|
1
|
Tujios S, Stravitz RT and Lee WM:
Management of acute liver failure: Update 2022. Semin Liver Dis.
42:362–378. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
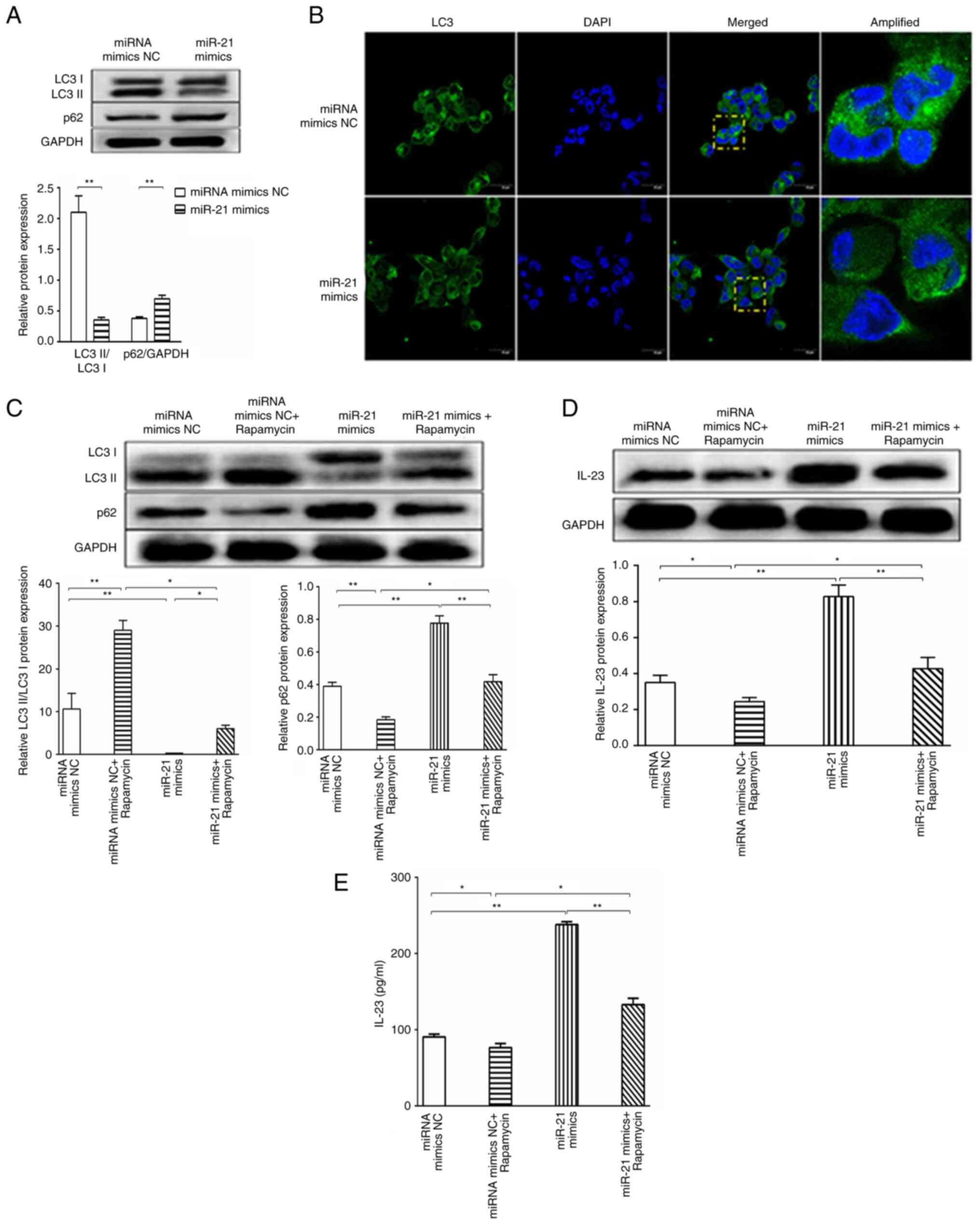
|
Bao S, Zheng J, Li N, Huang C, Chen M,
Cheng Q, Li Q, Lu Q, Zhu M, Ling Q, et al: Role of interleukin-23
in monocyte-derived dendritic cells of HBV-related acute-on-chronic
liver failure and its correlation with the severity of liver
damage. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol. 41:147–155. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
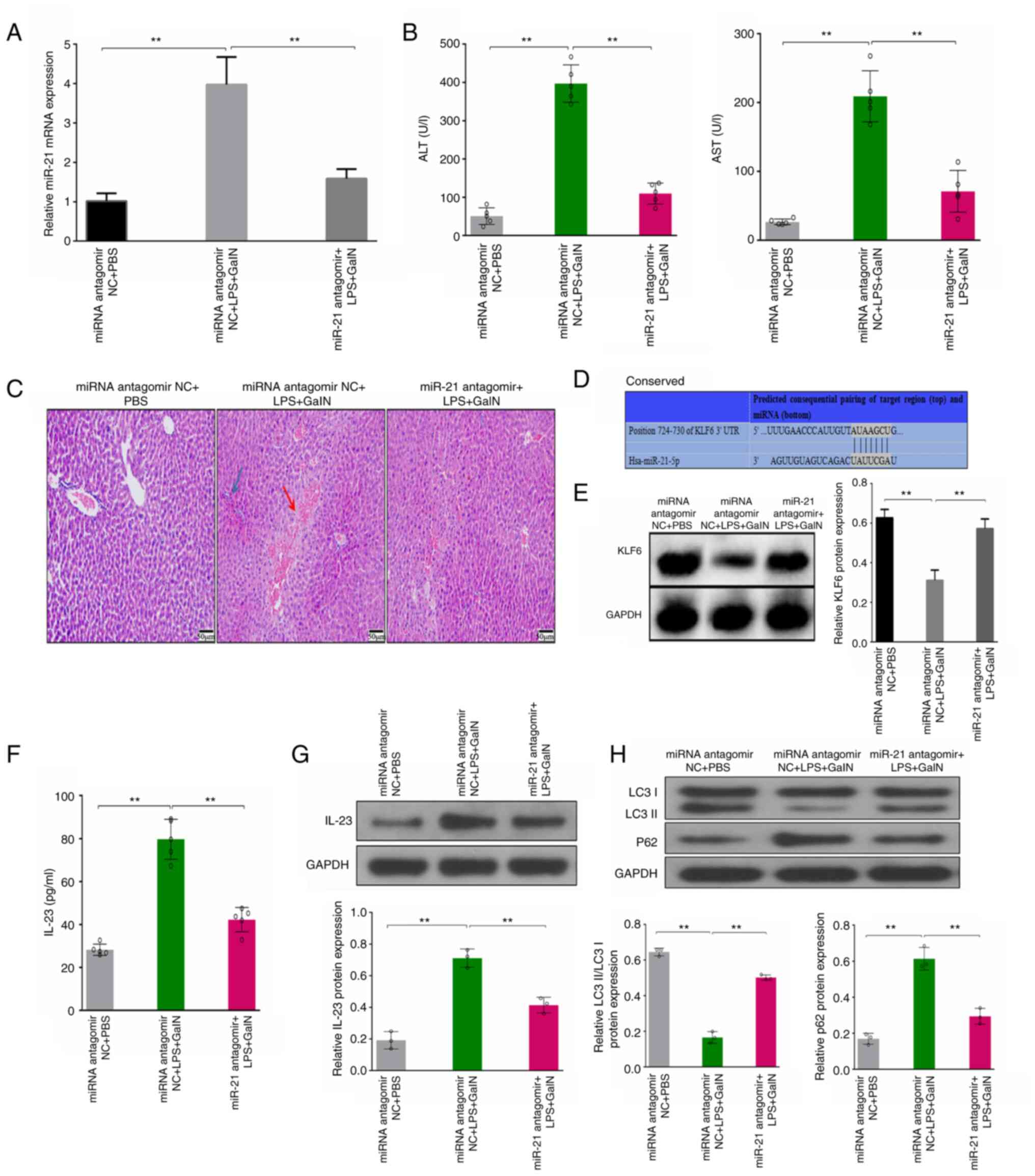
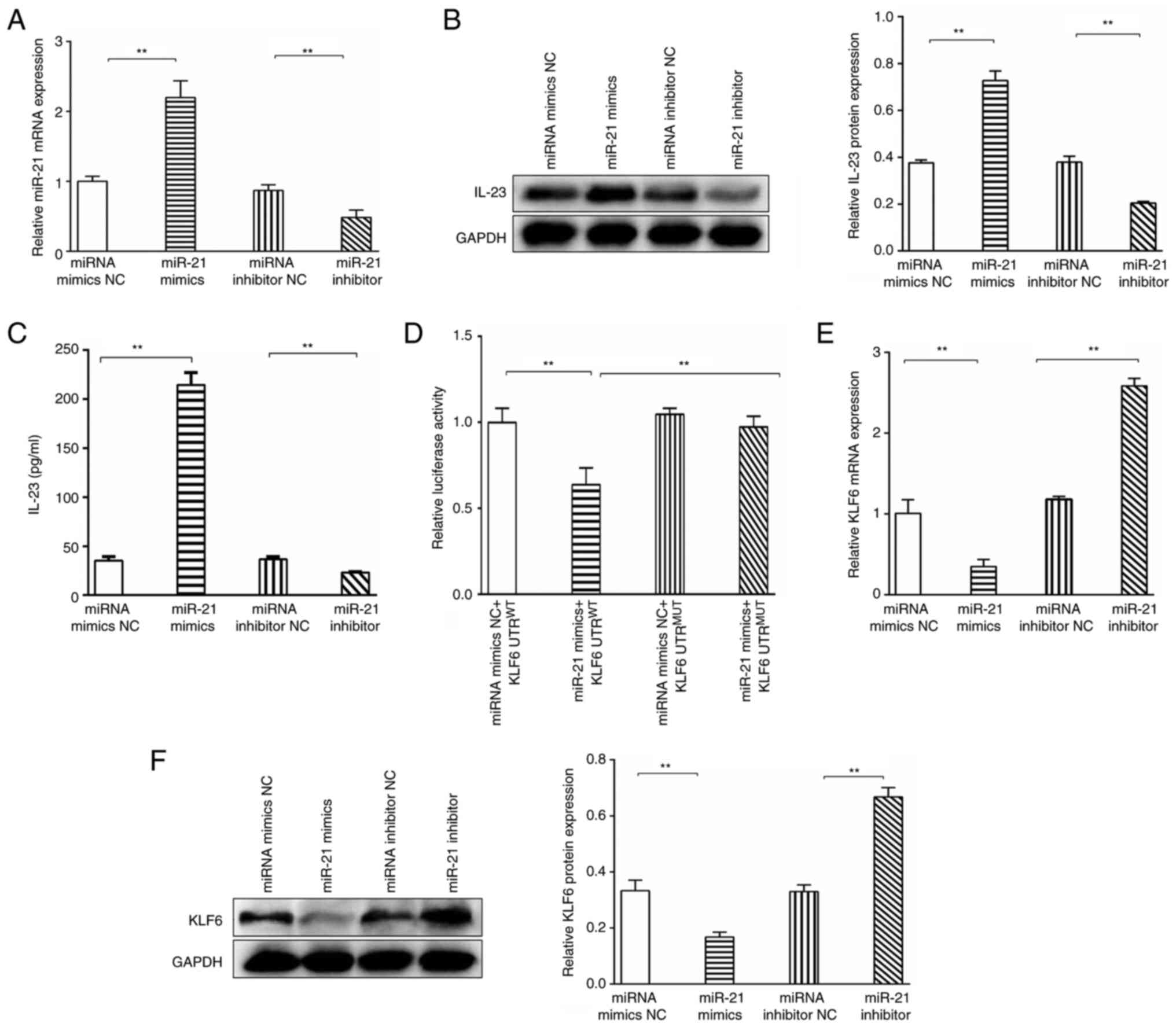
Bao S, Zhao Q, Zheng J, Li N, Huang C,
Chen M, Cheng Q, Zhu M, Yu K, Liu C and Shi G: Interleukin-23
mediates the pathogenesis of LPS/GalN-induced liver injury in mice.
Int Immunopharmacol. 46:97–104. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
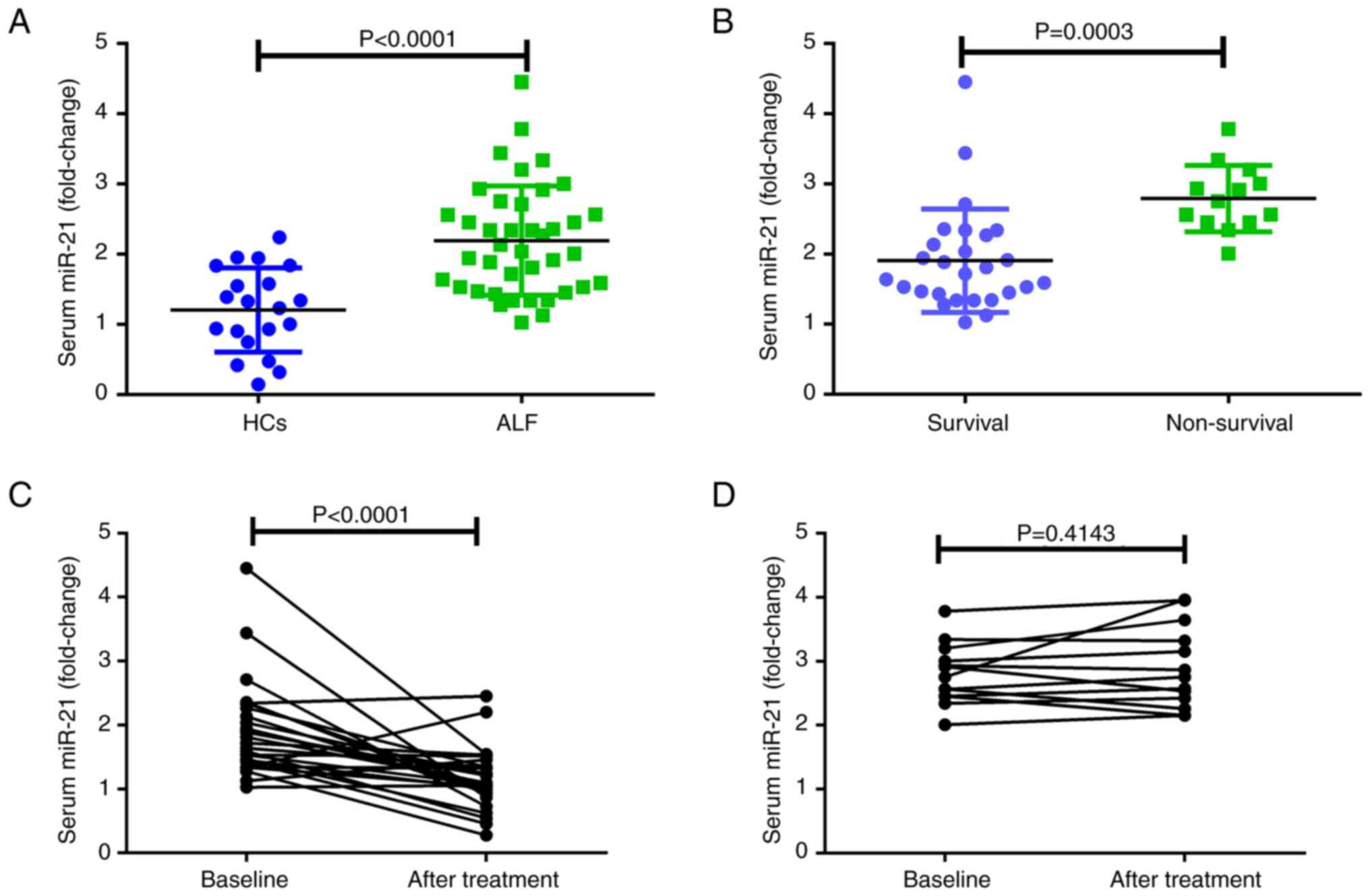
|
Portius D, Sobolewski C and Foti M:
MicroRNAs-dependent regulation of PPARs in metabolic diseases and
cancers. PPAR Res. 2017:70584242017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Xue Z, Xi Q, Liu H, Guo X, Zhang J, Zhang
Z, Li Y, Yang G, Zhou D, Yang H, et al: miR-21 promotes NLRP3
inflammasome activation to mediate pyroptosis and endotoxic shock.
Cell Death Dis. 10:4612019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hu K, Zheng QK, Ma RJ, Ma C, Sun ZG and
Zhang N: Kruppel-like factor 6 splice variant 1: An oncogenic
transcription factor involved in the progression of multiple
malignant tumors. Front Cell Dev Biol. 9:6617312021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mallipattu SK, Horne SJ, D'Agati V, Narla
G, Liu R, Frohman MA, Dickman K, Chen EY, Ma'ayan A, Bialkowska AB,
et al: Krüppel-like factor 6 regulates mitochondrial function in
the kidney. J Clin Invest. 125:1347–1361. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li J, Yu D, He C, Yu Q, Huo Z, Zhang Y and
Zhang S: KLF6 alleviates hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury by
inhibiting autophagy. Cell Death Dis. 14:3932023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sydor S, Manka P, Best J, Jafoui S, Sowa
JP, Zoubek ME, Hernandez-Gea V, Cubero FJ, Kälsch J, Vetter D, et
al: Kruppel-like factor 6 is a transcriptional activator of
autophagy in acute liver injury. Sci Rep. 7:81192017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hu C, Zhao L, Zhang F and Li L: Regulation
of autophagy protects against liver injury in liver surgery-induced
ischaemia/reperfusion. J Cell Mol Med. 25:9905–9917. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang T, Guo J, Gu J, Chen K, Li H and
Wang J: Protective Role of mTOR in liver ischemia/reperfusion
injury: Involvement of inflammation and autophagy. Oxid Med Cell
Longev. 2019:78612902019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zeng JJ, Shi HQ, Ren FF, Zhao XS, Chen QY,
Wang DJ, Wu LP, Chu MP, Lai TF and Li L: Notoginsenoside R1
protects against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice via
suppressing TAK1-JNK/p38 signaling. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
44:1366–1379. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jiang J, Ni L, Zhang X, Wang H, Liu L, Wei
M, Li G and Bei Y: Platelet membrane-fused circulating
extracellular vesicles protect the heart from ischemia/reperfusion
injury. Adv Healthc Mater. 12:e23000522023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen Y, Wu J, Zhu J, Yang G, Tian J, Zhao
Y and Wang Y: Artesunate provides neuroprotection against cerebral
ischemia-reperfusion injury via the TLR-4/NF-κB pathway in rats.
Biol Pharm Bull. 44:350–356. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang Y, Niu H, Li L, Han J, Liu Z, Chu M,
Sha X and Zhao J: Anti-CHAC1 exosomes for nose-to-brain delivery of
miR-760-3p in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury mice inhibiting
neuron ferroptosis. J Nanobiotechnology. 21:1092023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hsieh PN, Zhou G, Yuan Y, Zhang R,
Prosdocimo DA, Sangwung P, Borton AH, Boriushkin E, Hamik A,
Fujioka H, et al: A conserved KLF-autophagy pathway modulates
nematode lifespan and mammalian age-associated vascular
dysfunction. Nat Commun. 8:9142017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Guixé-Muntet S, de Mesquita FC, Vila S,
Hernández-Gea V, Peralta C, García-Pagán JC, Bosch J and
Gracia-Sancho J: Cross-talk between autophagy and KLF2 determines
endothelial cell phenotype and microvascular function in acute
liver injury. J Hepatol. 66:86–94. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Squires JE, McKiernan P and Squires RH:
Acute liver failure: An update. Clin Liver Dis. 22:773–805. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
National Research Council (US) Institute
for Laboratory Animal Research, . Guide for the care and use of
laboratory animals. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US);
1996
|
|
20
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tong M, Zheng Q, Liu M, Chen L, Lin YH,
Tang SG and Zhu YM: 5-methoxytryptophan alleviates liver fibrosis
by modulating FOXO3a/miR-21/ATG5 signaling pathway mediated
autophagy. Cell Cycle. 20:676–688. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Parrish A, Srivastava A, Juskeviciute E,
Hoek JB and Vadigepalli R: Dysregulation of miR-21-associated miRNA
regulatory networks by chronic ethanol consumption impairs liver
regeneration. Physiol Genomics. 53:546–555. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Rowe MM and Kaestner KH: The role of
non-coding RNAs in liver disease, injury, and regeneration. Cells.
12:3592023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lu TX, Munitz A and Rothenberg ME:
MicroRNA-21 is up-regulated in allergic airway inflammation and
regulates IL-12p35 expression. J Immunol. 182:4994–5002. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Du X, Wu M, Tian D, Zhou J, Wang L and
Zhan L: MicroRNA-21 contributes to acute liver injury in
LPS-induced sepsis mice by inhibiting PPAR α expression. PPAR Res.
2020:66330222020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chen X, Song M, Chen W,
Dimitrova-Shumkovska J, Zhao Y, Cao Y, Song Y, Yang W, Wang F,
Xiang Y and Yang C: MicroRNA-21 contributes to liver regeneration
by targeting PTEN. Med Sci Monit. 22:83–91. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Na L, Ding H, Xing E, Zhang Y, Gao J, Liu
B, Yu J and Zhao Y: The predictive value of microRNA-21 for sepsis
risk and its correlation with disease severity, systemic
inflammation, and 28-day mortality in sepsis patients. J Clin Lab
Anal. 34:e231032020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liechty C, Hu J, Zhang L, Liechty KW and
Xu J: Role of microRNA-21 and its underlying mechanisms in
inflammatory responses in diabetic wounds. Int J Mol Sci.
21:33282020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Klionsky DJ, Petroni G, Amaravadi RK,
Baehrecke EH, Ballabio A, Boya P, Bravo-San Pedro JM, Cadwell K,
Cecconi F, Choi AMK, et al: Autophagy in major human diseases. EMBO
J. 40:e1088632021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Klionsky DJ, Abdel-Aziz AK, Abdelfatah S,
Abdellatif M, Abdoli A, Abel S, Abeliovich H, Abildgaard MH, Abudu
YP, Acevedo-Arozena A, et al: Guidelines for the use and
interpretation of assays for monitoring autophagy (4th
edition)1. Autophagy. 17:1–382. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Vargas JNS, Hamasaki M, Kawabata T, Youle
RJ and Yoshimori T: The mechanisms and roles of selective autophagy
in mammals. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 24:167–185. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mishra J, Vishwakarma J, Malik R, Gupta K,
Pandey R, Maurya SK, Garg A, Shukla M, Chattopadhyay N and
Bandyopadhyay S: Hypothyroidism induces interleukin-1-dependent
autophagy mechanism as a key mediator of hippocampal neuronal
apoptosis and cognitive decline in postnatal rats. Mol Neurobiol.
58:1196–1211. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
He WS, Zou MX, Yan YG, Yao NZ, Chen WK, Li
Z, Wang WJ and Ouyang ZH: Interleukin-17A promotes human disc
degeneration by inhibiting autophagy through the activation of the
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt/Bcl2 signaling pathway. World
Neurosurg. 143:e215–e223. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Maneechotesuwan K, Kasetsinsombat K,
Wongkajornsilp A and Barnes PJ: Role of autophagy in regulating
interleukin-10 and the responses to corticosteroids and statins in
asthma. Clin Exp Allergy. 51:1553–1565. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Han D, Huang M, Chang Z and Sun W: KLF15
transcriptionally activates ATG14 to promote autophagy and
attenuate damage of ox-LDL-induced HAECs. Mol Biotechnol.
66:112–122. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zheng Y, Wu J, Chen H, Lin D, Chen H,
Zheng J, Xia H, Huang L and Zeng C: KLF4 targets RAB26 and
decreases 5-FU resistance through inhibiting autophagy in colon
cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 24:22263532023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Prateeksha P, Naidu P, Das M, Barthels D
and Das H: KLF2 regulates neural differentiation of dental
pulp-derived stem cells by modulating autophagy and mitophagy. Stem
Cell Rev Rep. 19:2886–2900. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Santamaria J, Darrigues J, van Meerwijk
JPM and Romagnoli P: Antigen-presenting cells and T-lymphocytes
homing to the thymus shape T cell development. Immunol Lett.
204:9–15. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kim GD, Ng HP, Chan ER and Mahabeleshwar
GH: Kruppel-like factor 6 promotes macrophage inflammatory and
hypoxia response. FASEB J. 34:3209–3223. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Wei G, Zhu D, Sun Y, Zhang L, Liu X, Li M
and Gu J: The protective effects of azilsartan against oscillatory
shear stress-induced endothelial dysfunction and inflammation are
mediated by KLF6. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 35:1–8. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zou Z, Long X, Zhao Q, Zheng Y, Song M, Ma
S, Jing Y, Wang S, He Y, Esteban CR, et al: A single-cell
transcriptomic atlas of human skin aging. Dev Cell. 56:383–397.e8.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Sydor S, Manka P, van Buren L, Theurer S,
Schwertheim S, Best J, Heegsma J, Saeed A, Vetter D, Schlattjan M,
et al: Hepatocyte KLF6 expression affects FXR signalling and the
clinical course of primary sclerosing cholangitis. Liver Int.
40:2172–2181. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Syafruddin SE, Rodrigues P, Vojtasova E,
Patel SA, Zaini MN, Burge J, Warren AY, Stewart GD, Eisen T, Bihary
D, et al: A KLF6-driven transcriptional network links lipid
homeostasis and tumour growth in renal carcinoma. Nat Commun.
10:11522019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Wu B and Wan Y: Molecular control of
pathogenic Th17 cells in autoimmune diseases. Int Immunopharmacol.
80:1061872020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Chang D, Xing Q, Su Y, Zhao X, Xu W, Wang
X and Dong C: The conserved non-coding sequences CNS6 and CNS9
control cytokine-induced Rorc transcription during T helper 17 cell
differentiation. Immunity. 53:614–626.e4. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Abraham C and Cho JH: IL-23 and
autoimmunity: New insights into the pathogenesis of inflammatory
bowel disease. Annu Rev Med. 60:97–110. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|