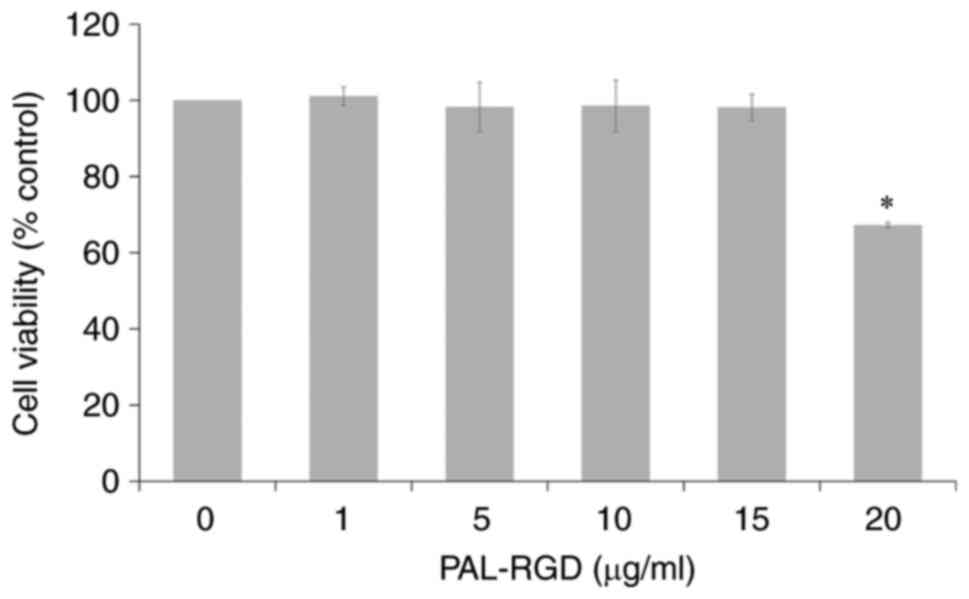
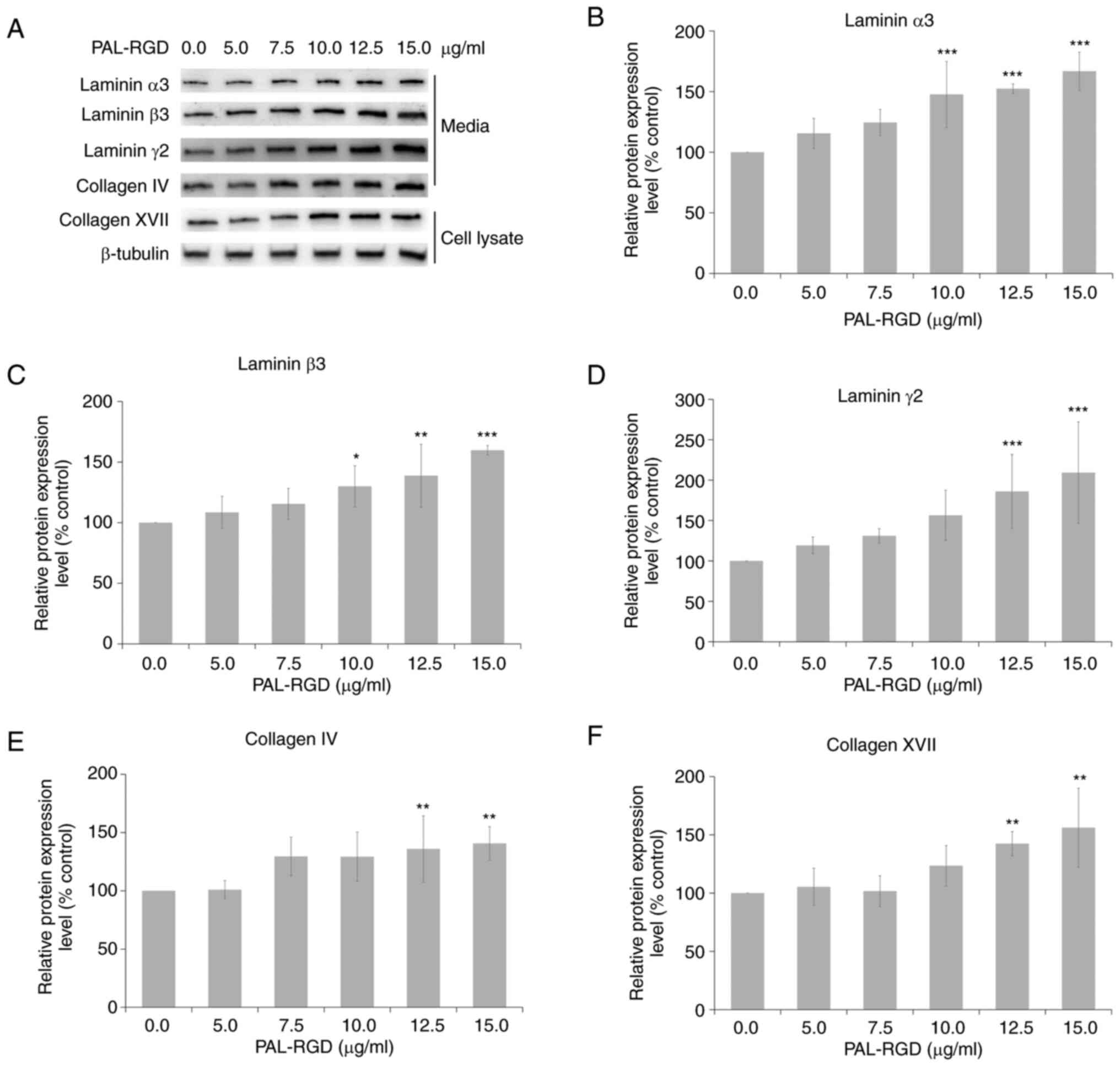
|
1
|
Burgeson RE and Christiano AM: The
dermal-epidermal junction. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 9:651–658. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Roig-Rosello E and Rousselle P: The human
epidermal basement membrane: A shaped and cell instructive platform
that aging slowly alters. Biomolecules. 10:16072020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Marionnet C, Vioux-Chagnoleau C, Pierrard
C, Sok J, Asselineau D and Bernerd F: Morphogenesis of
dermal-epidermal junction in a model of reconstructed skin:
Beneficial effects of vitamin C. Exp Dermatol. 15:625–633. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lavker RM, Zheng P and Dong G: Aged skin:
A study by light, transmission electron, and scanning electron
microscopy. J Invest Dermatol. 88 (3 Suppl):44s–51s. 1987.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Vázquez F, Palacios S, Alemañ N and
Guerrero F: Changes of the basement membrane and type IV collagen
in human skin during aging. Maturitas. 25:209–215. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Langton AK, Halai P, Griffiths CE,
Sherratt MJ and Watson RE: The impact of intrinsic ageing on the
protein composition of the dermal-epidermal junction. Mech Ageing
Dev. 156:14–16. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mondon P, Hillion M, Peschard O, Andre N,
Marchand T, Doridot E, Feuilloley MG, Pionneau C and Chardonnet S:
Evaluation of dermal extracellular matrix and epidermal-dermal
junction modifications using matrix-assisted laser
desorption/ionization mass spectrometric imaging, in vivo
reflectance confocal microscopy, echography, and histology: Effect
of age and peptide applications. J Cosmet Dermatol. 14:152–160.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Contet-Audonneau JL, Jeanmaire C and Pauly
G: A histological study of human wrinkle structures: Comparison
between sun-exposed areas of the face, with or without wrinkles,
and sun-protected areas. Br J Dermatol. 140:1038–1047. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Varlet BL, Chaudagne C, Barré P, Sauvage
C, Berthouloux B, Meybeck A, Dumas M, Saunois A and Bonté F:
Age-related functional and structural changes in human
dermo-epidermal junction components. Journal of Investigative
Dermatology Symposium Proceedings. Vol. 3. Elsevier; pp. 172–179.
1998, View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ishihara J, Ishihara A, Fukunaga K, Sasaki
K, White MJV, Briquez PS and Hubbell JA: Laminin heparin-binding
peptides bind to several growth factors and enhance diabetic wound
healing. Nat Commun. 9:21632018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Iorio V, Troughton LD and Hamill KJ:
Laminins: Roles and utility in wound repair. Adv Wound Care (New
Rochelle). 4:250–263. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chung HJ and Uitto J: Type VII collagen:
The anchoring fibril protein at fault in dystrophic epidermolysis
bullosa. Dermatol Clin. 28:93–105. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Watanabe M, Natsuga K, Nishie W, Kobayashi
Y, Donati G, Suzuki S, Fujimura Y, Tsukiyama T, Ujiie H, Shinkuma
S, et al: Type XVII collagen coordinates proliferation in the
interfollicular epidermis. Elife. 6:e266352017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jeong S, Yoon S, Kim S, Jung J, Kor M,
Shin K, Lim C, Han HS, Lee H, Park KY, et al: Anti-wrinkle benefits
of peptides complex stimulating skin basement membrane proteins
expression. Int J Mol Sci. 21:732019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Amano S: Possible involvement of basement
membrane damage in skin photoaging. Journal of Investigative
Dermatology Symposium Proceedings. Vol. 14. Elsevier; pp. 2–7.
2009, View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kusumaningrum N, Oh JH, Lee DH, Shin CY,
Jang JH, Kim YK and Chung JH: Topical treatment with a cathepsin G
inhibitor, β-keto-phosphonic acid, blocks ultraviolet
irradiation-induced basement membrane damage in hairless mouse
skin. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 35:148–156. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bae JS, Kim JM, Kim JY, Choi CH, Kim JY,
Moon WK, Lee MS, Moon SH, Lim JH, Park SJ, et al: Topical
application of palmitoyl-RGD reduces human facial wrinkle formation
in Korean women. Arch Dermatol Res. 309:665–671. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Peters BP, Hartle RJ, Krzesicki RF, Kroll
TG, Perini F, Balun JE, Goldstein IJ and Ruddon RW: The
biosynthesis, processing, and secretion of laminin by human
choriocarcinoma cells. J Biol Chem. 260:14732–1442. 1985.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Korang K, Christiano AM, Uitto J and
Mauviel A: Differential cytokine modulation of the genes LAMA3,
LAMB3, and LAMC2, encoding the constitutive polypeptides, alpha 3,
beta 3, and gamma 2, of human laminin 5 in epidermal keratinocytes.
FEBS Lett. 368:556–558. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Feru J, Delobbe E, Ramont L, Brassart B,
Terryn C, Dupont-Deshorgue A, Garbar C, Monboisse JC, Maquart FX
and Brassart-Pasco S: Aging decreases collagen IV expression in
vivo in the dermo-epidermal junction and in vitro in dermal
fibroblasts: Possible involvement of TGF-β1. Eur J Dermatol.
26:350–360. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Huilaja L, Hurskainen T, Autio-Harmainen
H, Hofmann SC, Sormunen R, Räsänen J, Ilves M, Franzke CW,
Bruckner-Tuderman L and Tasanen K: Pemphigoid gestationis
autoantigen, transmembrane collagen XVII, promotes the migration of
cytotrophoblastic cells of placenta and is a structural component
of fetal membranes. Matrix Biol. 27:190–200. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sugawara K, Tsuruta D, Ishii M, Jones JC
and Kobayashi H: Laminin-332 and −511 in skin. Exp Dermatol.
17:473–480. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Miner JH and Yurchenco PD: Laminin
functions in tissue morphogenesis. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol.
20:255–284. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tsuruta D, Kobayashi H, Imanishi H,
Sugawara K, Ishii M and Jones JC: Laminin-332-integrin interaction:
A target for cancer therapy? Curr Med Chem. 15:1968–1975. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kariya Y and Gu J: Roles of laminin-332
and alpha6beta4 integrin in tumor progression. Mini Rev Med Chem.
9:1284–1291. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gonzales M, Haan K, Baker SE, Fitchmun M,
Todorov I, Weitzman S and Jones JC: A cell signal pathway involving
laminin-5, alpha3beta1 integrin, and mitogen-activated protein
kinase can regulate epithelial cell proliferation. Mol Biol Cell.
10:259–270. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Choma DP, Milano V, Pumiglia KM and
DiPersio CM: Integrin alpha3beta1-dependent activation of FAK/Src
regulates Rac1-mediated keratinocyte polarization on laminin-5. J
Invest Dermatol. 127:31–40. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mainiero F, Pepe A, Wary KK, Spinardi L,
Mohammadi M, Schlessinger J and Giancotti F: Signal transduction by
the alpha 6 beta 4 integrin: Distinct beta 4 subunit sites mediate
recruitment of Shc/Grb2 and association with the cytoskeleton of
hemidesmosomes. EMBO J. 14:4470–4481. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Pöschl E, Schlötzer-Schrehardt U,
Brachvogel B, Saito K, Ninomiya Y and Mayer U: Collagen IV is
essential for basement membrane stability but dispensable for
initiation of its assembly during early development. Development.
131:1619–1628. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Brown KL, Cummings CF, Vanacore RM and
Hudson BG: Building collagen IV smart scaffolds on the outside of
cells. Protein Sci. 26:2151–2161. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Good MC, Zalatan JG and Lim WA: Scaffold
proteins: Hubs for controlling the flow of cellular information.
Science. 332:680–686. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Trappmann B, Gautrot JE, Connelly JT,
Strange DG, Li Y, Oyen ML, Cohen Stuart MA, Boehm H, Li B, Vogel V,
et al: Extracellular-matrix tethering regulates stem-cell fate. Nat
Mater. 11:642–649. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Nishimura M, Nishie W, Shirafuji Y,
Shinkuma S, Natsuga K, Nakamura H, Sawamura D, Iwatsuki K and
Shimizu H: Extracellular cleavage of collagen XVII is essential for
correct cutaneous basement membrane formation. Hum Mol Genet.
25:328–339. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Natsuga K, Watanabe M, Nishie W and
Shimizu H: Life before and beyond blistering: The role of collagen
XVII in epidermal physiology. Exp Dermatol. 28:1135–1141. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kamaguchi M, Iwata H, Nishie W, Toyonaga
E, Ujiie H, Natsuga K, Kitagawa Y and Shimizu H: The direct binding
of collagen XVII and collagen IV is disrupted by pemphigoid
autoantibodies. Lab Invest. 99:48–57. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|