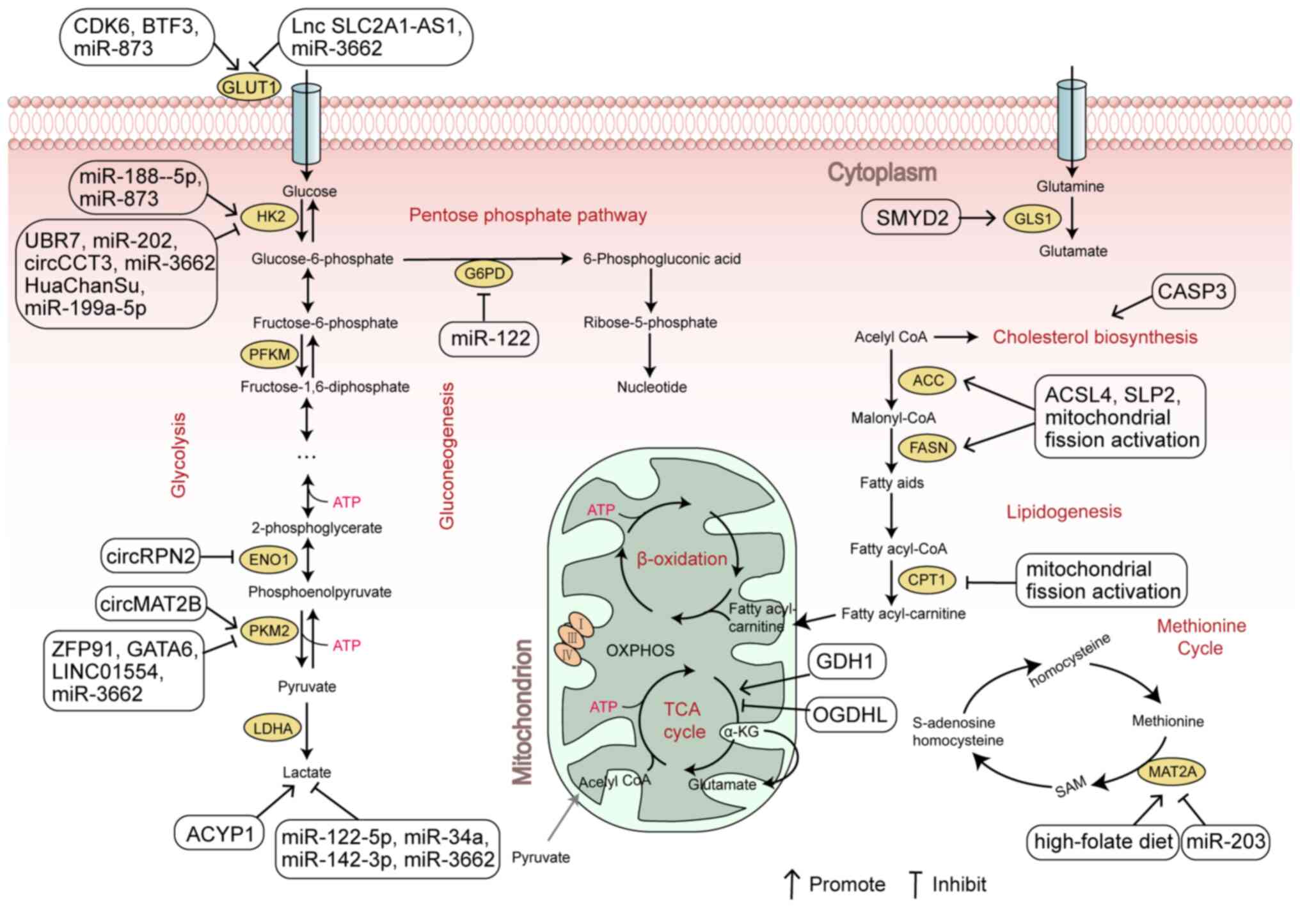
|
1
|
Llovet JM, Kelley RK, Villanueva A, Singal
AG, Pikarsky E, Roayaie S, Lencioni R, Koike K, Zucman-Rossi J and
Finn RS: Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 7:62021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Xing Y, Zhao S, Zhou BP and Mi J:
Metabolic reprogramming of the tumour microenvironment. FEBS J.
282:3892–3898. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Martínez-Reyes I and Chandel NS: Cancer
metabolism: Looking forward. Nat Rev Cancer. 21:669–680. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ward PS and Thompson CB: Metabolic
reprogramming: A cancer hallmark even warburg did not anticipate.
Cancer Cell. 21:297–308. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Vander Heiden MG, Cantley LC and Thompson
CB: Understanding the Warburg effect: The metabolic requirements of
cell proliferation. Science. 324:1029–1033. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Warburg O: On the origin of cancer cells.
Science. 123:309–314. 1956. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li C, Chen J, Li Y, Wu B, Ye Z, Tian X,
Wei Y, Hao Z, Pan Y, Zhou H, et al: 6-Phosphogluconolactonase
promotes hepatocellular carcinogenesis by activating pentose
phosphate pathway. Front Cell Dev Biol. 9:7531962021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liu Y, Lu LL, Wen D, Liu DL, Dong LL, Gao
DM, Bian XY, Zhou J, Fan J and Wu WZ: MiR-612 regulates invadopodia
of hepatocellular carcinoma by HADHA-mediated lipid reprogramming.
J Hematol Oncol. 13:122020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Vettore L, Westbrook RL and Tennant DA:
New aspects of amino acid metabolism in cancer. Br J Cancer.
122:150–156. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhuang X, Chen Y, Wu Z, Xu Q, Chen M, Shao
M, Cao X, Zhou Y, Xie M, Shi Y, et al: Mitochondrial miR-181a-5p
promotes glucose metabolism reprogramming in liver cancer by
regulating the electron transport chain. Carcinogenesis.
41:972–983. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Xia L, Oyang L, Lin J, Tan S, Han Y, Wu N,
Yi P, Tang L, Pan Q, Rao S, et al: The cancer metabolic
reprogramming and immune response. Mol Cancer. 20:282021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Vaupel P, Schmidberger H and Mayer A: The
Warburg effect: essential part of metabolic reprogramming and
central contributor to cancer progression. Int J Radiat Biol.
95:912–919. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Enzo E, Santinon G, Pocaterra A, Aragona
M, Bresolin S, Forcato M, Grifoni D, Pession A, Zanconato F, Guzzo
G, et al: Aerobic glycolysis tunes YAP/TAZ transcriptional
activity. EMBO J. 34:1349–1370. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liao W, Du J, Wang Z, Feng Q, Liao M, Liu
H, Yuan K and Zeng Y: The role and mechanism of noncoding RNAs in
regulation of metabolic reprogramming in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Int J Cancer. 151:337–347. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li J, Eu JQ, Kong LR, Wang L, Lim YC, Goh
BC and Wong ALA: Targeting Metabolism in Cancer Cells and the
Tumour Microenvironment for Cancer Therapy. Molecules. 25:48312020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Amann T, Maegdefrau U, Hartmann A, Agaimy
A, Marienhagen J, Weiss TS, Stoeltzing O, Warnecke C, Schölmerich
J, Oefner PJ, et al: GLUT1 expression is increased in
hepatocellular carcinoma and promotes tumorigenesis. Am J Pathol.
174:1544–1552. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yao J, Tang S, Shi C, Lin Y, Ge L, Chen Q,
Ou B, Liu D, Miao Y, Xie Q, et al: Isoginkgetin, a potential CDK6
inhibitor, suppresses SLC2A1/GLUT1 enhancer activity to induce
AMPK-ULK1-mediated cytotoxic autophagy in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Autophagy. 19:1221–1238. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shang R, Pu M, Li Y and Wang D: FOXM1
regulates glycolysis in hepatocellular carcinoma by transactivating
glucose transporter 1 expression. Oncol Rep. 37:2261–2269. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang P, Sun J, Sun C, Zhao H, Zhang Y and
Chen J: BTF3 promotes proliferation and glycolysis in
hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating GLUT1. Cancer Biol Ther.
24:22258842023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shang R, Wang M, Dai B, Du J, Wang J, Liu
Z, Qu S, Yang X, Liu J, Xia C, et al: Long noncoding RNA SLC2A1-AS1
regulates aerobic glycolysis and progression in hepatocellular
carcinoma via inhibiting the STAT3/FOXM1/GLUT1 pathway. Mol Oncol.
14:1381–1396. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yang H, Zhang MZ, Sun HW, Chai YT, Li X,
Jiang Q and Hou J: A Novel Microcrystalline BAY-876 formulation
achieves long-acting antitumor activity against aerobic glycolysis
and proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma. Front Oncol.
11:7831942021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
DeWaal D, Nogueira V, Terry AR, Patra KC,
Jeon SM, Guzman G, Au J, Long CP, Antoniewicz MR and Hay N:
Hexokinase-2 depletion inhibits glycolysis and induces oxidative
phosphorylation in hepatocellular carcinoma and sensitizes to
metformin. Nat Commun. 9:4462018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Garcia SN, Guedes RC and Marques MM:
Unlocking the Potential of HK2 in Cancer Metabolism and
Therapeutics. Curr Med Chem. 26:7285–7322. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhao L, Kang M, Liu X, Wang Z, Wang Y,
Chen H, Liu W, Liu S, Li B, Li C, et al: UBR7 inhibits HCC
tumorigenesis by targeting Keap1/Nrf2/Bach1/HK2 and glycolysis. J
Exp Clin Cancer Res. 41:3302022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ding Z, Guo L, Deng Z and Li P: Circ-PRMT5
enhances the proliferation, migration and glycolysis of hepatoma
cells by targeting miR-188-5p/HK2 axis. Ann Hepatol. 19:269–279.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang J, Chen J, Sun F, Wang Z, Xu W, Yu Y,
Ding F and Shen H: miR-202 functions as a tumor suppressor in
hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting HK2. Oncol Lett.
19:2265–2271. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lv B, Zhu W and Feng C: Coptisine Blocks
Secretion of Exosomal circCCT3 from cancer-associated fibroblasts
to reprogram glucose metabolism in hepatocellular carcinoma. DNA
Cell Biol. Oct 2–2020.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Wu Q, Wang SP, Sun XX, Tao YF, Yuan XQ,
Chen QM, Dai L, Li CL, Zhang JY and Yang AL: HuaChanSu suppresses
tumor growth and interferes with glucose metabolism in
hepatocellular carcinoma cells by restraining Hexokinase-2. Int J
Biochem Cell Biol. 142:1061232022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Huang J, Chen F, Zhong Z, Tan HY, Wang N,
Liu Y, Fang X, Yang T and Feng Y: Interpreting the pharmacological
mechanisms of huachansu capsules on hepatocellular carcinoma
through combining network pharmacology and experimental evaluation.
Front Pharmacol. 11:4142020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Laussel C and Léon S: Cellular toxicity of
the metabolic inhibitor 2-deoxyglucose and associated resistance
mechanisms. Biochem Pharmacol. 182:1142132020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ma WK, Voss DM, Scharner J, Costa ASH, Lin
KT, Jeon HY, Wilkinson JE, Jackson M, Rigo F, Bennett CF and
Krainer AR: ASO-Based PKM splice-switching therapy inhibits
hepatocellular carcinoma growth. Cancer Res. 82:900–915. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Israelsen WJ and Vander Heiden MG:
Pyruvate kinase: Function, regulation and role in cancer. Semin
Cell Dev Biol. 43:43–51. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chen D, Wang Y, Lu R, Jiang X, Chen X,
Meng N, Chen M, Xie S and Yan GR: E3 ligase ZFP91 inhibits
Hepatocellular Carcinoma Metabolism Reprogramming by regulating PKM
splicing. Theranostics. 10:8558–8572. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tan HW, Leung CO, Chan KK, Ho DW, Leung
MS, Wong CM, Ng IO and Lo RC: Deregulated GATA6 modulates stem
cell-like properties and metabolic phenotype in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 145:1860–1873. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Panda AC: Circular RNAs Act as miRNA
Sponges. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1087:67–79. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Li Q, Pan X, Zhu D, Deng Z, Jiang R and
Wang X: Circular RNA MAT2B promotes glycolysis and malignancy of
hepatocellular carcinoma through the miR-338-3p/PKM2 axis under
hypoxic stress. Hepatology. 70:1298–1316. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhang M, Zhang H, Hong H and Zhang Z:
MiR-374b re-sensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma cells to sorafenib
therapy by antagonizing PKM2-mediated glycolysis pathway. Am J
Cancer Res. 9:765–778. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Tang W, Chen Z, Zhang W, Cheng Y, Zhang B,
Wu F, Wang Q, Wang S, Rong D, Reiter FP, et al: The mechanisms of
sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma: theoretical basis
and therapeutic aspects. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 5:872020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Chen M, Liu H, Li Z, Ming AL and Chen H:
Mechanism of PKM2 affecting cancer immunity and metabolism in tumor
microenvironment. J Cancer. 12:3566–3574. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Feng Y, Xiong Y, Qiao T, Li X, Jia L and
Han Y: Lactate dehydrogenase A: A key player in carcinogenesis and
potential target in cancer therapy. Cancer Med. 7:6124–6136. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Malvi P, Rawat V, Gupta R and Wajapeyee N:
Transcriptional, chromatin, and metabolic landscapes of LDHA
inhibitor-resistant pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Front Oncol.
12:9264372022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wang S, Zhou L, Ji N, Sun C, Sun L, Sun J,
Du Y, Zhang N, Li Y, Liu W and Lu W: Targeting ACYP1-mediated
glycolysis reverses lenvatinib resistance and restricts
hepatocellular carcinoma progression. Drug Resist Updat.
69:1009762023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wang X, Zhang P and Deng K: MYC Promotes
LDHA Expression through MicroRNA-122-5p to potentiate glycolysis in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Anal Cell Pathol (Amst).
2022:14351732022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhang HF, Wang YC and Han YD: MicroRNA-34a
inhibits liver cancer cell growth by reprogramming glucose
metabolism. Mol Med Rep. 17:4483–4489. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Hua S, Liu C, Liu L and Wu D: miR-142-3p
inhibits aerobic glycolysis and cell proliferation in
hepatocellular carcinoma via targeting LDHA. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 496:947–954. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Cai J, Chen Z, Zhang Y, Wang J, Zhang Z,
Wu J, Mao J and Zuo X: CircRHBDD1 augments metabolic rewiring and
restricts immunotherapy efficacy via m(6)A modification in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 24:755–771. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Luo X, Zheng E, Wei L, Zeng H, Qin H,
Zhang X, Liao M, Chen L, Zhao L, Ruan XZ, et al: The fatty acid
receptor CD36 promotes HCC progression through activating
Src/PI3K/AKT axis-dependent aerobic glycolysis. Cell Death Dis.
12:3282021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Zhao C, Wang B, Liu E and Zhang Z: Loss of
PTEN expression is associated with PI3K pathway-dependent metabolic
reprogramming in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Commun Signal.
18:1312020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Zheng YL, Li L, Jia YX, Zhang BZ, Li JC,
Zhu YH, Li MQ, He JZ, Zeng TT, Ban XJ, et al: LINC01554-Mediated
glucose metabolism reprogramming suppresses tumorigenicity in
hepatocellular carcinoma via downregulating PKM2 expression and
inhibiting Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Theranostics. 9:796–810.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Li J, Hu ZQ, Yu SY, Mao L, Zhou ZJ, Wang
PC, Gong Y, Su S, Zhou J, Fan J, et al: CircRPN2 inhibits aerobic
glycolysis and metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res.
82:1055–1069. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Li X, Zhang Y, Ma W, Fu Q, Liu J, Yin G,
Chen P, Dai D, Chen W, Qi L, et al: Enhanced glucose metabolism
mediated by CD147 contributes to immunosuppression in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 69:535–548.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Lin D and Wu J: Hypoxia inducible factor
in hepatocellular carcinoma: A therapeutic target. World J
Gastroenterol. 21:12171–12178. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Iyer NV, Kotch LE, Agani F, Leung SW,
Laughner E, Wenger RH, Gassmann M, Gearhart JD, Lawler AM, Yu AY
and Semenza GL: Cellular and developmental control of O2
homeostasis by hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha. Genes Dev.
12:149–162. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Guo W, Qiu Z, Wang Z, Wang Q, Tan N, Chen
T, Chen Z, Huang S, Gu J, Li J, et al: MiR-199a-5p is negatively
associated with malignancies and regulates glycolysis and lactate
production by targeting hexokinase 2 in liver cancer. Hepatology.
62:1132–1144. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Chen Z, Zuo X, Zhang Y, Han G, Zhang L, Wu
J and Wang X: MiR-3662 suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma growth
through inhibition of HIF-1α-mediated Warburg effect. Cell Death
Dis. 9:5492018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Luo W, Hu H, Chang R, Zhong J, Knabel M,
O'Meally R, Cole RN, Pandey A and Semenza GL: Pyruvate kinase M2 is
a PHD3-stimulated coactivator for hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Cell.
145:732–744. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Zhang Y, Zhang C, Zhao Q, Wei W, Dong Z,
Shao L, Li J, Wu W, Zhang H, Huang H, et al: The miR-873/NDFIP1
axis promotes hepatocellular carcinoma growth and metastasis
through the AKT/mTOR-mediated Warburg effect. Am J Cancer Res.
9:927–944. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Kowalik MA, Columbano A and Perra A:
Emerging role of the pentose phosphate pathway in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Front Oncol. 7:872017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Stincone A, Prigione A, Cramer T, Wamelink
MM, Campbell K, Cheung E, Olin-Sandoval V, Grüning NM, Krüger A,
Tauqeer Alam M, et al: The return of metabolism: biochemistry and
physiology of the pentose phosphate pathway. Biol Rev Camb Philos
Soc. 90:927–963. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Lu M, Lu L, Dong Q, Yu G, Chen J, Qin L,
Wang L, Zhu W and Jia H: Elevated G6PD expression contributes to
migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by
inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Acta Biochim Biophys
Sin (Shanghai). 50:370–380. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Barajas JM, Reyes R, Guerrero MJ, Jacob
ST, Motiwala T and Ghoshal K: The role of miR-122 in the
dysregulation of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD)
expression in hepatocellular cancer. Sci Rep. 8:91052018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Qin Z, Xiang C, Zhong F, Liu Y, Dong Q, Li
K, Shi W, Ding C, Qin L and He F: Transketolase (TKT) activity and
nuclear localization promote hepatocellular carcinoma in a
metabolic and a non-metabolic manner. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
38:1542019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Jia D, Liu C, Zhu Z, Cao Y, Wen W, Hong Z,
Liu Y, Liu E, Chen L, Chen C, et al: Novel transketolase inhibitor
oroxylin A suppresses the non-oxidative pentose phosphate pathway
and hepatocellular carcinoma tumour growth in mice and
patient-derived organoids. Clin Transl Med. 12:e10952022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Luo X, Cheng C, Tan Z, Li N, Tang M, Yang
L and Cao Y: Emerging roles of lipid metabolism in cancer
metastasis. Mol Cancer. 16:762017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Shimano H and Sato R: SREBP-regulated
lipid metabolism: Convergent physiology-divergent pathophysiology.
Nat Rev Endocrinol. 13:710–730. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Muku GE, Blazanin N, Dong F, Smith PB,
Thiboutot D, Gowda K, Amin S, Murray IA and Perdew GH: Selective Ah
Receptor Ligands Mediate Enhanced SREBP1 Proteolysis to Restrict
Lipogenesis in Sebocytes. Toxicol Sci. 171:146–158. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Li H, Chen Z, Zhang Y, Yuan P, Liu J, Ding
L and Ye Q: MiR-4310 regulates hepatocellular carcinoma growth and
metastasis through lipid synthesis. Cancer Lett. 519:161–171. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Chen J, Ding C, Chen Y, Hu W, Yu C, Peng
C, Feng X, Cheng Q, Wu W, Lu Y, et al: ACSL4 reprograms fatty acid
metabolism in hepatocellular carcinoma via c-Myc/SREBP1 pathway.
Cancer Lett. 502:154–165. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Liu Y, Sun L, Guo H, Zhou S, Wang C, Ji C,
Meng F, Liang S, Zhang B, Yuan Y, et al: Targeting SLP2-mediated
lipid metabolism reprograming restricts proliferation and
metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma and promotes sensitivity to
Lenvatinib. Oncogene. 42:374–388. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Chan DC: Mitochondrial dynamics and its
involvement in disease. Annu Rev Pathol. 15:235–259. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Wu D, Yang Y, Hou Y, Zhao Z, Liang N, Yuan
P, Yang T, Xing J and Li J: Increased mitochondrial fission drives
the reprogramming of fatty acid metabolism in hepatocellular
carcinoma cells through suppression of Sirtuin 1. Cancer Commun
(Lond). 42:37–55. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Li Q, Yao H, Wang Y, Wu Y, Thorne RF, Zhu
Y, Wu M and Liu L: circPRKAA1 activates a Ku80/Ku70/SREBP-1 axis
driving de novo fatty acid synthesis in cancer cells. Cell Rep.
41:1117072022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Mok EHK, Leung CON, Zhou L, Lei MML, Leung
HW, Tong M, Wong TL, Lau EYT, Ng IOL, Ding J, et al:
Caspase-3-Induced Activation of SREBP2 Drives drug resistance via
promotion of cholesterol biosynthesis in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Cancer Res. 82:3102–3115. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Svensson RU, Parker SJ, Eichner LJ, Kolar
MJ, Wallace M, Brun SN, Lombardo PS, Van Nostrand JL, Hutchins A,
Vera L, et al: Inhibition of acetyl-CoA carboxylase suppresses
fatty acid synthesis and tumor growth of non-small-cell lung cancer
in preclinical models. Nat Med. 22:1108–1119. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Zaytseva YY, Rychahou PG, Le AT, Scott TL,
Flight RM, Kim JT, Harris J, Liu J, Wang C, Morris AJ, et al:
Preclinical evaluation of novel fatty acid synthase inhibitors in
primary colorectal cancer cells and a patient-derived xenograft
model of colorectal cancer. Oncotarget. 9:24787–24800. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Peck B, Schug ZT, Zhang Q, Dankworth B,
Jones DT, Smethurst E, Patel R, Mason S, Jiang M, Saunders R, et
al: Inhibition of fatty acid desaturation is detrimental to cancer
cell survival in metabolically compromised environments. Cancer
Metab. 4:62016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Stine ZE, Schug ZT, Salvino JM and Dang
CV: Targeting cancer metabolism in the era of precision oncology.
Nat Rev Drug Discov. 21:141–162. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Cheng C, Geng F, Cheng X and Guo D: Lipid
metabolism reprogramming and its potential targets in cancer.
Cancer Commun (Lond). 38:272018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Li B, Cao Y, Meng G, Qian L, Xu T, Yan C,
Luo O, Wang S, Wei J, Ding Y and Yu D: Targeting glutaminase 1
attenuates stemness properties in hepatocellular carcinoma by
increasing reactive oxygen species and suppressing Wnt/beta-catenin
pathway. EBioMedicine. 39:239–254. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Altman BJ, Stine ZE and Dang CV: From
Krebs to clinic: Glutamine metabolism to cancer therapy. Nat Rev
Cancer. 16:619–634. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Marsico M, Santarsiero A, Pappalardo I,
Convertini P, Chiummiento L, Sardone A, Di Noia MA, Infantino V and
Todisco S: Mitochondria-Mediated Apoptosis of HCC cells triggered
by knockdown of glutamate dehydrogenase 1: Perspective for its
inhibition through quercetin and permethylated anigopreissin A.
Biomedicines. 9:16642021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Dai W, Xu L, Yu X, Zhang G, Guo H, Liu H,
Song G, Weng S, Dong L, Zhu J, et al: OGDHL silencing promotes
hepatocellular carcinoma by reprogramming glutamine metabolism. J
Hepatol. 72:909–923. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Xu K, Ding J, Zhou L, Li D, Luo J, Wang W,
Shang M, Lin B, Zhou L and Zheng S: SMYD2 promotes hepatocellular
carcinoma progression by reprogramming glutamine metabolism via
c-Myc/GLS1 Axis. Cells. 12:252022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Meric-Bernstam F, Tannir NM, Iliopoulos O,
Lee RJ, Telli ML, Fan AC, DeMichele A, Haas NB, Patel MR, Harding
JJ, et al: Telaglenastat plus cabozantinib or everolimus for
advanced or metastatic renal cell carcinoma: An open-label phase I
trial. Clin Cancer Res. 28:1540–1548. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Li C, Gui G, Zhang L, Qin A, Zhou C and
Zha X: Overview of methionine adenosyltransferase 2A (MAT2A) as an
anticancer target: Structure, function, and inhibitors. J Med Chem.
65:9531–9547. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Hung MH, Lee JS, Ma C, Diggs LP, Heinrich
S, Chang CW, Ma L, Forgues M, Budhu A, Chaisaingmongkol J, et al:
Tumor methionine metabolism drives T-cell exhaustion in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Commun. 12:14552021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Simile MM, Peitta G, Tomasi ML, Brozzetti
S, Feo CF, Porcu A, Cigliano A, Calvisi DF, Feo F and Pascale RM:
MicroRNA-203 impacts on the growth, aggressiveness and prognosis of
hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting MAT2A and MAT2B genes.
Oncotarget. 10:2835–2854. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Li JT, Yang H, Lei MZ, Zhu WP, Su Y, Li
KY, Zhu WY, Wang J, Zhang L, Qu J, et al: Dietary folate drives
methionine metabolism to promote cancer development by stabilizing
MAT IIA. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 7:1922022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Chaturvedi S, Hoffman RM and Bertino JR:
Exploiting methionine restriction for cancer treatment. Biochem
Pharmacol. 154:170–173. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Kawaguchi K, Han Q, Li S, Tan Y, Igarashi
K, Miyake K, Kiyuna T, Miyake M, Chemielwski B, Nelson SD, et al:
Intra-tumor L-methionine level highly correlates with tumor size in
both pancreatic cancer and melanoma patient-derived orthotopic
xenograft (PDOX) nude-mouse models. Oncotarget. 9:11119–11125.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Wang Z, Yip LY, Lee JHJ, Wu Z, Chew HY,
Chong PKW, Teo CC, Ang HY, Peh KLE, Yuan J, et al: Methionine is a
metabolic dependency of tumor-initiating cells. Nat Med.
25:825–837. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Yang C, Zhang H, Zhang L, Zhu AX, Bernards
R, Qin W and Wang C: Evolving therapeutic landscape of advanced
hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol.
20:203–222. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Todisco S, Convertini P, Iacobazzi V and
Infantino V: TCA cycle rewiring as emerging metabolic signature of
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancers (Basel). 12:682019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Wang H, Zhou Y, Xu H, Wang X, Zhang Y,
Shang R, O'Farrell M, Roessler S, Sticht C, Stahl A, et al:
Therapeutic efficacy of FASN inhibition in preclinical models of
HCC. Hepatology. 76:951–966. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Jin H, Wang S, Zaal EA, Wang C, Wu H,
Bosma A, Jochems F, Isima N, Jin G, Lieftink C, et al: A powerful
drug combination strategy targeting glutamine addiction for the
treatment of human liver cancer. Elife. 9:e567492020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Hay N: Reprogramming glucose metabolism in
cancer: can it be exploited for cancer therapy? Nat Rev Cancer.
16:635–649. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Raez LE, Papadopoulos K, Ricart AD,
Chiorean EG, Dipaola RS, Stein MN, Rocha Lima CM, Schlesselman JJ,
Tolba K, Langmuir VK, et al: A phase I dose-escalation trial of
2-deoxy-D-glucose alone or combined with docetaxel in patients with
advanced solid tumors. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 71:523–530.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Reyes R, Wani NA, Ghoshal K, Jacob ST and
Motiwala T: Sorafenib and 2-Deoxyglucose synergistically inhibit
proliferation of both sorafenib-sensitive and -resistant HCC cells
by inhibiting ATP production. Gene Expr. 17:129–140. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|