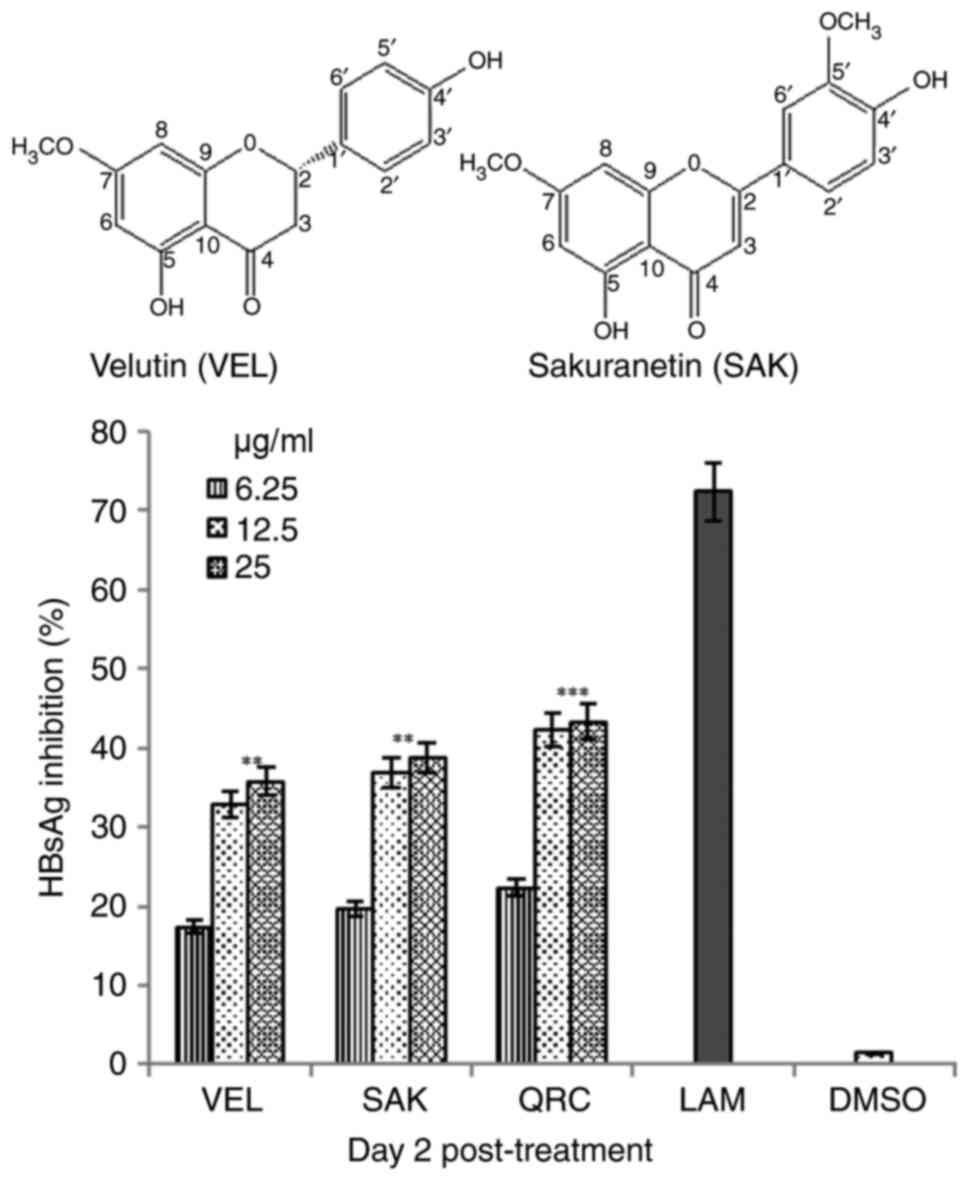
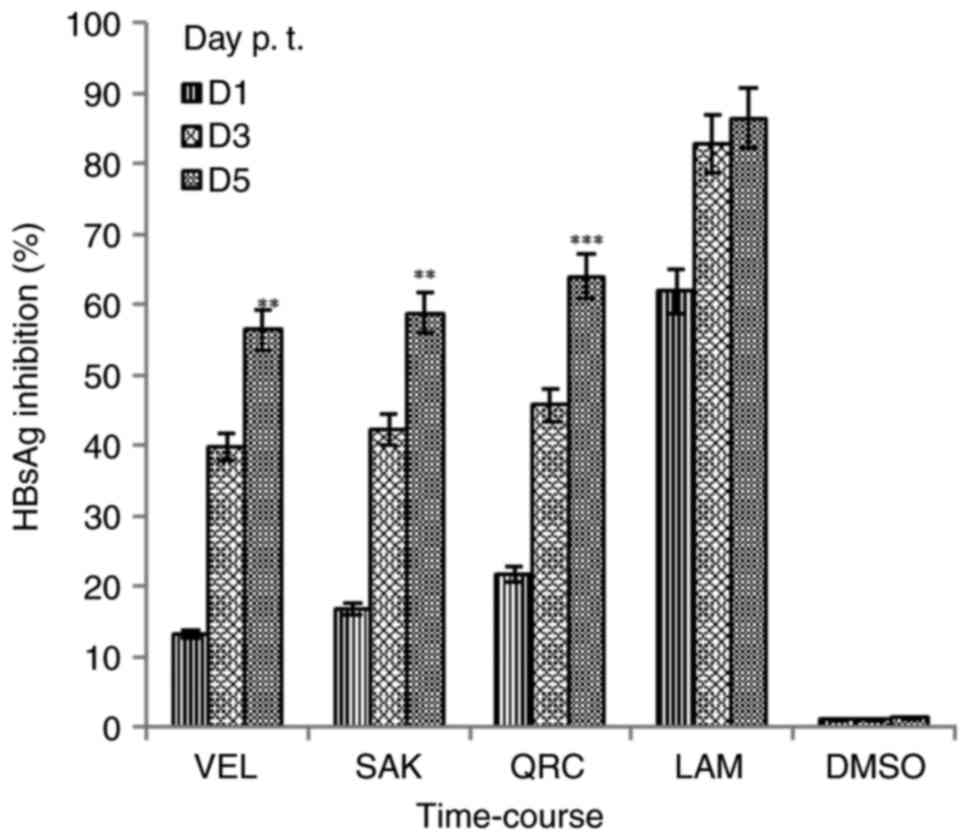
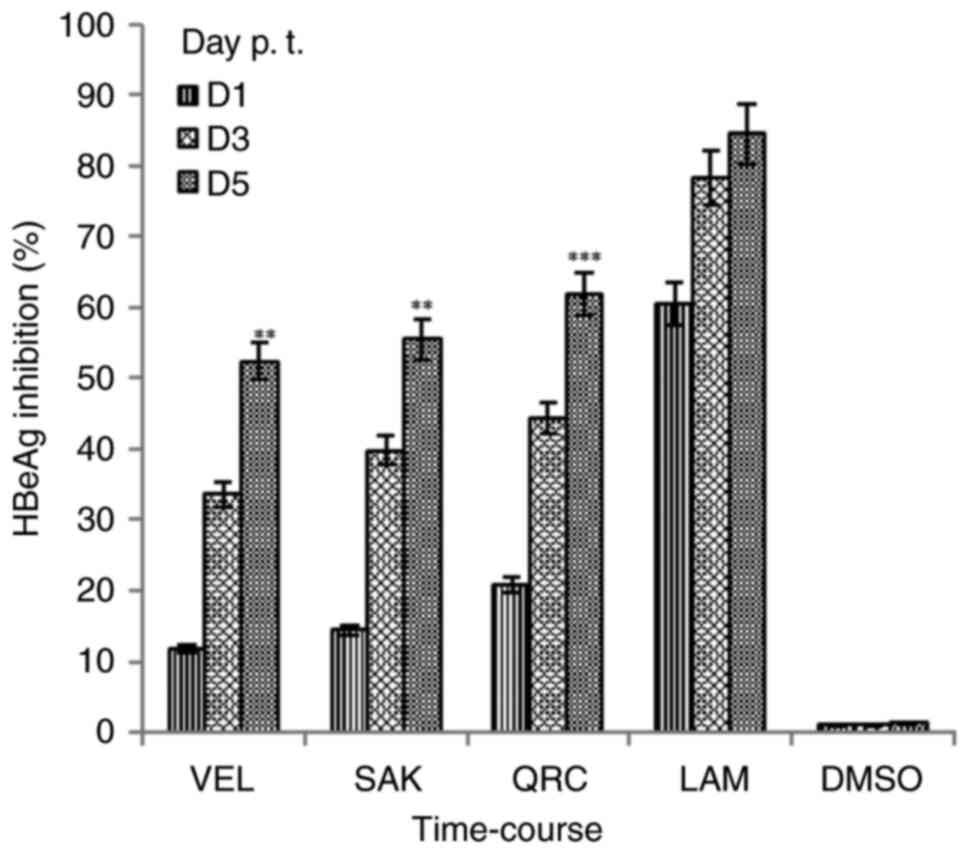
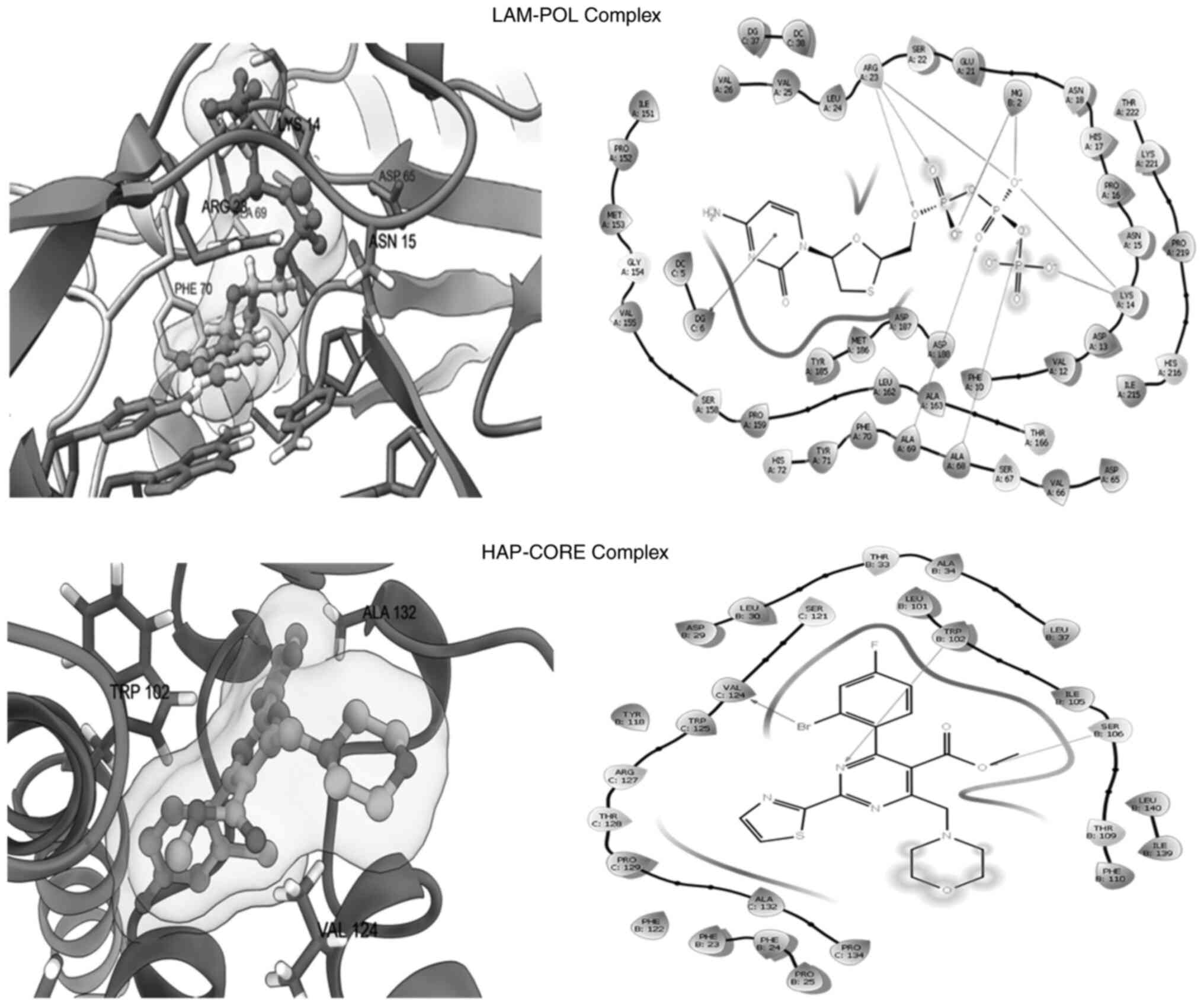
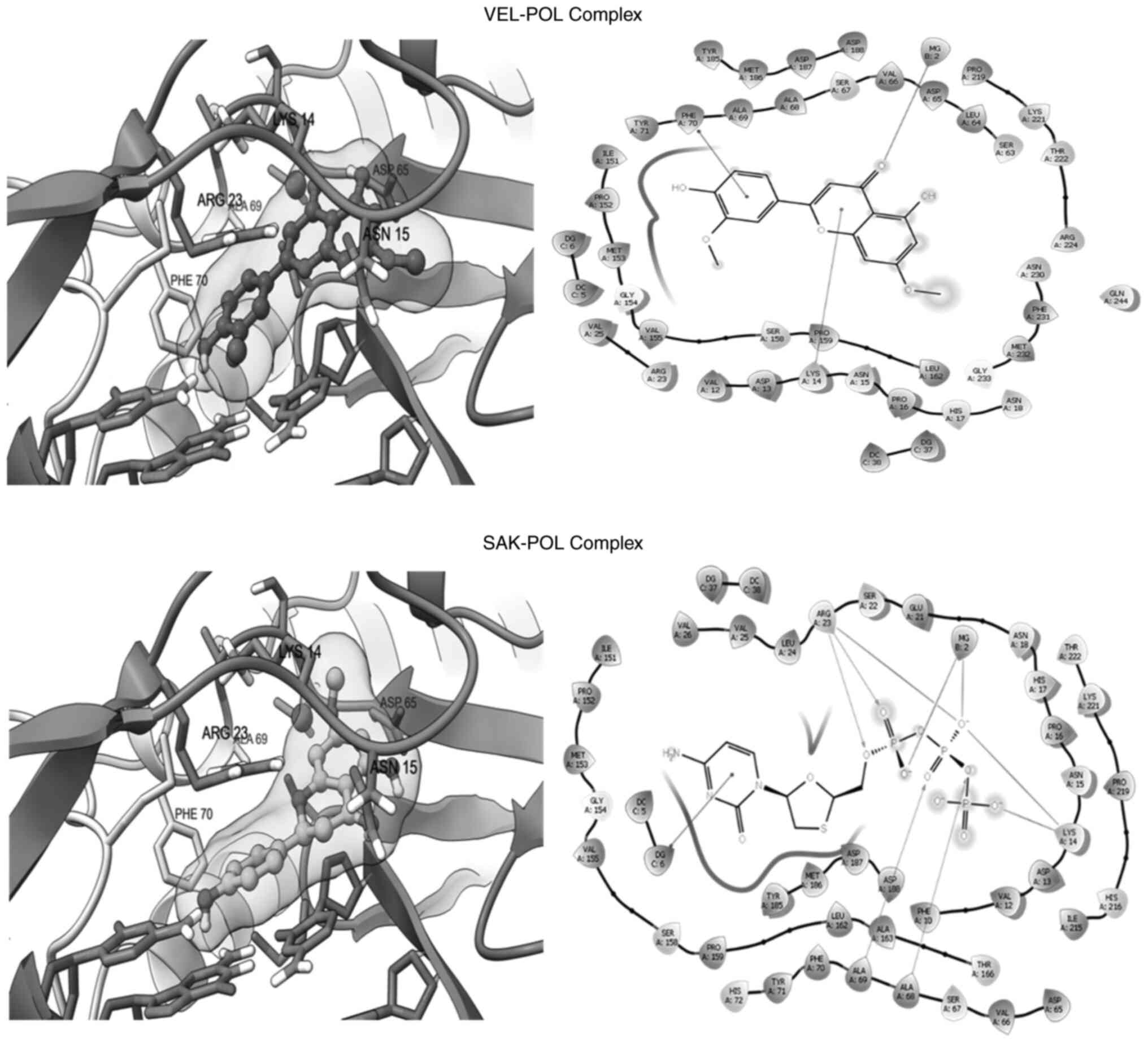
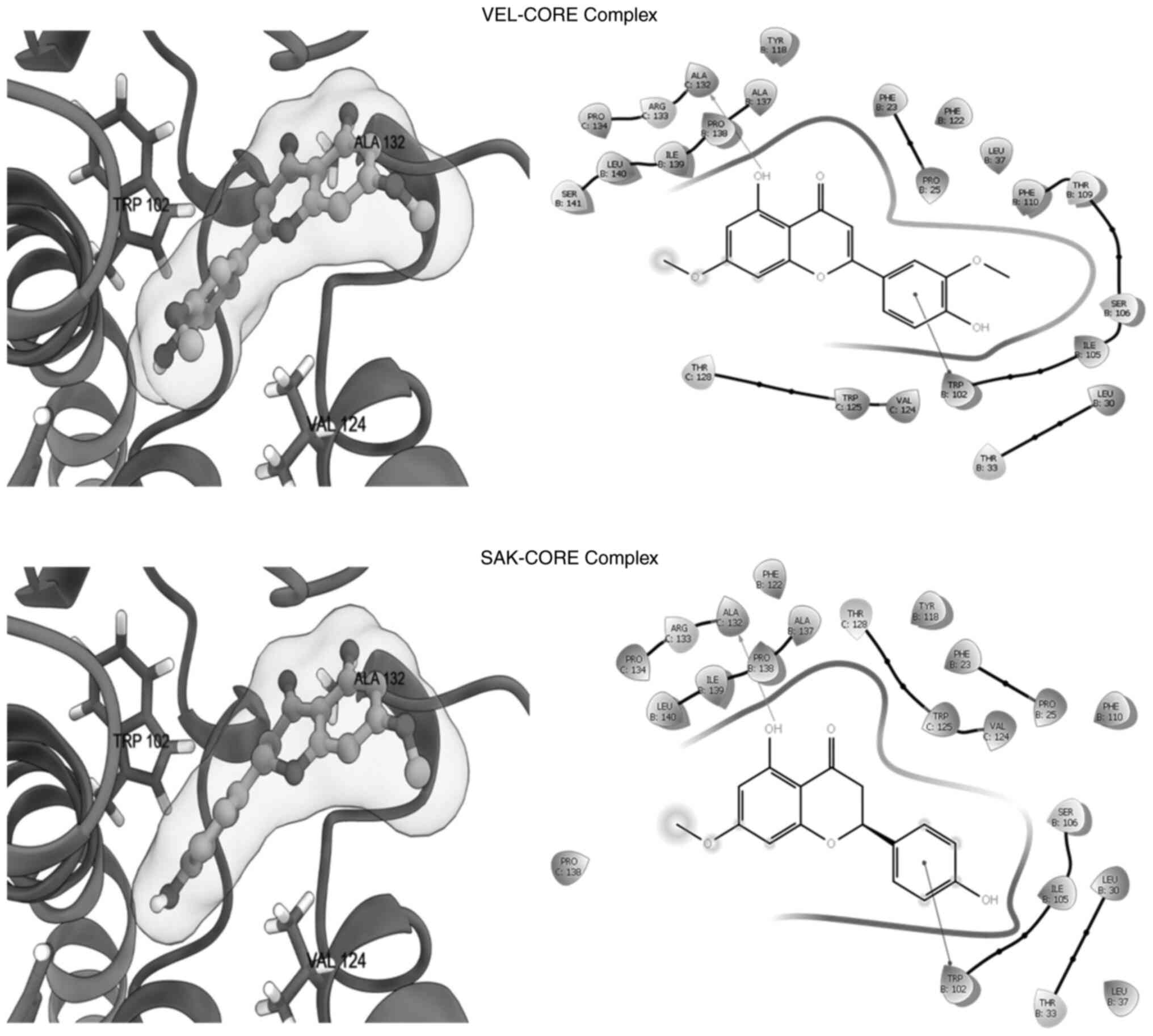
|
1
|
Rayne S and Mazza G: Biological activities
of extracts from sumac (Rhus spp.): A review. Plant Foods Hum Nutr.
62:165–175. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Van Wyk BE and Wink M: Medicinal plants of
the world. Portland, Oregon, USA: Timber Press; pp. pp4252004
|
|
3
|
Opiyo SA, Njoroge PW, Ndirangu EG and
Kuria KM: A review of biological activities and phytochemistry of
Rhus species. Am J Chem. 11:28–36. 2021.
|
|
4
|
Itidel C, Chokri M, Mohamed B and Yosr Z:
Antioxidant activity, total phenolic and flavonoid content
variation among Tunisian natural populations of Rhus
tripartite (Ucria) Grande and Rhus pentaphylla desf. Ind
Crops Prod. 51:171–177. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
El-Mokasabi FM: The state of the art of
traditional herbal medicine in the eastern mediterranean coastal
region of Libya. Middle East J Sci Res. 21:575–582. 2014.
|
|
6
|
Shahat AA, Alsaid MS, Rafatullah S,
Al-Sohaibani MO, Parvez MK, Al-Dosari MS, Exarchou V and Pieters L:
Treatment with Rhus tripartita extract curtails
isoproterenol-elicited cardiotoxicity and oxidative stress in rats.
BMC Complement Altern Med. 16:3512016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Erichsen-Brown C: Medicinal and other uses
of North American plants: A historical survey with special
reference to the Eastern Indian Tribes. Mineola, New York, USA:
Dover Publications; 1989
|
|
8
|
Sezik E, Tabata M, Yeşilada E, Honda G,
Goto K and Ikeshiro Y: Traditional medicine in Turkey. I. Folk
medicine in northeast Anatolia. J Ethnopharmacol. 35:191–196. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jang JY, Shin H, Lim JW, Ahn JH, Jo YH,
Lee KY, Hwang BY, Jung SJ, Kang SY and Lee MK: Comparison of
antibacterial activity and phenolic constituents of bark, lignum,
leaves and fruit of Rhus verniciflua. PLoS One.
13:e02002572018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kang SY, Kang JY and Oh MJ: Antiviral
activities of flavonoids isolated from the bark of Rhus
verniciflua stokes against fish pathogenic viruses in vitro. J
Microbiol. 50:293–300. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ahmed MS, Galal AM, Ross SA, Ferreira D,
ElSohly MA, Ibrahim AS, Mossa JS and El-Feraly FS: A weakly
antimalarial biflavanone from Rhus retinorrhoea.
Phytochemistry. 58:599–602. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mahjoub MA, Ammar S and Mighri Z: A new
biflavonoid and an isobiflavonoid from Rhus tripartitum. Nat
Prod Res. 19:723–729. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Alimi H, Mbarki S, Barka ZB, Feriani A,
Bouoni Z, Hfaeidh N, Sakly M, Tebourbi O and Rhouma KB:
Phytochemical, antioxidant and protective effect of Rhus
tripartitum root bark extract against ethanol-induced ulcer in
rats. Gen Physiol Biophys. 32:115–127. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mohammed AESI: Phytoconstituents and the
study of antioxidant, antimalarial and antimicrobial activities of
Rhus tripartite growing in Egypt. J Pharmacogn Phytochem.
4:276–281. 2015.
|
|
15
|
Alqahtani AS, Abdel-Mageed WM, Shahat AA,
Parvez MK, Al-Dosari MS, Malik A, Abdel-Kader MS and Alsaid MS:
Proanthocyanidins from the stem bark of Rhus tripartita
ameliorate methylgloxal-induced endothelial cell apoptosis. J Food
Drug Anal. 27:758–765. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Collenetle S: An illustrated guide to the
flowersof Saudi Arabia. Scorpion Publishing LTD; London: pp. 45–49.
1985
|
|
17
|
Mothana RA, Gruenert R, Bednarski PJ and
Lindequist U: Evaluation of the in vitro anticancer, antimicrobial
and antioxidant activities of some Yemeni plants used in folk
medicine. Pharmazie. 64:260–268. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mossa JS, Abdel Sattar E, Abou-Shoer M and
Galal AM: Free flavonoids from Rhus retinorrhoea steud, ex
olive. Int J Pharmacog. 34:198–201. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Alam P, Parvez MK, Arbab AH, Siddiqui NA,
Al-Dosary MS, Al-Rehaily AJ, Ahmed S, Kalam MA and Ahmad MS:
Inter-species comparative antioxidant assay and HPTLC analysis of
sakuranetin in the chloroform and ethanol extracts of aerial parts
of Rhus retinorrhoea and Rhus tripartita. Pharm Biol.
55:1450–1457. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Adewusi E and Afolayan AJ: A review of
natural products with hepatoprotective activity. J Med Plants Res.
4:1318–1334. 2010.
|
|
21
|
Tang LSY, Cover E, Wilson E and Kottilil
S: Chronic hepatitis B infection: A review. JAMA. 319:1802–1813.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
World Health Organisation, . Hepatitis B.
https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-bFebruary
18–2023
|
|
23
|
Devi U and f Locarnini S, . Hepatitis B
antivirals and resistance. Curr Opin Virol. 3:495–500. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang G, Zhang L and Bonkovsky HL: Chinese
medicine for treatment of chronic hepatitis B. Chin J Integr Med.
18:253–255. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Parvez MK, Arbab AH and Al-Dosari MS: An
update on natural or herbal drugs against hepatitis B virus. In
Hepatitis B: Diagnosis, Prevention and Treatment. NOVA Science
Publishers; USA: pp. 159–184. 2021
|
|
26
|
Parvez MK, Rehman MT, Alam P, Al-Dosari
MS, Alqasoumi SI and Alajmi MF: Plant-derived antiviral drugs as
novel hepatitis B virus inhibitors: Cell culture and molecular
docking study. Saudi Pharm J. 27:389–400. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Parvez MK, Al-Dosari MS, Alam P, Rehman
MT, Alajmi MF and Alqahtani AS: The anti-hepatitis B virus
therapeutic potential of anthraquinones derived from Aloe
vera. Phytother Res. 33:1960–1970. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Parvez MK, Al-Dosari MS, Arbab AH,
Al-Rehaily AJ and Abdelwahid MAS: Bioassay-guided isolation of
anti-hepatitis B virus flavonoid myricetin-3-O-rhamnoside along
with quercetin from Guiera senegalensis leaves. Saudi Pharm
J. 28:550–559. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Parvez MK, Ahmed S, Al-Dosari MS,
Abdelwahid MAS, Arbab AH, Al-Rehaily AJ and Al-Oqail MM: Novel
anti-hepatitis B virus activity of Euphorbia schimperi and
its quercetin and kaempferol derivatives. ACS Omega. 6:29100–29110.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ahmed S, Parvez MK, Zia K, Nur-e-Alam M,
Ul-Haq Z, Al-Dosari MS and Al-Rehaily AJ: Natural anti-hepatitis B
virus flavones isolated from Stachys schimperi Vatke growing
in Saudi Arabia. Pharmacog Mag. 18:386–392. 2022.
|
|
31
|
Gharabolagh AF, Sabahi F, Karimi M,
Kamalinejad M, Mirshahabi H, Dawood S, Nasab M and Ahmadi NA:
Effects of Rhus Coriaria L. (Sumac) extract on hepatitis B
virus replication and HBs Ag secretion. J Rep Pharm Sci. 7:100–107.
2018.
|
|
32
|
Zembower DE, Lin YM, Flavin MT, Chen FC
and Korba BE: Robustaflavone, a potential non-nucleoside
anti-hepatitis B agent. Antiviral Res. 39:81–88. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Parvez MK, Al-Dosari MS, Abdelwahid MAS,
Alqahtani AS and Alanzi AR: Novel anti-hepatitis B virus-active
catechin and epicatechin from Rhus tripartita. Exp Ther Med.
23:3982022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zhou Z, Hu T, Zhou X, Wildum S,
Garcia-Alcalde F, Xu Z, Wu D, Mao Y, Tian X, Zhou Y, et al:
Heteroaryldihydropyrimidine (HAP) and sulfamoylbenzamide (SBA)
inhibit hepatitis B virus replication by different molecular
mechanisms. Sci Rep. 7:423742017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Bertoletti N, Chan AH, Schinazi RF, Yin YW
and Anderson KS: Structural insights into the recognition of
nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors by HIV-1 reverse
transcriptase: First crystal structures with reverse transcriptase
and the active triphosphate forms of lamivudine and emtricitabine.
Protein Sci. 28:1664–1675. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Bietz S and Rarey M: SIENA: Efficient
compilation of selective protein binding site ensembles. J Chem Inf
Model. 56:248–259. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Maestro, . Schrödinger Release 2021-3.
Maestro, Schrödinger, LLC; New York, NY: 2021
|
|
38
|
Pettersen EF, Goddard TD, Huang CC, Meng
EC, Couch GS, Croll TI, Morris JH and Ferrin TE: UCSF ChimeraX:
Structure visualization for researchers, educators, and developers.
Protein Sci. 30:70–82. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Eberhardt J, Santos-Martins D, Tillack AF
and Forli S: AutoDock Vina 1.2.0: New docking methods, expanded
force field, and python bindings. J Chem Inf Model. 61:3891–3898.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Hollman PCH: Absorption, bioavailability
and metabolism of flavonoids. Pharm Biol. 42:74–83. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Badshah SL, Faisal S, Muhammad A, Poulson
BG, Emwas AH and Jaremko M: Antiviral activities of flavonoids.
Biomed Pharmacother. 140:1115962021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zakaryan H, Arabyan E, Oo A and Zandi K:
Flavonoids: Promising natural compounds against viral infections.
Arch Virol. 162:2539–2551. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Parvez MK and Rishi V: Herb-drug
interactions and hepatotoxicity. Curr Drug Metab. 20:275–282. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Wang L, Song J, Liu A, Xiao B, Li S, Wen
Z, Lu Y and Du G: Research progress of the antiviral bioactivities
of natural flavonoids. Nat Prod Bioprospect. 10:271–283. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Stompor M: A review on sources and
pharmacological aspects of sakuranetin. Nutrients. 12:5132020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Soarse DG, Andreazza AC and Salvador M:
Evaluation of compounds with antioxidant activity in
Sachhromyces cerevisiae yeast cells. Rev Bras Cienc Farm.
41:95–100. 2005.
|
|
47
|
Zhang X, Hung TM, Phuong PT, Ngoc TM, Min
BS, Song KS, Seong YH and Bae K: Anti-inflammatory activity of
flavonoids from Populus davidiana. Arch Pharm Res.
29:1102–1108. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Cruz MP, Andrade CM, Silva KO, de Souza
EP, Yatsuda R, Marques LM, David JP, David JM, Napimoga MH and
Clemente-Napimoga JT: Antinoceptive and anti-inflammatory
activities of the ethanol extract, fractions and flavones isolated
from Mimosa tenuiflora (Willd.) Poir (Leguminosae). PLoS One.
11:e01508392016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Charles C, Nachtergael A, Ouedraogo M,
Belayew A and Duez P: Effects of chemopreventive natural products
on non-homologous end-joining DNA double-strand break repair. Mutat
Res Genet Toxicol Environ Mutagen. 768:33–41. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Kwon DH, Ji JH, Yim SH, Kim BS and Choi
HJ: Suppression of influenza B virus replication by sakuranetin and
mode of its action. Phytother Res. 32:2475–2479. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Choi HJ: In vitro antiviral activity of
sakuranetin against human rhinovirus 3. Osong Public Health Res
Perspect. 8:415–420. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Kang J, Xie C, Li Z, Nagarajan S, Schauss
AG, Wu T and Wu X: Flavonoids from acai (Euterpe oleracea
Mart.) pulp and their antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities.
Food Chem. 128:152–157. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Xie CH, Kang J, Li ZM, Schauss AG, Badger
TM, Nagarajan S, Wu T and Wu XL: The açaí flavonoid velutin is a
potent anti-inflammatory agent: Blockade of LPS-mediated TNF-α and
IL-6 production through inhibiting NF-κB activation and MAPK
pathway. J Nutr Biochem. 23:1184–1191. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Hassan S, Hamed S, Almuhayawi M, Hozzein
W, Selim S and AbdElgawad H: Bioactivity of ellagic acid and
velutin: Two phenolic compounds isolated from marine algae. Egypt J
Botany. 16:219–231. 2012.
|
|
55
|
Rangsinth P, Sillapachaiyaporn C, Nilkhet
S, Tencomnao T, Ung AT and Chuchawankul S: Mushroom-derived
bioactive compounds potentially serve as the inhibitors of
SARS-CoV-2 main protease: An in silico approach. J Tradit
Complement Med. 11:158–172. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|