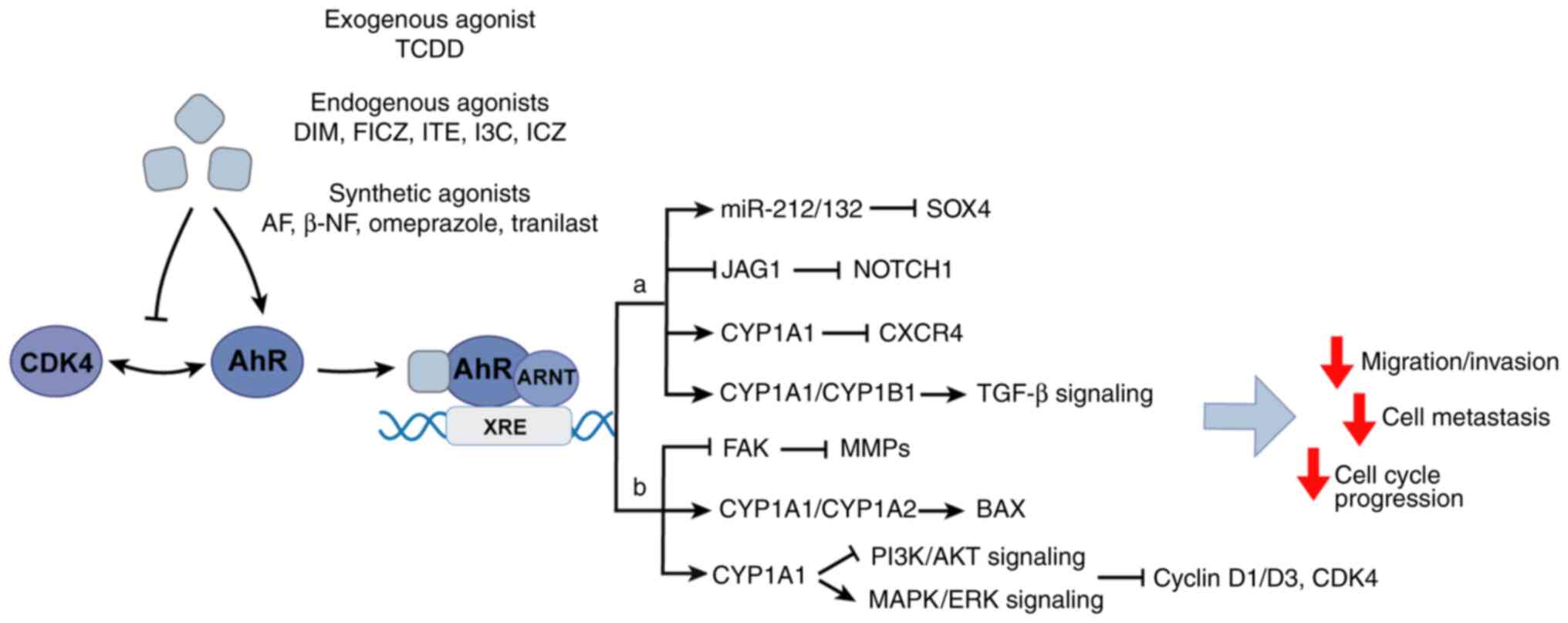
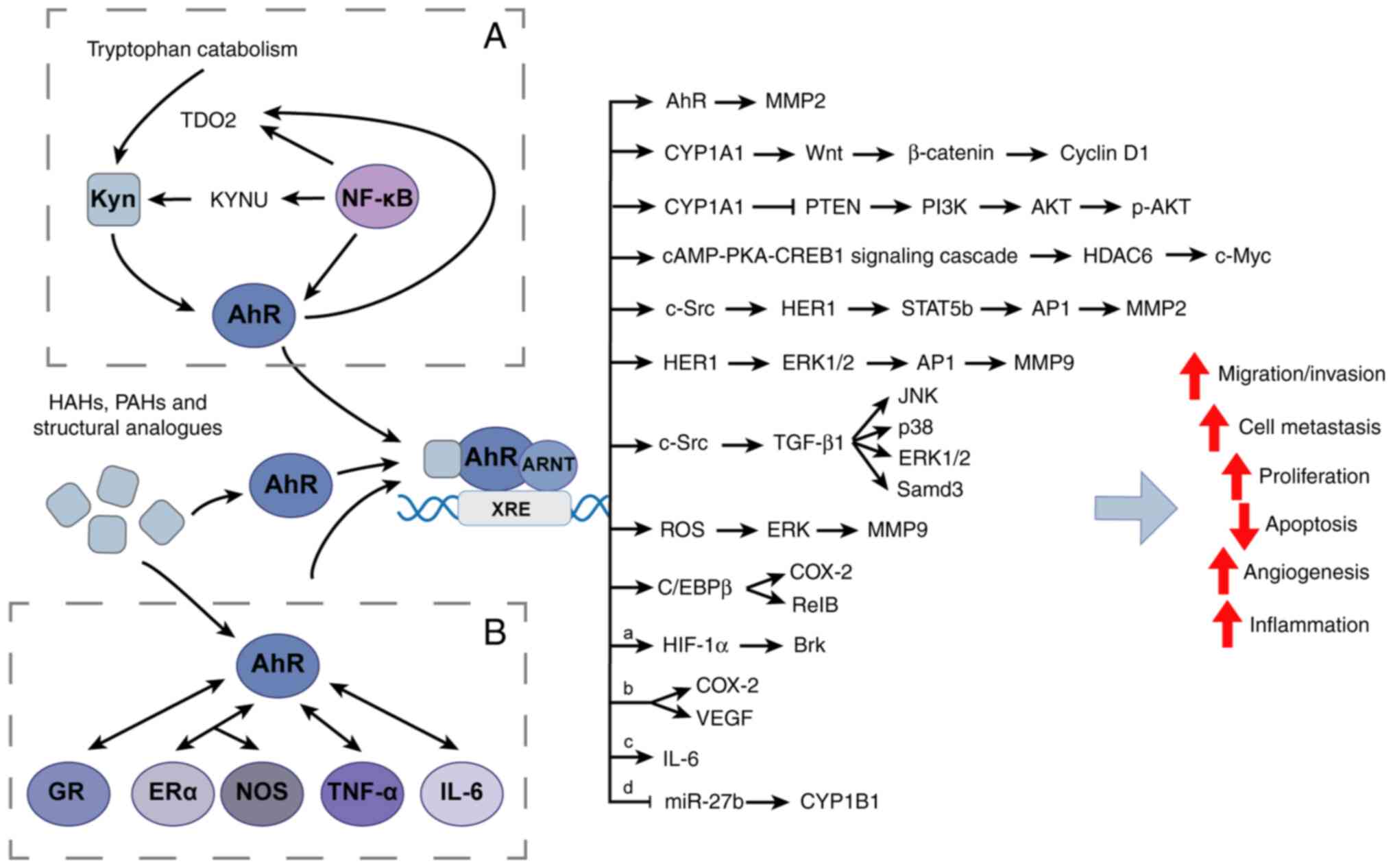
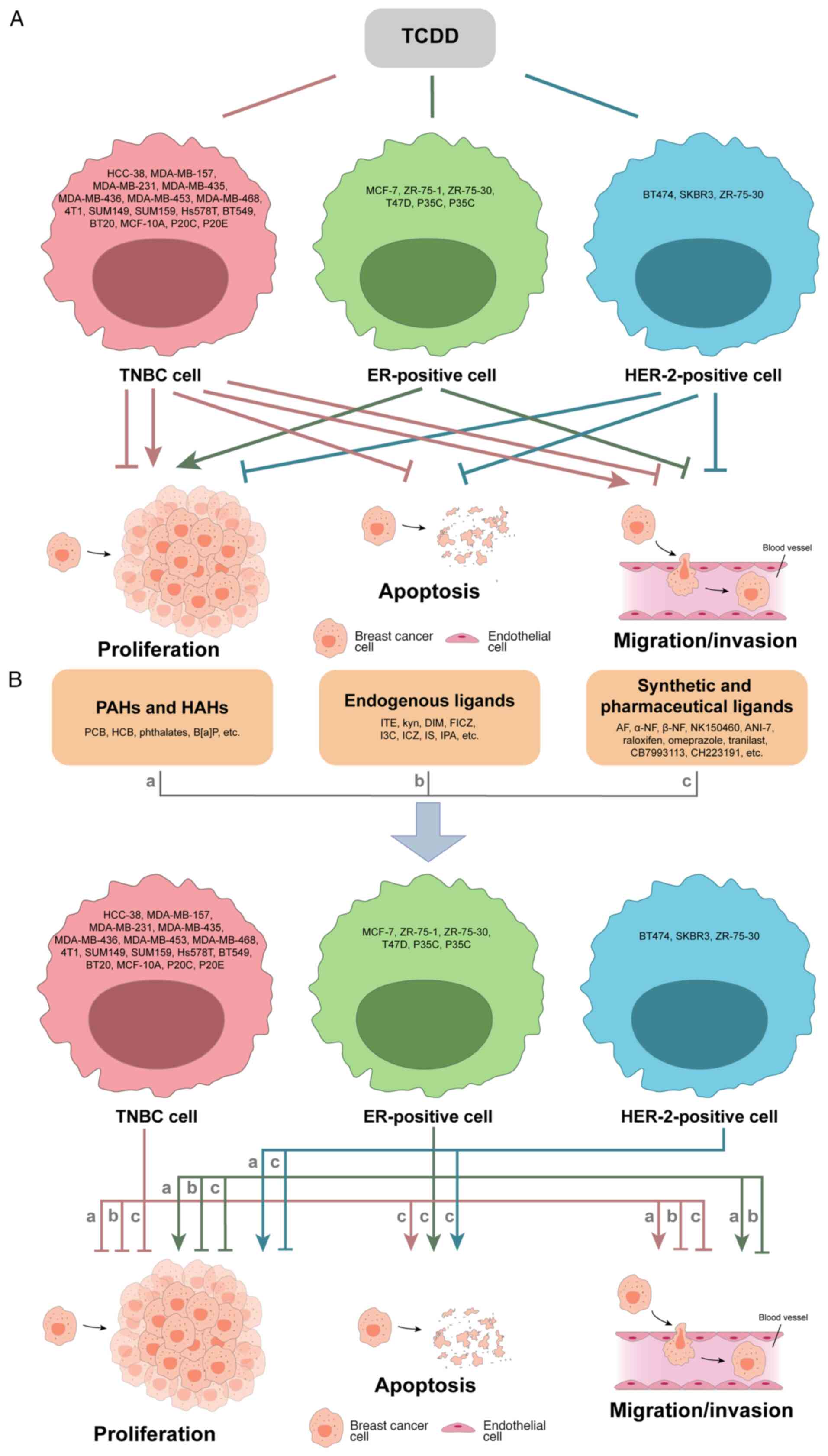
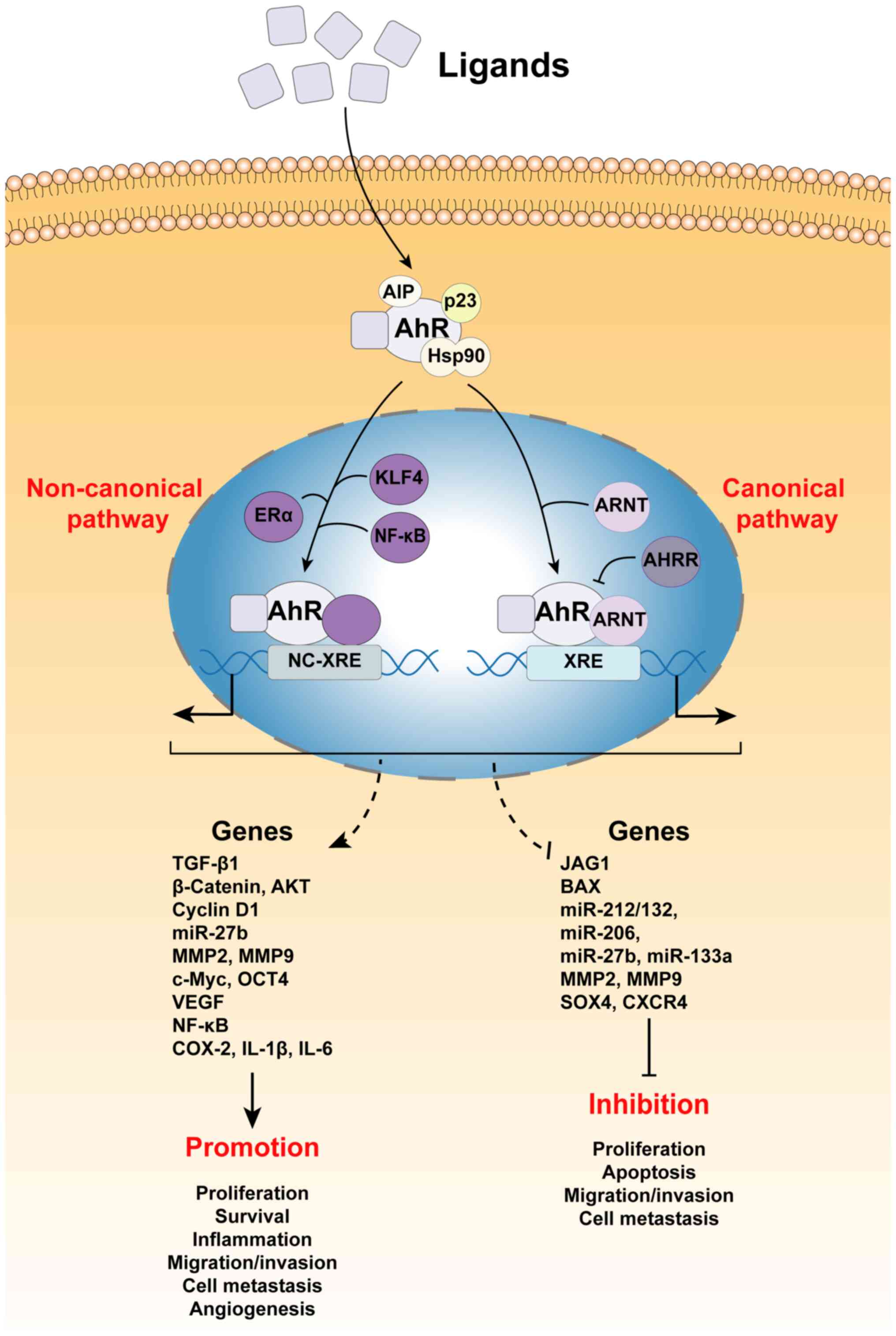
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE and Jemal
A: Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin. 72:7–33. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Miller KD, Nogueira L, Devasia T, Mariotto
AB, Yabroff KR, Jemal A, Kramer J and Siegel RL: Cancer treatment
and survivorship statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J Clin. 72:409–436.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Verrill M: Metastatic disease of the
breast and local recurrence. Surgery (Oxford). 37:181–185. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Flatley MJ and Dodwell DJ: Adjuvant
treatment for breast cancer. Surgery (Oxford). 34:43–46. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Burstein HJ, Curigliano G, Thürlimann B,
Weber WP, Poortmans P, Regan MM, Senn HJ, Winer EP and Gnant M;
Panelists of the St Gallen Consensus Conference, : Customizing
local and systemic therapies for women with early breast cancer:
The St. Gallen international consensus guidelines for treatment of
early breast cancer 2021. Ann Oncol. 32:1216–1235. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Harbeck N and Gnant M: Breast cancer.
Lancet. 389:1134–1150. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Pondé NF, Zardavas D and Piccart M:
Progress in adjuvant systemic therapy for breast cancer. Nat Rev
Clin Oncol. 16:27–44. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Poland A, Glover E and Kende AS:
Stereospecific, high affinity binding of
2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin by hepatic cytosol. Evidence
that the binding species is receptor for induction of aryl
hydrocarbon hydroxylase. J Biol Chem. 251:4936–4946. 1976.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kung T, Murphy KA and White LA: The aryl
hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) pathway as a regulatory pathway for cell
adhesion and matrix metabolism. Biochem Pharmacol. 77:536–546.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Murray IA, Patterson AD and Perdew GH:
Aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligands in cancer: Friend and foe. Nat
Rev Cancer. 14:801–814. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bersten DC, Sullivan AE, Peet DJ and
Whitelaw ML: bHLH-PAS proteins in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
13:827–841. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Opitz CA, Litzenburger UM, Sahm F, Ott M,
Tritschler I, Trump S, Schumacher T, Jestaedt L, Schrenk D, Weller
M, et al: An endogenous tumour-promoting ligand of the human aryl
hydrocarbon receptor. Nature. 478:197–203. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Denison MS and Nagy SR: Activation of the
aryl hydrocarbon receptor by structurally diverse exogenous and
endogenous chemicals. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 43:309–334. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Baker JR, Sakoff JA and McCluskey A: The
aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) as a breast cancer drug target. Med
Res Rev. 40:972–1001. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Rothhammer V and Quintana FJ: The aryl
hydrocarbon receptor: An environmental sensor integrating immune
responses in health and disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 19:184–197. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Stockinger B, Di Meglio P, Gialitakis M
and Duarte JH: The aryl hydrocarbon receptor: Multitasking in the
immune system. Annu Rev Immunol. 32:403–432. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Denison MS, Soshilov AA, He G, DeGroot DE
and Zhao B: Exactly the same but different: Promiscuity and
diversity in the molecular mechanisms of action of the aryl
hydrocarbon (dioxin) receptor. Toxicol Sci. 124:1–22. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mimura J, Ema M, Sogawa K and
Fujii-Kuriyama Y: Identification of a novel mechanism of regulation
of Ah (dioxin) receptor function. Genes Dev. 13:20–25. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Whitlock JP Jr: Induction of cytochrome
P4501A1. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 39:103–125. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Brauze D, Widerak M, Cwykiel J, Szyfter K
and Baer-Dubowska W: The effect of aryl hydrocarbon receptor
ligands on the expression of AhR, AhRR, ARNT, Hif1alpha, CYP1A1 and
NQO1 genes in rat liver. Toxicol Lett. 167:212–220. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hu W, Sorrentino C, Denison MS, Kolaja K
and Fielden MR: Induction of cyp1a1 is a nonspecific biomarker of
aryl hydrocarbon receptor activation: Results of large scale
screening of pharmaceuticals and toxicants in vivo and in vitro.
Mol Pharmacol. 71:1475–1486. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gao X, Xie C, Wang Y, Luo Y, Yagai T, Sun
D, Qin X, Krausz KW and Gonzalez FJ: The antiandrogen flutamide is
a novel aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligand that disrupts bile acid
homeostasis in mice through induction of Abcc4. Biochem Pharmacol.
119:93–104. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Swedenborg E and Pongratz I: AhR and ARNT
modulate ER signaling. Toxicology. 268:132–138. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tarnow P, Tralau T and Luch A: Chemical
activation of estrogen and aryl hydrocarbon receptor signaling
pathways and their interaction in toxicology and metabolism. Expert
Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 15:219–229. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Göttel M, Le Corre L, Dumont C, Schrenk D
and Chagnon MC: Estrogen receptor α and aryl hydrocarbon receptor
cross-talk in a transfected hepatoma cell line (HepG2) exposed to
2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Toxicol Rep. 1:1029–1036.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kang HJ, Kim HJ, Kim SK, Barouki R, Cho
CH, Khanna KK, Rosen EM and Bae I: BRCA1 modulates xenobiotic
stress-inducible gene expression by interacting with ARNT in human
breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 281:14654–14662. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tian Y, Rabson AB and Gallo MA: Ah
receptor and NF-kappaB interactions: Mechanisms and physiological
implications. Chem Biol Interact. 141:97–115. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Marshall NB and Kerkvliet NI: Dioxin and
immune regulation: Emerging role of aryl hydrocarbon receptor in
the generation of regulatory T cells. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1183:25–37.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gutiérrez-Vázquez C and Quintana FJ:
Regulation of the immune response by the Aryl hydrocarbon receptor.
Immunity. 48:19–33. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Esser C and Rannug A: The aryl hydrocarbon
receptor in barrier organ physiology, immunology, and toxicology.
Pharmacol Rev. 67:259–279. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lee JH, Wada T, Febbraio M, He J,
Matsubara T, Lee MJ, Gonzalez FJ and Xie W: A novel role for the
dioxin receptor in fatty acid metabolism and hepatic steatosis.
Gastroenterology. 139:653–663. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lahvis GP, Lindell SL, Thomas RS, McCuskey
RS, Murphy C, Glover E, Bentz M, Southard J and Bradfield CA:
Portosystemic shunting and persistent fetal vascular structures in
aryl hydrocarbon receptor-deficient mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
97:10442–10447. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Huang S, Shui X, He Y, Xue Y, Li J, Li G,
Lei W and Chen C: AhR expression and polymorphisms are associated
with risk of coronary arterial disease in Chinese population. Sci
Rep. 5:80222015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Neavin DR, Liu D, Ray B and Weinshilboum
RM: The role of the Aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) in immune and
inflammatory diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 19:38512018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Stockinger B, Shah K and Wincent E: AHR in
the intestinal microenvironment: Safeguarding barrier function. Nat
Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 18:559–570. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Bock KW: Aryl hydrocarbon or dioxin
receptor: Biologic and toxic responses. Rev Physiol Biochem
Pharmacol. 125:1–42. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Bradshaw TD and Bell DR: Relevance of the
aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) for clinical toxicology. Clin
Toxicol (Phila). 47:632–642. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Knerr S and Schrenk D: Carcinogenicity of
2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in experimental models. Mol
Nutr Food Res. 50:897–907. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Roman ÁC, Carvajal-Gonzalez JM, Merino JM,
Mulero-Navarro S and Fernández-Salguero PM: The aryl hydrocarbon
receptor in the crossroad of signalling networks with therapeutic
value. Pharmacol Ther. 185:50–63. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Stanford EA, Wang Z, Novikov O, Mulas F,
Landesman-Bollag E, Monti S, Smith BW, Seldin DC, Murphy GJ and
Sherr DH: The role of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor in the
development of cells with the molecular and functional
characteristics of cancer stem-like cells. BMC Biol. 14:202016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Stanford EA, Ramirez-Cardenas A, Wang Z,
Novikov O, Alamoud K, Koutrakis P, Mizgerd JP, Genco CA,
Kukuruzinska M, Monti S, et al: Role for the Aryl hydrocarbon
receptor and diverse ligands in oral squamous cell carcinoma
migration and tumorigenesis. Mol Cancer Res. 14:696–706. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Liu Z, Wu X, Zhang F, Han L, Bao G, He X
and Xu Z: AhR expression is increased in hepatocellular carcinoma.
J Mol Histol. 44:455–461. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Chang JT, Chang H, Chen PH, Lin SL and Lin
P: Requirement of aryl hydrocarbon receptor overexpression for
CYP1B1 up-regulation and cell growth in human lung adenocarcinomas.
Clin Cancer Res. 13:38–45. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Koliopanos A, Kleeff J, Xiao Y, Safe S,
Zimmermann A, Büchler MW and Friess H: Increased arylhydrocarbon
receptor expression offers a potential therapeutic target for
pancreatic cancer. Oncogene. 21:6059–6070. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Guarnieri T: Aryl hydrocarbon receptor
connects inflammation to breast cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 21:52642020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Benoit L, Jornod F, Zgheib E, Tomkiewicz
C, Koual M, Coustillet T, Barouki R, Audouze K, Vinken M and
Coumoul X: Adverse outcome pathway from activation of the AhR to
breast cancer-related death. Environ Int. 165:1073232022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Narasimhan S, Stanford Zulick E, Novikov
O, Parks AJ, Schlezinger JJ, Wang Z, Laroche F, Feng H, Mulas F,
Monti S and Sherr DH: Towards resolving the pro- and anti-tumor
effects of the Aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Int J Mol Sci.
19:13882018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Waks AG and Winer EP: Breast cancer
treatment: A review. JAMA. 321:288–300. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Loibl S, Poortmans P, Morrow M, Denkert C
and Curigliano G: Breast cancer. Lancet. 397:1750–1769. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Yu F, Quan F, Xu J, Zhang Y, Xie Y, Zhang
J, Lan Y, Yuan H, Zhang H, Cheng S, et al: Breast cancer prognosis
signature: Linking risk stratification to disease subtypes. Brief
Bioinform. 20:2130–2140. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Eroles P, Bosch A, Pérez-Fidalgo JA and
Lluch A: Molecular biology in breast cancer: Intrinsic subtypes and
signaling pathways. Cancer Treat Rev. 38:698–707. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Loibl S and Gianni L: HER2-positive breast
cancer. Lancet. 389:2415–2429. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Patel HK and Bihani T: Selective estrogen
receptor modulators (SERMs) and selective estrogen receptor
degraders (SERDs) in cancer treatment. Pharmacol Ther. 186:1–24.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Goodwin PJ: Extended aromatase inhibitors
in hormone-receptor-positive breast cancer. N Engl J Med.
385:462–463. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Goel S, Bergholz JS and Zhao JJ: Targeting
CDK4 and CDK6 in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 22:356–372. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Hushka LJ, Williams JS and Greenlee WF:
Characterization of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzofuran-dependent
suppression and AH receptor pathway gene expression in the
developing mouse mammary gland. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
152:200–210. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
O'Donnell EF, Koch DC, Bisson WH, Jang HS
and Kolluri SK: The aryl hydrocarbon receptor mediates
raloxifene-induced apoptosis in estrogen receptor-negative hepatoma
and breast cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 5:e10382014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Romagnolo DF, Papoutsis AJ, Laukaitis C
and Selmin OI: Constitutive expression of AhR and BRCA-1 promoter
CpG hypermethylation as biomarkers of ERα-negative breast
tumorigenesis. BMC Cancer. 15:10262015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Mohamed HT, Gadalla R, El-Husseiny N,
Hassan H, Wang Z, Ibrahim SA, El-Shinawi M, Sherr DH and Mohamed
MM: Inflammatory breast cancer: Activation of the aryl hydrocarbon
receptor and its target CYP1B1 correlates closely with
Wnt5a/b-β-catenin signalling, the stem cell phenotype and disease
progression. J Adv Res. 16:75–86. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Jeschke U, Zhang X, Kuhn C, Jalaguier S,
Colinge J, Pfender K, Mayr D, Ditsch N, Harbeck N, Mahner S, et al:
The prognostic impact of the Aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) in
primary breast cancer depends on the lymph node status. Int J Mol
Sci. 20:10162019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Vacher S, Castagnet P, Chemlali W,
Lallemand F, Meseure D, Pocard M, Bieche I and Perrot-Applanat M:
High AHR expression in breast tumors correlates with expression of
genes from several signaling pathways namely inflammation and
endogenous tryptophan metabolism. PLoS One. 13:e01906192018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Tryggvadottir H, Sandén E, Björner S,
Bressan A, Ygland Rödström M, Khazaei S, Edwards DP, Nodin B,
Jirström K, Isaksson K, et al: The prognostic impact of
intratumoral Aryl hydrocarbon receptor in primary breast cancer
depends on the type of endocrine therapy: A population-based cohort
study. Front Oncol. 11:6427682021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Goode G, Pratap S and Eltom SE: Depletion
of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor in MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer
cells altered the expression of genes in key regulatory pathways of
cancer. PLoS One. 9:e1001032014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Goode GD, Ballard BR, Manning HC, Freeman
ML, Kang Y and Eltom SE: Knockdown of aberrantly upregulated aryl
hydrocarbon receptor reduces tumor growth and metastasis of
MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cell line. Int J Cancer.
133:2769–2780. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Koual M, Tomkiewicz C, Cano-Sancho G,
Antignac JP, Bats AS and Coumoul X: Environmental chemicals, breast
cancer progression and drug resistance. Environ Health. 19:1172020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Li Y, Qin HZ, Song Q, Wu XD and Zhu JH:
Lack of association between the aryl hydrocarbon receptor rs2066853
polymorphism and breast cancer: A meta-analysis on Ahr polymorphism
and breast cancer. Genet Mol Res. 14:16162–16168. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Ali S and Coombes RC: Endocrine-responsive
breast cancer and strategies for combating resistance. Nat Rev
Cancer. 2:101–112. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Xu Y, Huangyang P, Wang Y, Xue L,
Devericks E, Nguyen HG, Yu X, Oses-Prieto JA, Burlingame AL,
Miglani S, et al: ERα is an RNA-binding protein sustaining tumor
cell survival and drug resistance. Cell. 184:5215–5229.e17. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Shiau AK, Barstad D, Loria PM, Cheng L,
Kushner PJ, Agard DA and Greene GL: The structural basis of
estrogen receptor/coactivator recognition and the antagonism of
this interaction by tamoxifen. Cell. 95:927–937. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Metcalfe C, Friedman LS and Hager JH:
Hormone-targeted therapy and resistance. Annu Rev Cancer Biol.
2:291–312. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Safe S and Wormke M: Inhibitory aryl
hydrocarbon receptor-estrogen receptor alpha cross-talk and
mechanisms of action. Chem Res Toxicol. 16:807–816. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Niwa A, Kumaki K, Nebert DW and Poland AP:
Genetic expression of aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase activity in the
mouse. Distinction between the ‘responsive’ homozygote and
heterozygote at the Ah locus. Arch Biochem Biophys. 166:559–564.
1975. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Hankinson O: Single-step selection of
clones of a mouse hepatoma line deficient in aryl hydrocarbon
hydroxylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 76:373–376. 1979. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Stark K, Burger A, Wu J, Shelton P, Polin
L and Li J: Reactivation of estrogen receptor α by vorinostat
sensitizes mesenchymal-like triple-negative breast cancer to
aminoflavone, a ligand of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. PLoS One.
8:e745252013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Go RE, Hwang KA and Choi KC: Cytochrome
P450 1 family and cancers. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 147:24–30.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Luzzani GA, Callero MA, Kuruppu AI,
Trapani V, Flumian C, Todaro L, Bradshaw TD and Loaiza Perez AI: In
vitro antitumor effects of AHR ligands aminoflavone (AFP 464) and
benzothiazole (5F 203) in human renal carcinoma cells. J Cell
Biochem. 118:4526–4535. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Brunnberg S, Pettersson K, Rydin E,
Matthews J, Hanberg A and Pongratz I: The basic
helix-loop-helix-PAS protein ARNT functions as a potent coactivator
of estrogen receptor-dependent transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 100:6517–6522. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Ohtake F, Takeyama K, Matsumoto T,
Kitagawa H, Yamamoto Y, Nohara K, Tohyama C, Krust A, Mimura J,
Chambon P, et al: Modulation of oestrogen receptor signalling by
association with the activated dioxin receptor. Nature.
423:545–550. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Kociba RJ, Keyes DG, Beyer JE, Carreon RM,
Wade CE, Dittenber DA, Kalnins RP, Frauson LE, Park CN, Barnard SD,
et al: Results of a two-year chronic toxicity and oncogenicity
study of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in rats. Toxicol Appl
Pharmacol. 46:279–303. 1978. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Low Dog T: Menopause: A review of
botanical dietary supplements. Am J Med. 118 (Suppl 12B):S98–S108.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Gong P, Madak-Erdogan Z, Flaws JA, Shapiro
DJ, Katzenellenbogen JA and Katzenellenbogen BS: Estrogen
receptor-alpha and aryl hydrocarbon receptor involvement in the
actions of botanical estrogens in target cells. Mol Cell
Endocrinol. 437:190–200. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Moynahan ME: The cancer connection: BRCA1
and BRCA2 tumor suppression in mice and humans. Oncogene.
21:8994–9007. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Baek HJ, Kim SE, Choi EK, Kim JK, Shin DH,
Park EJ, Kim TH, Kim JY, Kim KG, Deng CX and Kim SS: Inhibition of
estrogen signaling reduces the incidence of BRCA1-associated
mammary tumor formation. Int J Biol Sci. 14:1755–1768. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Wang L and Di LJ: BRCA1 and
estrogen/estrogen receptor in breast cancer: Where they interact?
Int J Biol Sci. 10:566–575. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Kang HJ, Kim HJ, Cho CH, Hu Y, Li R and
Bae I: BRCA1 transcriptional activity is enhanced by interactions
between its AD1 domain and AhR. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol.
62:965–975. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Tapia T, Smalley SV, Kohen P, Muñoz A,
Solis LM, Corvalan A, Faundez P, Devoto L, Camus M, Alvarez M and
Carvallo P: Promoter hypermethylation of BRCA1 correlates with
absence of expression in hereditary breast cancer tumors.
Epigenetics. 3:157–163. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Papoutsis AJ, Selmin OI, Borg JL and
Romagnolo DF: Gestational exposure to the AhR agonist
2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin induces BRCA-1 promoter
hypermethylation and reduces BRCA-1 expression in mammary tissue of
rat offspring: Preventive effects of resveratrol. Mol Carcinog.
54:261–269. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Wormke M, Stoner M, Saville B, Walker K,
Abdelrahim M, Burghardt R and Safe S: The aryl hydrocarbon receptor
mediates degradation of estrogen receptor alpha through activation
of proteasomes. Mol Cell Biol. 23:1843–1855. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Crimini E, Repetto M, Aftimos P,
Botticelli A, Marchetti P and Curigliano G: Precision medicine in
breast cancer: From clinical trials to clinical practice. Cancer
Treat Rev. 98:1022232021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Zhang S, Lei P, Liu X, Li X, Walker K,
Kotha L, Rowlands C and Safe S: The aryl hydrocarbon receptor as a
target for estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer chemotherapy.
Endocr Relat Cancer. 16:835–844. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Zhang S, Kim K, Jin UH, Pfent C, Cao H,
Amendt B, Liu X, Wilson-Robles H and Safe S: Aryl hydrocarbon
receptor agonists induce microRNA-335 expression and inhibit lung
metastasis of estrogen receptor negative breast cancer cells. Mol
Cancer Ther. 11:108–118. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Hanieh H: Aryl hydrocarbon
receptor-microRNA-212/132 axis in human breast cancer suppresses
metastasis by targeting SOX4. Mol Cancer. 14:1722015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Hall JM, Barhoover MA, Kazmin D, McDonnell
DP, Greenlee WF and Thomas RS: Activation of the aryl-hydrocarbon
receptor inhibits invasive and metastatic features of human breast
cancer cells and promotes breast cancer cell differentiation. Mol
Endocrinol. 24:359–369. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Barhoover MA, Hall JM, Greenlee WF and
Thomas RS: Aryl hydrocarbon receptor regulates cell cycle
progression in human breast cancer cells via a functional
interaction with cyclin-dependent kinase 4. Mol Pharmacol.
77:195–201. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Wang T, Wyrick KL, Meadows GG, Wills TB
and Vorderstrasse BA: Activation of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor
by TCDD inhibits mammary tumor metastasis in a syngeneic mouse
model of breast cancer. Toxicol Sci. 124:291–298. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Safe S and Zhang L: The role of the Aryl
hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) and its ligands in breast cancer.
Cancers (Basel). 14:55742022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Ho JN, Jun W, Choue R and Lee J: I3C and
ICZ inhibit migration by suppressing the EMT process and FAK
expression in breast cancer cells. Mol Med Rep. 7:384–388. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Nguyen CH, Brenner S, Huttary N, Atanasov
AG, Dirsch VM, Chatuphonprasert W, Holzner S, Stadler S, Riha J,
Krieger S, et al: AHR/CYP1A1 interplay triggers lymphatic barrier
breaching in breast cancer spheroids by inducing 12(S)-HETE
synthesis. Hum Mol Genet. 25:5006–5016. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Yerushalmi R, Bargil S, Ber Y, Ozlavo R,
Sivan T, Rapson Y, Pomerantz A, Tsoref D, Sharon E, Caspi O, et al:
3,3-Diindolylmethane (DIM): A nutritional intervention and its
impact on breast density in healthy BRCA carriers. A prospective
clinical trial. Carcinogenesis. 41:1395–1401. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Mobini K, Tamaddon G, Fardid R, Keshavarzi
M and Mohammadi-Bardbori A: Aryl hydrocarbon-estrogen alpha
receptor-dependent expression of miR-206, miR-27b, and miR-133a
suppress cell proliferation and migration in MCF-7 cells. J Biochem
Mol Toxicol. 33:e223042019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Piwarski SA, Thompson C, Chaudhry AR,
Denvir J, Primerano DA, Fan J and Salisbury TB: The putative
endogenous AHR ligand ITE reduces JAG1 and associated NOTCH1
signaling in triple negative breast cancer cells. Biochem
Pharmacol. 174:1138452020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Sári Z, Mikó E, Kovács T, Boratkó A,
Ujlaki G, Jankó L, Kiss B, Uray K and Bai P: Indoxylsulfate, a
metabolite of the microbiome, has cytostatic effects in breast
cancer via activation of AHR and PXR receptors and induction of
oxidative stress. Cancers (Basel). 12:29152020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Sári Z, Mikó E, Kovács T, Jankó L, Csonka
T, Lente G, Sebő É, Tóth J, Tóth D, Árkosy P, et al:
Indolepropionic acid, a metabolite of the microbiome, has
cytostatic properties in breast cancer by activating AHR and PXR
receptors and inducing oxidative stress. Cancers (Basel).
12:24112020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Safe S, Jin UH, Park H, Chapkin RS and
Jayaraman A: Aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) ligands as selective
AHR modulators (SAhRMs). Int J Mol Sci. 21:66542020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Akama T, Ishida H, Shida Y, Kimura U, Gomi
K, Saito H, Fuse E, Kobayashi S, Yoda N and Kasai M: Design and
synthesis of potent antitumor 5,4′-diaminoflavone derivatives based
on metabolic considerations. J Med Chem. 40:1894–1900. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Akama T, Shida Y, Sugaya T, Ishida H, Gomi
K and Kasai M: Novel 5-aminoflavone derivatives as specific
antitumor agents in breast cancer. J Med Chem. 39:3461–3469. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Kenz S, Haas CS, Werth SC, Bohnet S and
Brabant G: High sensitivity to tolvaptan in paraneoplastic syndrome
of inappropriate ADH secretion (SIADH). Ann Oncol. 22:26962011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Kuffel MJ, Schroeder JC, Pobst LJ, Naylor
S, Reid JM, Kaufmann SH and Ames MM: Activation of the antitumor
agent aminoflavone (NSC 686288) is mediated by induction of tumor
cell cytochrome P450 1A1/1A2. Mol Pharmacol. 62:143–153. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Loaiza-Perez AI, Kenney S, Boswell J,
Hollingshead M, Alley MC, Hose C, Ciolino HP, Yeh GC, Trepel JB,
Vistica DT and Sausville EA: Aryl hydrocarbon receptor activation
of an antitumor aminoflavone: Basis of selective toxicity for MCF-7
breast tumor cells. Mol Cancer Ther. 3:715–725. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Loaiza-Perez AI, Kenney S, Boswell J,
Hollingshead M, Hose C, Linehan WM, Worrell R, Rubinstein L,
Sausville EA and Vistica DT: Sensitivity of renal cell carcinoma to
aminoflavone: role of CYP1A1. J Urol. 171:1688–1697. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Meng LH, Shankavaram U, Chen C, Agama K,
Fu HQ, Gonzalez FJ, Weinstein J and Pommier Y: Activation of
aminoflavone (NSC 686288) by a sulfotransferase is required for the
antiproliferative effect of the drug and for induction of histone
gamma-H2AX. Cancer Res. 66:9656–9664. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Mavingire N, Campbell P, Liu T, Wooten J,
Khan S, Chen X, Matthews J, Wang C and Brantley E: Aminoflavone
upregulates putative tumor suppressor miR-125b-2-3p to inhibit
luminal A breast cancer stem cell-like properties. Precis Clin Med.
5:pbac0082022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Campbell PS, Mavingire N, Khan S, Rowland
LK, Wooten JV, Opoku-Agyeman A, Guevara A, Soto U, Cavalli F,
Loaiza-Pérez AI, et al: AhR ligand aminoflavone suppresses
α6-integrin-Src-Akt signaling to attenuate tamoxifen resistance in
breast cancer cells. J Cell Physiol. 234:108–121. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Brantley E, Callero MA, Berardi DE,
Campbell P, Rowland L, Zylstra D, Amis L, Yee M, Simian M, Todaro
L, et al: AhR ligand Aminoflavone inhibits α6-integrin expression
and breast cancer sphere-initiating capacity. Cancer Lett.
376:53–61. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Hu T, Zhou R, Zhao Y and Wu G: Integrin
α6/Akt/Erk signaling is essential for human breast cancer
resistance to radiotherapy. Sci Rep. 6:333762016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Zhao S, Kanno Y, Nakayama M, Makimura M,
Ohara S and Inouye Y: Activation of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor
represses mammosphere formation in MCF-7 cells. Cancer Lett.
317:192–198. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Wang C, Xu CX, Bu Y, Bottum KM and
Tischkau SA: Beta-naphthoflavone (DB06732) mediates estrogen
receptor-positive breast cancer cell cycle arrest through
AhR-dependent regulation of PI3K/AKT and MAPK/ERK signaling.
Carcinogenesis. 35:703–713. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Fukasawa K, Kagaya S, Maruyama S, Kuroiwa
S, Masuda K, Kameyama Y, Satoh Y, Akatsu Y, Tomura A, Nishikawa K,
et al: A novel compound, NK150460, exhibits selective antitumor
activity against breast cancer cell lines through activation of
aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Mol Cancer Ther. 14:343–354. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Tarleton M, Gilbert J, Robertson MJ,
McCluskey A and Sakoff JA: Library synthesis and cytotoxicity of a
family of 2-phenylacrylonitriles and discovery of an estrogen
dependent breast cancer lead compound†. Med Chem Commun. 2:31–37.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
121
|
Gilbert J, De Iuliis GN, Tarleton M,
McCluskey A and Sakoff JA: (Z)-2-(3,4-Dichlorophenyl)-3-(1
H-Pyrrol-2-yl)acrylonitrile exhibits selective antitumor activity
in breast cancer cell lines via the aryl hydrocarbon receptor
pathway. Mol Pharmacol. 93:168–177. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Corsello SM, Bittker JA, Liu Z, Gould J,
McCarren P, Hirschman JE, Johnston SE, Vrcic A, Wong B, Khan M, et
al: The drug repurposing Hub: A next-generation drug library and
information resource. Nat Med. 23:405–408. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Quattrochi LC and Tukey RH: Nuclear uptake
of the Ah (dioxin) receptor in response to omeprazole:
Transcriptional activation of the human CYP1A1 gene. Mol Pharmacol.
43:504–508. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Prud'homme GJ, Glinka Y, Toulina A, Ace O,
Subramaniam V and Jothy S: Breast cancer stem-like cells are
inhibited by a non-toxic aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonist. PLoS
One. 5:e138312010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Jin UH, Lee SO and Safe S: Aryl
hydrocarbon receptor (AHR)-active pharmaceuticals are selective AHR
modulators in MDA-MB-468 and BT474 breast cancer cells. J Pharmacol
Exp Ther. 343:333–341. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Cummings SR, Tice JA, Bauer S, Browner WS,
Cuzick J, Ziv E, Vogel V, Shepherd J, Vachon C, Smith-Bindman R and
Kerlikowske K: Prevention of breast cancer in postmenopausal women:
Approaches to estimating and reducing risk. J Natl Cancer Inst.
101:384–398. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Moen MD and Keating GM: Raloxifene: A
review of its use in the prevention of invasive breast cancer.
Drugs. 68:2059–2083. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Bevers TB: Raloxifene and the prevention
of breast cancer. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 7:2301–2307. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Martino S, Cauley JA, Barrett-Connor E,
Powles TJ, Mershon J, Disch D, Secrest RJ and Cummings SR; CORE
Investigators, : Continuing outcomes relevant to Evista: Breast
cancer incidence in postmenopausal osteoporotic women in a
randomized trial of raloxifene. J Natl Cancer Inst. 96:1751–1761.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Clemens JA, Bennett DR, Black LJ and Jones
CD: Effects of a new antiestrogen, keoxifene (LY156758), on growth
of carcinogen-induced mammary tumors and on LH and prolactin
levels. Life Sci. 32:2869–2875. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Kleinberg DL, Todd J and Babitsky G:
Inhibition by estradiol of the lactogenic effect of prolactin in
primate mammary tissue: Reversal by antiestrogens LY 156758 and
tamoxifen. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 80:4144–4148. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Ning M, Zhou C, Weng J, Zhang S, Chen D,
Yang C, Wang H, Ren J, Zhou L, Jin C and Wang MW: Biological
activities of a novel selective oestrogen receptor modulator
derived from raloxifene (Y134). Br J Pharmacol. 150:19–28. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Jang HS, Pearce M, O'Donnell EF, Nguyen
BD, Truong L, Mueller MJ, Bisson WH, Kerkvliet NI, Tanguay RL and
Kolluri SK: Identification of a raloxifene analog that promotes
AhR-mediated apoptosis in cancer cells. Biology (Basel).
6:412017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Hyder T, Marino CC, Ahmad S, Nasrazadani A
and Brufsky AM: Aromatase inhibitor-associated musculoskeletal
syndrome: Understanding mechanisms and management. Front Endocrinol
(Lausanne). 12:7137002021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Dzeletovic N, McGuire J, Daujat M,
Tholander J, Ema M, Fujii-Kuriyama Y, Bergman J, Maurel P and
Poellinger L: Regulation of dioxin receptor function by omeprazole.
J Biol Chem. 272:12705–12713. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Jin UH, Kim SB and Safe S: Omeprazole
inhibits pancreatic cancer cell invasion through a nongenomic Aryl
hydrocarbon receptor pathway. Chem Res Toxicol. 28:907–918. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Lesca P, Peryt B, Larrieu G, Alvinerie M,
Galtier P, Daujat M, Maurel P and Hoogenboom L: Evidence for the
ligand-independent activation of the AH receptor. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 209:474–482. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Jin UH, Lee SO, Pfent C and Safe S: The
aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligand omeprazole inhibits breast cancer
cell invasion and metastasis. BMC Cancer. 14:4982014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Koda A, Nagai H, Watanabe S, Yanagihara Y
and Sakamoto K: Inhibition of hypersensitivity reactions by a new
drug, N(3′,4′-dimethoxycinnamoyl) anthranilic acid (N-5′). J
Allergy Clin. Immunol. 57:396–407. 1976.
|
|
140
|
Azuma H, Banno K and Yoshimura T:
Pharmacological properties of N-(3′,4′-dimethoxycinnamoyl)
anthranilic acid (N-5′), a new anti-atopic agent. Br J Pharmacol.
58:483–488. 1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Batlle E and Clevers H: Cancer stem cells
revisited. Nat Med. 23:1124–1134. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Chakrabarti R, Subramaniam V, Abdalla S,
Jothy S and Prud'homme GJ: Tranilast inhibits the growth and
metastasis of mammary carcinoma. Anticancer Drugs. 20:334–345.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Subramaniam V, Ace O, Prud'homme GJ and
Jothy S: Tranilast treatment decreases cell growth, migration and
inhibits colony formation of human breast cancer cells. Exp Mol
Pathol. 90:116–122. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Ciolino HP, MacDonald CJ, Memon OS, Bass
SE and Yeh GC: Sulindac regulates the aryl hydrocarbon
receptor-mediated expression of phase 1 metabolic enzymes in vivo
and in vitro. Carcinogenesis. 27:1586–1592. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Hahn ME: Aryl hydrocarbon receptors:
Diversity and evolution. Chem Biol Interact. 141:131–160. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Schlezinger JJ, Liu D, Farago M, Seldin
DC, Belguise K, Sonenshein GE and Sherr DH: A role for the aryl
hydrocarbon receptor in mammary gland tumorigenesis. Biol Chem.
387:1175–1187. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Vogel CFA, Lazennec G, Kado SY, Dahlem C,
He Y, Castaneda A, Ishihara Y, Vogeley C, Rossi A,
Haarmann-Stemmann T, et al: Targeting the Aryl hydrocarbon receptor
signaling pathway in breast cancer development. Front Immunol.
12:6253462021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
Kolasa E, Houlbert N, Balaguer P and
Fardel O: AhR- and NF-κB-dependent induction of interleukin-6 by
co-exposure to the environmental contaminant benzanthracene and the
cytokine tumor necrosis factor-α in human mammary MCF-7 cells. Chem
Biol Interact. 203:391–400. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Shan A, Leng L, Li J, Luo XM, Fan YJ, Yang
Q, Xie QH, Chen YS, Ni CS, Guo LM, et al: TCDD-induced antagonism
of MEHP-mediated migration and invasion partly involves aryl
hydrocarbon receptor in MCF7 breast cancer cells. J Hazard Mater.
398:1228692020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Bekki K, Vogel H, Li W, Ito T, Sweeney C,
Haarmann-Stemmann T, Matsumura F and Vogel CF: The aryl hydrocarbon
receptor (AhR) mediates resistance to apoptosis induced in breast
cancer cells. Pestic Biochem Physiol. 120:5–13. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
Pontillo C, Español A, Chiappini F, Miret
N, Cocca C, Alvarez L, Kleiman de Pisarev D, Sales ME and Randi AS:
Hexachlorobenzene promotes angiogenesis in vivo, in a breast cancer
model and neovasculogenesis in vitro, in the human microvascular
endothelial cell line HMEC-1. Toxicol Lett. 239:53–64. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Vogel CFA, Li W, Wu D, Miller JK, Sweeney
C, Lazennec G, Fujisawa Y and Matsumura F: Interaction of aryl
hydrocarbon receptor and NF-κB subunit RelB in breast cancer is
associated with interleukin-8 overexpression. Arch Biochem Biophys.
512:78–86. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Novikov O, Wang Z, Stanford EA, Parks AJ,
Ramirez-Cardenas A, Landesman E, Laklouk I, Sarita-Reyes C,
Gusenleitner D, Li A, et al: An Aryl hydrocarbon receptor-mediated
amplification loop that enforces cell migration in
ER-/PR-/Her2-human breast cancer cells. Mol Pharmacol. 90:674–688.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
154
|
Hsieh TH, Tsai CF, Hsu CY, Kuo PL, Lee JN,
Chai CY, Wang SC and Tsai EM: Phthalates induce proliferation and
invasiveness of estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer through
the AhR/HDAC6/c-Myc signaling pathway. FASEB J. 26:778–787. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Miret N, Pontillo C, Ventura C, Carozzo A,
Chiappini F, Kleiman de Pisarev D, Fernández N, Cocca C and Randi
A: Hexachlorobenzene modulates the crosstalk between the aryl
hydrocarbon receptor and transforming growth factor-β1 signaling,
enhancing human breast cancer cell migration and invasion.
Toxicology. 366–367. 20–31. 2016.
|
|
156
|
Pontillo CA, Rojas P, Chiappini F,
Sequeira G, Cocca C, Crocci M, Colombo L, Lanari C, Kleiman de
Pisarev D and Randi A: Action of hexachlorobenzene on tumor growth
and metastasis in different experimental models. Toxicol Appl
Pharmacol. 268:331–342. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
Al-Dhfyan A, Alhoshani A and Korashy HM:
Aryl hydrocarbon receptor/cytochrome P450 1A1 pathway mediates
breast cancer stem cells expansion through PTEN inhibition and
β-catenin and Akt activation. Mol Cancer. 16:142017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Jung JW, Park SB, Lee SJ, Seo MS, Trosko
JE and Kang KS: Metformin represses self-renewal of the human
breast carcinoma stem cells via inhibition of estrogen
receptor-mediated OCT4 expression. PLoS One. 6:e280682011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
159
|
Malik DE, David RM and Gooderham NJ:
Interleukin-6 selectively induces drug metabolism to potentiate the
genotoxicity of dietary carcinogens in mammary cells. Arch Toxicol.
93:3005–3020. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
160
|
Zárate LV, Pontillo CA, Español A, Miret
NV, Chiappini F, Cocca C, Álvarez L, de Pisarev DK, Sales ME and
Randi AS: Angiogenesis signaling in breast cancer models is induced
by hexachlorobenzene and chlorpyrifos, pesticide ligands of the
aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 401:1150932020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
161
|
Pontillo CA, Garcia MA, Peña D, Cocca C,
Chiappini F, Alvarez L, Kleiman de Pisarev D and Randi AS:
Activation of c-Src/HER1/STAT5b and HER1/ERK1/2 signaling pathways
and cell migration by hexachlorobenzene in MDA-MB-231 human breast
cancer cell line. Toxicol Sci. 120:284–296. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Castillo-Sanchez R, Villegas-Comonfort S,
Galindo-Hernandez O, Gomez R and Salazar EP: Benzo-[a]-pyrene
induces FAK activation and cell migration in MDA-MB-231 breast
cancer cells. Cell Biol Toxicol. 29:303–319. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
163
|
Guo J, Xu Y, Ji W, Song L, Dai C and Zhan
L: Effects of exposure to benzo[a]pyrene on metastasis of breast
cancer are mediated through ROS-ERK-MMP9 axis signaling. Toxicol
Lett. 234:201–210. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
164
|
Cirillo F, Lappano R, Bruno L, Rizzuti B,
Grande F, Guzzi R, Briguori S, Miglietta AM, Nakajima M, Di Martino
MT and Maggiolini M: AHR and GPER mediate the stimulatory effects
induced by 3-methylcholanthrene in breast cancer cells and
cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs). J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
38:3352019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
165
|
Yamashita N, Saito N, Zhao S, Terai K,
Hiruta N, Park Y, Bujo H, Nemoto K and Kanno Y: Heregulin-induced
cell migration is promoted by aryl hydrocarbon receptor in
HER2-overexpressing breast cancer cells. Exp Cell Res. 366:34–40.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
166
|
D'Amato NC, Rogers TJ, Gordon MA, Greene
LI, Cochrane DR, Spoelstra NS, Nemkov TG, D'Alessandro A, Hansen KC
and Richer JK: A TDO2-AhR signaling axis facilitates anoikis
resistance and metastasis in triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer
Res. 75:4651–4664. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
167
|
Parks AJ, Pollastri MP, Hahn ME, Stanford
EA, Novikov O, Franks DG, Haigh SE, Narasimhan S, Ashton TD, Hopper
TG, et al: In silico identification of an aryl hydrocarbon receptor
antagonist with biological activity in vitro and in vivo. Mol
Pharmacol. 86:593–608. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
168
|
Nassar D and Blanpain C: Cancer stem
cells: Basic concepts and therapeutic implications. Annu Rev
Pathol. 11:47–76. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
169
|
Peitzsch C, Tyutyunnykova A, Pantel K and
Dubrovska A: Cancer stem cells: The root of tumor recurrence and
metastases. Semin Cancer Biol. 44:10–24. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
170
|
Regan Anderson TM, Ma S, Perez Kerkvliet
C, Peng Y, Helle TM, Krutilina RI, Raj GV, Cidlowski JA, Ostrander
JH, Schwertfeger KL, et al: Taxol induces Brk-dependent prosurvival
phenotypes in TNBC cells through an AhR/GR/HIF-driven signaling
axis. Mol Cancer Res. 16:1761–1772. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
171
|
Toomey DP, Murphy JF and Conlon KC: COX-2,
VEGF and tumour angiogenesis. Surgeon. 7:174–180. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
172
|
Kirkpatrick K, Ogunkolade W, Elkak A,
Bustin S, Jenkins P, Ghilchik M and Mokbel K: The mRNA expression
of cyclo-oxygenase-2 (COX-2) and vascular endothelial growth factor
(VEGF) in human breast cancer. Curr Med Res Opin. 18:237–241. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
173
|
Sansone P, Storci G, Tavolari S, Guarnieri
T, Giovannini C, Taffurelli M, Ceccarelli C, Santini D, Paterini P,
Marcu KB, et al: IL-6 triggers malignant features in mammospheres
from human ductal breast carcinoma and normal mammary gland. J Clin
Invest. 117:3988–4002. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
174
|
Baumgarten SC and Frasor J: Minireview:
Inflammation: An instigator of more aggressive estrogen receptor
(ER) positive breast cancers. Mol Endocrinol. 26:360–371. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
175
|
Sasser AK, Sullivan NJ, Studebaker AW,
Hendey LF, Axel AE and Hall BM: Interleukin-6 is a potent growth
factor for ER-alpha-positive human breast cancer. FASEB J.
21:3763–3770. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
176
|
Fouad TM, Barrera AMG, Reuben JM, Lucci A,
Woodward WA, Stauder MC, Lim B, DeSnyder SM, Arun B, Gildy B, et
al: Inflammatory breast cancer: A proposed conceptual shift in the
UICC-AJCC TNM staging system. Lancet Oncol. 18:e228–e232. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
177
|
Wang Z, Wang H, Ding X, Chen X and Shen K:
A large-cohort retrospective study of metastatic patterns and
prognostic outcomes between inflammatory and non-inflammatory
breast cancer. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 12:17588359209326742020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
178
|
Sovak MA, Bellas RE, Kim DW, Zanieski GJ,
Rogers AE, Traish AM and Sonenshein GE: Aberrant nuclear
factor-kappaB/Rel expression and the pathogenesis of breast cancer.
J Clin Invest. 100:2952–2960. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
179
|
Kim DW, Sovak MA, Zanieski G, Nonet G,
Romieu-Mourez R, Lau AW, Hafer LJ, Yaswen P, Stampfer M, Rogers AE,
et al: Activation of NF-kappaB/Rel occurs early during neoplastic
transformation of mammary cells. Carcinogenesis. 21:871–879. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
180
|
Kim DW, Gazourian L, Quadri SA,
Romieu-Mourez R, Sherr DH and Sonenshein GE: The RelA NF-kappaB
subunit and the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) cooperate to
transactivate the c-myc promoter in mammary cells. Oncogene.
19:5498–5506. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
181
|
Currier N, Solomon SE, Demicco EG, Chang
DL, Farago M, Ying H, Dominguez I, Sonenshein GE, Cardiff RD, Xiao
ZX, et al: Oncogenic signaling pathways activated in DMBA-induced
mouse mammary tumors. Toxicol Pathol. 33:726–737. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
182
|
Vyas D, Lopez-Hisijos N, Shah P, Deshpande
KS, Basson MD, Vyas A and Chaturvedi LS: A second-generation
proteasome inhibitor and doxorubicin modulates IL-6, pSTAT-3 and
NF-kB activity in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. J Nanosci
Nanotechnol. 17:175–185. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
183
|
Sakamoto K, Wehde BL, Yoo KH, Kim T,
Rajbhandari N, Shin HY, Triplett AA, Rädler PD, Schuler F,
Villunger A, et al: Janus kinase 1 is essential for inflammatory
cytokine signaling and mammary gland remodeling. Mol Cell Biol.
36:1673–1690. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
184
|
Poland A and Knutson JC:
2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin and related halogenated
aromatic hydrocarbons: Examination of the mechanism of toxicity.
Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 22:517–554. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|