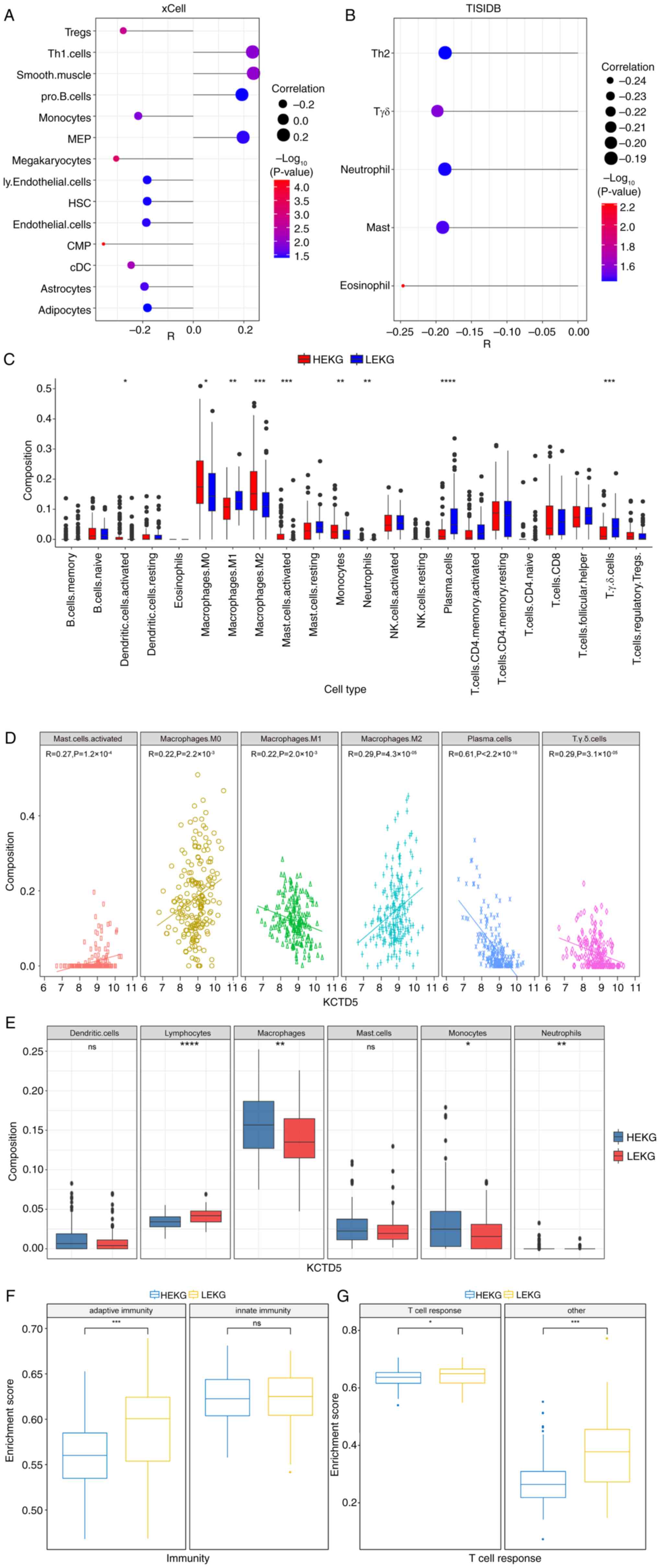
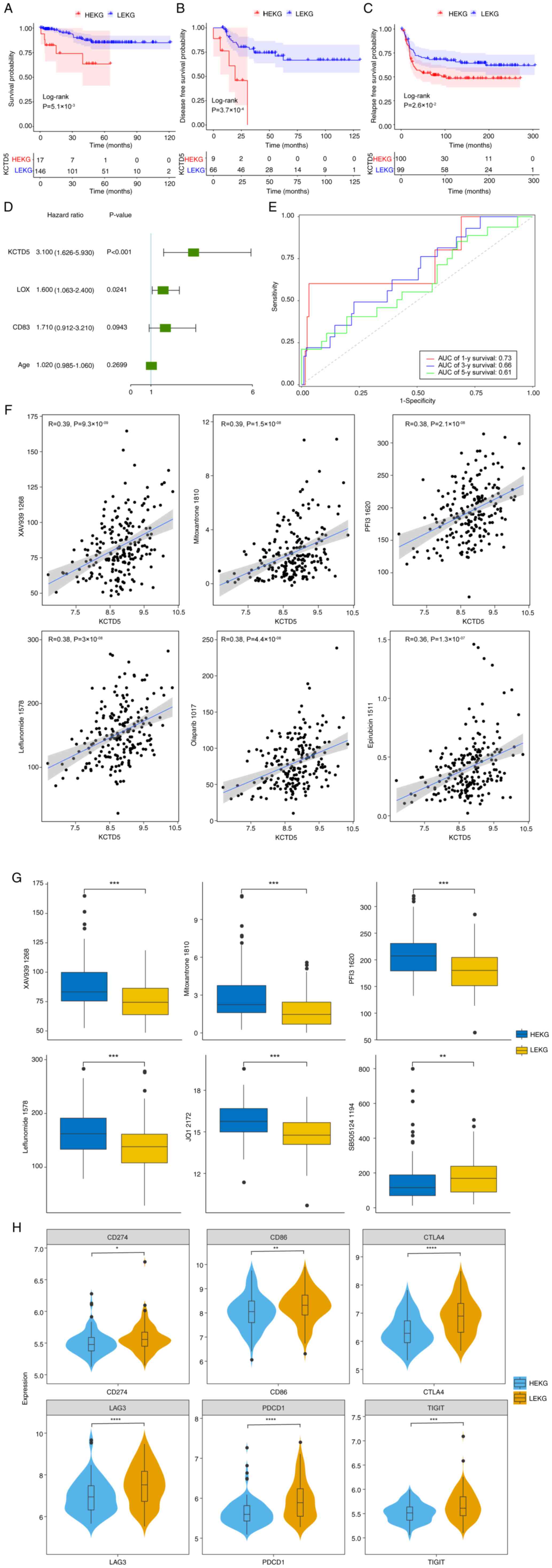
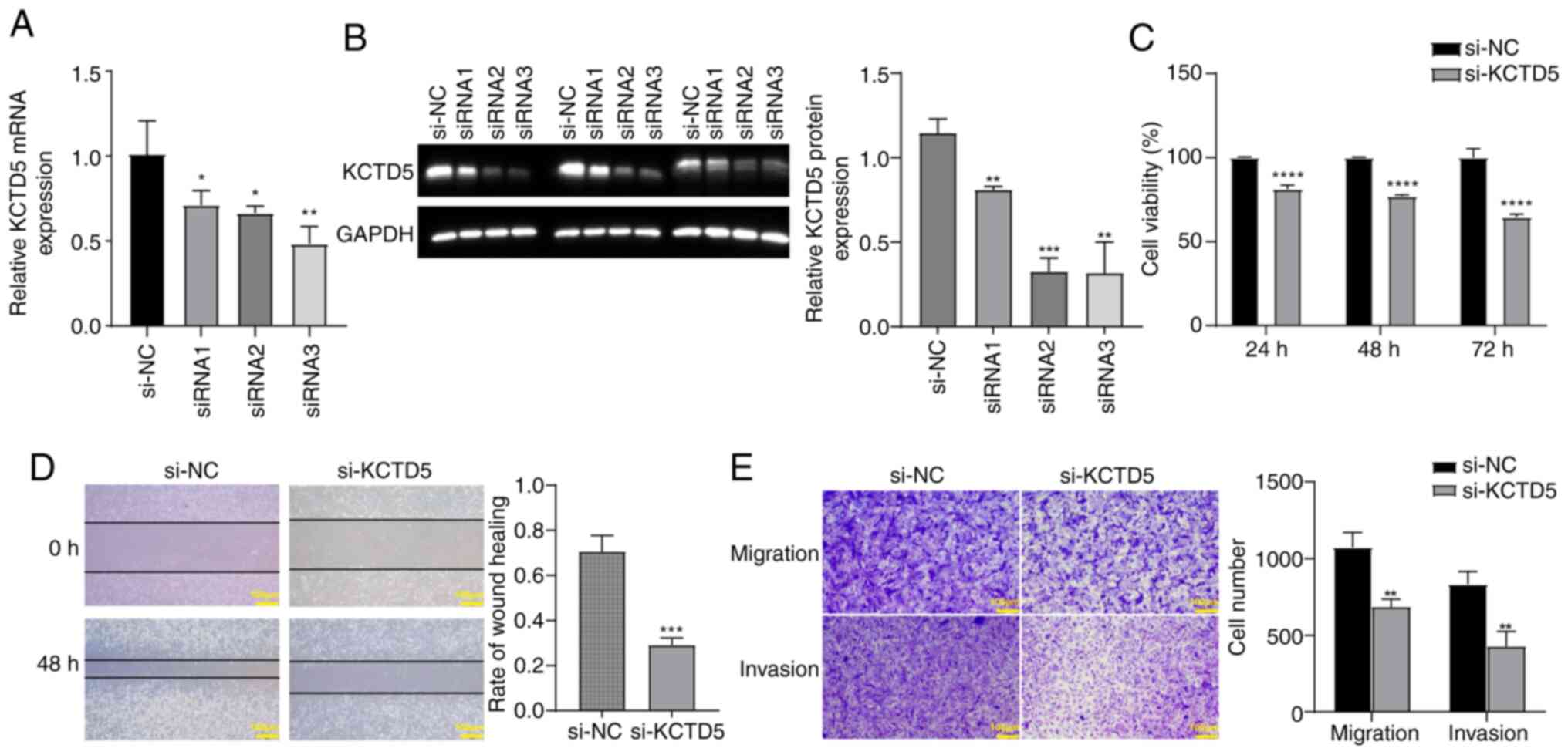
|
1
|
Oze I, Ito H, Kasugai Y, Yamaji T, Kijima
Y, Ugai T, Kasuga Y, Ouellette TK, Taniyama Y, Koyanagi YN, et al:
A personal breast cancer risk stratification model using common
variants and environmental risk factors in japanese females.
Cancers (Basel). 13:37962021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Weidle UH and Birzele F: Triple-negative
breast cancer: Identification of circRNAs with efficacy in
preclinical in vivo models. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 20:117–31.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bergin ART and Loi S: Triple-negative
breast cancer: Recent treatment advances. F1000Res. 8:F1000 Faculty
Rev. –1342. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Abdollahi A and Etemadi M: Pathological
characteristics of triple-negative breast cancer at main referral
teaching hospital, April 2014 to April 2015, Tehran, Iran. Int J
Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Res. 10:200–205. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Johnson R, Sabnis N, McConathy WJ and
Lacko AG: The potential role of nanotechnology in therapeutic
approaches for triple negative breast cancer. Pharmaceutics.
5:353–370. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Nandini D, Jennifer A and Pradip D:
Therapeutic strategies for metastatic triple-negative breast
cancers: From negative to positive. Pharmaceuticals (Basel).
14:4552021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
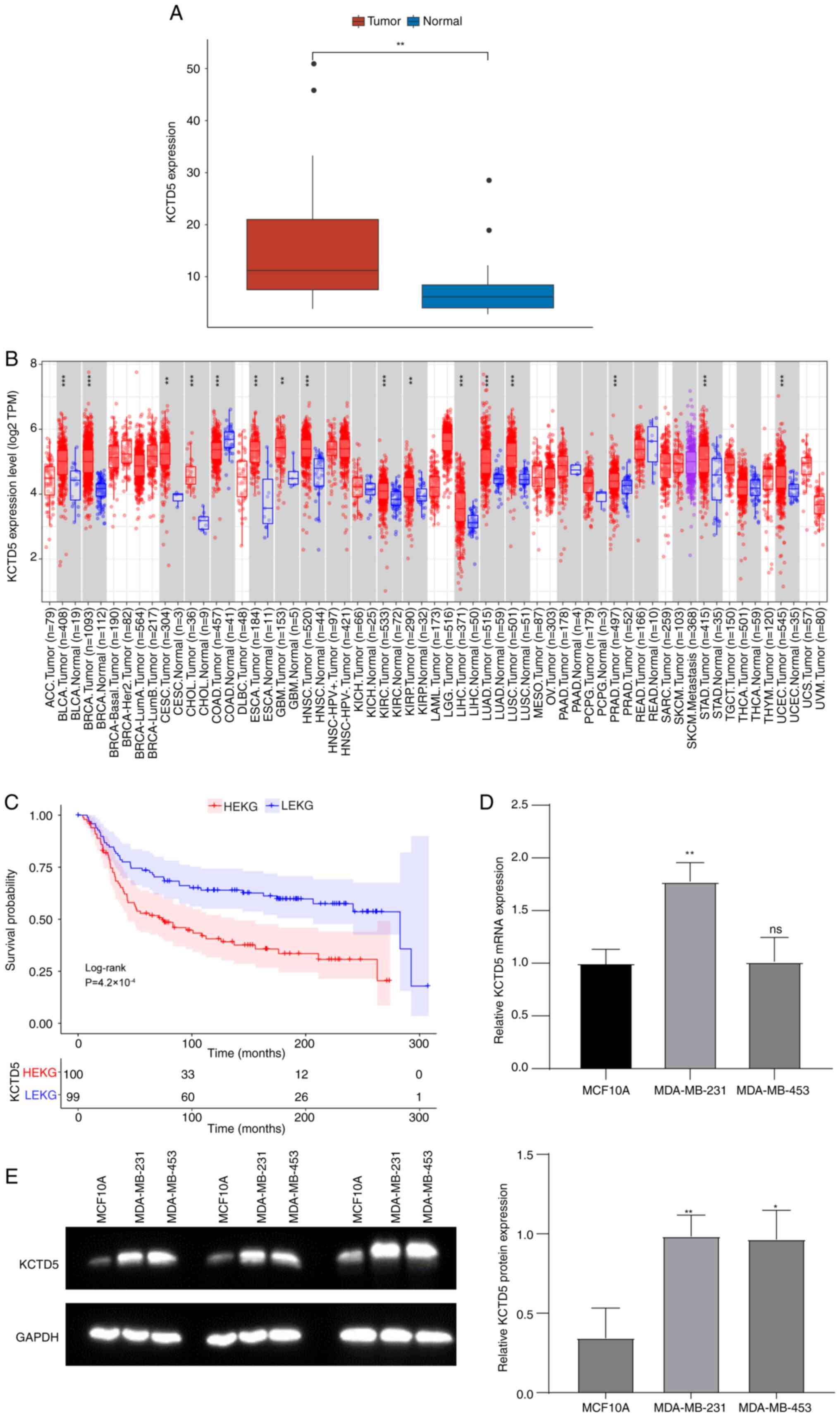
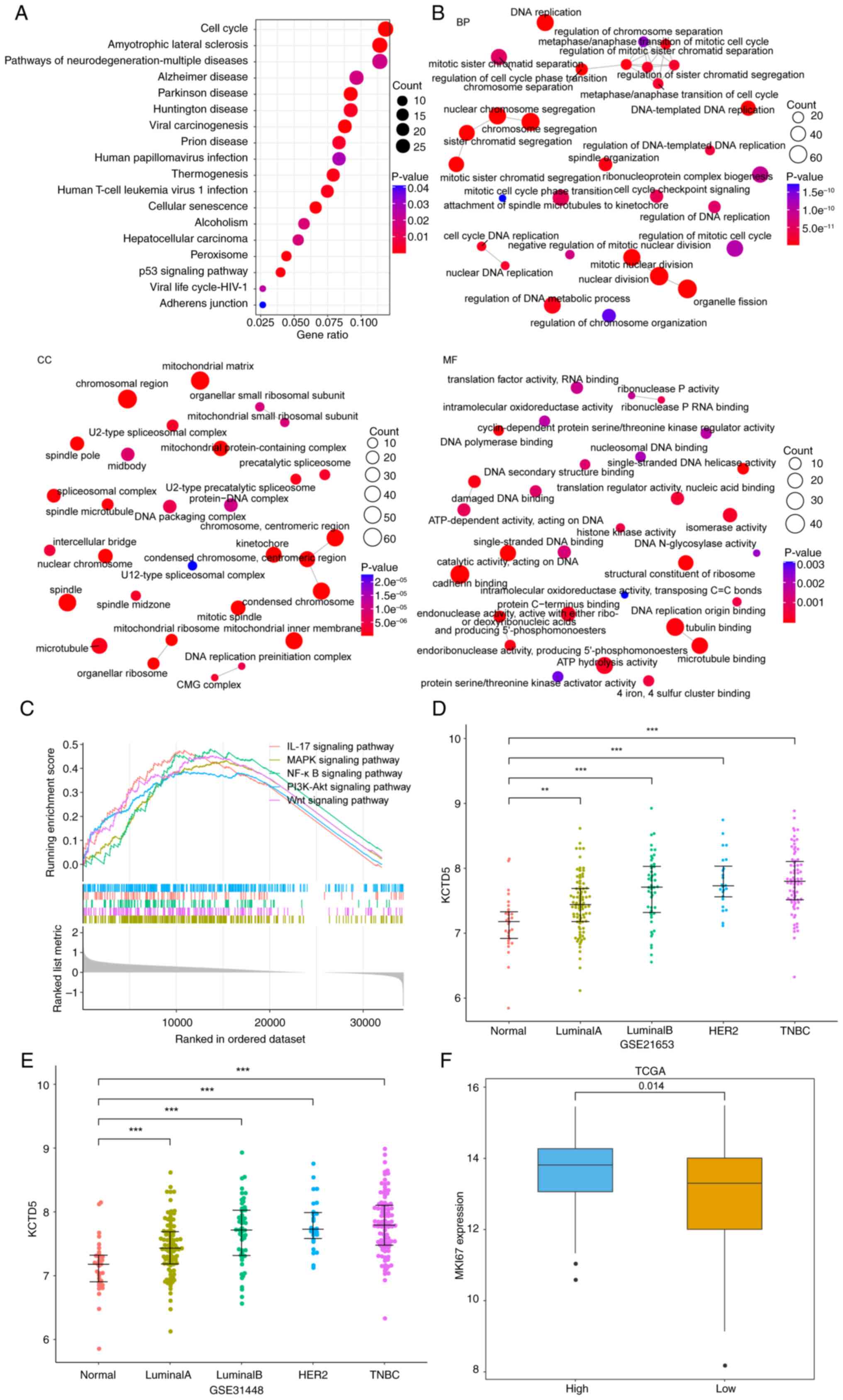
7
|
Anderson NM and Simon MC: The tumor
microenvironment. Curr Biol. 30:R921–R925. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Raskov H, Orhan A, Christensen JP and
Gögenur I: Cytotoxic CD8+ T cells in cancer and cancer
immunotherapy. Br J Cancer. 124:359–367. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Oshi M, Asaoka M, Tokumaru Y, Yan L,
Matsuyama R, Ishikawa T, Endo I and Takabe K: CD8 T cell score as a
prognostic biomarker for triple negative breast cancer. Int J Mol
Sci. 21:69682020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li X, Gruosso T, Zuo D, Omeroglu A,
Meterissian S, Guiot MC, Salazar A, Park M and Levine H:
Infiltration of CD8+ T cells into tumor cell clusters in
triple-negative breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
116:3678–3687. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Provenzano PP, Cuevas C, Chang AE, Goel
VK, Von Hoff DD and Hingorani SR: Enzymatic targeting of the stroma
ablates physical barriers to treatment of pancreatic ductal
adenocarcinoma. Cancer Cell. 21:418–429. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zboralski D, Hoehlig K, Eulberg D,
Fromming A and Vater A: Increasing tumor-infiltrating T cells
through inhibition of CXCL12 with NOX-A12 synergizes with PD-1
blockade. Cancer Immunol Res. 5:950–956. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Durgeau A, Virk Y, Corgnac S and
Mami-Chouaib F: Recent advances in targeting CD8 T-cell immunity
for more effective cancer immunotherapy. Front Immunol. 9:142018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Virassamy B, Caramia F, Savas P, Sant S,
Wang J, Christo SN, Byrne A, Clarke K, Brown E, Teo ZL, et al:
Intratumoral CD8+ T cells with a tissue-resident memory
phenotype mediate local immunity and immune checkpoint responses in
breast cancer. Cancer Cell. 41:585–601.e8. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li K, Li T, Feng Z, Huang M, Wei L, Yan Z,
Long M, Hu Q, Wang J, Liu S, et al: CD8+ T cell immunity
blocks the metastasis of carcinogen-exposed breast cancer. Sci Adv.
7:eabd89362021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Liu YR, Jiang YZ, Xu XE, Hu X, Yu KD and
Shao ZM: Comprehensive transcriptome profiling reveals multigene
signatures in triple-negative breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
22:1653–1662. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Komatsu M, Yoshimaru T, Matsuo T, Kiyotani
K, Miyoshi Y, Tanahashi T, Rokutan K, Yamaguchi R, Saito A, Imoto
S, et al: Molecular features of triple negative breast cancer cells
by genome-wide gene expression profiling analysis. Int J Oncol.
42:478–506. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sabatier R, Finetti P, Cervera N,
Lambaudie E, Esterni B, Mamessier E, Tallet A, Chabannon C, Extra
JM, Jacquemier J, et al: A gene expression signature identifies two
prognostic subgroups of basal breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res
Treat. 126:407–420. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sabatier R, Finetti P, Adelaide J, Guille
A, Borg JP, Chaffanet M, Lane L, Birnbaum D and Bertucci F:
Down-regulation of ECRG4, a candidate tumor suppressor gene, in
human breast cancer. PLoS One. 6:e276562011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chin K, DeVries S, Fridlyand J, Spellman
PT, Roydasgupta R, Kuo WL, Lapuk A, Neve RM, Qian Z, Ryder T, et
al: Genomic and transcriptional aberrations linked to breast cancer
pathophysiologies. Cancer Cell. 10:529–541. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Nagalla S, Chou JW, Willingham MC, Ruiz J,
Vaughn JP, Dubey P, Lash TL, Hamilton-Dutoit SJ, Bergh J, Sotiriou
C, et al: Interactions between immunity, proliferation and
molecular subtype in breast cancer prognosis. Genome Boil.
14:R342013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kim SK, Ahn SG, Mun JY, Jeong MS, Bae SJ,
Lee JS, Jeong J, Leem SH and Chu IS: Genomic signature of the
standardized uptake value in 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose
positron emission tomography in breast cancer. Cancers (Basel).
12:4972020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Maire V, Baldeyron C, Richardson M, Tesson
B, Vincent-Salomon A, Gravier E, Marty-Prouvost B, De Koning L,
Rigaill G, Dumont A, et al: TTK/hMPS1 is an attractive therapeutic
target for triple-negative breast cancer. PLoS One. 8:e637122013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
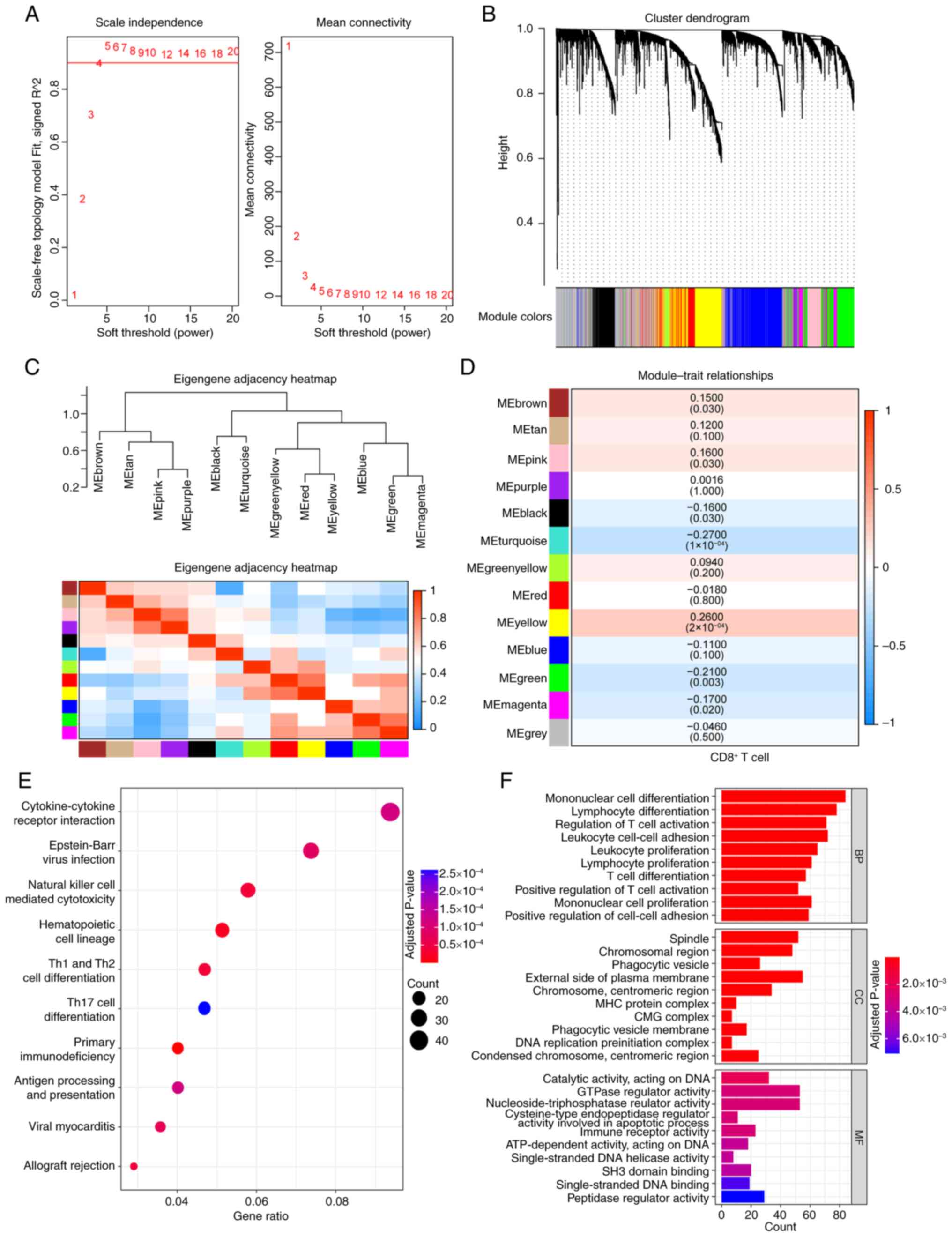
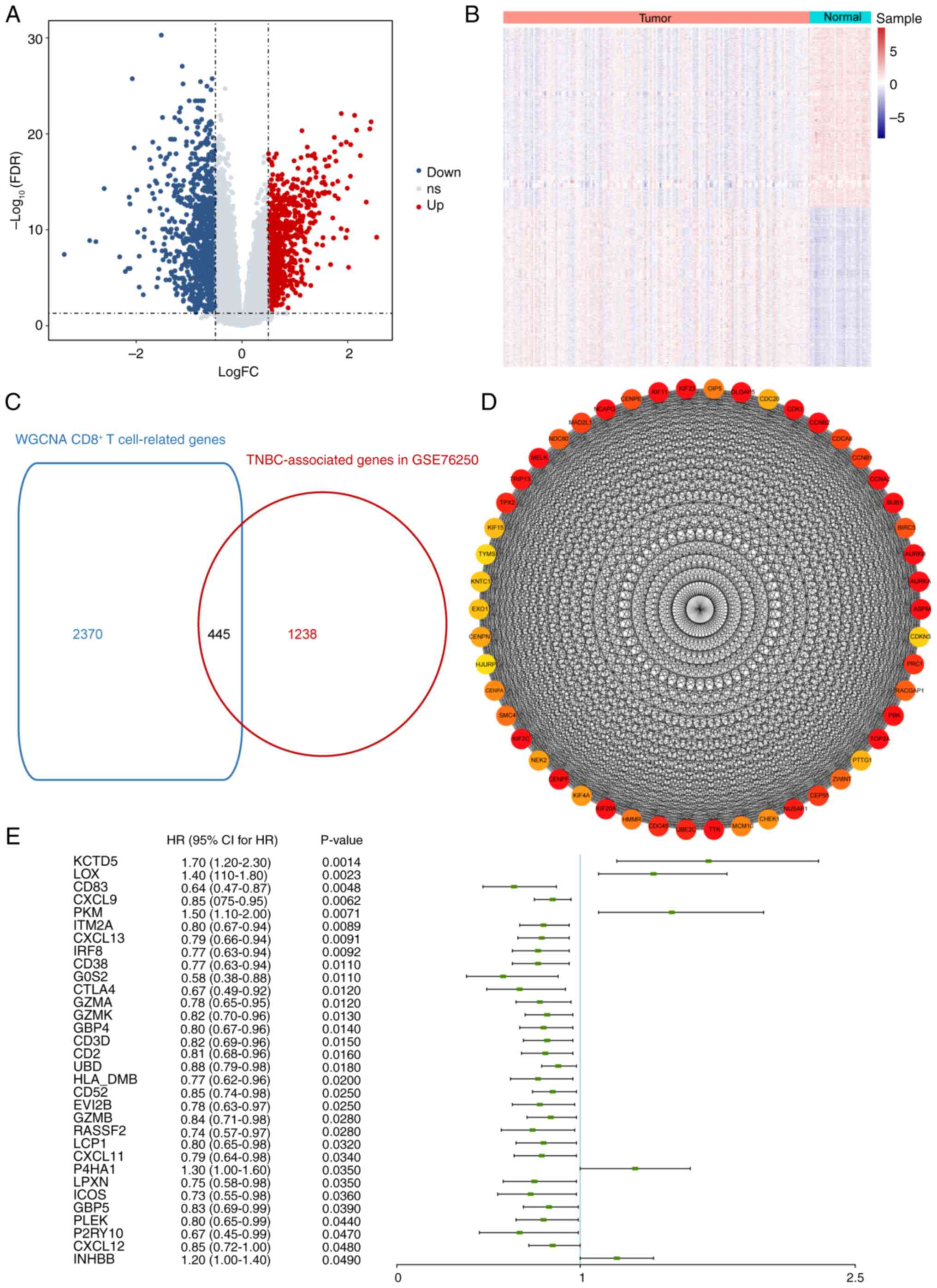
Langfelder P and Horvath S: WGCNA: An R
package for weighted correlation network analysis. BMC
Bioinformatics. 9:5592008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D, Hu Y, Law CW,
Shi W and Smyth GK: limma powers differential expression analyses
for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res.
43:e472015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yu G, Wang LG, Han Y and He QY:
clusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among
gene clusters. OMICS. 16:284–287. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Szklarczyk D, Gable AL, Lyon D, Junge A,
Wyder S, Huerta-Cepas J, Simonovic M, Doncheva NT, Morris JH, Bork
P, et al: STRING v11: Protein-protein association networks with
increased coverage, supporting functional discovery in genome-wide
experimental datasets. Nucleic Acids Res. 47(D1): D607–D613. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chin CH, Chen SH, Wu HH, Ho CW, Ko MT and
Lin CY: cytoHubba: Identifying hub objects and sub-networks from
complex interactome. BMC Syst Biol. 8 (Suppl 4):S112014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Newman AM, Liu CL, Green MR, Gentles AJ,
Feng W, Xu Y, Hoang CD, Diehn M and Alizadeh AA: Robust enumeration
of cell subsets from tissue expression profiles. Nat Methods.
12:453–457. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li J, Yao J and Qi L: Identification of
TUBB2A as a cancer-immunity cycle-related therapeutic target in
triple-negative breast cancer. Mol Biotechnol. Sep 24–2023.(Epub
ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Li L and Li S: miR-205-5p inhibits cell
migration and invasion in prostatic carcinoma by targeting ZEB1.
Oncol Lett. 16:1715–1721. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Goenka A, Khan F, Verma B, Sinha P, Dmello
CC, Jogalekar MP, Gangadaran P and Ahn BC: Tumor microenvironment
signaling and therapeutics in cancer progression. Cancer Commun
(Lond). 43:525–561. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Meng L, Wu H, Wu J, Ding P, He J, Sang M
and Liu L: Mechanisms of immune checkpoint inhibitors: Insights
into the regulation of circular RNAS involved in cancer hallmarks.
Cell Death Dis. 15:32024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Angrisani A, Di Fiore A, De Smaele E and
Moretti M: The emerging role of the KCTD proteins in cancer. Cell
Commun Signal. 19:562021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
He H, Peng Y, Fan S, Chen Y, Zheng X and
Li C: Cullin3/KCTD5 induces monoubiquitination of ΔNp63α and
impairs its activity. FEBS Lett. 592:2334–2340. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Coppola L, Baselice S, Messina F,
Giannatiempo R, Farina A, Vitagliano L, Smaldone G and Salvatore M:
KCTD15 is overexpressed in her2+ positive breast cancer patients
and its silencing attenuates proliferation in SKBR3 cell line.
Diagnostics (Basel). 12:5912022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Rivas J, Diaz N, Silva I, Morales D,
Lavanderos B, Álvarez A, Saldias MP, Pulgar E, Cruz P, Maureira D,
et al: KCTD5, a novel TRPM4-regulatory protein required for cell
migration as a new predictor for breast cancer prognosis. FASEB J.
34:7847–7865. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Canales J, Cruz P, Diaz N, Riquelme D,
Leiva-Salcedo E and Cerda O: K+ channel tetramerization
domain 5 (KCTD5) protein regulates cell migration, focal adhesion
dynamics and spreading through modulation of Ca2+
signaling and Rac1 activity. Cells. 9:22732020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Bayón Y, Trinidad AG, de la Puerta ML, Del
Carmen Rodriguez M, Bogetz J, Rojas A, De Pereda JM, Rahmouni S,
Williams S, Matsuzawa SI, et al: KCTD5, a putative substrate
adaptor for cullin3 ubiquitin ligases. FEBS J. 275:3900–3910. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Davidge B, Rebola KGO, Agbor LN, Sigmund
CD and Singer JD: Cul3 regulates cyclin E1 protein abundance via a
degron located within the N-terminal region of cyclin E. J Cell
Sci. 132:jcs2330492019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Ohtsubo M, Theodoras AM, Schumacher J,
Roberts JM and Pagano M: Human cyclin E, a nuclear protein
essential for the G1-to-S phase transition. Mol Cell Biol.
15:2612–2624. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Shi YX, Zhang WD, Dai PH, Deng J and Tan
LH: Comprehensive analysis of KCTD family genes associated with
hypoxic microenvironment and immune infiltration in lung
adenocarcinoma. Sci Rep. 12:99382022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Martinez FO and Gordon S: The M1 and M2
paradigm of macrophage activation: Time for reassessment.
F1000Prime Rep. 6:132014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Weng YS, Tseng HY, Chen YA, Shen PC, Al
Haq AT, Chen LM, Tung YC and Hsu HL: MCT-1/miR-34a/IL-6/IL-6R
signaling axis promotes EMT progression, cancer stemness and M2
macrophage polarization in triple-negative breast cancer. Mol
Cancer. 18:422019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Fang WB, Yao M, Brummer G, Acevedo D,
Alhakamy N, Berkland C and Cheng N: Targeted gene silencing of CCL2
inhibits triple negative breast cancer progression by blocking
cancer stem cell renewal and M2 macrophage recruitment. Oncotarget.
7:49349–49367. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Nguyen LK, Kholodenko BN and von
Kriegsheim A: Rac1 and RhoA: Networks, loops and bistability. Small
GTPases. 9:316–321. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Glading A, Lauffenburger DA and Wells A:
Cutting to the chase: Calpain proteases in cell motility. Trends
Cell Biol. 12:46–54. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Shi YX, Yan JH, Liu W and Deng J:
Identifies KCTD5 as a novel cancer biomarker associated with
programmed cell death and chemotherapy drug sensitivity. BMC
Cancer. 23:4082023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|