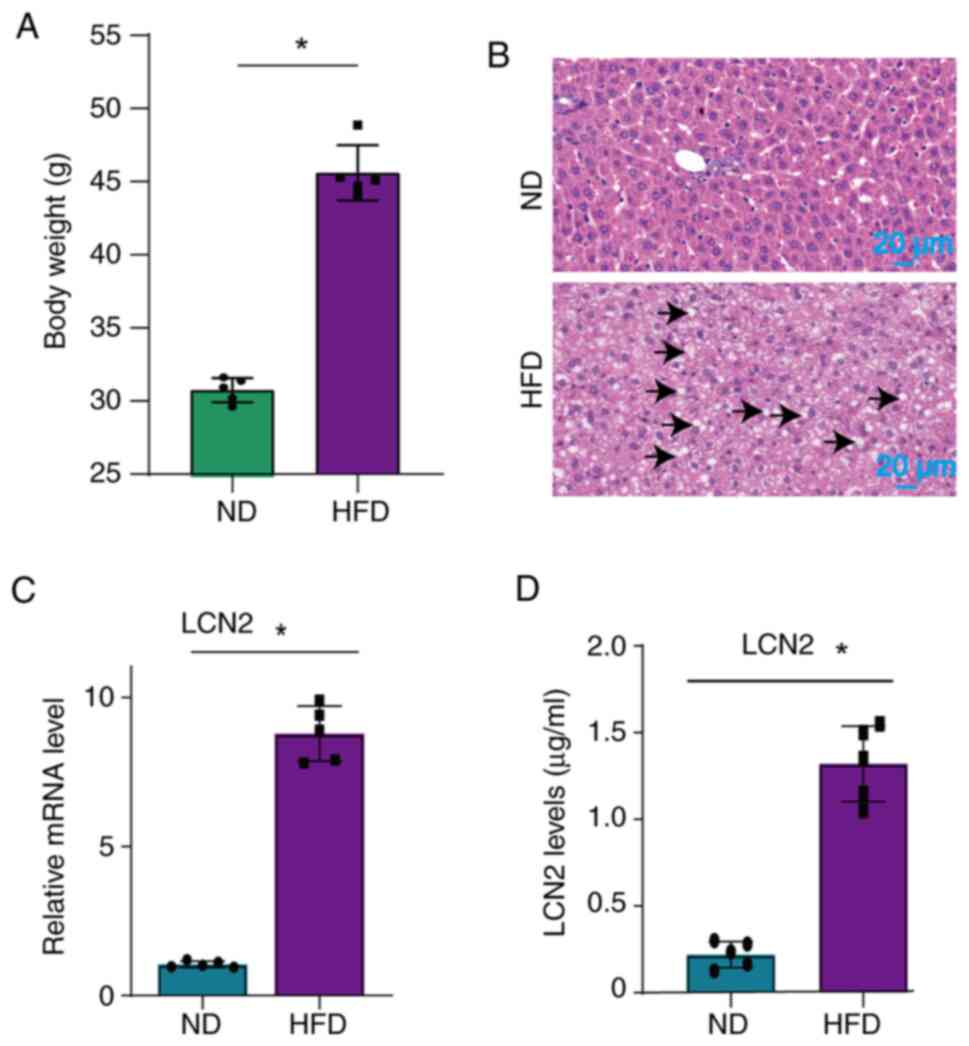
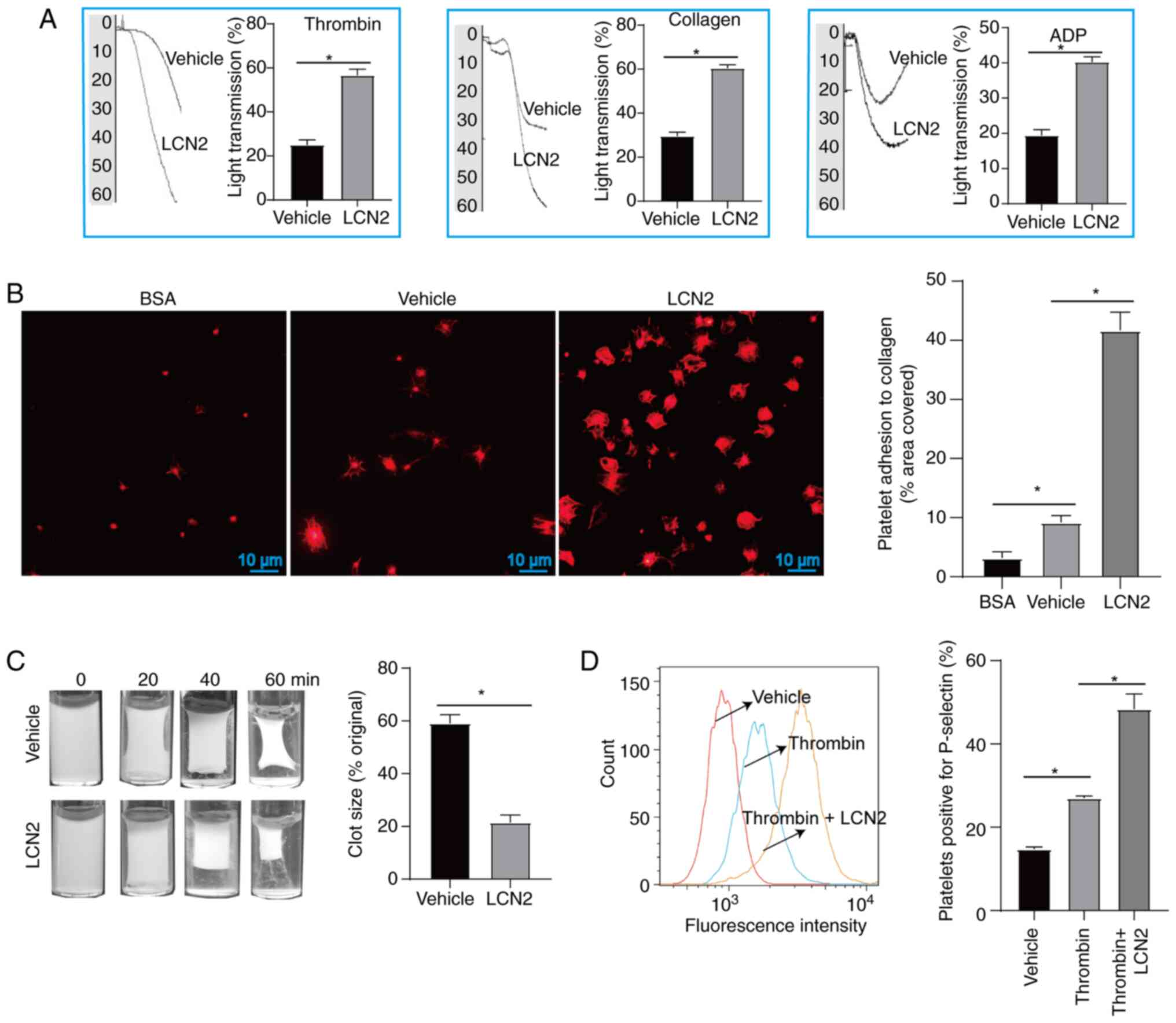
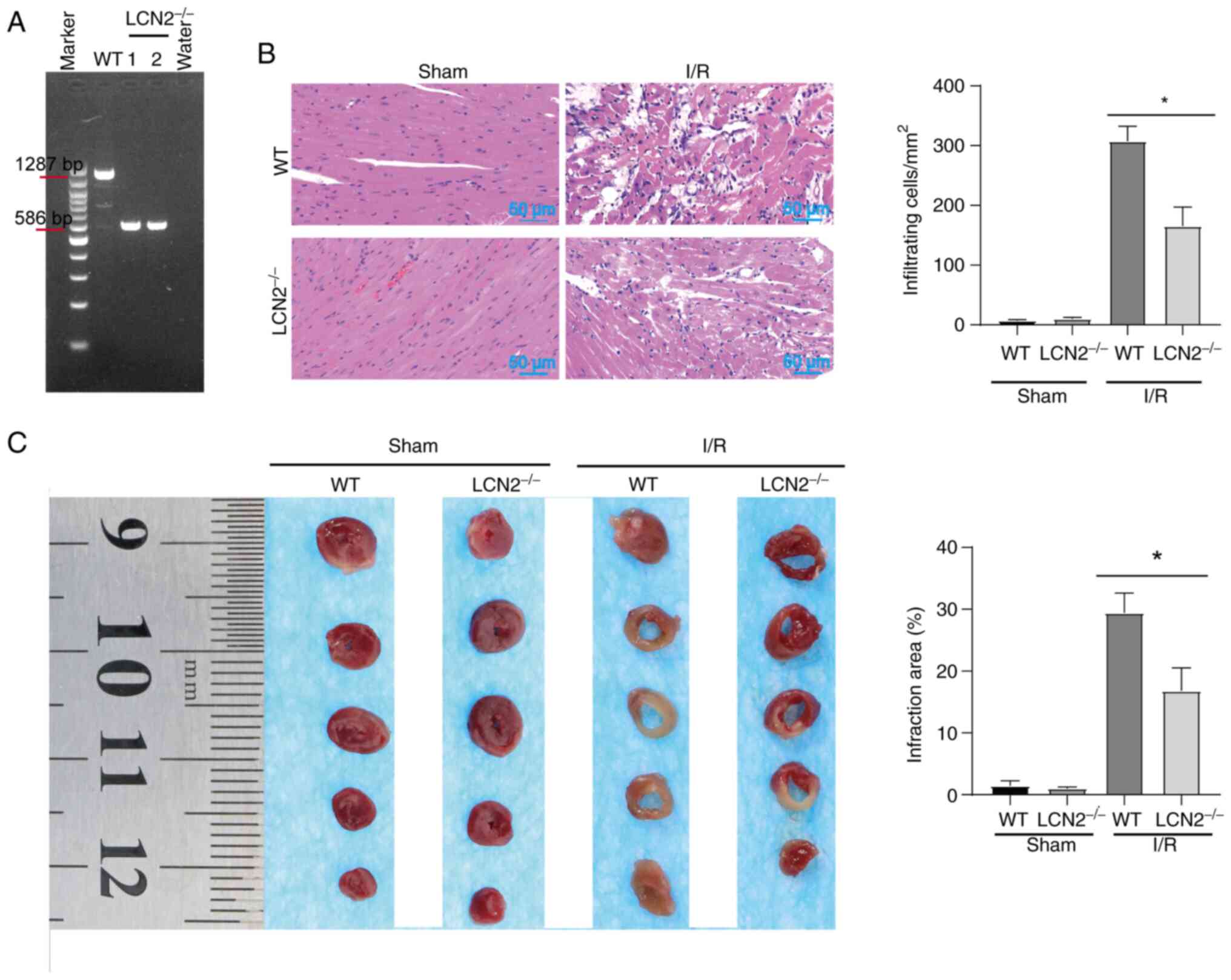
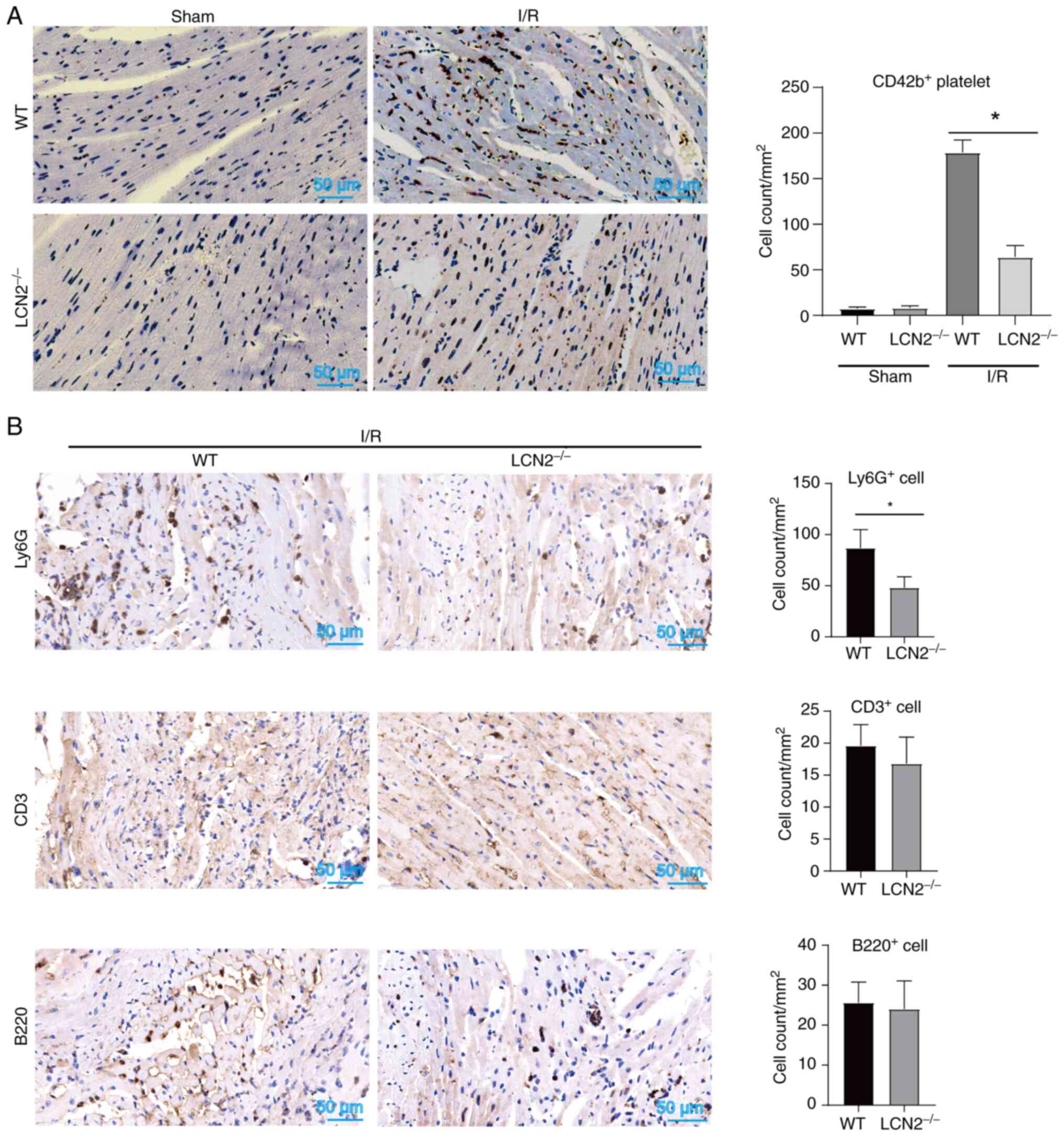
|
1
|
Harrington DH, Stueben F and Lenahan CM:
ST-elevation myocardial infarction and non-ST-elevation myocardial
infarction: Medical and surgical interventions. Crit Care Nurs Clin
North Am. 31:49–64. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wu MY, Yiang GT, Liao WT, Tsai AP, Cheng
YL, Cheng PW, Li CY and Li CJ: Current mechanistic concepts in
ischemia and reperfusion injury. Cell Physiol Biochem.
46:1650–1667. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Visseren FLJ, Mach F, Smulders YM,
Carballo D, Koskinas KC, Bäck M, Benetos A, Biffi A, Boavida JM,
Capodanno D, et al: 2021 ESC guidelines on cardiovascular disease
prevention in clinical practice. Eur Heart J. 42:3227–3337. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Algoet M, Janssens S, Himmelreich U, Gsell
W, Pusovnik M, Van den Eynde J and Oosterlinck W: Myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion injury and the influence of inflammation.
Trends Cardiovasc Med. 33:357–366. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wei Y, Xing J, Su X, Li X, Yan X, Zhao J
and Tao H: IL-38 attenuates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury
by inhibiting macrophage inflammation. Immun Inflamm Dis.
11:e8982023. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang J, Hu S, Gao Y, Wei X, Qu Y, Gao R,
Lv Y, Wang J, Wang Y, Yang J, et al: Galangin alleviated myocardial
ischemia-reperfusion injury by enhancing autophagic flux and
inhibiting inflammation. Eur J Pharmacol. 945:1756212023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chen LQ, Wang WS, Li SQ and Liu JH:
Minocycline relieves myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats
by inhibiting inflammation, oxidative stress and apoptosis. Eur Rev
Med Pharmacol Sci. 26:3001–3009. 2022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Seeger JP, Benda NM, Riksen NP, van Dijk
AP, Bellersen L, Hopman MT, Cable NT and Thijssen DH: Heart failure
is associated with exaggerated endothelial ischaemia-reperfusion
injury and attenuated effect of ischaemic preconditioning. Eur J
Prev Cardiol. 23:33–40. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wereski R, Kimenai DM, Bularga A, Taggart
C, Lowe DJ, Mills NL and Chapman AR: Risk factors for type 1 and
type 2 myocardial infarction. Eur Heart J. 43:127–135. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cameron SJ, Ture SK, Mickelsen D,
Chakrabarti E, Modjeski KL, McNitt S, Seaberry M, Field DJ, Le NT,
Abe J and Morrell CN: Platelet extracellular regulated protein
kinase 5 is a redox switch and triggers maladaptive platelet
responses and myocardial infarct expansion. Circulation. 132:47–58.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Schanze N, Bode C and Duerschmied D:
Platelet contributions to myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury.
Front Immunol. 10:12602019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
van der Meijden PEJ and Heemskerk JWM:
Platelet biology and functions: New concepts and clinical
perspectives. Nat Rev Cardiol y. 16:166–179. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jaberi SA, Cohen A, D'Souza C, Abdulrazzaq
YM, Ojha S, Bastaki S and Adeghate EA: Lipocalin-2: Structure,
function, distribution and role in metabolic disorders. Biomed
Pharmacother. 142:1120022021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ghosh S, Stepicheva N, Yazdankhah M, Shang
P, Watson AM, Hose S, Liu H, Weiss J, Zigler JS Jr, Valapala M, et
al: The role of lipocalin-2 in age-related macular degeneration
(AMD). Cell Mol Life Sci. 77:835–851. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Eilenberg W, Stojkovic S,
Piechota-Polanczyk A, Kaun C, Rauscher S, Gröger M, Klinger M,
Wojta J, Neumayer C, Huk I and Demyanets S: Neutrophil
gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) is associated with
symptomatic carotid atherosclerosis and drives pro-inflammatory
state in vitro. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 51:623–631. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Mosialou I, Shikhel S, Luo N, Petropoulou
PI, Panitsas K, Bisikirska B, Rothman NJ, Tenta R, Cariou B, Wargny
M, et al: Lipocalin-2 counteracts metabolic dysregulation in
obesity and diabetes. J Exp Med. 217:e201912612020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Catalán V, Gómez-Ambrosi J, Rodríguez A,
Ramírez B, Silva C, Rotellar F, Gil MJ, Cienfuegos JA, Salvador J
and Frühbeck G: Increased adipose tissue expression of lipocalin-2
in obesity is related to inflammation and matrix
metalloproteinase-2 and metalloproteinase-9 activities in humans. J
Mol Med (Berl). 87:803–813. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Flo TH, Smith KD, Sato S, Rodriguez DJ,
Holmes MA, Strong RK, Akira S and Aderem A: Lipocalin 2 mediates an
innate immune response to bacterial infection by sequestrating
iron. Nature. 432:917–921. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang Y, Lam KS, Kraegen EW, Sweeney G,
Zhang J, Tso AW, Chow WS, Wat NM, Xu JY, Hoo RL and Xu A:
Lipocalin-2 is an inflammatory marker closely associated with
obesity, insulin resistance, and hyperglycemia in humans. Clin
Chem. 53:34–41. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Jang Y, Lee JH, Wang Y and Sweeney G:
Emerging clinical and experimental evidence for the role of
lipocalin-2 in metabolic syndrome. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol.
39:194–199. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wu G, Li H, Zhou M, Fang Q, Bao Y, Xu A
and Jia W: Mechanism and clinical evidence of lipocalin-2 and
adipocyte fatty acid-binding protein linking obesity and
atherosclerosis. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 30:447–456. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Abella V, Scotece M, Conde J, Gómez R,
Lois A, Pino J, Gómez-Reino JJ, Lago F, Mobasheri A and Gualillo O:
The potential of lipocalin-2/NGAL as biomarker for inflammatory and
metabolic diseases. Biomarkers. 20:565–571. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Schanze N, Hamad MA, Nührenberg TG, Bode C
and Duerschmied D: Platelets in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion
injury. Hamostaseologie. 43:110–121. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chen Y, Fu W, Zheng Y, Yang J, Liu Y, Qi
Z, Wu M, Fan Z, Yin K, Chen Y, et al: Galectin 3 enhances platelet
aggregation and thrombosis via Dectin-1 activation: A translational
study. Eur Heart J. 43:3556–3574. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chen J, Liu G, Hong Y, Han J, Yang Z, Yang
Y, Li H, Wang S, Jue L and Wang Q: Regulation of atherosclerosis by
toll-like receptor 4 induced by serum amyloid 1: A systematic in
vitro study. Biomed Res Int. 2022:48875932022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Anfossi G, Russo I and Trovati M: Platelet
dysfunction in central obesity. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis.
19:440–449. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Santilli F, Vazzana N, Liani R, Guagnano
MT and Davì G: Platelet activation in obesity and metabolic
syndrome. Obes Rev. 13:27–42. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Barale C and Russo I: Influence of
cardiometabolic risk factors on platelet function. Int J Mol Sci.
21:6232020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Mauler M, Herr N, Schoenichen C, Witsch T,
Marchini T, Härdtner C, Koentges C, Kienle K, Ollivier V, Schell M,
et al: Platelet serotonin aggravates myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion injury via neutrophil degranulation.
Circulation. 139:918–931. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Davidson SM, Andreadou I, Barile L,
Birnbaum Y, Cabrera-Fuentes HA, Cohen MV, Downey JM, Girao H,
Pagliaro P, Penna C, et al: Circulating blood cells and
extracellular vesicles in acute cardioprotection. Cardiovasc Res.
115:1156–1166. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Gumiężna K, Baruś P, Sygitowicz G,
Wiśniewska A, Ochijewicz D, Pasierb K, Klimczak-Tomaniak D,
Kuca-Warnawin E, Kochman J, Grabowski M, et al: Immature platelet
fraction in cardiovascular diagnostics and antiplatelet therapy
monitoring. Cardiol J. 30:817–824. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Margraf A and Zarbock A: Platelets in
inflammation and resolution. J Immunol. 203:2357–2367. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Huilcaman R, Venturini W, Fuenzalida L,
Cayo A, Segovia R, Valenzuela C, Brown N and Moore-Carrasco R:
Platelets, a key cell in inflammation and atherosclerosis
progression. Cells. 11:10142022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Shao S, Cao T, Jin L, Li B, Fang H, Zhang
J, Zhang Y, Hu J and Wang G: Increased lipocalin-2 contributes to
the pathogenesis of psoriasis by modulating neutrophil chemotaxis
and cytokine secretion. J Invest Dermatol. 136:1418–1428. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Jang HM, Lee JY, An HS, Ahn YJ, Jeong EA,
Shin HJ, Kim KE, Lee J, Koh JS and Roh GS: LCN2 deficiency
ameliorates doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy in mice. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 588:8–14. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Li D, Yang Z, Gao S, Zhang H and Fan G:
Tanshinone IIA ameliorates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury
in rats by regulation of NLRP3 inflammasome activation and Th17
cells differentiation. Acta Cir Bras. 37:e3707012022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hau CS, Kanda N, Tada Y, Shibata S, Uozaki
H, Fukusato T, Sato S and Watanabe S: Lipocalin-2 exacerbates
psoriasiform skin inflammation by augmenting T-helper 17 response.
J Dermatol. 43:785–794. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Chen PC, Ho CH, Fan CK, Liu SP and Cheng
PC: Antimicrobial peptide LCN2 inhibited uropathogenic escherichia
coli infection in bladder cells in a high-glucose environment
through JAK/STAT signaling pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 23:157632022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kim SL, Shin MW, Seo SY and Kim SW:
Lipocalin 2 potentially contributes to tumorigenesis from colitis
via IL-6/STAT3/NF-κB signaling pathway. Biosci Rep.
42:BSR202124182022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|