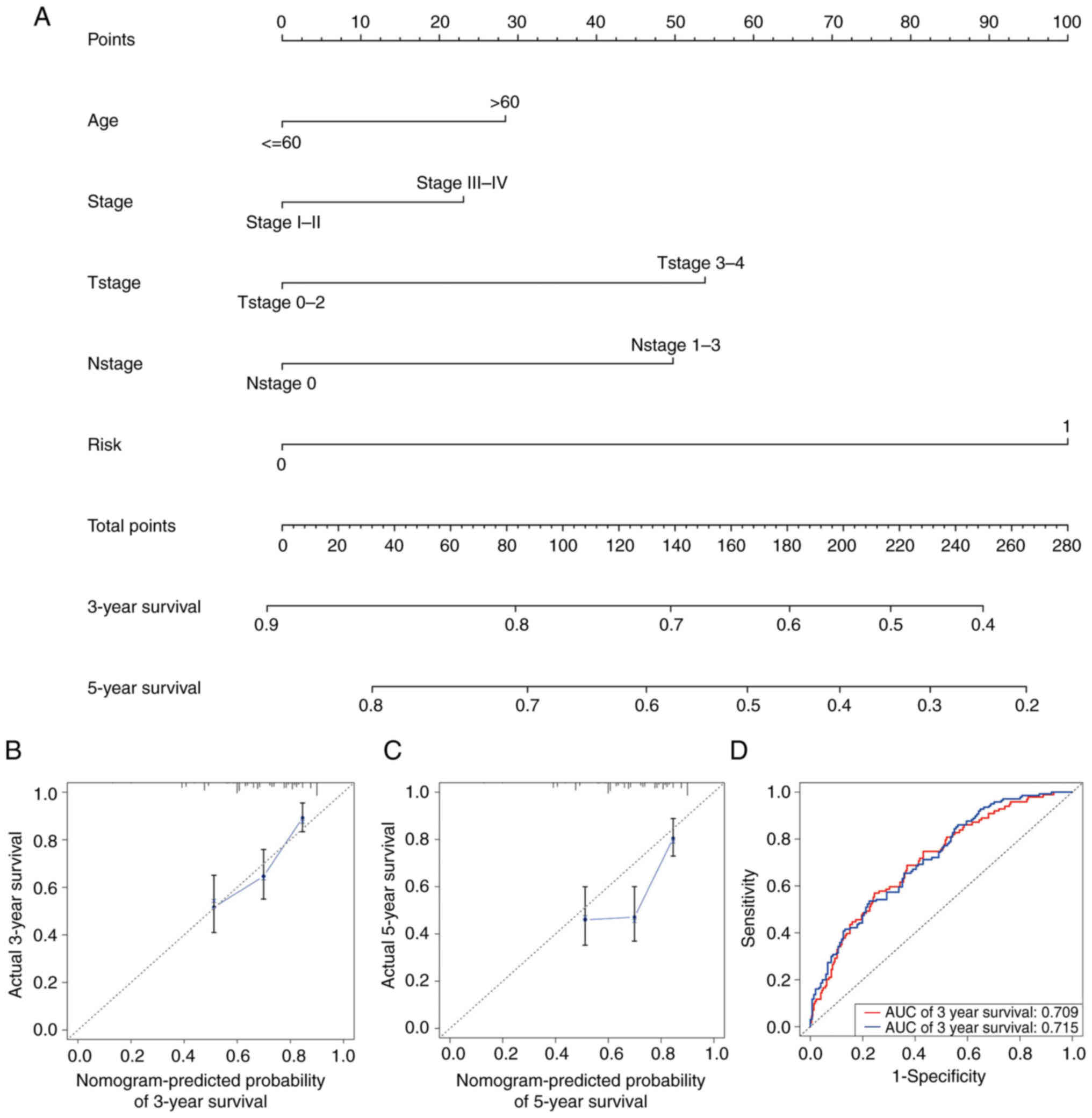
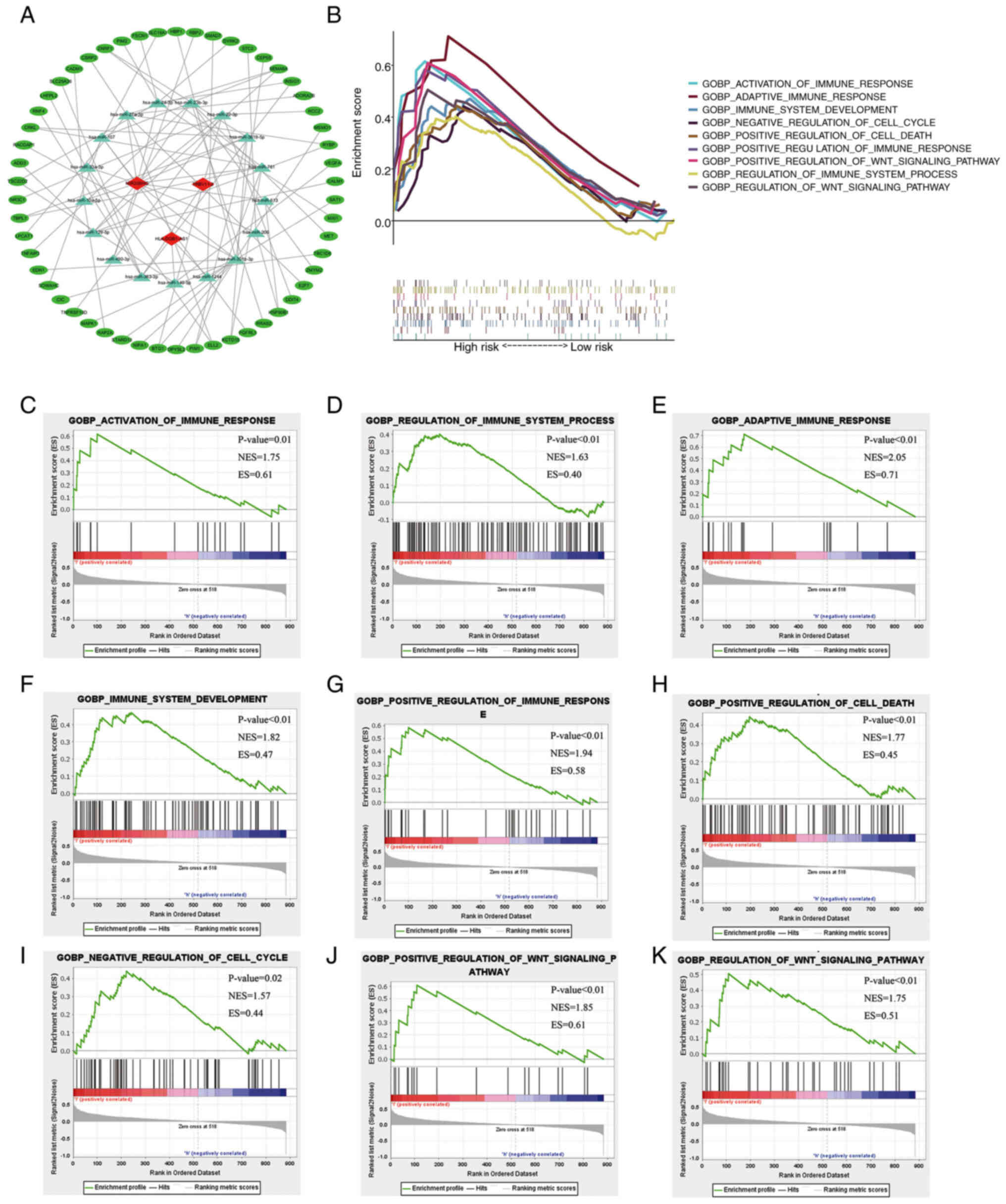
|
1
|
Leonardi GC, Falzone L, Salemi R, Zanghì
A, Spandidos DA, Mccubrey JA, Candido S and Libra M: Cutaneous
melanoma: From pathogenesis to therapy (Review). Int J Oncol.
52:1071–1080. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Davey MG, Miller N and McInerney NM: A
review of epidemiology and cancer biology of malignant melanoma.
Cureus. 13:e150872021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Carr S, Smith C and Wernberg J:
Epidemiology and risk factors of melanoma. Surg Clin North Am.
100:1–12. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lu X and Kang Y: Hypoxia and
hypoxia-inducible factors: Master regulators of metastasis. Clin
Cancer Res. 16:5928–5935. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Liu Y, Ciotti GE and Eisinger-Mathason
TSK: Hypoxia and the tumor secretome. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1136:57–69.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Graham K and Unger E: Overcoming tumor
hypoxia as a barrier to radiotherapy, chemotherapy and
immunotherapy in cancer treatment. Int J Nanomedicine.
13:6049–6058. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jing X, Yang F, Shao C, Wei K, Xie M, Shen
H and Shu Y: Role of hypoxia in cancer therapy by regulating the
tumor microenvironment. Mol Cancer. 18:1572019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Qiu H, Chen F and Chen M: MicroRNA-138
negatively regulates the hypoxia-inducible factor 1α to suppress
melanoma growth and metastasis. Biol Open. 8:bio0429372019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Dong L, You S, Zhang Q, Osuka S, Devi NS,
Kaluz S, Ferguson JH, Yang H, Chen G, Wang B, et al:
Arylsulfonamide 64B inhibits hypoxia/HIF-induced expression of
c-Met and CXCR4 and reduces primary tumor growth and metastasis of
uveal melanoma. Clin Cancer Res. 25:2206–2218. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Quinn JJ and Chang HY: Unique features of
long non-coding RNA biogenesis and function. Nat Rev Genet.
17:47–62. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jarroux J, Morillon A and Pinskaya M:
History, discovery, and classification of lncRNAs. Adv Exp Med
Biol. 1008:1–46. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu M, Zhong J, Zeng Z, Huang K, Ye Z,
Deng S, Chen H, Xu F, Li Q and Zhao G: Hypoxia-induced feedback of
HIF-1α and lncRNA-CF129 contributes to pancreatic cancer
progression through stabilization of p53 protein. Theranostics.
9:4795–4810. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Piao HY, Liu Y, Kang Y, Wang Y, Meng XY,
Yang D and Zhang J: Hypoxia associated lncRNA HYPAL promotes
proliferation of gastric cancer as ceRNA by sponging miR-431-5p to
upregulate CDK14. Gastric Cancer. 25:44–63. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yu Z, Wang Y, Deng J, Liu D, Zhang L, Shao
H, Wang Z, Zhu W, Zhao C and Ke Q: Long non-coding RNA COL4A2-AS1
facilitates cell proliferation and glycolysis of colorectal cancer
cells via miR-20b-5p/hypoxia inducible factor 1 alpha subunit axis.
Bioengineered. 12:6251–6263. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu Y, He D, Xiao M, Zhu Y, Zhou J and Cao
K: Long noncoding RNA LINC00518 induces radioresistance by
regulating glycolysis through an miR-33a-3p/HIF-1α negative
feedback loop in melanoma. Cell Death Dis. 12:2452021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen Y, Cao K, Li J, Wang A, Sun L, Tang
J, Xiong W, Zhou X, Chen X, Zhou J and Liu Y: Overexpression of
long non-coding RNA NORAD promotes invasion and migration in
malignant melanoma via regulating the MIR-205-EGLN2 pathway. Cancer
Med. 8:1744–1754. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wu L, Liu G, He YW, Chen R and Wu ZY:
Identification of a pyroptosis-associated long non-coding RNA
signature for predicting the immune status and prognosis in skin
cutaneous melanoma. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 25:5597–5609.
2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chen H, Pan Y, Jin X and Chen G:
Identification of a four hypoxia-associated long non-coding RNA
signature and establishment of a nomogram predicting prognosis of
clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Front Oncol. 11:7133462021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Raimondi S, Suppa M and Gandini S:
Melanoma epidemiology and sun exposure. Acta Derm Venereol.
100:adv001362020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Pavri SN, Clune J, Ariyan S and Narayan D:
Narayan, malignant melanoma: Beyond the basics. Plast Reconstr
Surg. 138:330e–340e. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang H, Qin C, Liu HW, Guo X and Gan H:
An effective hypoxia-related long non-coding RNAs assessment model
for prognosis of clear cell renal carcinoma. Front Oncol.
11:6167222021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gong PJ, Shao YC, Huang SR, Zeng YF, Yuan
XN, Xu JJ, Yin WN, Wei L and Zhang JW: Hypoxia-associated
prognostic markers and competing endogenous RNA Co-expression
networks in breast cancer. Front Oncol. 10:5798682020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chi Y, Wang D, Wang J, Yu W and Yang J:
Long non-coding RNA in the pathogenesis of cancers. Cells.
8:10152019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang J, Liu H, Zhang W, Li Y, Fan Z,
Jiang H and Luo J: Identification of lncRNA-mRNA regulatory module
to explore the pathogenesis and prognosis of melanoma. Front Cell
Dev Biol. 8:6156712020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sun L, Sun P, Zhou QY, Gao X and Han Q:
Long noncoding RNA MALAT1 promotes uveal melanoma cell growth and
invasion by silencing of miR-140. Am J Transl Res. 8:3939–3946.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yu X, Zheng H, Chan MT and Wu WKK: BANCR:
A cancer-related long non-coding RNA. Am J Cancer Res. 7:1779–1787.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gao Y, Zhu H and Mao Q: Expression of
lncRNA FGD5-AS1 correlates with poor prognosis in melanoma
patients. J Gene Med. 22:e32782020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yu X, Zheng H, Tse G, Chan MT and Wu WK:
Long non-coding RNAs in melanoma. Cell Prolif. 51:e124572018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Karagkouni D, Karavangeli A,
Paraskevopoulou MD and Hatzigeorgiou AG: Characterizing
miRNA-lncRNA interplay. Methods Mol Biol. 2372:243–262. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lai X, Eberhardt M, Schmitz U and Vera J:
Systems biology-based investigation of cooperating microRNAs as
monotherapy or adjuvant therapy in cancer. Nucleic Acids Res.
47:7753–7766. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang T, Choi S, Zhang T, Chen Z, Chi Y,
Huang S, Xiang JZ and Du YN: miR-431 promotes metastasis of
pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors by targeting DAB2 interacting
protein, a ras GTPase activating protein tumor suppressor. Am J
Pathol. 190:689–701. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Feng J, Li K, Liu G, Feng Y, Shi H and
Zhang X: Precision hyperthermia-induced miRNA-409-3p upregulation
inhibits migration, invasion, and EMT of gastric cancer cells by
targeting KLF17. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 549:113–119. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Salminen A, Kaarniranta K, Kauppinen A,
Ojala J, Haapasalo A, Soininen H and Hiltunen M: Impaired autophagy
and APP processing in Alzheimer's disease: The potential role of
Beclin 1 interactome. Prog Neurobiol. 106-107:33–54. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Su J, Morgani SM, David CJ, Wang Q, Er EE,
Huang YH, Basnet H, Zou Y, Shu W, Soni RK, et al: TGF-β
orchestrates fibrogenic and developmental EMTs via the RAS effector
RREB1. Nature. 577:566–571. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhang B, Tang B, Gao J, Li J, Kong L and
Qin L: A hypoxia-related signature for clinically predicting
diagnosis, prognosis and immune microenvironment of hepatocellular
carcinoma patients. J Transl Med. 18:3422020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Souri Z, Wierenga APA, Mulder A, Jochemsen
AG and Jager MJ: HLA expression in uveal melanoma: An indicator of
malignancy and a modifiable immunological target. Cancers (Basel).
11:11322019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Serana F, Sottini A, Caimi L, Palermo B,
Natali PG, Nisticò P and Imberti L: Identification of a public CDR3
motif and a biased utilization of T-cell receptor V beta and J beta
chains in HLA-A2/Melan-A-specific T-cell clonotypes of melanoma
patients. J Transl Med. 7:212009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Guo J, Gan Q, Gan C, Zhang X, Ma X and
Dong M: LncRNA MIR205HG regulates melanomagenesis via the
miR-299-3p/VEGFA axis. Aging (Albany NY). 13:5297–5311. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Liu N, Liu Z, Liu X and Chen H:
Comprehensive analysis of a competing endogenous RNA network
identifies seven-lncRNA signature as a prognostic biomarker for
melanoma. Front Oncol. 9:9352019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Gu L, Zhu Y, Lin X and Li Y, Cui K,
Prochownik EV and Li Y: Amplification of glyceronephosphate
O-acyltransferase and recruitment of USP30 stabilize DRP1 to
promote hepatocarcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 78:5808–5819. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lv Y, Wei W, Huang Z, Chen Z, Fang Y, Pan
L, Han X and Xu Z: Long non-coding RNA expression profile can
predict early recurrence in hepatocellular carcinoma after curative
resection. Hepatol Res. 48:1140–1148. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
He Y and Wang X: Identification of
molecular features correlating with tumor immunity in gastric
cancer by multi-omics data analysis. Ann Transl Med. 8:10502020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Xu W and McArthur G: Cell cycle regulation
and melanoma. Curr Oncol Rep. 18:342016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Barnaba N and LaRocque JR: Targeting cell
cycle regulation via the G2-M checkpoint for synthetic lethality in
melanoma. Cell Cycle. 20:1041–1051. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Afrang N and Honardoost M: Cell cycle
regulatory markers in melanoma: New strategies in diagnosis and
treatment. Med J Islam Repub Iran. 33:962019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Nishiya N: Screening for chemical
suppressors of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Yakugaku
Zasshi. 137:133–136. 2017.(In Japanese). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Xue G, Romano E, Massi D and Mandalà M:
Wnt/β-catenin signaling in melanoma: Preclinical rationale and
novel therapeutic insights. Cancer Treat Rev. 49:1–12. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Xu L, Zhang Y, Zhao Z, Chen Z, Wang Z, Xu
S, Zhang X, Liu T and Yu S: The long non-coding RNA CRNDE competed
endogenously with miR-205 to promote proliferation and metastasis
of melanoma cells by targeting CCL18. Cell Cycle. 17:2296–2308.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Sahranavardfard P, Madjd Z, Emami Razavi
AN, Ghanadan AR, Firouzi J, Khosravani P, Ghavami S, Ebrahimie E
and Ebrahimi M: An integrative analysis of the Micro-RNAs
contributing in stemness, metastasis and B-Raf pathways in
malignant melanoma and melanoma stem cell. Cell J. 23:261–272.
2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Sánchez-Sendra B, Serna E, Navarro L,
González-Muñoz JF, Portero J, Ramos A, Murgui A and Monteagudo C:
Transcriptomic identification of miR-205 target genes potentially
involved in metastasis and survival of cutaneous malignant
melanoma. Sci Rep. 10:47712020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|