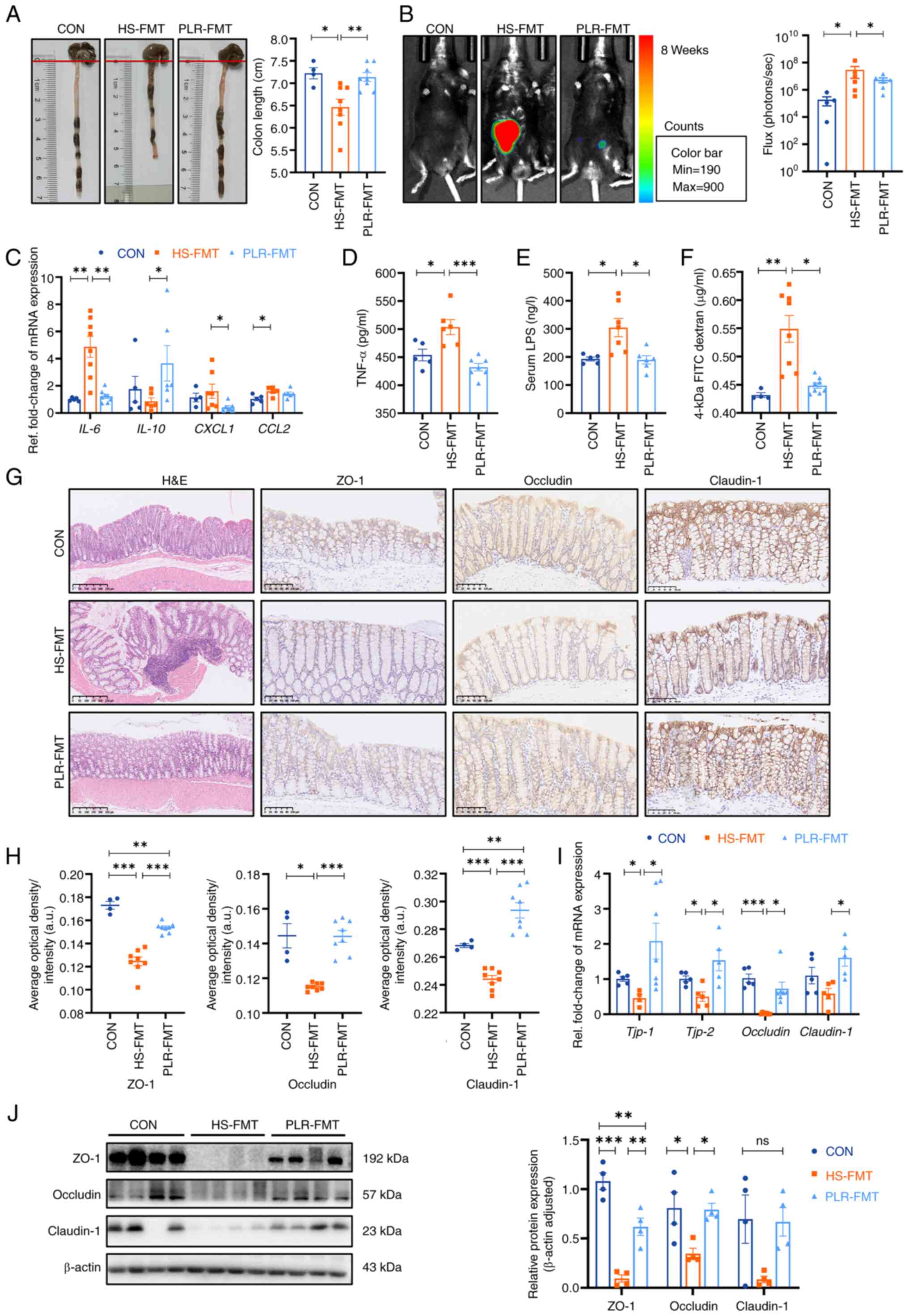
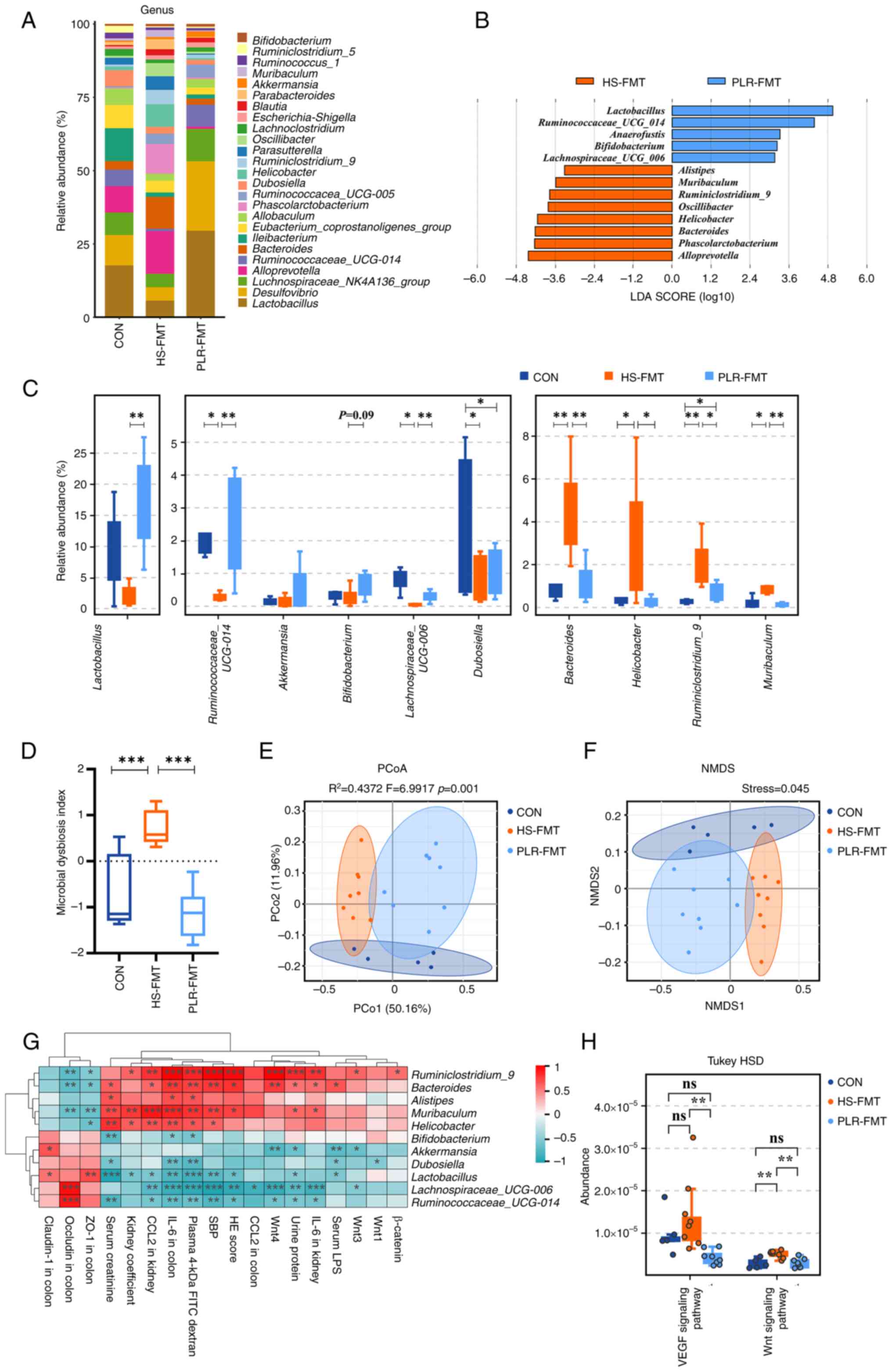
|
1
|
Cockwell P and Fisher LA: The global
burden of chronic kidney disease. Lancet. 395:662–664. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Garofalo C, Borrelli S, Provenzano M, De
Stefano T, Vita C, Chiodini P, Minutolo R, De Nicola L and Conte G:
Dietary salt restriction in chronic kidney disease: A meta-analysis
of randomized clinical trials. Nutrients. 10:7322018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kim SM and Jung JY: Nutritional management
in patients with chronic kidney disease. Korean J Intern Med.
35:1279–1290. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Oppelaar JJ and Vogt L: Body
Fluid-Independent effects of dietary salt consumption in chronic
kidney disease. Nutrients. 11:27792019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yu HC, Burrell LM, Black MJ, Wu LL, Dilley
RJ, Cooper ME and Johnston CI: Salt induces myocardial and renal
fibrosis in normotensive and hypertensive rats. Circulation.
98:2621–2628. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhou B, Liu Y, Kahn M, Ann DK, Han A, Wang
H, Nguyen C, Flodby P, Zhong Q, Krishnaveni MS, et al: Interactions
between β-catenin and transforming growth factor-β signaling
pathways mediate epithelial-mesenchymal transition and are
dependent on the transcriptional co-activator cAMP-response
element-binding protein (CREB)-binding protein (CBP). J Biol Chem.
287:7026–7038. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zmora N, Suez J and Elinav E: You are what
you eat: Diet, health and the gut microbiota. Nat Rev Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 16:35–56. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
He FJ, Tan M, Ma Y and MacGregor GA: Salt
reduction to prevent hypertension and cardiovascular disease: JACC
State-of-the-Art review. J Am Coll Cardiol. 75:632–647. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Miranda PM, De Palma G, Serkis V, Lu J,
Louis-Auguste MP, McCarville JL, Verdu EF, Collins SM and Bercik P:
High salt diet exacerbates colitis in mice by decreasing
Lactobacillus levels and butyrate production. Microbiome. 6:572018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yan X, Jin J, Su X, Yin X, Gao J, Wang X,
Zhang S, Bu P, Wang M, Zhang Y, et al: Intestinal flora modulates
blood pressure by regulating the synthesis of Intestinal-derived
corticosterone in high salt-induced hypertension. Circ Res.
126:839–853. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hu J, Luo H, Wang J, Tang W, Lu J, Wu S,
Xiong Z, Yang G, Chen Z, Lan T, et al: Enteric dysbiosis-linked gut
barrier disruption triggers early renal injury induced by chronic
high salt feeding in mice. Exp Mol Med. 49:e370. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li HB, Xu ML, Xu XD, Tang YY, Jiang HL, Li
L, Xia WJ, Cui N, Bai J, Dai ZM, et al: Faecalibacterium
prausnitzii attenuates CKD via Butyrate-Renal GPR43 axis. Circ Res.
131:e120–e134. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kalantar-Zadeh K, Jafar TH, Nitsch D,
Neuen BL and Perkovic V: Chronic kidney disease. Lancet.
398:786–802. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Huang L, Liu Z, Wu P, Yue X, Lian Z, He P,
Liu Y, Zhou R and Zhao J: Puerariae lobatae radix alleviates
Pre-Eclampsia by remodeling gut microbiota and protecting the gut
and placental barriers. Nutrients. 14:50252022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Inker LA, Astor BC, Fox CH, Isakova T,
Lash JP, Peralta CA, Kurella Tamura M and Feldman HI: KDOQI US
commentary on the 2012 KDIGO clinical practice guideline for the
evaluation and management of CKD. Am J Kidney Dis. 63:713–735.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li Q, Liu W, Feng Y, Hou H, Zhang Z, Yu Q,
Zhou Y, Luo Q, Luo Y, Ouyang H, et al: Radix Puerariae thomsonii
polysaccharide (RPP) improves inflammation and lipid peroxidation
in alcohol and high-fat diet mice by regulating gut microbiota. Int
J Biol Macromol. 209:858–870. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang SS, Zhang NN, Guo S, Liu SJ, Hou YF,
Li S, Ho CT and Bai NS: Glycosides and flavonoids from the extract
of Pueraria thomsonii Benth leaf alleviate type 2 diabetes in
high-fat diet plus streptozotocin-induced mice by modulating the
gut microbiota. Food Funct. 13:3931–3945. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chen R, Wu P, Cai Z, Fang Y, Zhou H,
Lasanajak Y, Tang L, Ye L, Hou C and Zhao J: Puerariae
lobatae Radix with chuanxiong Rhizoma for treatment of cerebral
ischemic stroke by remodeling gut microbiota to regulate the
brain-gut barriers. J Nutr Biochem. 65:101–114. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Avila-Carrasco L, García-Mayorga EA,
Díaz-Avila DL, Garza-Veloz I, Martinez-Fierro ML and González-Mateo
GT: Potential therapeutic effects of natural plant compounds in
kidney disease. Molecules. 26:60962021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang W, Sheng L, Chen Y, Li Z, Wu H, Ma J,
Zhang D, Chen X and Zhang S: Total coumarin derivates from
Hydrangea paniculata attenuate renal injuries in cationized-BSA
induced membranous nephropathy by inhibiting complement activation
and interleukin 10-mediated interstitial fibrosis. Phytomedicine.
96:1538862022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ma L, Huang M, Sun G, Lin Y, Lu D and Wu
B: Puerariae lobatae radix protects against UVB-induced skin
aging via antagonism of REV-ERBα in mice. Front Pharmacol.
13:10882942022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
National Research Council (US) Committee
for the Update of the Guide for the care use of Laboratory Animals:
Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 8th edition.
National Academies Press (US); Washington (DC): 2011
|
|
23
|
Li Z, Zhang X, Wu H, Ma Z, Liu X, Ma J,
Zhang D, Sheng L, Chen X and Zhang S: Hydrangea paniculata
coumarins attenuate experimental membranous nephritis by
bidirectional interactions with the gut microbiota. Commun Biol.
6:11892023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhou Z, Qiu Y, Li K, Sun Q, Xie M, Huang
P, Yu Y, Wang B, Xue J, Zhu Z, et al: Unraveling the impact of
Lactobacillus spp. and other urinary microorganisms on the efficacy
of mirabegron in female patients with overactive bladder. Front
Cell Infect Microbiol. 12:10303152022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Qiu Y, Gao Y, Chen C, Xie M, Huang P, Sun
Q, Zhou Z, Li B, Zhao J and Wu P: Deciphering the influence of
urinary microbiota on FoxP3+ regulatory T cell infiltration and
prognosis in Chinese patients with non-muscle-invasive bladder
cancer. Human Cell. 35:511–521. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J,
Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Peña AG, Goodrich
JK, Gordon JI, et al: QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput
community sequencing data. Nat Methods. 7:335–336. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ondov BD, Bergman NH and Phillippy AM:
Interactive metagenomic visualization in a Web browser. BMC
Bioinformatics. 12:3852011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Segata N, Izard J, Waldron L, Gevers D,
Miropolsky L, Garrett WS and Huttenhower C: Metagenomic biomarker
discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 12:R602011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Aßhauer KP, Wemheuer B, Daniel R and
Meinicke P: Tax4Fun: Predicting functional profiles from
metagenomic 16S rRNA data. Bioinformatics. 31:2882–2884. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Love MI, Huber W and Anders S: Moderated
estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with
DESeq2. Genome Biol. 15:5502014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK,
Mukherjee S, Ebert BL, Gillette MA, Paulovich A, Pomeroy SL, Golub
TR, Lander ES and Mesirov JP: Gene set enrichment analysis: A
knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression
profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:15545–15550. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wirtz S, Popp V, Kindermann M, Gerlach K,
Weigmann B, Fichtner-Feigl S and Neurath MF: Chemically induced
mouse models of acute and chronic intestinal inflammation. Nat
Protoc. 12:1295–1309. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Manabe E, Ito S, Ohno Y, Tanaka T, Naito
Y, Sasaki N, Asakura M, Masuyama T, Ishihara M and Tsujino T:
Reduced lifespan of erythrocytes in Dahl/Salt sensitive rats is the
cause of the renal proximal tubule damage. Sci Rep. 10:220232020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Gunathilake M, Lee J, Choi IJ, Kim YI,
Yoon J, Sul WJ, Kim JF and Kim J: Alterations in gastric microbial
communities are associated with risk of gastric cancer in a Korean
population: A Case-Control study. Cancers. 12:26192020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yan AW, Fouts DE, Brandl J, Stärkel P,
Torralba M, Schott E, Tsukamoto H, Nelson KE, Brenner DA and
Schnabl B: Enteric dysbiosis associated with a mouse model of
alcoholic liver disease. Hepatology. 53:96–105. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Yu LC, Shih YA, Wu LL, Lin YD, Kuo WT,
Peng WH, Lu KS, Wei SC, Turner JR and Ni YH: Enteric dysbiosis
promotes antibiotic-resistant bacterial infection: Systemic
dissemination of resistant and commensal bacteria through
epithelial transcytosis. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol.
307:G824–G835. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Miao C, Zhu X, Wei X, Long M, Jiang L, Li
C, Jin D and Du Y: Pro- and anti-fibrotic effects of vascular
endothelial growth factor in chronic kidney diseases. Ren Fail.
44:881–892. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Keung WM, Lazo O, Kunze L and Vallee BL:
Potentiation of the bioavailability of daidzin by an extract of
Radix puerariae. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 93:4284–4288. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Chen F, Wen Q, Jiang J, Li HL, Tan YF, Li
YH and Zeng NK: Could the gut microbiota reconcile the oral
bioavailability conundrum of traditional herbs? J Ethnopharmacol.
179:253–264. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wang HX and Wang YP: Gut Microbiota-brain
Axis. Chin Med J (Engl). 129:2373–2380. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yang T, Richards EM, Pepine CJ and Raizada
MK: The gut microbiota and the brain-gut-kidney axis in
hypertension and chronic kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol.
14:442–456. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Belzer C and de Vos WM: Microbes
inside-from diversity to function: The case of Akkermansia. ISME J.
6:1449–1458. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Lopez-Siles M, Enrich-Capó N, Aldeguer X,
Sabat-Mir M, Duncan SH, Garcia-Gil LJ and Martinez-Medina M:
Alterations in the abundance and Co-occurrence of Akkermansia
muciniphila and Faecalibacterium prausnitzii in the colonic
mucosa of inflammatory bowel disease subjects. Front Cell Infect
Microbiol. 8:2812018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Wade H, Pan K, Duan Q, Kaluzny S, Pandey
E, Fatumoju L, Saraswathi V, Wu R, Harris EN and Su Q:
Akkermansia muciniphila and its membrane protein Ameliorates
intestinal inflammatory stress and promotes epithelial wound
healing via CREBH and miR-143/145. J Biomed Sci. 30:382023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Li F, Wang M, Wang J, Li R and Zhang Y:
Alterations to the gut microbiota and their correlation with
inflammatory factors in chronic kidney disease. Front Cell Infect
Microbiol. 9:2062019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Keshavarz Azizi Raftar S, Ashrafian F,
Yadegar A, Lari A, Moradi HR, Shahriary A, Azimirad M, Alavifard H,
Mohsenifar Z, Davari M, et al: The protective effects of live and
pasteurized Akkermansia muciniphila and its extracellular
vesicles against HFD/CCl4-induced liver injury. Microbiol Spectr.
9:e00484212021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Pei T, Hu R, Wang F, Yang S, Feng H, Li Q,
Zhang J, Yan S, Ju L, He Z, et al: Akkermansia muciniphila
ameliorates chronic kidney disease interstitial fibrosis via the
gut-renal axis. Microb Pathog. 174:1058912023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Lian Z, Xu Y, Wang C, Chen Y, Yuan L, Liu
Z, Liu Y, He P, Cai Z and Zhao J: Gut microbiota-derived melatonin
from Puerariae lobatae Radix-resistant starch
supplementation attenuates ischemic stroke injury via a positive
microbial co-occurrence pattern. Pharmacol Res. 190:1067142023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Engevik MA, Luk B, Chang-Graham AL, Hall
A, Herrmann B, Ruan W, Endres BT, Shi Z, Garey KW, Hyser JM and
Versalovic J: Bifidobacterium dentium fortifies the intestinal
mucus layer via autophagy and calcium signaling pathways. mBio.
10:e01087–19. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Wang J, Ji H, Wang S, Liu H, Zhang W,
Zhang D and Wang Y: Probiotic lactobacillus plantarum promotes
intestinal barrier function by strengthening the epithelium and
modulating gut microbiota. Front Microbiol. 9:19532018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Wang B, Chen X, Chen Z, Xiao H, Dong J, Li
Y, Zeng X, Liu J, Wan G, Fan S and Cui M: Stable colonization of
Akkermansia muciniphila educates host intestinal
microecology and immunity to battle against inflammatory intestinal
diseases. Exp Mol Med. 55:55–68. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Cozzolino A, Vergalito F, Tremonte P,
Iorizzo M, Lombardi SJ, Sorrentino E, Luongo D, Coppola R, Di Marco
R and Succi M: Preliminary evaluation of the safety and probiotic
potential of Akkermansia muciniphila DSM 22959 in comparison
with lactobacillus rhamnosus GG. Microorganisms. 8:1892020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Wang X, Yang S, Li S, Zhao L, Hao Y, Qin
J, Zhang L, Zhang C, Bian W, Zuo L, et al: Aberrant gut microbiota
alters host metabolome and impacts renal failure in humans and
rodents. Gut. 69:2131–2142. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Tian N, Li L, Ng JKC and Li PKT: The
potential benefits and controversies of probiotics use in patients
at different stages of chronic kidney disease. Nutrients.
14:40442022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Mitrović M, Stanković-Popović V, Tolinački
M, Golić N, Soković Bajić S, Veljović K, Nastasijević B, Soldatović
I, Svorcan P and Dimković N: The Impact of synbiotic treatment on
the levels of gut-derived uremic toxins, inflammation, and gut
microbiome of chronic kidney disease Patients-A randomized trial. J
Ren Nutr. 33:278–288. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Yue SY, Zhou RR, Nan TG, Huang LQ and Yuan
Y: Comparison of major chemical components in puerariae thomsonii
radix and Puerariae lobatae radix. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za
Zhi. 47:2689–2697. 2022.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Luo Y, Xiao Y, Zhao J, Zhang H, Chen W and
Zhai Q: The role of mucin and oligosaccharides via cross-feeding
activities by Bifidobacterium: A review. Int J Biol Macromol.
167:1329–1337. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Wu Z, Huang S, Li T, Li N, Han D, Zhang B,
Xu ZZ, Zhang S, Pang J, Wang S, et al: Gut microbiota from green
tea polyphenol-dosed mice improves intestinal epithelial
homeostasis and ameliorates experimental colitis. Microbiome.
9:1842021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Chen R, Xu Y, Wu P, Zhou H, Lasanajak Y,
Fang Y, Tang L, Ye L, Li X, Cai Z and Zhao J: Transplantation of
fecal microbiota rich in short chain fatty acids and butyric acid
treat cerebral ischemic stroke by regulating gut microbiota.
Pharmacol Res. 148:1044032019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Lee J, d'Aigle J, Atadja L, Quaicoe V,
Honarpisheh P, Ganesh BP, Hassan A, Graf J, Petrosino J, Putluri N,
et al: Gut Microbiota-derived Short-chain fatty acids promote
poststroke recovery in aged mice. Circ Res. 127:453–465. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Feng Y, Ren J, Gui Y, Wei W, Shu B, Lu Q,
Xue X, Sun X, He W, Yang J and Dai C: Wnt/β-Catenin-Promoted
macrophage alternative activation contributes to kidney fibrosis. J
Am Soc Nephrol. 29:182–193. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Schunk SJ, Floege J, Fliser D and Speer T:
WNT-β-catenin signalling-a versatile player in kidney injury and
repair. Nat Rev Nephrol. 17:172–184. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Yamamoto M, Takahashi-Yanaga F, Arioka M,
Igawa K, Tomooka K, Yamaura K and Sasaguri T: Cardiac and renal
protective effects of 2,5-dimethylcelecoxib in angiotensin II and
high-salt-induced hypertension model mice. J Hypertens. 39:892–903.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Manning JA, Shah SS, Nikolic A, Henshall
TL, Khew-Goodall Y and Kumar S: The ubiquitin ligase NEDD4-2/NEDD4L
regulates both sodium homeostasis and fibrotic signaling to prevent
end-stage renal disease. Cell Death Dis. 12:3982021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Feng Q, Chen WD and Wang YD: Gut
Microbiota: An integral moderator in health and disease. Front
Microbiol. 9:1512018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Chen J, Zhao K-N and Vitetta L: Effects of
intestinal microbial−elaborated butyrate on oncogenic
signaling pathways. Nutrients. 11:10262019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Benito I, Encío IJ, Milagro FI, Alfaro M,
Martínez-Peñuela A, Barajas M and Marzo F: Microencapsulated
bifidobacterium bifidum and lactobacillus gasseri in combination
with quercetin inhibit colorectal cancer development in ApcMin/+
mice. Int J Mol Sci. 22:49062021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Hiyama A, Yokoyama K, Nukaga T, Sakai D
and Mochida J: A complex interaction between Wnt signaling and
TNF-α in nucleus pulposus cells. Arthritis Res Ther. 15:R1892013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Zhao Y, Wang C, Hong X, Miao J, Liao Y,
Hou FF, Zhou L and Liu Y: Wnt/β-catenin signaling mediates both
heart and kidney injury in type 2 cardiorenal syndrome. Kidney Int.
95:815–829. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Pan B, Zhang H, Hong Y, Ma M, Wan X and
Cao C: Indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase activates Wnt/β-catenin inducing
kidney fibrosis after acute kidney injury. Gerontology. 67:611–619.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Gelfand BD, Meller J, Pryor AW, Kahn M,
Bortz PDS, Wamhoff BR and Blackman BR: Hemodynamic activation of
beta-catenin and T-cell-specific transcription factor signaling in
vascular endothelium regulates fibronectin expression. Arterioscler
Thromb Vasc Biol. 31:1625–1633. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Xiang FL, Fang M and Yutzey KE: Loss of
β-catenin in resident cardiac fibroblasts attenuates fibrosis
induced by pressure overload in mice. Nat Commun. 8:7122017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Xiao L, Xu B, Zhou L, Tan RJ, Zhou D, Fu
H, Li A, Hou FF and Liu Y: Wnt/β-catenin regulates blood pressure
and kidney injury in rats. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis.
1865:1313–1322. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Lin Y, Dong MQ, Liu ZM, Xu M, Huang ZH,
Liu HJ, Gao Y and Zhou WJ: A strategy of vascular-targeted therapy
for liver fibrosis. Hepatology. 76:660–675. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Sun J, Shi L, Xiao T, Xue J, Li J, Wang P,
Wu L, Dai X, Ni X and Liu Q: microRNA-21, via the HIF-1α/VEGF
signaling pathway, is involved in arsenite-induced hepatic fibrosis
through aberrant cross-talk of hepatocytes and hepatic stellate
cells. Chemosphere. 266:1291772021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Jiang L, Yin M, Wei X, Liu J, Wang X, Niu
C, Kang X, Xu J, Zhou Z, Sun S, et al: Bach1 represses
Wnt/β-Catenin signaling and angiogenesis. Circ Res. 117:364–375.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Hung SW, Zhang R, Tan Z, Chung JPW, Zhang
T and Wang CC: Pharmaceuticals targeting signaling pathways of
endometriosis as potential new medical treatment: A review. Med Res
Rev. 41:2489–2564. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Hong F, Hong J, Wang L, Zhou Y, Liu D, Xu
B, Yu X and Sheng L: Chronic exposure to nanoparticulate TiO2
causes renal fibrosis involving activation of the Wnt pathway in
mouse kidney. J Agric Food Chem. 63:1639–1647. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Jiang F, Parsons CJ and Stefanovic B: Gene
expression profile of quiescent and activated rat hepatic stellate
cells implicates Wnt signaling pathway in activation. J Hepatol.
45:401–409. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Yoo EJ, Oh KH, Piao H, Kang HJ, Jeong GW,
Park H, Lee CJ, Ryu H, Yang SH, Kim MG, et al: Macrophage
transcription factor TonEBP promotes systemic lupus erythematosus
and kidney injury via damage-induced signaling pathways. Kidney
Int. 104:163–180. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Huynh C, Ryu J, Lee J, Inoki A and Inoki
K: Nutrient-sensing mTORC1 and AMPK pathways in chronic kidney
diseases. Nat Rev Nephrol. 19:102–122. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|