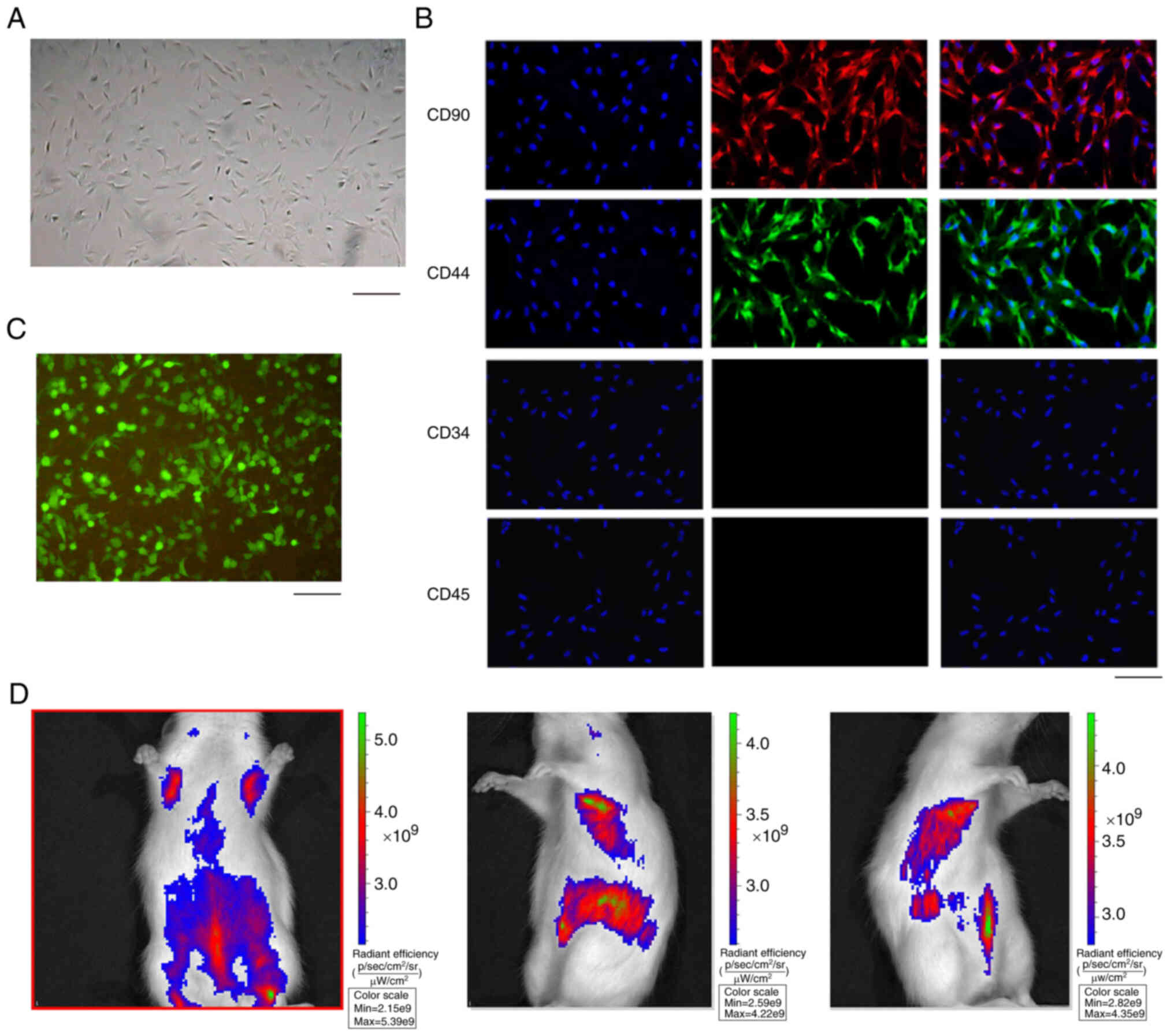
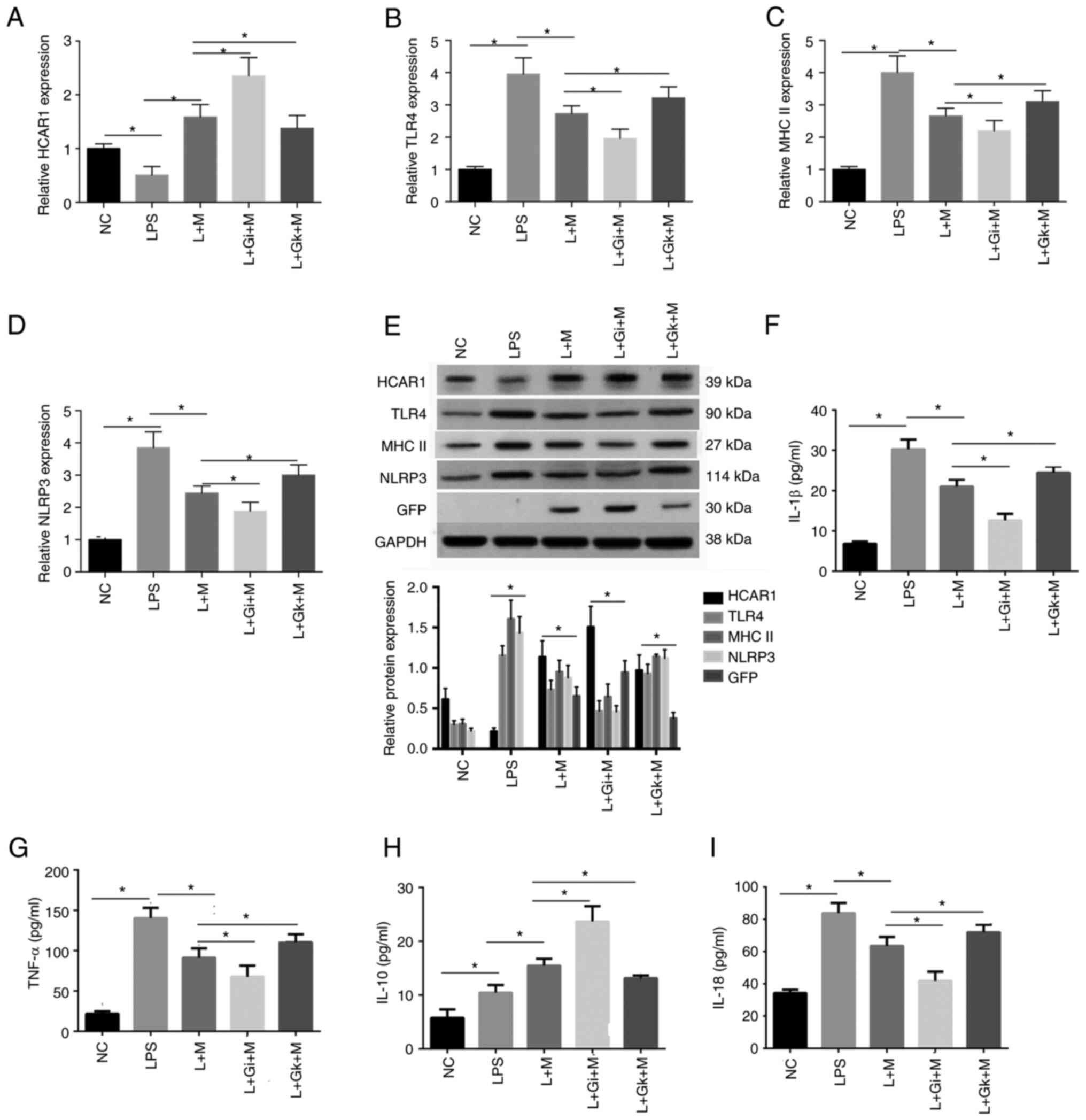
|
1
|
Singer M, Deutschman CS, Seymour CW,
Shankar-Hari M, Annane D, Bauer M, Bellomo R, Bernard GR, Chiche
JD, Coopersmith CM, et al: The third international consensus
definitions for sepsis and septic shock (sepsis-3). JAMA.
315:801–810. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rudd KE, Johnson SC, Agesa KM, Shackelford
KA, Tsoi D, Kievlan DR, Colombara DV, Ikuta KS, Kissoon N, Finfer
S, et al: Global, regional, and national sepsis incidence and
mortality, 1990–2017: Analysis for the global burden of disease
study. Lancet. 395:200–211. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Perman SM, Goyal M and Gaieski DF: Initial
emergency department diagnosis and management of adult patients
with severe sepsis and septic shock. Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg
Med. 20:412012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Iwashyna TJ, Ely EW, Smith DM and Langa
KM: Long-term cognitive impairment and functional disability among
survivors of severe sepsis. JAMA. 304:1787–1794. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Huang CY, Daniels R, Lembo A, Hartog C,
O'Brien J, Heymann T, Reinhart K and Nguyen HB; Sepsis Survivors
Engagement Project (SSEP), : Life after sepsis: an international
survey of survivors to understand the post-sepsis syndrome. Int J
Qual Health Care. 31:191–198. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kim EY, Ner-Gaon H, Varon J, Cullen AM,
Guo J, Choi J, Barragan-Bradford D, Higuera A, Pinilla-Vera M,
Short SA, et al: Post-sepsis immunosuppression depends on NKT cell
regulation of mTOR/IFN-γ in NK cells. J Clin Invest. 130:3238–3252.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Koh H, Sun HN, Xing Z, Liu R, Chandimali
N, Kwon T and Lee DS: Wogonin influences osteosarcoma stem cell
stemness through ROS-dependent signaling. In Vivo. 34:1077–1084.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sun W, Li H and Gu J: Up-regulation of
microRNA-574 attenuates lipopolysaccharide- or cecal ligation and
puncture-induced sepsis associated with acute lung injury. Cell
Biochem Funct. 38:847–858. 2020. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Qiu N, Xu X and He Y: LncRNA TUG1
alleviates sepsis-induced acute lung injury by targeting
miR-34b-5p/GAB1. BMC Pulm Med. 20:492020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Laroye C, Gibot S, Reppel L and Bensoussan
D: Concise review: Mesenchymal stromal/stem cells: A new treatment
for sepsis and septic shock? Stem Cells. 35:2331–2339. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kariminekoo S, Movassaghpour A, Rahimzadeh
A, Talebi M, Shamsasenjan K and Akbarzadeh A: Implications of
mesenchymal stem cells in regenerative medicine. Artif Cells
Nanomed Biotechnol. 44:749–757. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Thomas ED: Bone marrow transplantation
from the personal viewpoint. Int J Hematol. 81:89–93. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I,
Slaper-Cortenbach I, Marini F, Krause D, Deans R, Keating A,
Prockop Dj and Horwitz E: Minimal criteria for defining multipotent
mesenchymal stromal cells. The international society for cellular
therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 8:315–317. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Perlee D, de Vos AF, Scicluna BP, Mancheño
P, de la Rosa O, Dalemans W, Nürnberg P, Lombardo E and van der
Poll T: Human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells modify lung
immunity and improve antibacterial defense in pneumosepsis caused
by Klebsiella pneumoniae. Stem Cells Transl Med. 8:785–796. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Hackstein H, Lippitsch A, Krug P,
Schevtschenko I, Kranz S, Hecker M, Dietert K, Gruber AD, Bein G,
Brendel C and Baal N: Prospectively defined murine mesenchymal stem
cells inhibit Klebsiella pneumoniae-induced acute lung injury and
improve pneumonia survival. Respir Res. 16:1232015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Argentati C, Morena F, Bazzucchi M,
Armentano I, Emiliani C and Martino S: Adipose stem cell
translational applications: From bench-to-bedside. Int J Mol Sci.
19:34752018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kapur SK and Katz AJ: Review of the
adipose derived stem cell secretome. Biochimie. 95:2222–2228. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Horie S, Gaynard S, Murphy M, Barry F,
Scully M, O'Toole D and Laffey JG: Cytokine pre-activation of
cryopreserved xenogeneic-free human mesenchymal stromal cells
enhances resolution and repair following ventilator-induced lung
injury potentially via a KGF-dependent mechanism. Intensive Care
Med Exp. 8:82020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jung YJ, Park YY, Huh JW and Hong SB: The
effect of human adipose-derived stem cells on
lipopolysaccharide-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome in
mice. Ann Transl Med. 7:6742019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Turesson C: Endothelial expression of MHC
class II molecules in autoimmune disease. Curr Pharm Des.
10:129–143. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Brooks GA: Lactate as a fulcrum of
metabolism. Redox Biol. 35:1014542020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hoque R, Farooq A, Ghani A, Gorelick F and
Mehal WZ: Lactate reduces liver and pancreatic injury in Toll-like
receptor- and inflammasome-mediated inflammation via GPR81-mediated
suppression of innate immunity. Gastroenterology. 146:1763–1774.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Raychaudhuri D, Bhattacharya R, Sinha BP,
Liu CSC, Ghosh AR, Rahaman O, Bandopadhyay P, Sarif J, D'Rozario R,
Paul S, et al: Lactate induces pro-tumor reprogramming in
intratumoral plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Front Immunol.
10:18782019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liu Z, Meng Z, Li Y, Zhao J, Wu S, Gou S
and Wu H: Prognostic accuracy of the serum lactate level, the SOFA
score and the qSOFA score for mortality among adults with Sepsis.
Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg Med. 27:512019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kalyanaraman B, Darley-Usmar V, Davies KJ,
Dennery PA, Forman HJ, Grisham MB, Mann GE, Moore K, Roberts LJ II
and Ischiropoulos H: Measuring reactive oxygen and nitrogen species
with fluorescent probes: Challenges and limitations. Free Radic
Biol Med. 52:1–6. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Vicente-Dueñas C, González-Herrero I,
García Cenador MB, García Criado FJ and Sánchez-García I: Loss of
p53 exacerbates multiple myeloma phenotype by facilitating the
reprogramming of hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells to malignant
plasma cells by MafB. Cell Cycle. 11:3896–3900. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Rosengarten B, Wolff S, Klatt S and
Schermuly RT: Effects of inducible nitric oxide synthase inhibition
or norepinephrine on the neurovascular coupling in an endotoxic rat
shock model. Crit Care. 13:R1392009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liang Y, Su Y, Xu C, Zhang N, Liu D, Li G,
Tong T and Chen J: Protein kinase D1 phosphorylation of KAT7
enhances its protein stability and promotes replication licensing
and cell proliferation. Cell Death Discov. 6:892020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Salomão R, Ferreira BL, Salomão MC, Santos
SS, Azevedo LCP and Brunialti MKC: Sepsis: Evolving concepts and
challenges. Braz J Med Biol Res. 52:e85952019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Korbecki J and Bajdak-Rusinek K: The
effect of palmitic acid on inflammatory response in macrophages: An
overview of molecular mechanisms. Inflamm Res. 68:915–932. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Khatib-Massalha E, Bhattacharya S,
Massalha H, Biram A, Golan K, Kollet O, Kumari A, Avemaria F,
Petrovich-Kopitman E, Gur-Cohen S, et al: Lactate released by
inflammatory bone marrow neutrophils induces their mobilization via
endothelial GPR81 signaling. Nat Commun. 11:35472020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Xiang P, Chen T, Mou Y, Wu H, Xie P, Lu G,
Gong X, Hu Q, Zhang Y and Ji H: NZ suppresses TLR4/NF-κB signalings
and NLRP3 inflammasome activation in LPS-induced RAW264.7
macrophages. Inflamm Res. 64:799–808. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lee YJ, Shin KJ, Park SA, Park KS, Park S,
Heo K, Seo YK, Noh DY, Ryu SH and Suh PG: G-protein-coupled
receptor 81 promotes a malignant phenotype in breast cancer through
angiogenic factor secretion. Oncotarget. 7:70898–70911. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Xie Q, Zhu Z, He Y, Zhang Z, Zhang Y, Wang
Y, Luo J, Peng T, Cheng F, Gao J, et al: A lactate-induced
Snail/STAT3 pathway drives GPR81 expression in lung cancer cells.
Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 1866:1655762020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Popp FC, Piso P, Schlitt HJ and Dahlke MH:
Therapeutic potential of bone marrow stem cells for liver diseases.
Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 1:411–418. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang W, Zheng Y, Sun S, Li W, Song M, Ji
Q, Wu Z, Liu Z, Fan Y, Liu F, et al: A genome-wide CRISPR-based
screen identifies KAT7 as a driver of cellular senescence. Sci
Transl Med. 13:eabd26552021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Fu YJ, Xu B, Huang SW, Luo X, Deng XL, Luo
S, Liu C, Wang Q, Chen JY and Zhou L: Baicalin prevents LPS-induced
activation of TLR4/NF-κB p65 pathway and inflammation in mice via
inhibiting the expression of CD14. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 42:88–96.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bauer AK and Kleeberger SR: Genetic
mechanisms of susceptibility to ozone-induced lung disease. Ann NY
Acad Sci. 1203:113–119. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|