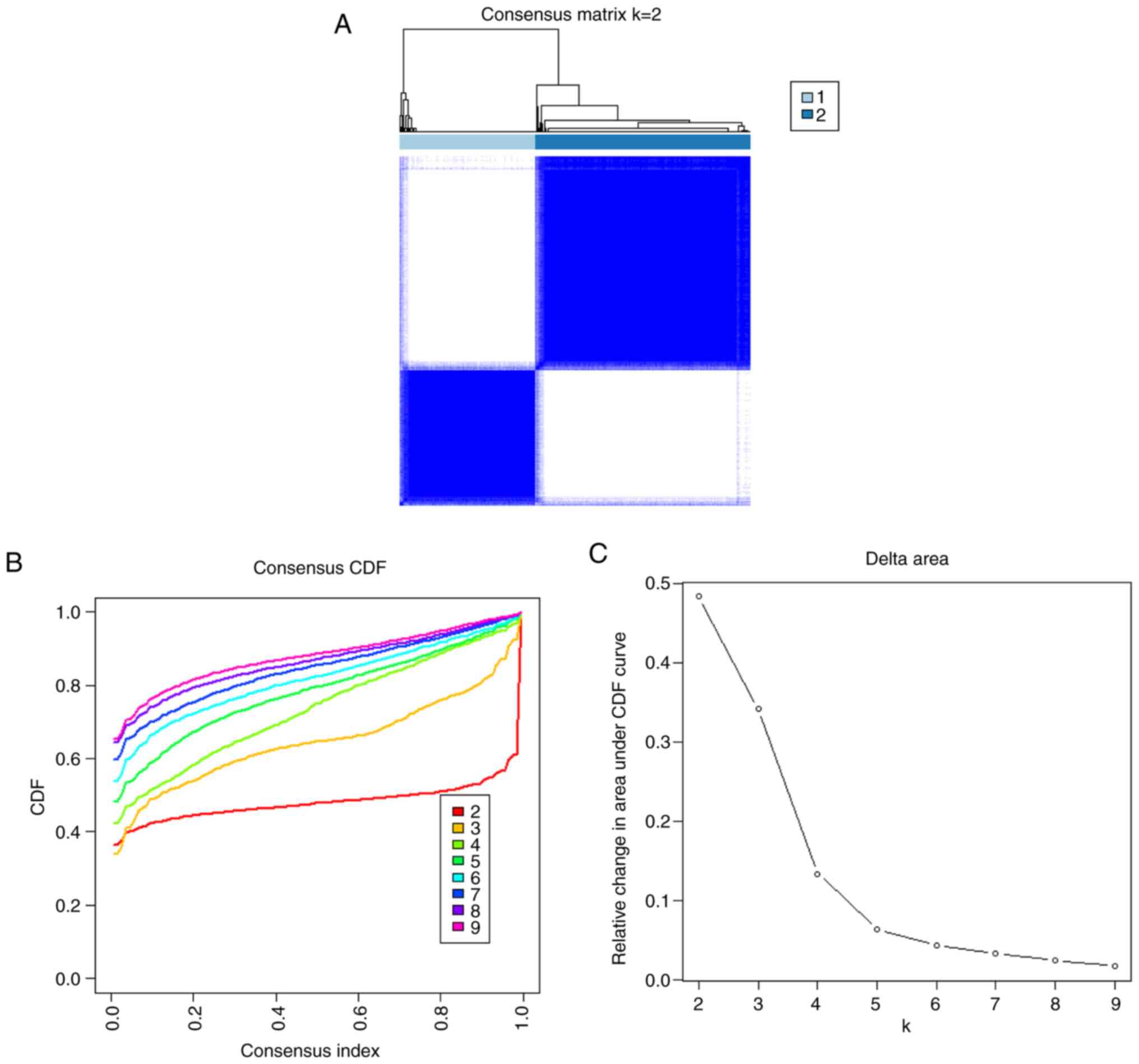
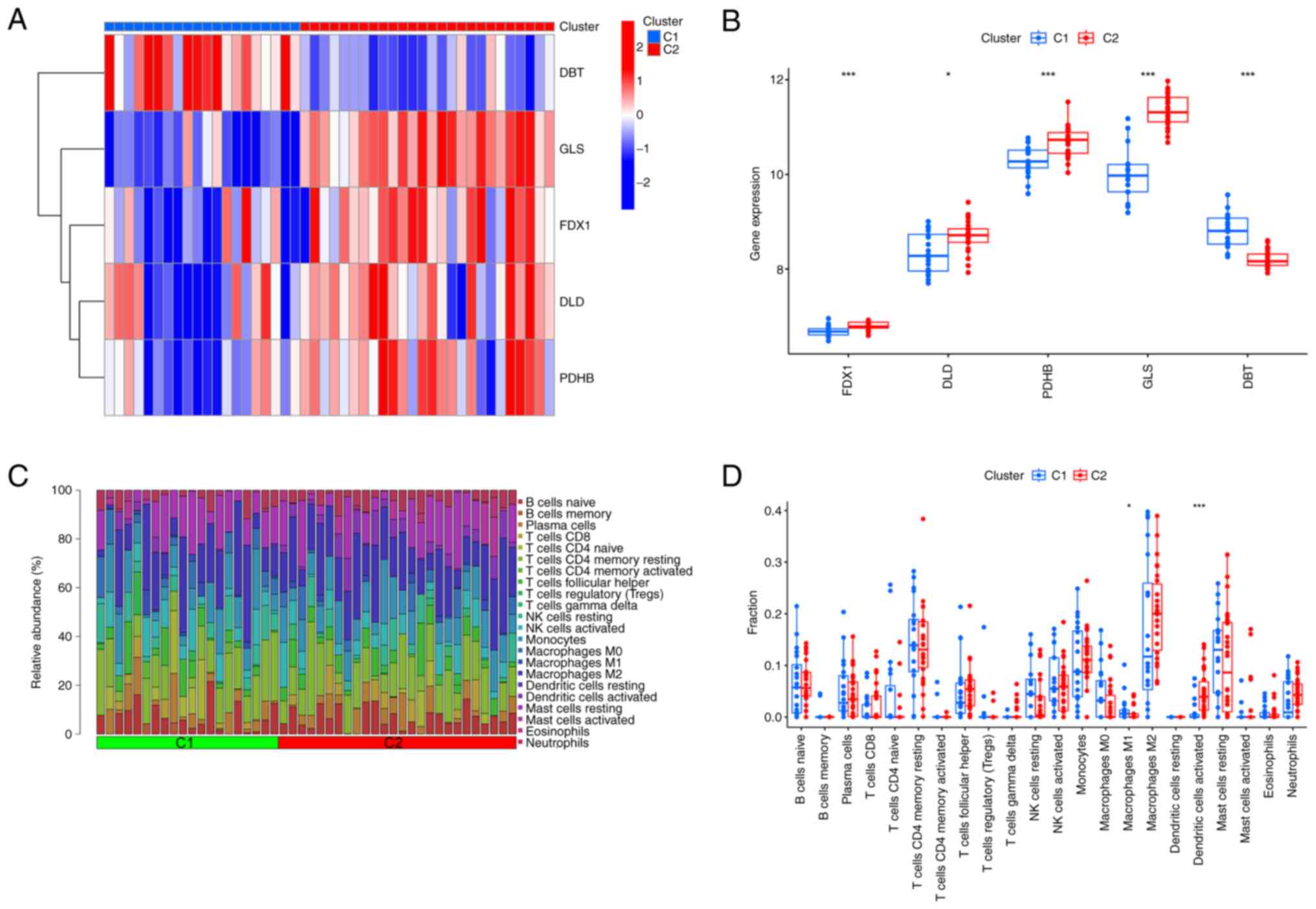
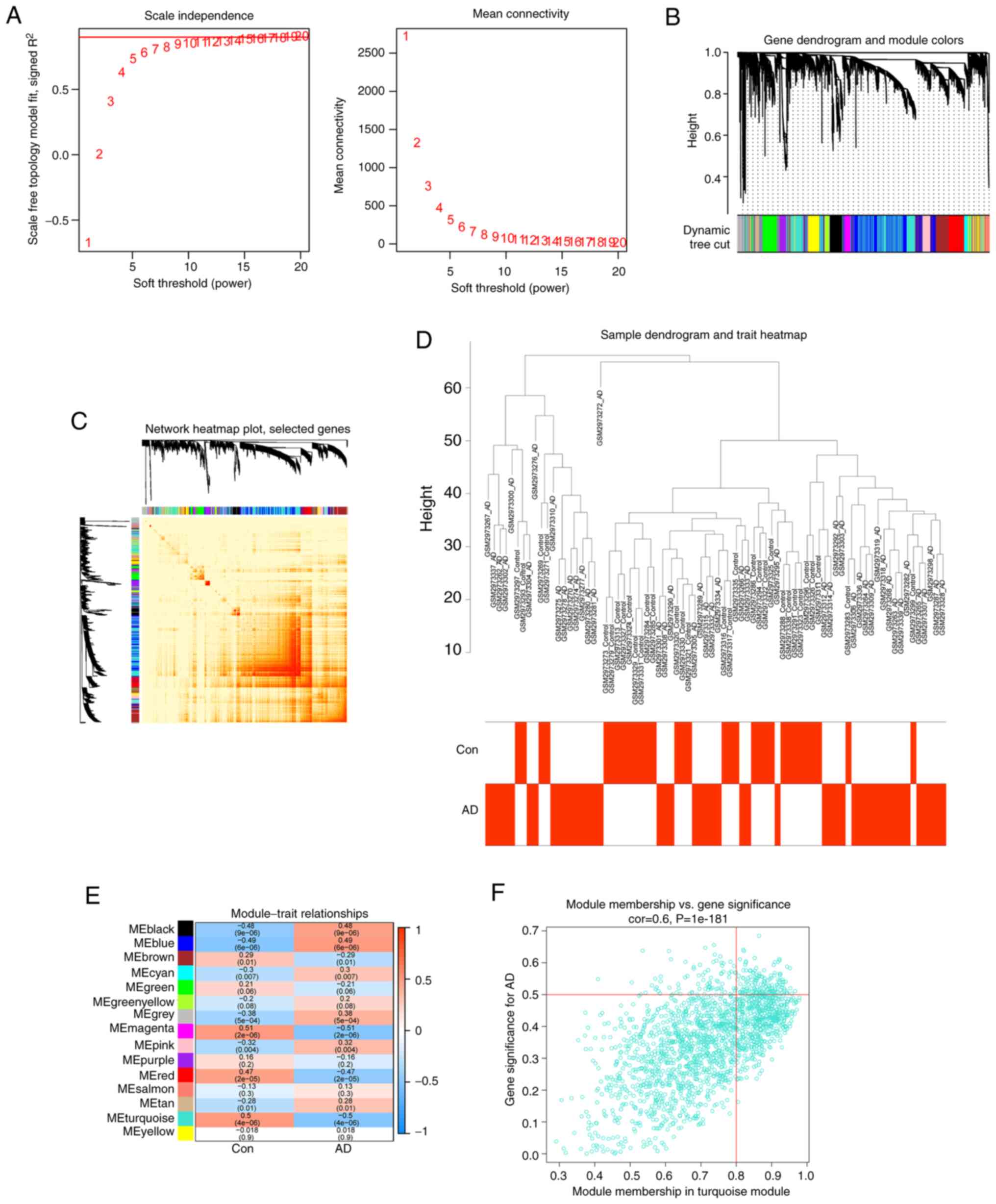
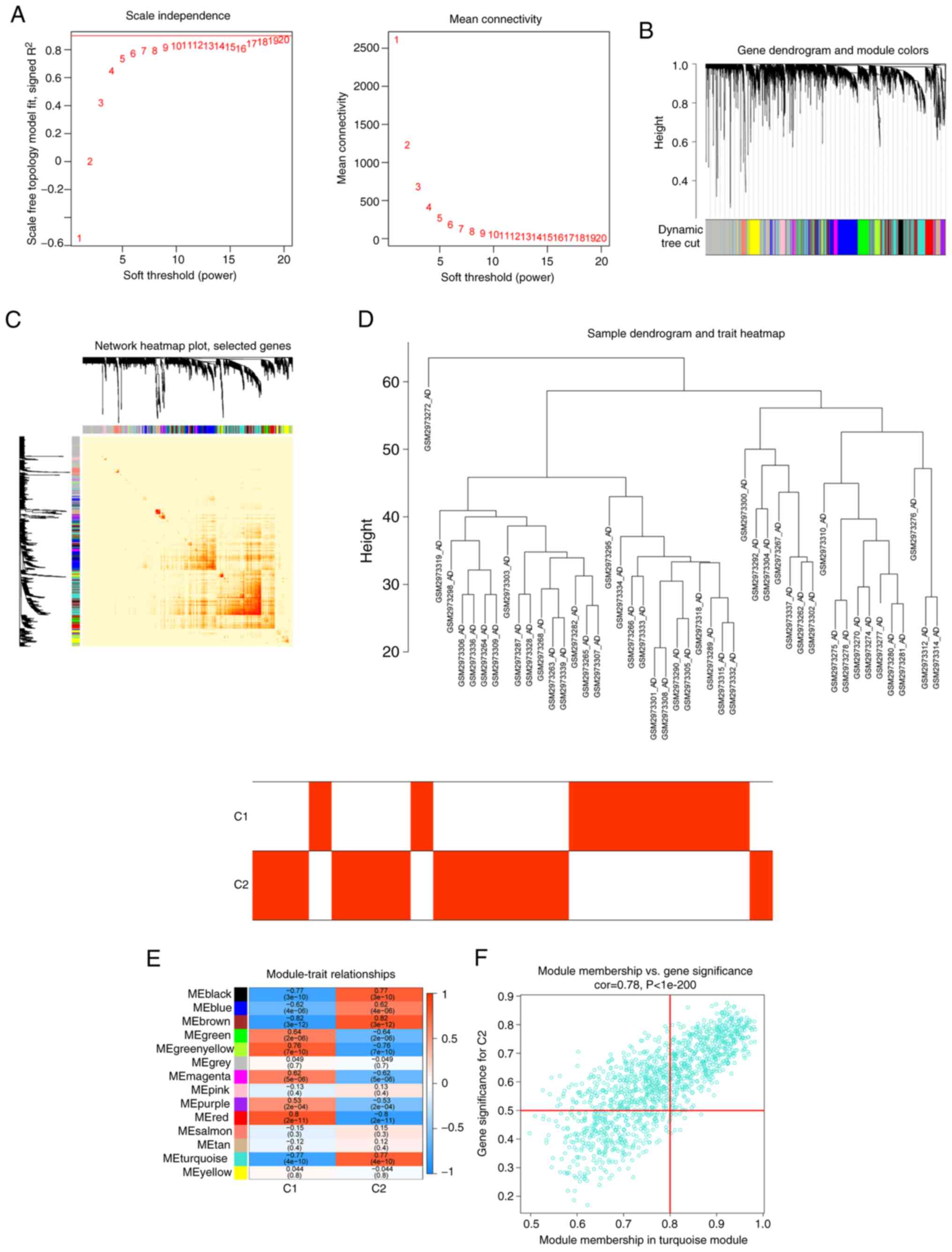
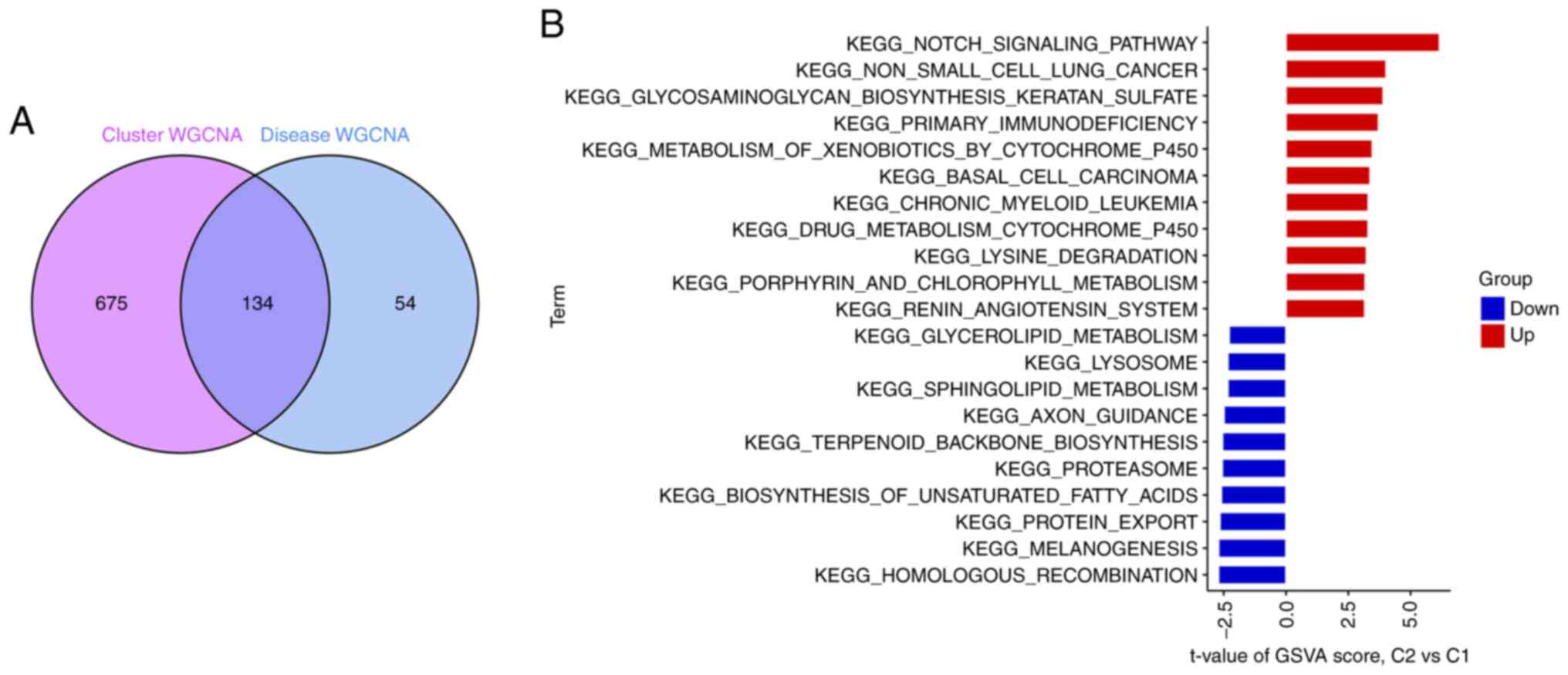
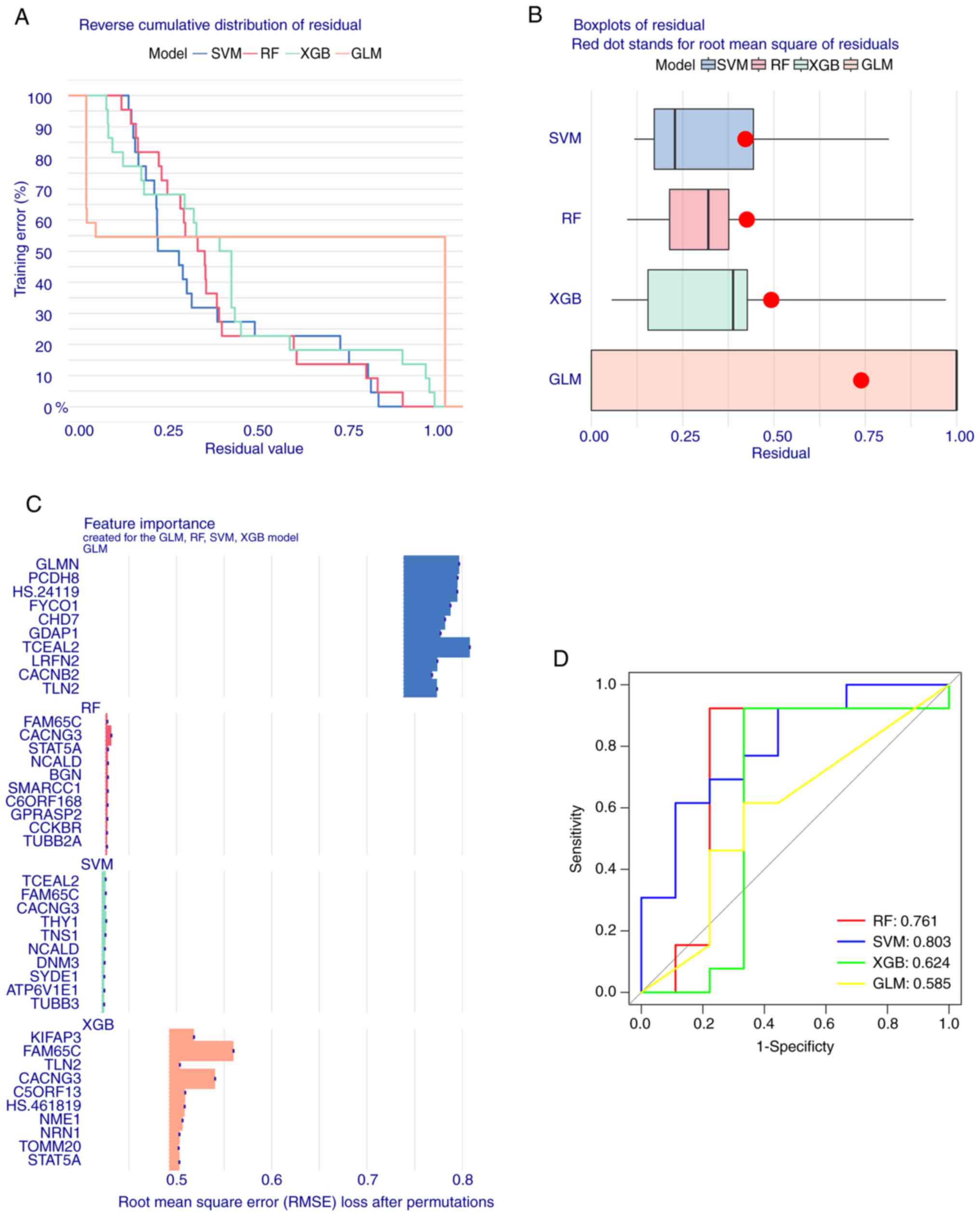
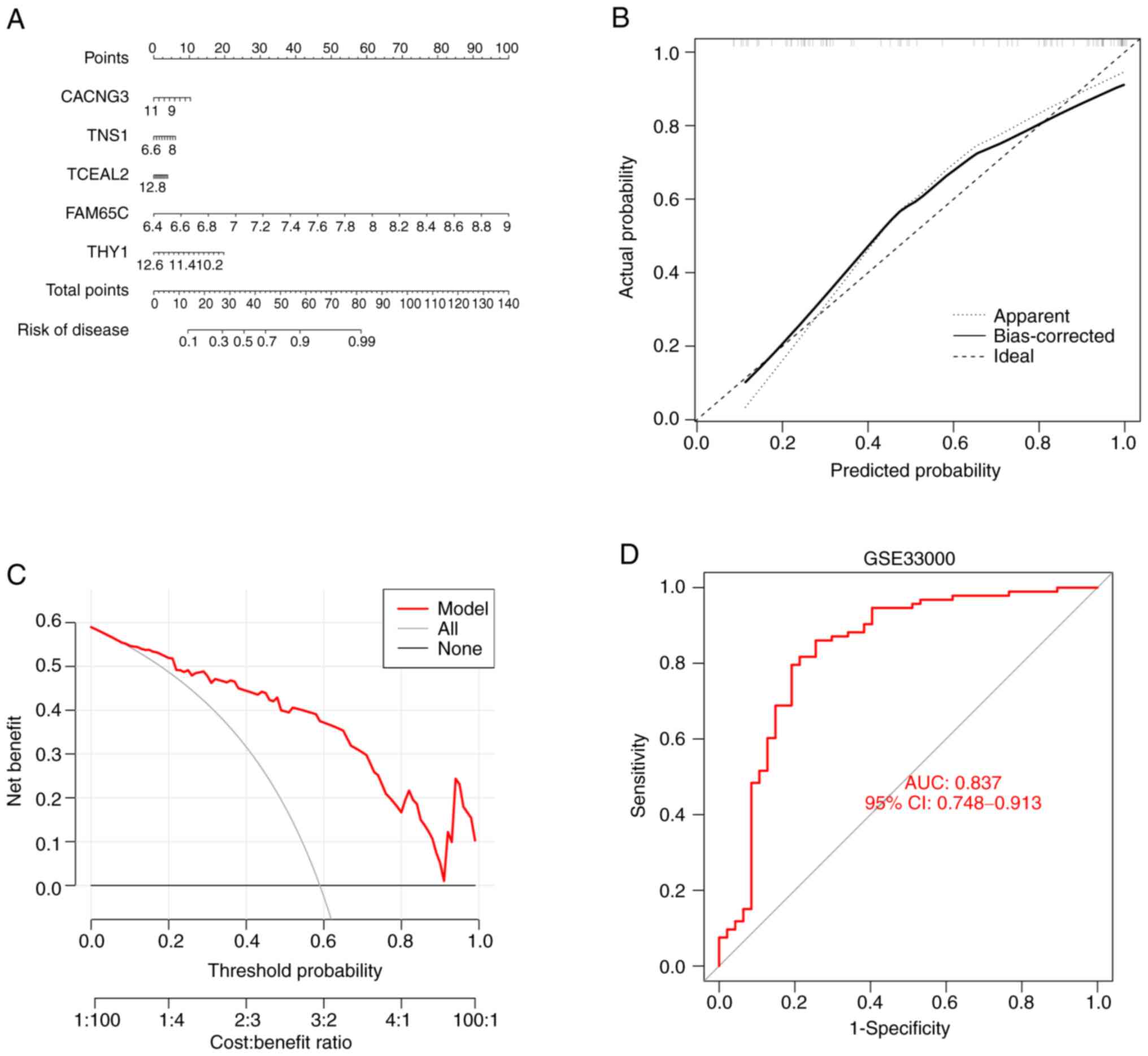
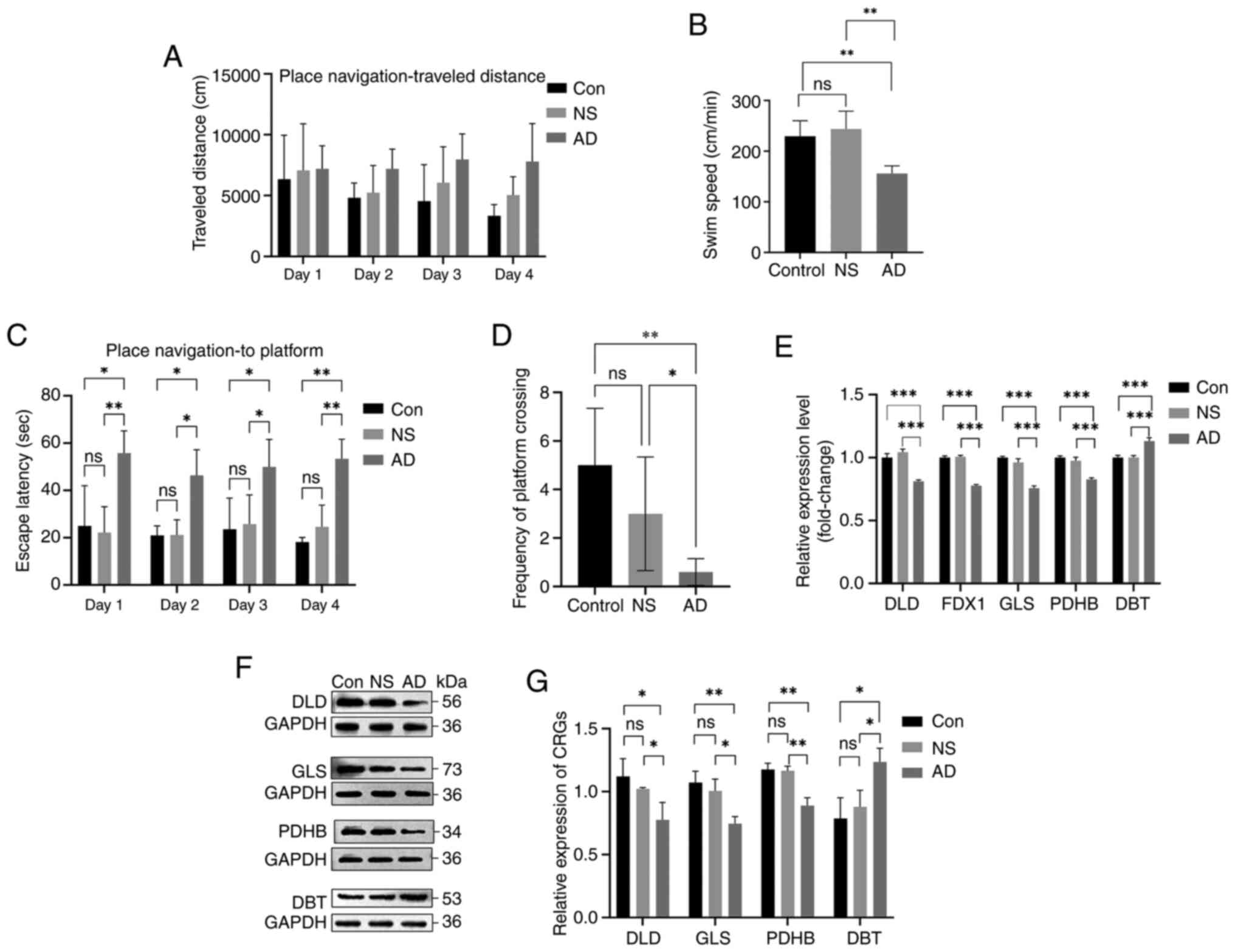
|
1
|
de San Román EG, Manuel I, Giralt MT,
Ferrer I and Rodríguez-Puertas R: Imaging mass spectrometry (IMS)
of cortical lipids from preclinical to severe stages of Alzheimer's
disease. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr. 1859((9 Pt B)): 1604–1614.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
GBD 2019 Dementia Forecasting
Collaborators, . Estimation of the global prevalence of dementia in
2019 and forecasted prevalence in 2050: An analysis for the global
burden of disease study 2019. Lancet Public health. 7:e105–e125.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rostagno AA: Pathogenesis of Alzheimer's
disease. Int J Mol Sci. 24:1072022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chen YG: Research progress in the
pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease. Chin Med J (Engl).
131:1618–1624. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Di Fede G, Catania M, Maderna E, Ghidoni
R, Benussi L, Tonoli E, Giaccone G, Moda F, Paterlini A, Campagnani
I, et al: Molecular subtypes of Alzheimer's disease. Sci Rep.
8:32692018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Scheltens P, De Strooper B, Kivipelto M,
Holstege H, Chételat G, Teunissen CE, Cummings J and van der Flier
WM: Alzheimer's disease. Lancet. 397:1577–1590. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sanchez-Mut JV and Gräff J: Epigenetic
alterations in Alzheimer's disease. Front Behav Neurosci.
9:3472015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kawamata H and Manfredi G: Import,
maturation, and function of SOD1 and its copper chaperone CCS in
the mitochondrial intermembrane space. Antioxid Redox Signal.
13:1375–1384. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Scheiber I, Dringen R and Mercer JF:
Copper: Effects of deficiency and overload. Met Ions Life Sci.
13:359–387. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gromadzka G, Tarnacka B, Flaga A and
Adamczyk A: Copper dyshomeostasis in neurodegenerative
diseases-therapeutic implications. Int J Mol Sci. 21:92592020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sayre LM, Perry G, Harris PL, Liu Y,
Schubert KA and Smith MA: In situ oxidative catalysis by
neurofibrillary tangles and senile plaques in Alzheimer's disease:
A central role for bound transition metals. J Neurochem.
74:270–279. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen LL, Fan YG, Zhao LX, Zhang Q and Wang
ZY: The metal ion hypothesis of Alzheimer's disease and the
anti-neuroinflammatory effect of metal chelators. Bioorg Chem.
131:1063012023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tang D, Chen X and Kroemer G: Cuproptosis:
A copper-triggered modality of mitochondrial cell death. Cell Res.
32:417–418. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Garza NM, Swaminathan AB, Maremanda KP,
Zulkifli M and Gohil VM: Mitochondrial copper in human genetic
disorders. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 34:21–33. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tsvetkov P, Coy S, Petrova B, Dreishpoon
M, Verma A, Abdusamad M, Rossen J, Joesch-Cohen L, Humeidi R,
Spangler RD, et al: Copper induces cell death by targeting
lipoylated TCA cycle proteins. Science. 375:1254–1261. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Xie J, Yang Y, Gao Y and He J:
Cuproptosis: Mechanisms and links with cancers. Mol Cancer.
22:462023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Swerdlow RH: Mitochondria and
mitochondrial cascades in Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimers Dis.
62:1403–1416. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Macdonald R, Barnes K, Hastings C and
Mortiboys H: Mitochondrial abnormalities in Parkinson's disease and
Alzheimer's disease: Can mitochondria be targeted therapeutically?
Biochem Soc Trans. 46:891–909. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nie B, Duan Y, Xie X, Qiu L, Shi S, Fan Z,
Zheng X and Jiang L: Systematic analysis of cuproptosis-related
genes in immunological characterization and predictive drugs in
Alzheimer's disease. Front Aging Neurosci. 15:12045302023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li R: Data mining and machine learning
methods for dementia research. Methods Mol Biol. 1750:363–370.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Duffy IR, Boyle AJ and Vasdev N: Improving
PET imaging acquisition and analysis with machine learning: A
narrative review with focus on Alzheimer's disease and oncology.
Mol Imaging. 18:15360121198690702019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lardenoije R, Roubroeks JAY, Pishva E,
Leber M, Wagner H, Iatrou A, Smith AR, Smith RG, Eijssen LMT,
Kleineidam L, et al: Alzheimer's disease-associated
(hydroxy)methylomic changes in the brain and blood. Clin
Epigenetics. 11:1642019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Narayanan M, Huynh JL, Wang K, Yang X, Yoo
S, McElwee J, Zhang B, Zhang C, Lamb JR, Xie T, et al: Common
dysregulation network in the human prefrontal cortex underlies two
neurodegenerative diseases. Mol Syst Biol. 10:7432014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kanehisa M, Furumichi M, Sato Y, Kawashima
M and Ishiguro-Watanabe M: KEGG for taxonomy-based analysis of
pathways and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 51((D1)): D587–D592. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D, Hu Y, Law CW,
Shi W and Smyth GK: limma powers differential expression analyses
for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res.
43:e472015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Varma S: Blind estimation and correction
of microarray batch effect. PLoS One. 15:e02314462020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Newman AM, Liu CL, Green MR, Gentles AJ,
Feng W, Xu Y, Hoang CD, Diehn M and Alizadeh AA: Robust enumeration
of cell subsets from tissue expression profiles. Nat Methods.
12:453–457. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hänzelmann S, Castelo R and Guinney J:
GSVA: Gene set variation analysis for microarray and RNA-seq data.
BMC Bioinformatics. 14:72013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
My S, Lazareva NA, Onufriev MV, Mitrokhina
OS, YuV M and Gulyaeva NV: Effects of doses of fragment (25–35) of
beta-amyloid peptide on behavior in rats. Neurosci Behav Physiol.
28:564–566. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li Z, Tong Q, Xu H, Hu L, Zhao R, Zhou F,
Pan W and Zhou L: Therapeutic effects of TianDiJingWan on the Aβ
25–35-induced Alzheimer's disease model rats. Evid Based Complement
Alternat Med. 2015:3073502015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Othman MZ, Hassan Z and Has AT: Morris
water maze: A versatile and pertinent tool for assessing spatial
learning and memory. Exp Anim. 71:264–280. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Amonruttanapun P, Chongthammakun S and
Chamniansawat S: The effects of okadaic acid-treated SH-SY5Y cells
on microglia activation and phagocytosis. Cell Biol Int.
46:234–242. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yang X, Zhong Y, Wang D and Lu Z: A simple
colorimetric method for viable bacteria detection based on cell
counting Kit-8. Anal Methods. 13:5211–5215. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhu X, Smith MA, Perry G and Aliev G:
Mitochondrial failures in Alzheimer's disease. Am J Alzheimers Dis
Other Demen. 19:345–352. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Mezzaroba L, Alfieri DF, Simão AN and
Reiche EM: The role of zinc, copper, manganese and iron in
neurodegenerative diseases. Neurotoxicology. 74:230–241. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hureau C and Faller P: Abeta-mediated ROS
production by Cu ions: Structural insights, mechanisms and
relevance to Alzheimer's disease. Biochimie. 91:1212–1217. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Butterfield DA and Boyd-Kimball D: Redox
proteomics and amyloid β-peptide: Insights into Alzheimer disease.
J Neurochem. 151:459–487. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Jansen IE, van der Lee SJ, Gomez-Fonseca
D, de Rojas I, Dalmasso MC, Grenier-Boley B, Zettergren A, Mishra
A, Ali M, Andrade V, et al: Genome-wide meta-analysis for
Alzheimer's disease cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers. Acta
Neuropathol. 144:821–842. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhang Y, Zhou Q, Lu L, Su Y, Shi W, Zhang
H, Liu R, Pu Y and Yin L: Copper induces cognitive impairment in
mice via modulation of cuproptosis and CREB signaling. Nutrients.
15:9722023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Pilozzi A, Yu Z, Carreras I, Cormier K,
Hartley D, Rogers J, Dedeoglu A and Huang X: A preliminary study of
Cu exposure effects upon Alzheimer's amyloid pathology.
Biomolecules. 10:4082020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Huang X: A concise review on oxidative
stress-mediated ferroptosis and cuproptosis in Alzheimer's disease.
Cells. 12:13692023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Starkov AA, Fiskum G, Chinopoulos C,
Lorenzo BJ, Browne SE, Patel MS and Beal MF: Mitochondrial
alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex generates reactive oxygen
species. J Neurosci. 24:7779–7788. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Yang W, Guo Q, Wu H, Tong L, Xiao J, Wang
Y, Liu R, Xu L, Yan H and Sun Z: Comprehensive analysis of the
cuproptosis-related gene DLD across cancers: A potential prognostic
and immunotherapeutic target. Front Pharmacol. 14:11114622023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Rajesh Y and Kanneganti TD: Innate immune
cell death in neuroinflammation and Alzheimer's disease. Cells.
11:18852022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Suliman IH, Kim K, Chen W, Kim Y, Moon JH,
Son S and Nam J: Metal-based nanoparticles for cancer
metalloimmunotherapy. Pharmaceutics. 15:20032023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Wang L, Cao Y, Guo W and Xu J: High
expression of cuproptosis-related gene FDX1 in relation to good
prognosis and immune cells infiltration in colon adenocarcinoma
(COAD). J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 149:15–24. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Huang LT, Zhang CP, Wang YB and Wang JH:
Association of peripheral blood cell profile with Alzheimer's
disease: A meta-analysis. Front Aging Neurosci. 14:8889462022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Song L, Yang YT and Guo Q; ZIB Consortium;
Zhao XM, : Cellular transcriptional alterations of peripheral blood
in Alzheimer's disease. BMC Med. 20:2662022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Waschkies KF, Soch J, Darna M, Richter A,
Altenstein S, Beyle A, Brosseron F, Buchholz F, Butryn M, Dobisch
L, et al: Machine learning-based classification of Alzheimer's
disease and its at-risk states using personality traits, anxiety,
and depression. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 38:e60072023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Wang T, Sun J and Zhao Q: Investigating
cardiotoxicity related with hERG channel blockers using molecular
fingerprints and graph attention mechanism. Comput Biol Med.
153:1064642023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Becker RE and Greig NH: Why so few drugs
for Alzheimer's disease? Are methods failing drugs? Curr Alzheimer
Res. 7:642–651. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Li L, Jin M, Tan J and Xiao B: NcRNAs: A
synergistically antiapoptosis therapeutic tool in Alzheimer's
disease. CNS Neurosci Ther. 30:e144762023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Wang W, Zhang L, Sun J, Zhao Q and Shuai
J: Predicting the potential human lncRNA-miRNA interactions based
on graph convolution network with conditional random field. Brief
Bioinform. 23:bbac4632022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Zhao J, Sun J, Shuai SC, Zhao Q and Shuai
J: Predicting potential interactions between lncRNAs and proteins
via combined graph auto-encoder methods. Brief Bioinform.
24:bbac5272023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Dreishpoon MB, Bick NR, Petrova B, Warui
DM, Cameron A, Booker SJ, Kanarek N, Golub TR and Tsvetkov P: FDX1
regulates cellular protein lipoylation through direct binding to
LIAS. bioRxiv: The preprint server for biology. 2023.02.03.526472.
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Patel MS, Nemeria NS, Furey W and Jordan
F: The pyruvate dehydrogenase complexes: Structure-based function
and regulation. J Biol Chem. 289:16615–16623. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Dreishpoon MB, Bick NR, Petrova B, Warui
DM, Cameron A, Booker SJ, Kanarek N, Golub TR and Tsvetkov P: FDX1
regulates cellular protein lipoylation through direct binding to
LIAS. J Biol Chem. 299:1050462023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Chen Z and Zhong C: Decoding Alzheimer's
disease from perturbed cerebral glucose metabolism: Implications
for diagnostic and therapeutic strategies. Prog Neurobiol.
108:21–43. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Hull J, Moraes MU, Brookes E, Love S and
Conway ME: Distribution of the branched-chain α-ketoacid
dehydrogenase complex E1α subunit and glutamate dehydrogenase in
the human brain and their role in neuro-metabolism. Neurochem Int.
112:49–58. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Griffin JWD, Liu Y, Bradshaw PC and Wang
K: In silico preliminary association of ammonia metabolism genes
GLS, CPS1, and GLUL with risk of Alzheimer's disease, major
depressive disorder, and type 2 diabetes. J Mol Neurosci.
64:385–396. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Kapoor A and Nation DA: Role of Notch
signaling in neurovascular aging and Alzheimer's disease. Semin
Cell Dev Biol. 116:90–97. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Perna A, Marathe S, Dreos R, Falquet L,
Egger HA and Auber LA: Revealing NOTCH-dependencies in synaptic
targets associated with Alzheimer's disease. Mol Cell Neurosci.
115:1036572021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|