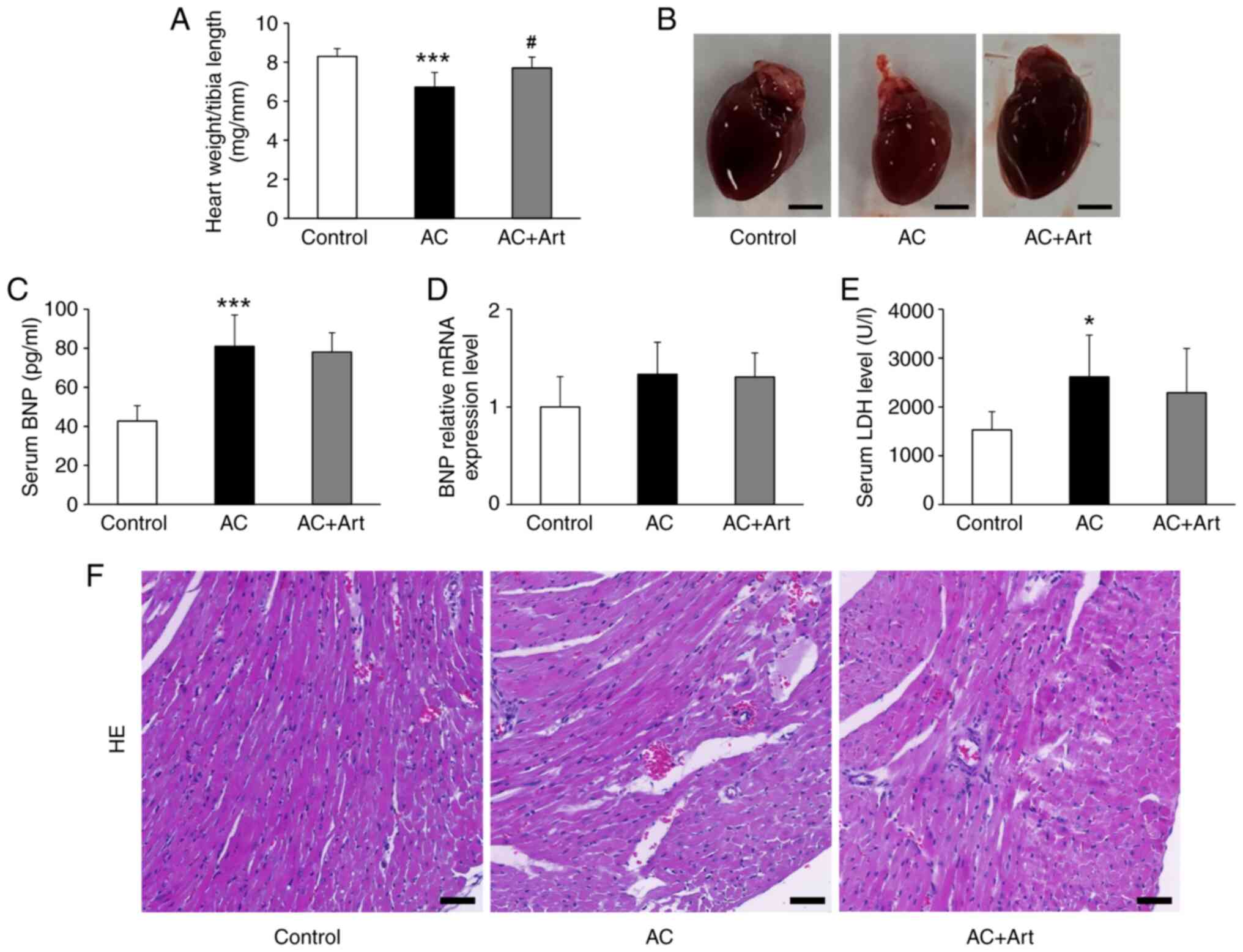
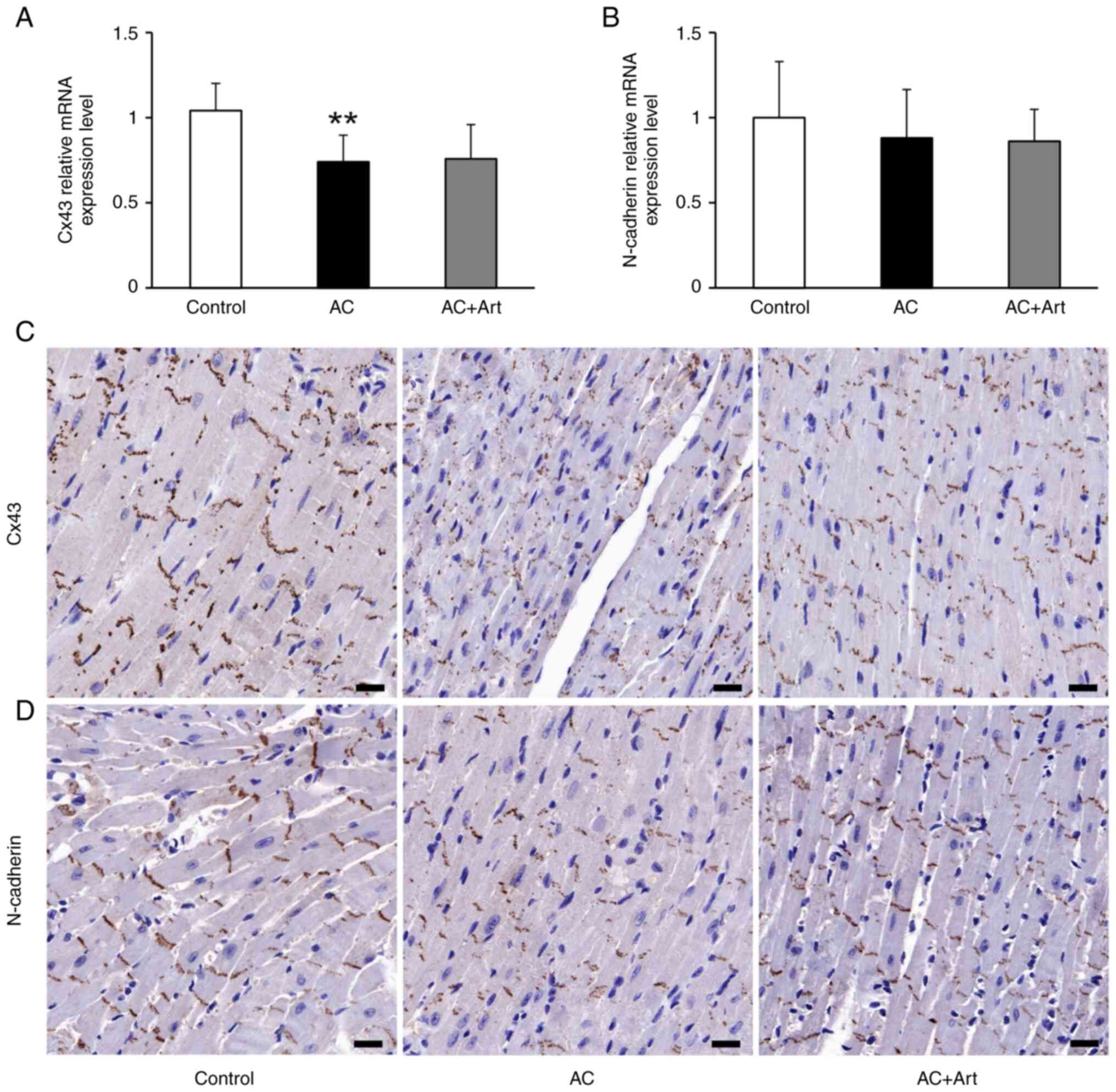
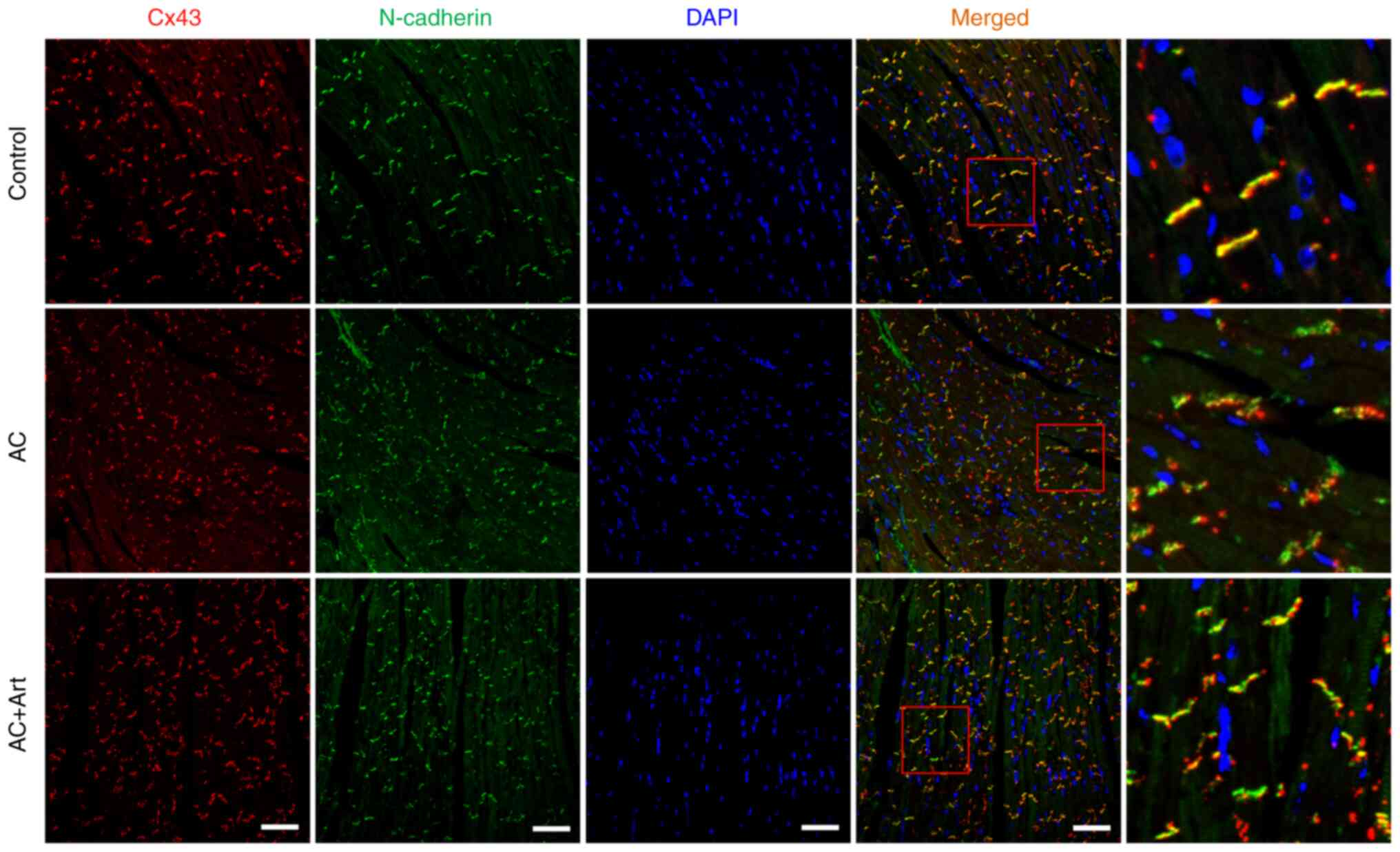
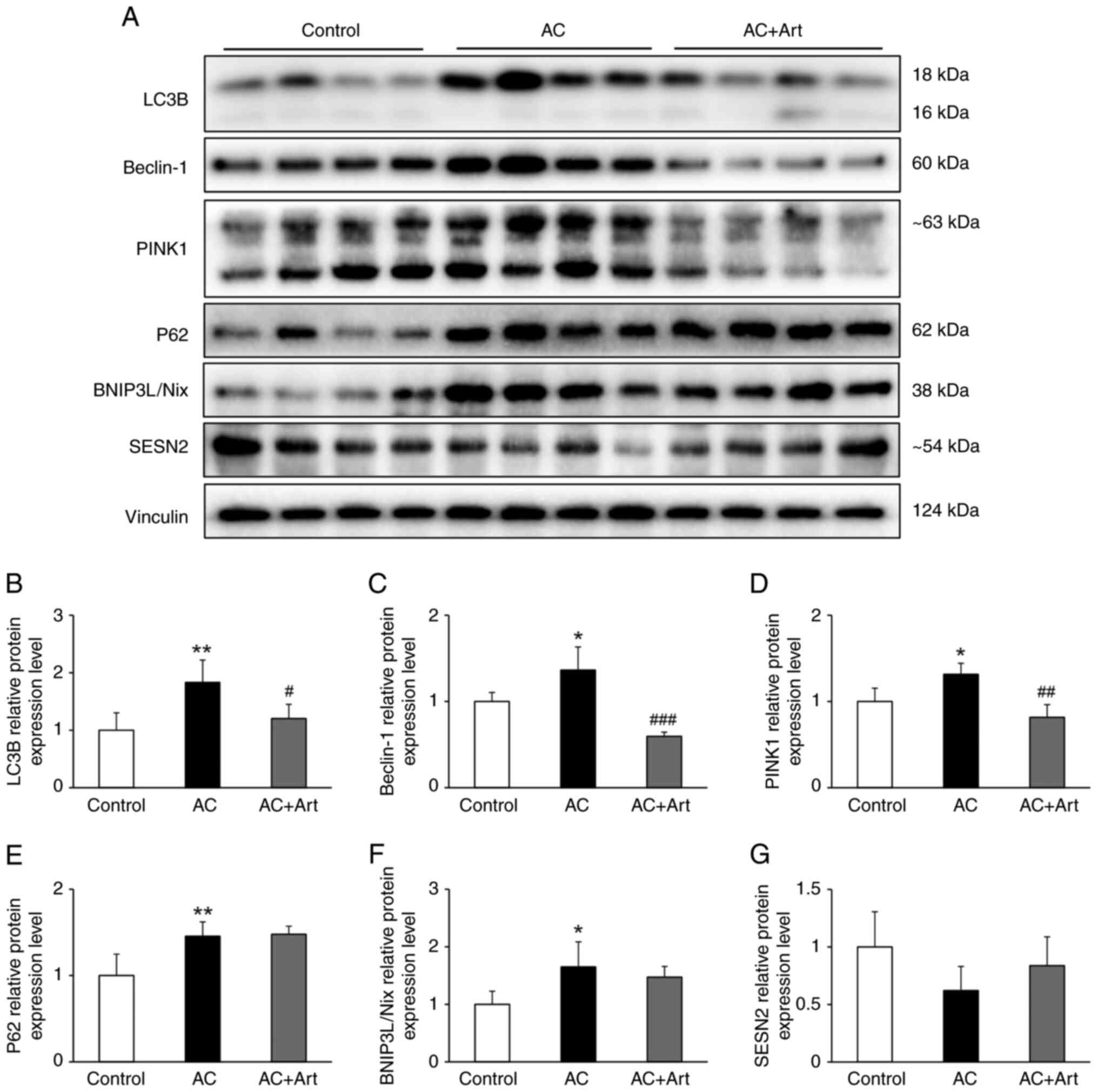
|
1
|
van der Zanden SY, Qiao X and Neefjes J:
New insights into the activities and toxicities of the old
anticancer drug doxorubicin. FEBS J. 288:6095–6111. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tacar O, Sriamornsak P and Dass CR:
Doxorubicin: An update on anticancer molecular action, toxicity and
novel drug delivery systems. J Pharm Pharmacol. 65:157–170. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sritharan S and Sivalingam N: A
comprehensive review on time-tested anticancer drug doxorubicin.
Life Sci. 278:1195272021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Pugazhendhi A, Edison TNJI, Velmurugan BK,
Jacob JA and Karuppusamy I: Toxicity of Doxorubicin (Dox) to
different experimental organ systems. Life Sci. 200:26–30. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Christidi E and Brunham LR: Regulated cell
death pathways in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity. Cell Death
Dis. 12:3392021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chen DS, Yan J and Yang PZ: Cardiomyocyte
Atrophy, an Underestimated Contributor in Doxorubicin-Induced
Cardiotoxicity. Front Cardiovasc Med. 9:8125782022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ferreira de Souza T, Quinaglia AC, Silva
T, Osorio Costa F, Shah R, Neilan TG, Velloso L, Nadruz W, Brenelli
F, Sposito AC, Matos-Souza JR, et al: Anthracycline therapy is
associated with cardiomyocyte atrophy and preclinical
manifestations of heart disease. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging.
11:1045–1055. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bartlett JJ, Trivedi PC and Pulinilkunnil
T: Autophagic dysregulation in doxorubicin cardiomyopathy. J Mol
Cell Cardiol. 104:1–8. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Willis MS, Parry TL, Brown DI, Mota RI,
Huang W, Beak JY, Sola M, Zhou C, Hicks ST, Caughey MC, et al:
Doxorubicin exposure causes subacute cardiac atrophy dependent on
the striated muscle-specific ubiquitin ligase MuRF1. Circ Heart
Fail. 12:e0052342019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ma N, Zhang Z, Liao F, Jiang T and Tu Y:
The birth of artemisinin. Pharmacol Ther. 216:1076582020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Esu EB, Effa EE, Opie ON and Meremikwu MM:
Artemether for severe malaria. Cochrane Database Syst Rev.
6:CD0106782019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang Y, Wang Y, You F and Xue J: Novel use
for old drugs: The emerging role of artemisinin and its derivatives
in fibrosis. Pharmacol Res. 157:1048292020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dolivo D, Weathers P and Dominko T:
Artemisinin and artemisinin derivatives as anti-fibrotic
therapeutics. Acta Pharm Sin B. 11:322–339. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Han P, Wang Y, Zhan H, Weng W, Yu X, Ge N,
Wang W, Song G, Yi T, Li S, et al: Artemether ameliorates type 2
diabetic kidney disease by increasing mitochondrial pyruvate
carrier content in db/db mice. Am J Transl Res. 11:1389–1402.
2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang Y, Han P, Wang M, Weng W, Zhan H, Yu
X, Yuan C, Shao M and Sun H: Artemether improves type 1 diabetic
kidney disease by regulating mitochondrial function. Am J Transl
Res. 11:3879–3889. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Han P, Cai Y, Wang Y, Weng W, Chen Y, Wang
M, Zhan H, Yu X, Wang T, Shao M and Sun H: Artemether ameliorates
kidney injury by restoring redox imbalance and improving
mitochondrial function in Adriamycin nephropathy in mice. Sci Rep.
11:12662021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cheng X, Zhou P, Weng W, Sun Z, Liu H,
Chen Y, Cai Y, Yu X, Wang T, Shao M, et al: Artemether attenuates
renal tubular injury by targeting mitochondria in adriamycin
nephropathy mice. Am J Transl Res. 14:2002–2012. 2022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Weng W, Liu H, Sun Z, Zhou P, Yu X, Shao
M, Han P and Sun H: Combined treatment with niclosamide
ethanolamine and artemether combination improves type 1 diabetes
via the targeting of liver mitochondria. Exp Ther Med. 23:2392022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wallace KB, Sardao VA and Oliveira PJ:
Mitochondrial determinants of doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy.
Circ Res. 126:926–941. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yin FC, Spurgeon HA, Rakusan K, Weisfeldt
ML and Lakatta EG: Use of tibial length to quantify cardiac
hypertrophy: Application in the aging rat. Am J Physiol.
243:H941–H947. 1982.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhao G, Qiu Y, Zhang HM and Yang D:
Intercalated discs: Cellular adhesion and signaling in heart health
and diseases. Heart Fail Rev. 24:115–132. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Leo-Macias A, Agullo-Pascual E and Delmar
M: The cardiac connexome: Non-canonical functions of connexin43 and
their role in cardiac arrhythmias. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 50:13–21.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Orogo AM and Gustafsson AB: Therapeutic
targeting of autophagy: Potential and concerns in treating
cardiovascular disease. Circ Res. 116:489–503. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gross A and Katz SG: Non-apoptotic
functions of BCL-2 family proteins. Cell Death Differ.
24:1348–1358. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chong SJF, Marchi S, Petroni G, Kroemer G,
Galluzzi L and Pervaiz S: Noncanonical cell fate regulation by
Bcl-2 Proteins. Trends Cell Biol. 30:537–555. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jang S and Javadov S: OPA1 regulates
respiratory supercomplexes assembly: The role of mitochondrial
swelling. Mitochondrion. 51:30–39. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Dan Dunn J, Alvarez LA, Zhang X and
Soldati T: Reactive oxygen species and mitochondria: A nexus of
cellular homeostasis. Redox Biol. 6:472–485. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Shimauchi T, Numaga-Tomita T, Ito T,
Nishimura A, Matsukane R, Oda S, Hoka S, Ide T, Koitabashi N,
Uchida K, et al: TRPC3-Nox2 complex mediates doxorubicin-induced
myocardial atrophy. JCI Insight. 2:e933582017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Nash PL: Brain type natriuretic peptide.
Neonatal Netw. 27:343–346. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Belardi B, Son S, Felce JH, Dustin ML and
Fletcher DA: Cell-cell interfaces as specialized compartments
directing cell function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 21:750–764. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Dikic I and Elazar Z: Mechanism and
medical implications of mammalian autophagy. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
19:349–364. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Montalvo RN, Doerr V, Min K, Szeto HH and
Smuder AJ: Doxorubicin-induced oxidative stress differentially
regulates proteolytic signaling in cardiac and skeletal muscle. Am
J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 318:R227–R233. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Wang Y, Branicky R, Noe A and Hekimi S:
Superoxide dismutases: Dual roles in controlling ROS damage and
regulating ROS signaling. J Cell Biol. 217:1915–1928. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Boyd SD, Ullrich MS, Skopp A and Winkler
DD: Copper Sources for Sod1 Activation. Antioxidants (Basel).
9:5002020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Papa L, Hahn M, Marsh EL, Evans BS and
Germain D: SOD2 to SOD1 switch in breast cancer. J Biol Chem.
289:5412–5416. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chang YC, Fong Y, Tsai EM, Chang YG, Chou
HL, Wu CY, Teng YN, Liu TC, Yuan SS and Chiu CC: Exogenous
C8-Ceramide induces apoptosis by overproduction of ROS
and the switch of superoxide dismutases SOD1 to SOD2 in human lung
cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci. 19:30102018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|