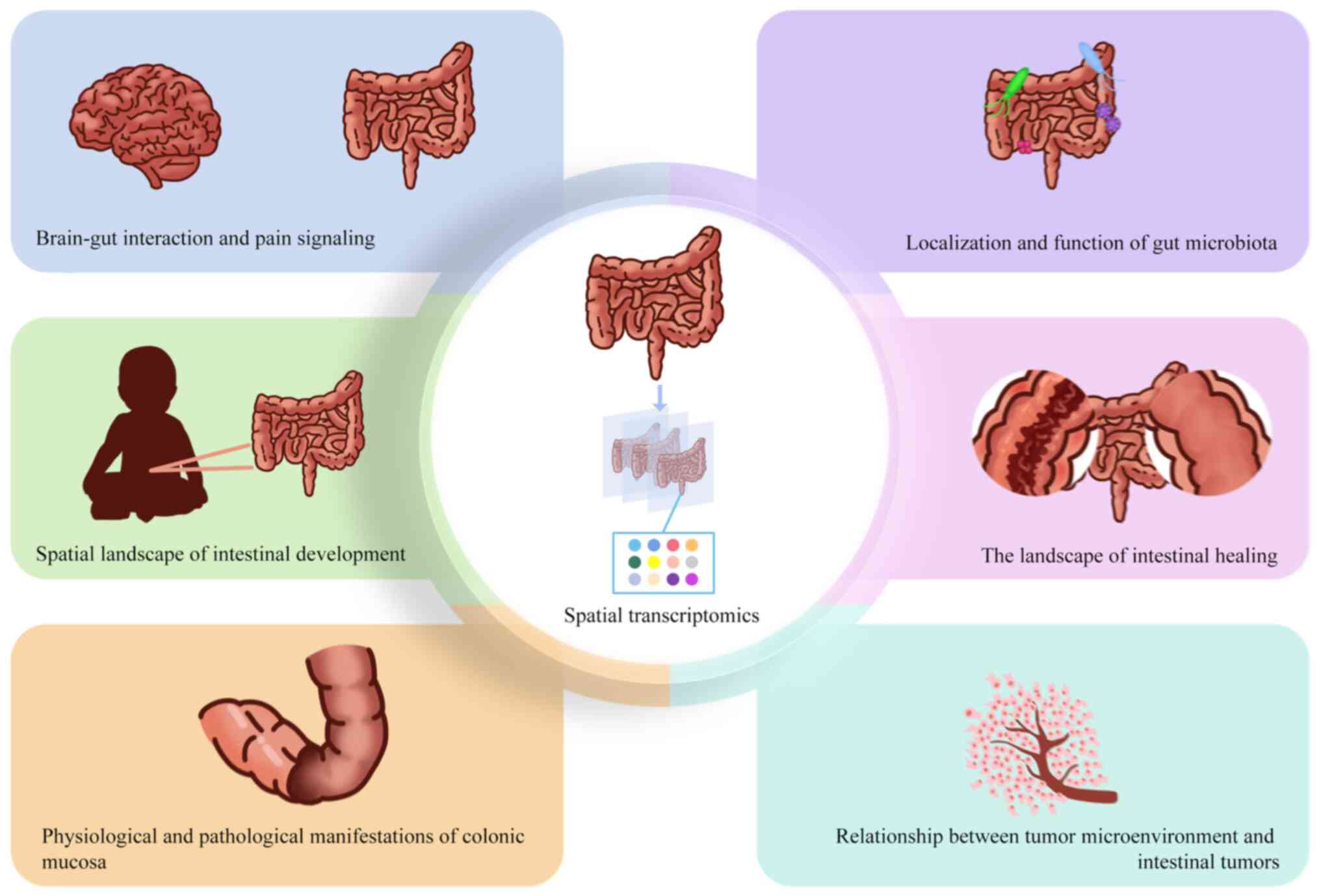
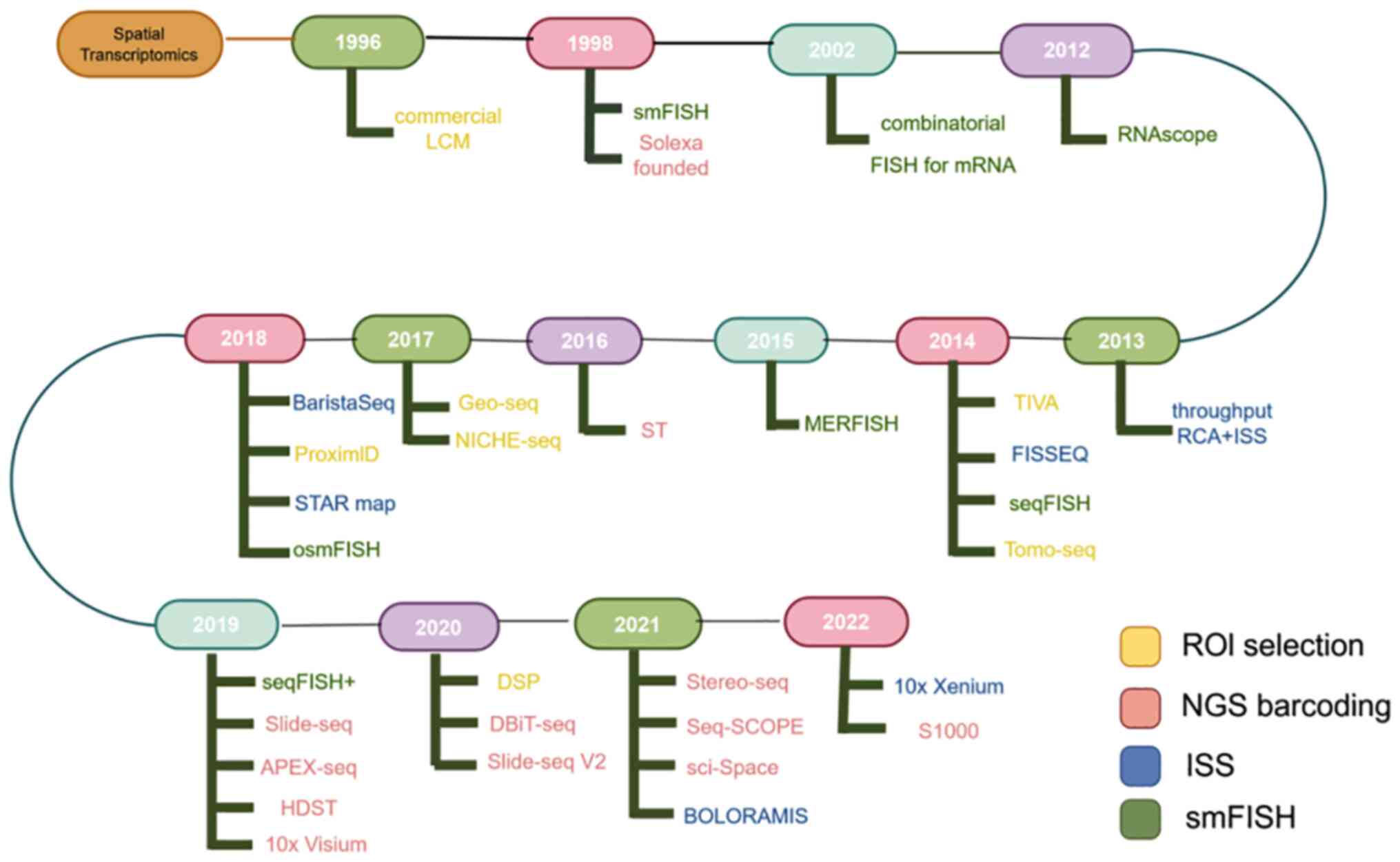
|
1
|
Caruso R, Lo BC and Núñez G:
Host-microbiota interactions in inflammatory bowel disease. Nat Rev
Immunol. 20:411–426. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Round JL and Mazmanian SK: The gut
microbiota shapes intestinal immune responses during health and
disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 9:313–323. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sardinha-Silva A, Alves-Ferreira EVC and
Grigg ME: Intestinal immune responses to commensal and pathogenic
protozoa. Front Immunol. 13:9637232022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Longstreth GF, Thompson WG, Chey WD,
Houghton LA, Mearin F and Spiller RC: Functional bowel disorders.
Gastroenterology. 130:1480–1491. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mayer EA, Ryu HJ and Bhatt RR: The
neurobiology of irritable bowel syndrome. Mol Psychiatry.
28:1451–1465. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Flynn S and Eisenstein S: Inflammatory
bowel disease presentation and diagnosis. Surg Clin North Am.
99:1051–1062. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bonetto S, Fagoonee S, Battaglia E,
Grassini M, Saracco GM and Pellicano R: Recent advances in the
treatment of irritable bowel syndrome. Pol Arch Intern Med.
131:709–715. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Saha L: Irritable bowel syndrome:
Pathogenesis, diagnosis, treatment, and evidence-based medicine.
World J Gastroenterol. 20:6759–6773. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Singh N and Bernstein CN: Environmental
risk factors for inflammatory bowel disease. United European
Gastroenterol J. 10:1047–1053. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Rosen MJ, Dhawan A and Saeed SA:
Inflammatory bowel disease in children and adolescents. JAMA
Pediatr. 169:1053–1060. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang YZ and Li YY: Inflammatory bowel
disease: Pathogenesis. World J Gastroenterol. 20:91–99. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Neurath MF: IL-23 in inflammatory bowel
diseases and colon cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 45:1–8.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Nadeem MS, Kumar V, Al-Abbasi FA, Kamal MA
and Anwar F: Risk of colorectal cancer in inflammatory bowel
diseases. Semin Cancer Biol. 64:51–60. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Brackmann S, Andersen SN, Aamodt G,
Langmark F, Clausen OPF, Aadland E, Fausa O, Rydning A and Vatn MH:
Relationship between clinical parameters and the colitis-colorectal
cancer interval in a cohort of patients with colorectal cancer in
inflammatory bowel disease. Scand J Gastroenterol. 44:46–55. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Borowitz SM: The epidemiology of
inflammatory bowel disease: Clues to pathogenesis? Front Pediatr.
10:11037132023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kaplan GG: The global burden of IBD: From
2015 to 2025. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 12:720–727. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zheng HB, de la Morena MT and Suskind DL:
The growing need to understand very early onset inflammatory bowel
disease. Front Immunol. 12:6751862021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Taylor S and Lobo AJ: Diagnosis and
treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. Practitioner. 260:19–23.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Chachu KA and Osterman MT: How to diagnose
and treat IBD mimics in the refractory IBD patient who does not
have IBD. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 22:1262–1274. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Parkin J and Cohen B: An overview of the
immune system. Lancet. 357:1777–1789. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kayama H, Okumura R and Takeda K:
Interaction between the microbiota, epithelia, and immune cells in
the intestine. Annu Rev Immunol. 38:23–48. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Groschwitz KR and Hogan SP: Intestinal
barrier function: Molecular regulation and disease pathogenesis. J
Allergy Clin Immunol. 124:3–22. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wu S, Yang L, Fu Y, Liao Z, Cai D and Liu
Z: Intestinal barrier function and neurodegenerative disease. CNS
Neurol Disord Drug Targets. Nov 24–2023.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
24
|
Wu Y, Tang L, Wang B, Sun Q, Zhao P and Li
W: The role of autophagy in maintaining intestinal mucosal barrier.
J Cell Physiol. 234:19406–19419. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ding JH, Jin Z, Yang XX, Lou J, Shan WX,
Hu YX, Du Q, Liao QS, Xie R and Xu JY: Role of gut microbiota via
the gut-liver-brain axis in digestive diseases. World J
Gastroenterol. 26:6141–6162. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Rutsch A, Kantsjö JB and Ronchi F: The
gut-brain axis: How microbiota and host inflammasome influence
brain physiology and pathology. Front Immunol. 11:6041792020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Integrative HMP (iHMP) Research Network
Consortium, . The integrative human microbiome project. Nature.
569:641–648. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gueimonde M and Collado MC: Metagenomics
and probiotics. Clin Microbiol Infect. 18 (Suppl 4):S32–S34. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Adak A and Khan MR: An insight into gut
microbiota and its functionalities. Cell Mol Life Sci. 76:473–493.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Patterson E, Ryan PM, Cryan JF, Dinan TG,
Ross RP, Fitzgerald GF and Stanton C: Gut microbiota, obesity and
diabetes. Postgrad Med J. 92:286–300. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Liu X, Chen Y, Zhang S and Dong L: Gut
microbiota-mediated immunomodulation in tumor. J Exp Clin Cancer
Res. 40:2212021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Qin J, Li R, Raes J, Arumugam M, Burgdorf
KS, Manichanh C, Nielsen T, Pons N, Levenez F, Yamada T, et al: A
human gut microbial gene catalogue established by metagenomic
sequencing. Nature. 464:59–65. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Marx V: Method of the year: Spatially
resolved transcriptomics. Nat Methods. 18:9–14. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ståhl PL, Salmén F, Vickovic S, Lundmark
A, Navarro JF, Magnusson J, Giacomello S, Asp M, Westholm JO, Huss
M, et al: Visualization and analysis of gene expression in tissue
sections by spatial transcriptomics. Science. 353:78–82. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang Y, Liu B, Zhao G, Lee Y, Buzdin A, Mu
X, Zhao J, Chen H and Li X: Spatial transcriptomics: Technologies,
applications and experimental considerations. Genomics.
115:1106712023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Shah S, Lubeck E, Zhou W and Cai L: In
situ transcription profiling of single cells reveals spatial
organization of cells in the mouse hippocampus. Neuron. 92:342–357.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lee JH, Daugharthy ER, Scheiman J, Kalhor
R, Yang JL, Ferrante TC, Terry R, Jeanty SS, Li C, Amamoto R, et
al: Highly multiplexed subcellular RNA sequencing in situ. Science.
343:1360–1363. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wang X, Allen WE, Wright MA, Sylwestrak
EL, Samusik N, Vesuna S, Evans K, Liu C, Ramakrishnan C, Liu J, et
al: Three-dimensional intact-tissue sequencing of single-cell
transcriptional states. Science. 361:eaat56912018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Asp M, Bergenstråhle J and Lundeberg J:
Spatially Resolved transcriptomes-Next generation tools for tissue
exploration. Bioessays. 42:e19002212020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Shi Y, Wu X, Zhou J, Cui W, Wang J, Hu Q,
Zhang S, Han L, Zhou M, Luo J, et al: Single-nucleus RNA sequencing
reveals that decorin expression in the amygdala regulates
perineuronal nets expression and fear conditioning response after
traumatic brain injury. Adv Sci (Weinh). 9:e21041122022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Li J, Wu C, Hu H, Qin G, Wu X, Bai F,
Zhang J, Cai Y, Huang Y, Wang C, et al: Remodeling of the immune
and stromal cell compartment by PD-1 blockade in mismatch
repair-deficient colorectal cancer. Cancer Cell. 41:1152–1169.e7.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Moses L and Pachter L: Museum of spatial
transcriptomics. Nat Methods. 19:534–546. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Chen KH, Boettiger AN, Moffitt JR, Wang S
and Zhuang X: RNA imaging. Spatially resolved, highly multiplexed
RNA profiling in single cells. Science. 348:aaa60902015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Schena M, Shalon D, Davis RW and Brown PO:
Quantitative monitoring of gene expression patterns with a
complementary DNA microarray. Science. 270:467–470. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Luo L, Salunga RC, Guo H, Bittner A, Joy
KC, Galindo JE, Xiao H, Rogers KE, Wan JS, Jackson MR and Erlander
MG: Gene expression profiles of laser-captured adjacent neuronal
subtypes. Nat Med. 5:117–122. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Bhatia HS, Brunner AD, Öztürk F, Kapoor S,
Rong Z, Mai H, Thielert M, Ali M, Al-Maskari R, Paetzold JC, et al:
Spatial proteomics in three-dimensional intact specimens. Cell.
185:5040–5058.e19. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Alfieri CM, Mattinzoli D, Ikehata M,
Cresseri D, Moroni G, Vaira V, Ferri G, Ferrero S and Messa P:
Laser capture microdissection on formalin-fixed and
paraffin-embedded renal transplanted biopsies: Technical
perspectives for clinical practice application. Exp Mol Pathol.
116:1045162020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Achanta S, Gorky J, Leung C, Moss A,
Robbins S, Eisenman L, Chen J, Tappan S, Heal M, Farahani N, et al:
A comprehensive integrated anatomical and molecular atlas of rat
intrinsic cardiac nervous system. iScience. 23:1011402020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Zhao T, Chiang ZD, Morriss JW, LaFave LM,
Murray EM, Del Priore I, Meli K, Lareau CA, Nadaf NM, Li J, et al:
Spatial genomics enables multi-modal study of clonal heterogeneity
in tissues. Nature. 601:85–91. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Liao J, Lu X, Shao X, Zhu L and Fan X:
Uncovering an organ's molecular architecture at single-cell
resolution by spatially resolved transcriptomics. Trends
Biotechnol. 39:43–58. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Satija R, Farrell JA, Gennert D, Schier AF
and Regev A: Spatial reconstruction of single-cell gene expression
data. Nat Biotechnol. 33:495–502. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Sun YM and Chen YQ: Principles and
innovative technologies for decrypting noncoding RNAs: From
discovery and functional prediction to clinical application. J
Hematol Oncol. 13:1092020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Zhang L, Yu X, Zheng L, Zhang Y, Li Y,
Fang Q, Gao R, Kang B, Zhang Q, Huang JY, et al: Lineage tracking
reveals dynamic relationships of T cells in colorectal cancer.
Nature. 564:268–272. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Zhang Q, He Y, Luo N, Patel SJ, Han Y, Gao
R, Modak M, Carotta S, Haslinger C, Kind D, et al: Landscape and
dynamics of single immune cells in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell.
179:829–845.e20. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Emmert-Buck MR, Bonner RF, Smith PD,
Chuaqui RF, Zhuang Z, Goldstein SR, Weiss RA and Liotta LA: Laser
capture microdissection. Science. 274:998–1001. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Liew LC, Narsai R, Wang Y, Berkowitz O,
Whelan J and Lewsey MG: Temporal tissue-specific regulation of
transcriptomes during barley (Hordeum vulgare) seed germination.
Plant J. 101:700–715. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Shaw R, Tian X and Xu J: Single-cell
transcriptome analysis in plants: Advances and challenges. Mol
Plant. 14:115–126. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Guo W, Hu Y, Qian J, Zhu L, Cheng J, Liao
J and Fan X: Laser capture microdissection for biomedical research:
Towards high-throughput, multi-omics, and single-cell resolution. J
Genet Genomics. 50:641–651. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Nichterwitz S, Chen G, Aguila Benitez J,
Yilmaz M, Storvall H, Cao M, Sandberg R, Deng Q and Hedlund E:
Laser capture microscopy coupled with Smart-seq2 for precise
spatial transcriptomic profiling. Nat Commun. 7:121392016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Chen J, Suo S, Tam PP, Han JDJ, Peng G and
Jing N: Spatial transcriptomic analysis of cryosectioned tissue
samples with Geo-seq. Nat Protoc. 12:566–580. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Casasent AK, Schalck A, Gao R, Sei E, Long
A, Pangburn W, Casasent T, Meric-Bernstam F, Edgerton ME and Navin
NE: Multiclonal invasion in breast tumors identified by topographic
single cell sequencing. Cell. 172:205–217.e12. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Junker JP, Noël ES, Guryev V, Peterson KA,
Shah G, Huisken J, McMahon AP, Berezikov E, Bakkers J and van
Oudenaarden A: Genome-wide RNA Tomography in the zebrafish embryo.
Cell. 159:662–675. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Moffitt JR, Bambah-Mukku D, Eichhorn SW,
Vaughn E, Shekhar K, Perez JD, Rubinstein ND, Hao J, Regev A, Dulac
C and Zhuang X: Molecular, spatial, and functional single-cell
profiling of the hypothalamic preoptic region. Science.
362:eaau53242018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Xia C, Fan J, Emanuel G, Hao J and Zhuang
X: Spatial transcriptome profiling by MERFISH reveals subcellular
RNA compartmentalization and cell cycle-dependent gene expression.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 116:19490–19499. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Femino AM, Fay FS, Fogarty K and Singer
RH: Visualization of single RNA transcripts in situ. Science.
280:585–590. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Wang F, Flanagan J, Su N, Wang LC, Bui S,
Nielson A, Wu X, Vo HT, Ma XJ and Luo Y: RNAscope: A novel in situ
RNA analysis platform for formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded
tissues. J Mol Diagn. 14:22–29. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Lubeck E, Coskun AF, Zhiyentayev T, Ahmad
M and Cai L: Single-cell in situ RNA profiling by sequential
hybridization. Nat Methods. 11:360–361. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Rodriques SG, Stickels RR, Goeva A, Martin
CA, Murray E, Vanderburg CR, Welch J, Chen LM, Chen F and Macosko
EZ: Slide-seq: A scalable technology for measuring genome-wide
expression at high spatial resolution. Science. 363:1463–1467.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Fazal FM, Han S, Parker KR, Kaewsapsak P,
Xu J, Boettiger AN, Chang HY and Ting AY: Atlas of subcellular RNA
localization revealed by APEX-seq. Cell. 178:473–490.e26. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Vickovic S, Eraslan G, Salmén F,
Klughammer J, Stenbeck L, Schapiro D, Äijö T, Bonneau R,
Bergenstråhle L, Navarro JF, et al: High-definition spatial
transcriptomics for in situ tissue profiling. Nat Methods.
16:987–990. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Srivatsan SR, Regier MC, Barkan E, Franks
JM, Packer JS, Grosjean P, Duran M, Saxton S, Ladd JJ, Spielmann M,
et al: Embryo-scale, single-cell spatial transcriptomics. Science.
373:111–117. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Liu Y, Yang M, Deng Y, Su G, Enninful A,
Guo CC, Tebaldi T, Zhang D, Kim D, Bai Z, et al:
High-spatial-resolution multi-omics sequencing via deterministic
barcoding in tissue. Cell. 183:1665–1681.e18. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Su G, Qin X, Enninful A, Bai Z, Deng Y,
Liu Y and Fan R: Spatial multi-omics sequencing for fixed tissue
via DBiT-seq. STAR Protoc. 2:1005322021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Dixon EE, Wu H, Sulvarán-Guel E, Guo J and
Humphreys BD: Spatially resolved transcriptomics and the kidney:
Many opportunities. Kidney Int. 102:482–491. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Chen A, Liao S, Cheng M, Ma K, Wu L, Lai
Y, Qiu X, Yang J, Xu J, Hao S, et al: Spatiotemporal transcriptomic
atlas of mouse organogenesis using DNA nanoball-patterned arrays.
Cell. 185:1777–1792.e21. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Cho CS, Xi J, Si Y, Park SR, Hsu JE, Kim
M, Jun G, Kang HM and Lee JH: Microscopic examination of spatial
transcriptome using Seq-Scope. Cell. 184:3559–3572.e22. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Levsky JM, Shenoy SM, Pezo RC and Singer
RH: Single-cell gene expression profiling. Science. 297:836–840.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Lubeck E and Cai L: Single-cell systems
biology by super- resolution imaging and combinatorial labeling.
Nat Methods. 9:743–748. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Ke R, Mignardi M, Pacureanu A, Svedlund J,
Botling J, Wählby C and Nilsson M: In situ sequencing for RNA
analysis in preserved tissue and cells. Nat Methods. 10:857–860.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Lee JH, Daugharthy ER, Scheiman J, Kalhor
R, Ferrante TC, Terry R, Turczyk BM, Yang JL, Lee HS, Aach J, et
al: Fluorescent in situ sequencing (FISSEQ) of RNA for gene
expression profiling in intact cells and tissues. Nat Protoc.
10:442–458. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Olin A, Henckel E, Chen Y, Lakshmikanth T,
Pou C, Mikes J, Gustafsson A, Bernhardsson AK, Zhang C, Bohlin K
and Brodin P: Stereotypic immune system development in newborn
children. Cell. 174:1277–1292.e14. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Soderholm AT and Pedicord VA: Intestinal
epithelial cells: At the interface of the microbiota and mucosal
immunity. Immunology. 158:267–280. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Schreurs RRCE, Baumdick ME, Sagebiel AF,
Kaufmann M, Mokry M, Klarenbeek PL, Schaltenberg N, Steinert FL,
van Rijn JM, Drewniak A, et al: Human fetal
TNF-α-cytokine-producing CD4+ effector memory T cells
promote intestinal development and mediate inflammation early in
life. Immunity. 50:462–476.e8. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Olsen TK and Baryawno N: Introduction to
single-cell RNA sequencing. Curr Protoc Mol Biol. 122:e572018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Rodaway A and Patient R: Mesendoderm. An
ancient germ layer? Cell. 105:169–172. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Zorn AM and Wells JM: Molecular basis of
vertebrate endoderm development. Int Rev Cytol. 259:49–111. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Zorn AM and Wells JM: Vertebrate endoderm
development and organ formation. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol.
25:221–251. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Kimelman D and Griffin KJ: Vertebrate
mesendoderm induction and patterning. Curr Opin Genet Dev.
10:350–356. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Spence JR, Lauf R and Shroyer NF:
Vertebrate intestinal endoderm development. Dev Dyn. 240:501–520.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Que J, Okubo T, Goldenring JR, Nam KT,
Kurotani R, Morrisey EE, Taranova O, Pevny LH and Hogan BL:
Multiple dose-dependent roles for Sox2 in the patterning and
differentiation of anterior foregut endoderm. Development.
134:2521–2531. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Sherwood RI, Chen TYA and Melton DA:
Transcriptional dynamics of endodermal organ formation. Dev Dyn.
238:29–42. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Walton KD, Whidden M, Kolterud Å, Shoffner
SK, Czerwinski MJ, Kushwaha J, Parmar N, Chandhrasekhar D, Freddo
AM, Schnell S and Gumucio DL: Villification in the mouse: Bmp
signals control intestinal villus patterning. Development.
143:427–436. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Grey RD: Morphogenesis of intestinal
villi. I. Scanning electron microscopy of the duodenal epithelium
of the developing chick embryo. J Morphol. 137:193–213. 1972.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Fawkner-Corbett D, Antanaviciute A, Parikh
K, Jagielowicz M, Gerós AS, Gupta T, Ashley N, Khamis D, Fowler D,
Morrissey E, et al: Spatiotemporal analysis of human intestinal
development at single-cell resolution. Cell. 184:810–826.e23. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Martin JC, Chang C, Boschetti G, Ungaro R,
Giri M, Grout JA, Gettler K, Chuang LS, Nayar S, Greenstein AJ, et
al: Single-cell analysis of Crohn's disease lesions identifies a
pathogenic cellular module associated with resistance to anti-TNF
therapy. Cell. 178:1493–1508.e20. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Parikh K, Antanaviciute A, Fawkner-Corbett
D, Jagielowicz M, Aulicino A, Lagerholm C, Davis S, Kinchen J, Chen
HH, Alham NK, et al: Colonic epithelial cell diversity in health
and inflammatory bowel disease. Nature. 567:49–55. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Smillie CS, Biton M, Ordovas-Montanes J,
Sullivan KM, Burgin G, Graham DB, Herbst RH, Rogel N, Slyper M,
Waldman J, et al: Intra- and inter-cellular rewiring of the human
colon during ulcerative colitis. Cell. 178:714–730.e22. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Fenderico N, van Scherpenzeel RC, Goldflam
M, Proverbio D, Jordens I, Kralj T, Stryeck S, Bass TZ, Hermans G,
Ullman C, et al: Anti-LRP5/6 VHHs promote differentiation of
Wnt-hypersensitive intestinal stem cells. Nat Commun. 10:3652019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Kinchen J, Chen HH, Parikh K,
Antanaviciute A, Jagielowicz M, Fawkner-Corbett D, Ashley N, Cubitt
L, Mellado-Gomez E, Attar M, et al: Structural remodeling of the
human colonic mesenchyme in inflammatory bowel disease. Cell.
175:372–386.e17. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Powell DW, Pinchuk IV, Saada JI, Chen X
and Mifflin RC: Mesenchymal cells of the intestinal lamina propria.
Annu Rev Physiol. 73:213–237. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
McCarthy N, Manieri E, Storm EE,
Saadatpour A, Luoma AM, Kapoor VN, Madha S, Gaynor LT, Cox C,
Keerthivasan S, et al: Distinct mesenchymal cell populations
generate the essential intestinal BMP signaling gradient. Cell Stem
Cell. 26:391–402.e5. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Degirmenci B, Valenta T, Dimitrieva S,
Hausmann G and Basler K: GLI1-expressing mesenchymal cells form the
essential Wnt-secreting niche for colon stem cells. Nature.
558:449–453. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
van Es JH, Sato T, van de Wetering M,
Lyubimova A, Yee Nee AN, Gregorieff A, Sasaki N, Zeinstra L, van
den Born M, Korving J, et al: Dll1+ secretory progenitor cells
revert to stem cells upon crypt damage. Nat Cell Biol.
14:1099–1104. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
van de Pavert SA and Mebius RE: New
insights into the development of lymphoid tissues. Nat Rev Immunol.
10:664–674. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Scheich S, Chen J, Liu J, Schnütgen F,
Enssle JC, Ceribelli M, Thomas CJ, Choi J, Morris V, Hsiao T, et
al: Targeting N-linked glycosylation for the therapy of aggressive
lymphomas. Cancer Discov. 13:1862–1883. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Guan Q: A comprehensive review and update
on the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease. J Immunol Res.
2019:72472382019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Tang F, Barbacioru C, Wang Y, Nordman E,
Lee C, Xu N, Wang X, Bodeau J, Tuch BB, Siddiqui A, et al: mRNA-Seq
whole-transcriptome analysis of a single cell. Nat Methods.
6:377–382. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Yu X, Abbas-Aghababazadeh F, Chen YA and
Fridley BL: Statistical and bioinformatics analysis of data from
bulk and single-cell RNA sequencing experiments. Methods Mol Biol.
2194:143–175. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Nath A and Bild AH: Leveraging single-cell
approaches in cancer precision medicine. Trends Cancer. 7:359–372.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Czarnewski P, Parigi SM, Sorini C, Diaz
OE, Das S, Gagliani N and Villablanca EJ: Conserved transcriptomic
profile between mouse and human colitis allows unsupervised patient
stratification. Nat Commun. 10:28922019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Parigi SM, Larsson L, Das S, Ramirez
Flores RO, Frede A, Tripathi KP, Diaz OE, Selin K, Morales RA, Luo
X, et al: The spatial transcriptomic landscape of the healing mouse
intestine following damage. Nat Commun. 13:8282022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Ayyaz A, Kumar S, Sangiorgi B, Ghoshal B,
Gosio J, Ouladan S, Fink M, Barutcu S, Trcka D, Shen J, et al:
Single-cell transcriptomes of the regenerating intestine reveal a
revival stem cell. Nature. 569:121–125. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Smythies LE, Sellers M, Clements RH,
Mosteller-Barnum M, Meng G, Benjamin WH, Orenstein JM and Smith PD:
Human intestinal macrophages display profound inflammatory anergy
despite avid phagocytic and bacteriocidal activity. J Clin Invest.
115:66–75. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Martinez FO and Gordon S: The M1 and M2
paradigm of macrophage activation: Time for reassessment.
F1000Prime Rep. 6:132014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Garrido-Trigo A, Corraliza AM, Veny M,
Dotti I, Melón-Ardanaz E, Rill A, Crowell HL, Corbí Á, Gudiño V,
Esteller M, et al: Macrophage and neutrophil heterogeneity at
single-cell spatial resolution in human inflammatory bowel disease.
Nat Commun. 14:45062023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Schoeler M and Caesar R: Dietary lipids,
gut microbiota and lipid metabolism. Rev Endocr Metab Disord.
20:461–472. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Milani C, Duranti S, Bottacini F, Casey E,
Turroni F, Mahony J, Belzer C, Delgado Palacio S, Arboleya Montes
S, Mancabelli L, et al: The first microbial colonizers of the human
gut: Composition, activities, and health implications of the infant
gut microbiota. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 81:e00036–17. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Human Microbiome Project Consortium, .
Structure, function and diversity of the healthy human microbiome.
Nature. 486:207–214. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Lloyd-Price J, Arze C, Ananthakrishnan AN,
Schirmer M, Avila-Pacheco J, Poon TW, Andrews E, Ajami NJ, Bonham
KS, Brislawn CJ, et al: Multi-omics of the gut microbial ecosystem
in inflammatory bowel diseases. Nature. 569:655–662. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Huang H, Ren Z, Gao X, Hu X, Zhou Y, Jiang
J, Lu H, Yin S, Ji J, Zhou L and Zheng S: Integrated analysis of
microbiome and host transcriptome reveals correlations between gut
microbiota and clinical outcomes in HBV-related hepatocellular
carcinoma. Genome Med. 12:1022020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Zhang SL, Cheng LS, Zhang ZY, Sun HT and
Li JJ: Untangling determinants of gut microbiota and tumor
immunologic status through a multi-omics approach in colorectal
cancer. Pharmacol Res. 188:1066332023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Pereira FC and Berry D: Microbial nutrient
niches in the gut. Environ Microbiol. 19:1366–1378. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Kim HJ, Boedicker JQ, Choi JW and
Ismagilov RF: Defined spatial structure stabilizes a synthetic
multispecies bacterial community. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
105:18188–18193. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Rausch P, Basic M, Batra A, Bischoff SC,
Blaut M, Clavel T, Gläsner J, Gopalakrishnan S, Grassl GA, Günther
C, et al: Analysis of factors contributing to variation in the
C57BL/6J fecal microbiota across German animal facilities. Int J
Med Microbiol. 306:343–355. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Seekatz AM, Schnizlein MK, Koenigsknecht
MJ, Baker JR, Hasler WL, Bleske BE, Young VB and Sun D: Spatial and
temporal analysis of the stomach and small-intestinal microbiota in
fasted healthy humans. mSphere. 4:e00126–19. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Sheth RU, Li M, Jiang W, Sims PA, Leong KW
and Wang HH: Spatial metagenomic characterization of microbial
biogeography in the gut. Nat Biotechnol. 37:877–883. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Choi CH and Chang SK: Role of small
intestinal bacterial overgrowth in functional gastrointestinal
disorders. J Neurogastroenterol Motil. 22:3–5. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Evans DF, Pye G, Bramley R, Clark AG,
Dyson TJ and Hardcastle JD: Measurement of gastrointestinal pH
profiles in normal ambulant human subjects. Gut. 29:1035–1041.
1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Macfarlane GT, Gibson GR and Cummings JH:
Comparison of fermentation reactions in different regions of the
human colon. J Appl Bacteriol. 72:57–64. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
Birchenough GM, Johansson ME, Gustafsson
JK, Bergström JH and Hansson GC: New developments in goblet cell
mucus secretion and function. Mucosal Immunol. 8:712–719. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Kotarsky K, Sitnik KM, Stenstad H,
Kotarsky H, Schmidtchen A, Koslowski M, Wehkamp J and Agace WW: A
novel role for constitutively expressed epithelial-derived
chemokines as antibacterial peptides in the intestinal mucosa.
Mucosal Immunol. 3:40–48. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
McCallum G and Tropini C: The gut
microbiota and its biogeography. Nat Rev Microbiol. 22:105–118.
2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Cremer J, Arnoldini M and Hwa T: Effect of
water flow and chemical environment on microbiota growth and
composition in the human colon. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
114:6438–6443. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Cremer J, Segota I, Yang CY, Arnoldini M,
Sauls JT, Zhang Z, Gutierrez E, Groisman A and Hwa T: Effect of
flow and peristaltic mixing on bacterial growth in a gut-like
channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 113:11414–11419. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Nagara Y, Takada T, Nagata Y, Kado S and
Kushiro A: Microscale spatial analysis provides evidence for
adhesive monopolization of dietary nutrients by specific intestinal
bacteria. PLoS One. 12:e01754972017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Walker AW, Duncan SH, Harmsen HJ, Holtrop
G, Welling GW and Flint HJ: The species composition of the human
intestinal microbiota differs between particle-associated and
liquid phase communities. Environ Microbiol. 10:3275–3283. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Leitch ECMW, Walker AW, Duncan SH, Holtrop
G and Flint HJ: Selective colonization of insoluble substrates by
human faecal bacteria. Environ Microbiol. 9:667–679. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Sobhani I, Bergsten E, Couffin S, Amiot A,
Nebbad B, Barau C, de'Angelis N, Rabot S, Canoui-Poitrine F,
Mestivier D, et al: Colorectal cancer-associated microbiota
contributes to oncogenic epigenetic signatures. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 116:24285–24295. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
David LA, Maurice CF, Carmody RN,
Gootenberg DB, Button JE, Wolfe BE, Ling AV, Devlin AS, Varma Y,
Fischbach MA, et al: Diet rapidly and reproducibly alters the human
gut microbiome. Nature. 505:559–563. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Nguyen J, Pepin DM and Tropini C: Cause or
effect? The spatial organization of pathogens and the gut
microbiota in disease. Microbes Infect. 23:1048152021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Borghini R, Donato G, Alvaro D and
Picarelli A: New insights in IBS-like disorders: Pandora's box has
been opened; a review. Gastroenterol Hepatol Bed Bench. 10:79–89.
2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Ng QX, Soh AYS, Loke W, Lim DY and Yeo WS:
The role of inflammation in irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). J
Inflamm Res. 11:345–349. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Qiao LY and Tiwari N: Spinal
neuron-glia-immune interaction in cross-organ sensitization. Am J
Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 319:G748–G760. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
North RY, Li Y, Ray P, Rhines LD, Tatsui
CE, Rao G, Johansson CA, Zhang H, Kim YH, Zhang B, et al:
Electrophysiological and transcriptomic correlates of neuropathic
pain in human dorsal root ganglion neurons. Brain. 142:1215–1226.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Tavares-Ferreira D, Shiers S, Ray PR,
Wangzhou A, Jeevakumar V, Sankaranarayanan I, Cervantes AM, Reese
JC, Chamessian A, Copits BA, et al: Spatial transcriptomics of
dorsal root ganglia identifies molecular signatures of human
nociceptors. Sci Transl Med. 14:eabj81862022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Bonaz BL and Bernstein CN: Brain-gut
interactions in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology.
144:36–49. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Tsigos C and Chrousos GP:
Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis, neuroendocrine factors and
stress. J Psychosom Res. 53:865–871. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
Kitaoka S: Inflammation in the brain and
periphery found in animal models of depression and its behavioral
relevance. J Pharmacol Sci. 148:262–266. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
De Bellis MD, Casey BJ, Dahl RE, Birmaher
B, Williamson DE, Thomas KM, Axelson DA, Frustaci K, Boring AM,
Hall J and Ryan ND: A pilot study of amygdala volumes in pediatric
generalized anxiety disorder. Biol Psychiatry. 48:51–57. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Schienle A, Ebner F and Schäfer A:
Localized gray matter volume abnormalities in generalized anxiety
disorder. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 261:303–307. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
Qiao J, Li A, Cao C, Wang Z, Sun J and Xu
G: Aberrant functional network connectivity as a biomarker of
generalized anxiety disorder. Front Hum Neurosci. 11:6262017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Moffitt JR, Hao J, Bambah-Mukku D, Lu T,
Dulac C and Zhuang X: High-performance multiplexed fluorescence in
situ hybridization in culture and tissue with matrix imprinting and
clearing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 113:14456–14461. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Zhou X, Lu Y, Zhao F, Dong J, Ma W, Zhong
S, Wang M, Wang B, Zhao Y, Shi Y, et al: Deciphering the
spatial-temporal transcriptional landscape of human hypothalamus
development. Cell Stem Cell. 29:328–343.e5. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
154
|
Oh SW, Harris JA, Ng L, Winslow B, Cain N,
Mihalas S, Wang Q, Lau C, Kuan L, Henry AM, et al: A mesoscale
connectome of the mouse brain. Nature. 508:207–214. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Qian J, Olbrecht S, Boeckx B, Vos H, Laoui
D, Etlioglu E, Wauters E, Pomella V, Verbandt S, Busschaert P, et
al: A pan-cancer blueprint of the heterogeneous tumor
microenvironment revealed by single-cell profiling. Cell Res.
30:745–762. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
Galeano Niño JL, Wu H, LaCourse KD,
Kempchinsky AG, Baryiames A, Barber B, Futran N, Houlton J, Sather
C, Sicinska E, et al: Effect of the intratumoral microbiota on
spatial and cellular heterogeneity in cancer. Nature. 611:810–817.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
Ozato Y, Kojima Y, Kobayashi Y, Hisamatsu
Y, Toshima T, Yonemura Y, Masuda T, Kagawa K, Goto Y, Utou M, et
al: Spatial and single-cell transcriptomics decipher the cellular
environment containing HLA-G+ cancer cells and SPP1+ macrophages in
colorectal cancer. Cell Rep. 42:1119292023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
159
|
Dekker E, Tanis PJ, Vleugels JLA, Kasi PM
and Wallace MB: Colorectal cancer. Lancet. 394:1467–1480. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
160
|
Zhao W, Dai S, Yue L, Xu F, Gu J, Dai X
and Qian X: Emerging mechanisms progress of colorectal cancer liver
metastasis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 13:10815852022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
161
|
Brouwer NP, Webbink L, Haddad TS, Rutgers
N, van Vliet S, Wood CS, Jansen PW, Lafarge MW; imCMS Consortium;
de Wilt JH, ; et al: Transcriptomics and proteomics reveal distinct
biology for lymph node metastases and tumour deposits in colorectal
cancer. J Pathol. 261:401–412. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Kobayashi H, Gieniec KA, Lannagan TRM,
Wang T, Asai N, Mizutani Y, Iida T, Ando R, Thomas EM, Sakai A, et
al: The origin and contribution of cancer-associated fibroblasts in
colorectal carcinogenesis. Gastroenterology. 162:890–906. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
163
|
Peng Z, Ye M, Ding H, Feng Z and Hu K:
Spatial transcriptomics atlas reveals the crosstalk between
cancer-associated fibroblasts and tumor microenvironment components
in colorectal cancer. J Transl Med. 20:3022022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
164
|
Qi J, Sun H, Zhang Y, Wang Z, Xun Z, Li Z,
Ding X, Bao R, Hong L, Jia W, et al: Single-cell and spatial
analysis reveal interaction of FAP+ fibroblasts and
SPP1+ macrophages in colorectal cancer. Nat Commun.
13:17422022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
165
|
Valdeolivas A, Amberg B, Giroud N,
Richardson M, Gálvez EJC, Badillo S, Julien-Laferrière A, Túrós D,
Voith von Voithenberg L, Wells I, et al: Profiling the
heterogeneity of colorectal cancer consensus molecular subtypes
using spatial transcriptomics. NPJ Precis Oncol. 8:102024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
166
|
Roelands J, van der Ploeg M, Ijsselsteijn
ME, Dang H, Boonstra JJ, Hardwick JCH, Hawinkels LJAC, Morreau H
and de Miranda NFCC: Transcriptomic and immunophenotypic profiling
reveals molecular and immunological hallmarks of colorectal cancer
tumourigenesis. Gut. 72:1326–1339. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
167
|
Zwing N, Failmezger H, Ooi CH, Hibar DP,
Cañamero M, Gomes B, Gaire F and Korski K: Analysis of spatial
organization of suppressive myeloid cells and effector T cells in
colorectal cancer-A potential tool for discovering prognostic
biomarkers in clinical research. Front Immunol. 11:5502502020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
168
|
Liu HT, Chen SY, Peng LL, Zhong L, Zhou L,
Liao SQ, Chen ZJ, Wang QL, He S and Zhou ZH: Spatially resolved
transcriptomics revealed local invasion-related genes in colorectal
cancer. Front Oncol. 13:10890902023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
169
|
Manfredi S, Lepage C, Hatem C, Coatmeur O,
Faivre J and Bouvier AM: Epidemiology and management of liver
metastases from colorectal cancer. Ann Surg. 244:254–259. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
170
|
Hu Z, Ding J, Ma Z, Sun R, Seoane JA,
Scott Shaffer J, Suarez CJ, Berghoff AS, Cremolini C, Falcone A, et
al: Quantitative evidence for early metastatic seeding in
colorectal cancer. Nat Genet. 51:1113–1122. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
171
|
Wang F, Long J, Li L, Wu ZX, Da TT, Wang
XQ, Huang C, Jiang YH, Yao XQ, Ma HQ, et al: Single-cell and
spatial transcriptome analysis reveals the cellular heterogeneity
of liver metastatic colorectal cancer. Sci Adv. 9:eadf54642023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
172
|
Garbarino O, Lambroia L, Basso G, Marrella
V, Franceschini B, Soldani C, Pasqualini F, Giuliano D, Costa G,
Peano C, et al: Spatial resolution of cellular senescence dynamics
in human colorectal liver metastasis. Aging Cell. 22:e138532023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
173
|
Cheng LK, O'Grady G, Du P, Egbuji JU,
Windsor JA and Pullan AJ: Gastrointestinal system. Wiley
Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2:65–79. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
174
|
Peterson LW and Artis D: Intestinal
epithelial cells: Regulators of barrier function and immune
homeostasis. Nat Rev Immunol. 14:141–153. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
175
|
Pelka K, Hofree M, Chen JH, Sarkizova S,
Pirl JD, Jorgji V, Bejnood A, Dionne D, Ge WH, Xu KH, et al:
Spatially organized multicellular immune hubs in human colorectal
cancer. Cell. 184:4734–4752.e20. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
176
|
Frede A, Czarnewski P, Monasterio G,
Tripathi KP, Bejarano DA, Ramirez Flores RO, Sorini C, Larsson L,
Luo X, Geerlings L, et al: B cell expansion hinders the
stroma-epithelium regenerative cross talk during mucosal healing.
Immunity. 55:2336–2351.e12. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
177
|
Zhang X, Hu C, Huang C, Wei Y, Li X, Hu M,
Li H, Wu J, Czajkowsky DM, Guo Y and Shao Z: Robust Acquisition of
spatial transcriptional programs in tissues with
immunofluorescence-guided laser capture microdissection. Front Cell
Dev Biol. 10:8531882022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
178
|
Ghaddar B and De S: Reconstructing
physical cell interaction networks from single-cell data using
Neighbor-seq. Nucleic Acids Res. 50:e822022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
179
|
Zhu Z, Cai J, Hou W, Xu K, Wu X, Song Y,
Bai C, Mo YY and Zhang Z: Microbiome and spatially resolved
metabolomics analysis reveal the anticancer role of gut Akkermansia
muciniphila by crosstalk with intratumoral microbiota and
reprogramming tumoral metabolism in mice. Gut Microbes.
15:21667002023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
180
|
Sun C, Wang A, Zhou Y, Chen P, Wang X,
Huang J, Gao J, Wang X, Shu L, Lu J, et al: Spatially resolved
multi-omics highlights cell-specific metabolic remodeling and
interactions in gastric cancer. Nat Commun. 14:26922023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
181
|
Tun HM, Peng Y, Massimino L, Sin ZY,
Parigi TL, Facoetti A, Rahman S, Danese S and Ungaro F: Gut virome
in inflammatory bowel disease and beyond. Gut. 73:350–360. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
182
|
Zhao E, Stone MR, Ren X, Guenthoer J,
Smythe KS, Pulliam T, Williams SR, Uytingco CR, Taylor SEB, Nghiem
P, et al: Spatial transcriptomics at subspot resolution with
BayesSpace. Nat Biotechnol. 39:1375–1384. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
183
|
Saviano A, Henderson NC and Baumert TF:
Single-cell genomics and spatial transcriptomics: Discovery of
novel cell states and cellular interactions in liver physiology and
disease biology. J Hepatol. 73:1219–1230. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
184
|
Peterson VM, Zhang KX, Kumar N, Wong J, Li
L, Wilson DC, Moore R, McClanahan TK, Sadekova S and Klappenbach
JA: Multiplexed quantification of proteins and transcripts in
single cells. Nat Biotechnol. 35:936–939. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
185
|
Thornton CA, Mulqueen RM, Torkenczy KA,
Nishida A, Lowenstein EG, Fields AJ, Steemers FJ, Zhang W,
McConnell HL, Woltjer RL, et al: Spatially mapped single-cell
chromatin accessibility. Nat Commun. 12:12742021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
186
|
Stoeckius M, Hafemeister C, Stephenson W,
Houck-Loomis B, Chattopadhyay PK, Swerdlow H, Satija R and Smibert
P: Simultaneous epitope and transcriptome measurement in single
cells. Nat Methods. 14:865–868. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
187
|
Vickovic S, Lötstedt B, Klughammer J,
Mages S, Segerstolpe Å, Rozenblatt-Rosen O and Regev A: SM-omics is
an automated platform for high-throughput spatial multi-omics. Nat
Commun. 13:7952022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
188
|
Park HE, Jo SH, Lee RH, Macks CP, Ku T,
Park J, Lee CW, Hur JK and Sohn CH: Spatial transcriptomics:
Technical aspects of recent developments and their applications in
neuroscience and cancer research. Adv Sci (Weinh). 10:e22069392023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
189
|
Rao A, Barkley D, França GS and Yanai I:
Exploring tissue architecture using spatial transcriptomics.
Nature. 596:211–220. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
190
|
Zhang L, Chen D, Song D, Liu X, Zhang Y,
Xu X and Wang X: Clinical and translational values of spatial
transcriptomics. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 7:1112022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
191
|
Li Y, Stanojevic S and Garmire LX:
Emerging artificial intelligence applications in spatial
transcriptomics analysis. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 20:2895–2908.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
192
|
Hao M, Hua K and Zhang X: SOMDE: A
scalable method for identifying spatially variable genes with
self-organizing map. Bioinformatics. 37:4392–4398. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
193
|
Dries R, Zhu Q, Dong R, Eng CL, Li H, Liu
K, Fu Y, Zhao T, Sarkar A, Bao F, et al: Giotto: A toolbox for
integrative analysis and visualization of spatial expression data.
Genome Biol. 22:782021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|