|
1
|
Reed J, Bain S and Kanamarlapudi V: A
review of current trends with type 2 diabetes epidemiology,
aetiology, pathogenesis, treatments and future perspectives.
Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes Targets Ther. 14:3567–3602. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ramanujam CL and Zgonis T: Salvage of
Charcot foot neuropathy superimposed with osteomyelitis: A case
report. J Wound Care. 19:pp. 485–487. 2010, View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Armstrong DG, Boulton AJM and Bus SA:
Diabetic Foot Ulcers and Their Recurrence. N Engl J Med.
376:2367–2375. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Louiselle AE, Niemiec SM, Zgheib C and
Liechty KW: Macrophage polarization and diabetic wound healing.
Transl Res J Lab Clin Med. 236:109–116. 2021.
|
|
5
|
den Dekker A, Davis FM, Kunkel SL and
Gallagher KA: Targeting epigenetic mechanisms in diabetic wound
healing. Transl Res J Lab Clin Med. 204:39–50. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wynn TA, Chawla A and Pollard JW:
Macrophage biology in development, homeostasis and disease. Nature.
496:445–455. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gordon S, Plüddemann A and Martinez
Estrada F: Macrophage heterogeneity in tissues: Phenotypic
diversity and functions. Immunol Rev. 262:36–55. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
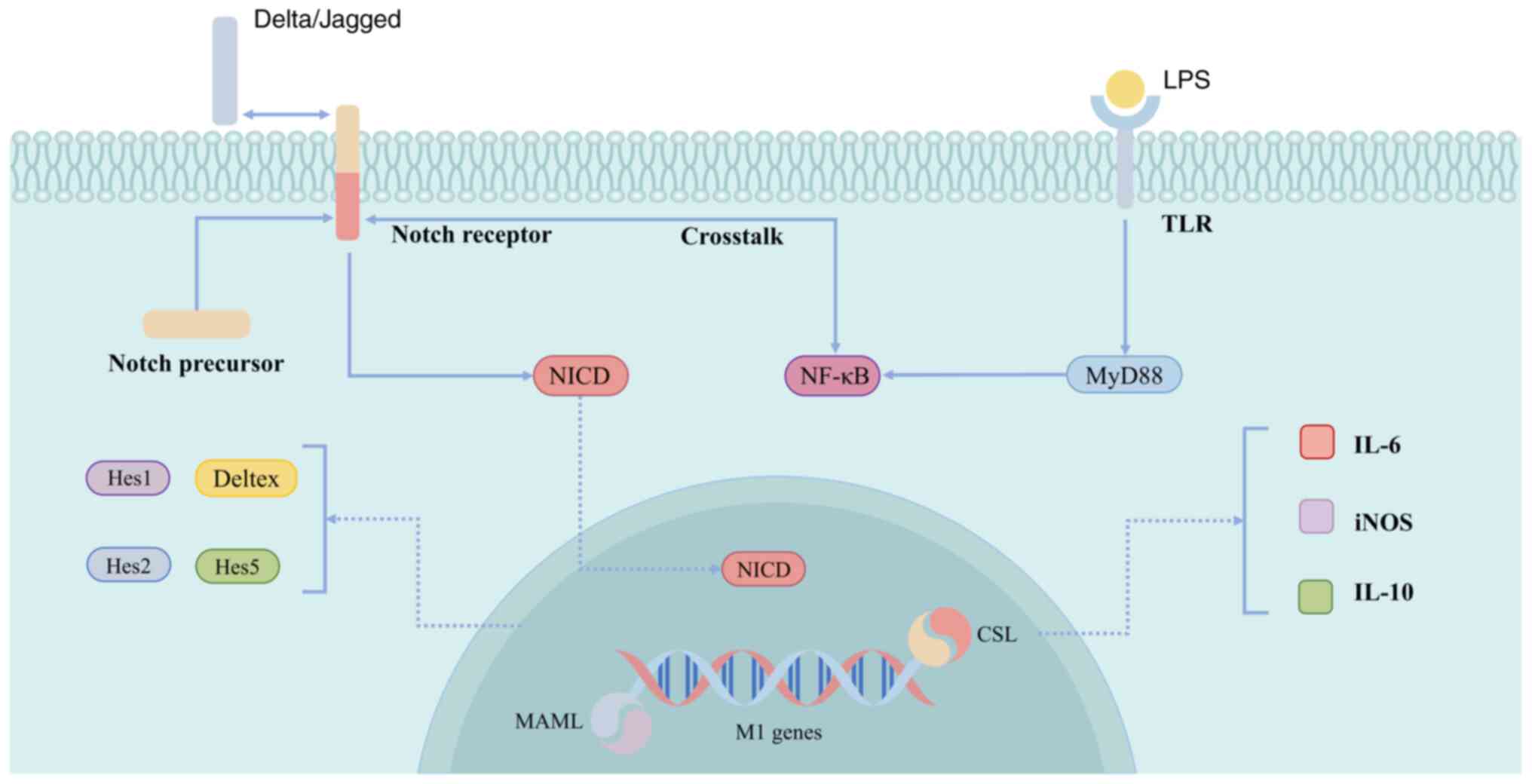
|
Mantovani A, Biswas SK, Galdiero MR, Sica
A and Locati M: Macrophage plasticity and polarization in tissue
repair and remodelling. J Pathol. 229:176–185. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mahdavian Delavary B, van der Veer WM, van
Egmond M, Niessen FB and Beelen RHJ: Macrophages in skin injury and
repair. Immunobiology. 216:753–762. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wen JH, Li DY, Liang S, Yang C, Tang JX
and Liu HF: Macrophage autophagy in macrophage polarization,
chronic inflammation and organ fibrosis. Front Immunol.
13:9468322022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Xie D and Ouyang S: The role and
mechanisms of macrophage polarization and hepatocyte pyroptosis in
acute liver failure. Front Immunol. 14:12792642023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shapouri-Moghaddam A, Mohammadian S,
Vazini H, Taghadosi M, Esmaeili SA, Mardani F, Seifi B, Mohammadi
A, Afshari JT and Sahebkar A: Macrophage plasticity, polarization,
and function in health and disease. J Cell Physiol. 233:6425–6440.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kelly B and O'Neill LA: Metabolic
reprogramming in macrophages and dendritic cells in innate
immunity. Cell Res. 25:771–784. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Martin KE and García AJ: Macrophage
phenotypes in tissue repair and the foreign body response:
Implications for biomaterial-based regenerative medicine
strategies. Acta Biomater. 133:4–16. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kolliniati O, Ieronymaki E, Vergadi E and
Tsatsanis C: Metabolic regulation of macrophage activation. J
Innate Immun. 14:51–68. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gordon S and Martinez FO: Alternative
activation of macrophages: Mechanism and functions. Immunity.
32:593–604. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Mills CD and Ley K: M1 and M2 Macrophages:
The chicken and the egg of immunity. J Innate Immun. 6:716–726.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Orecchioni M, Ghosheh Y, Pramod AB and Ley
K: Macrophage Polarization: Different Gene Signatures in M1(LPS+)
vs. Classically and M2(LPS-) vs. Alternatively Activated
Macrophages. Front Immunol. 10:10842019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wynn TA and Vannella KM: Macrophages in
tissue repair, regeneration, and fibrosis. Immunity. 44:450–462.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mantovani A, Sica A, Sozzani S, Allavena
P, Vecchi A and Locati M: The chemokine system in diverse forms of
macrophage activation and polarization. Trends Immunol. 25:677–686.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
De Paoli F, Staels B and Chinetti-Gbaguidi
G: Macrophage phenotypes and their modulation in atherosclerosis.
Circ J. 78:1775–1781. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang L, Zhang S, Wu H, Rong X and Guo J:
M2b macrophage polarization and its roles in diseases. J Leukoc
Biol. 106:345–358. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Mosser DM and Edwards JP: Exploring the
full spectrum of macrophage activation. Nat Rev Immunol. 8:958–969.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Matsui H, Sopko NA, Hannan JL, Reinhardt
AA, Kates M, Yoshida T, Liu X, Castiglione F, Hedlund P, Weyne E,
et al: M1 macrophages are predominantly recruited to the major
pelvic ganglion of the rat following cavernous nerve injury. J Sex
Med. 14:187–195. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yue Y, Yang X, Feng K, Wang L, Hou J, Mei
B, Qin H, Liang M, Chen G and Wu Z: M2b macrophages reduce early
reperfusion injury after myocardial ischemia in mice: A predominant
role of inhibiting apoptosis via A20. Int J Cardiol. 245:228–235.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lefèvre L, Lugo-Villarino G, Meunier E,
Valentin A, Olagnier D, Authier H, Duval C, Dardenne C, Bernad J,
Lemesre JL, et al: The C-type lectin receptors dectin-1, MR, and
SIGNR3 contribute both positively and negatively to the macrophage
response to Leishmania infantum. Immunity. 38:1038–1049. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zizzo G, Hilliard BA, Monestier M and
Cohen PL: Efficient clearance of early apoptotic cells by human
macrophages requires ‘M2c’ polarization and MerTK induction. J
Immunol. 189:3508–3520. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Martinez FO, Sica A, Mantovani A and
Locati M: Macrophage activation and polarization. Front Biosci J
Virtual Libr. 13:453–461. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
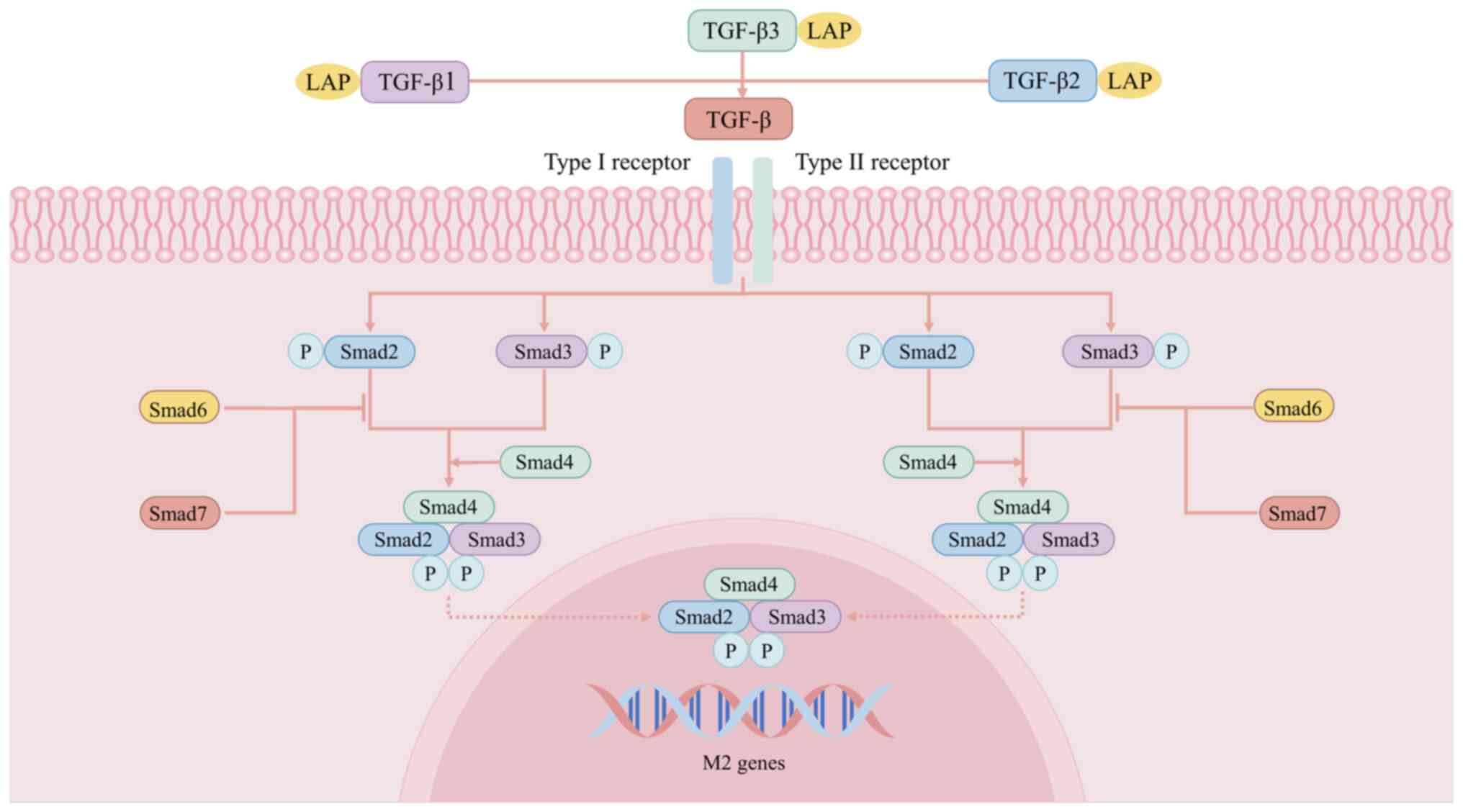
|
|
29
|
Yang Z, Lin S, Feng W, Liu Y, Song Z, Pan
G, Zhang Y, Dai X, Ding X, Chen L and Wang Y: A potential
therapeutic target in traditional Chinese medicine for ulcerative
colitis: Macrophage polarization. Front Pharmacol. 13:9991792022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Nikovics K, Morin H, Riccobono D,
Bendahmane A and Favier AL: Hybridization-chain-reaction is a
relevant method for in situ detection of M2d-like macrophages in a
mini-pig model. FASEB J. 34:15675–15686. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Atri C, Guerfali FZ and Laouini D: Role of
human macrophage polarization in inflammation during infectious
diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 19:18012018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang Q, Ni H, Lan L, Wei X, Xiang R and
Wang Y: Fra-1 protooncogene regulates IL-6 expression in
macrophages and promotes the generation of M2d macrophages. Cell
Res. 20:701–712. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Frantz C, Stewart KM and Weaver VM: The
extracellular matrix at a glance. J Cell Sci. 123((Pt 24)):
4195–4200. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Semenza GL: Hypoxia-inducible factors in
physiology and medicine. Cell. 148:399–408. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wallace HA, Basehore BM and Zito PM: Wound
Healing Phases. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; Treasure Island
(FL): 2023
|
|
36
|
Huang CJ, Pu CM, Su SY, Lo SL, Lee CH and
Yen YH: Improvement of wound healing by capsaicin through
suppression of the inflammatory response and amelioration of the
repair process. Mol Med Rep. 28:1552023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Furie B and Furie BC: Mechanisms of
Thrombus Formation. N Engl J Med. 359:938–949. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Goto S: Blood constitution: platelet
aggregation, bleeding, and involvement of leukocytes. Rev Neurol
Dis. 5 (Suppl 1):S22–S27. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Guo S and Dipietro LA: Factors affecting
wound healing. J Dent Res. 89:219–229. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Rodrigues M, Kosaric N, Bonham CA and
Gurtner GC: Wound Healing: A cellular perspective. Physiol Rev.
99:665–706. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ding JY, Chen MJ, Wu LF, Shu GF, Fang SJ,
Li ZY, Chu XR, Li XK, Wang ZG and Ji JS: Mesenchymal stem
cell-derived extracellular vesicles in skin wound healing: Roles,
opportunities and challenges. Mil Med Res. 10:362023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wu X, He W, Mu X, Liu Y, Deng J, Liu Y and
Nie X: Macrophage polarization in diabetic wound healing. Burns
Trauma. 10:tkac0512022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Pastar I, Marjanovic J, Stone RC, Chen V,
Burgess JL, Mervis JS and Tomic-Canic M: Epigenetic regulation of
cellular functions in wound healing. Exp Dermatol. 30:1073–1089.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Rawat K and Shrivastava A: Neutrophils as
emerging protagonists and targets in chronic inflammatory diseases.
Inflamm Res. 71:1477–1488. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Li M, Hou Q, Zhong L, Zhao Y and Fu X:
Macrophage Related Chronic Inflammation in Non-Healing Wounds.
Front Immunol. 12:6817102021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Fortingo N, Melnyk S, Sutton SH, Watsky MA
and Bollag WB: Innate immune system activation, inflammation and
corneal wound healing. Int J Mol Sci. 23:149332022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Portou MJ, Baker D, Abraham D and Tsui J:
The innate immune system, toll-like receptors and dermal wound
healing: A review. Vascul Pharmacol. 71:31–36. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Landén NX, Li D and Ståhle M: Transition
from inflammation to proliferation: A critical step during wound
healing. Cell Mol Life Sci. 73:3861–3885. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Kotwal GJ and Chien S: Macrophage
differentiation in normal and accelerated wound healing. Results
Probl Cell Differ. 62:353–364. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Yu H, Xiong J, Qiu J, He X, Sheng H, Dai
Q, Li D, Xin R, Jiang L, Li Q, et al: Type III Secretion Protein,
PcrV, Impairs Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilm Formation by
Increasing M1 Macrophage-Mediated Anti-bacterial Activities. Front
Microbiol. 11:19712020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Won YW, Patel AN and Bull DA: Cell surface
engineering to enhance mesenchymal stem cell migration toward an
SDF-1 gradient. Biomaterials. 35:5627–5635. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Yao Y, Xu XH and Jin L: Macrophage
polarization in physiological and pathological pregnancy. Front
Immunol. 10:7922019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Keewan E and Naser SA: The role of notch
signaling in macrophages during inflammation and infection:
Implication in rheumatoid arthritis? Cells. 9:1112020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Delgado AV, McManus AT and Chambers JP:
Production of tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin 1-beta,
interleukin 2, and interleukin 6 by rat leukocyte subpopulations
after exposure to substance P. Neuropeptides. 37:355–361. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Andreou I, Sun X, Stone PH, Edelman ER and
Feinberg MW: miRNAs in atherosclerotic plaque initiation,
progression, and rupture. Trends Mol Med. 21:307–318. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Deng JY, Wu XQ, He WJ, Liao X, Tang M and
Nie XQ: Targeting DNA methylation and demethylation in diabetic
foot ulcers. J Adv Res. 54:119–131. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Abbasi S, Sinha S, Labit E, Rosin NL, Yoon
G, Rahmani W, Jaffer A, Sharma N, Hagner A, Shah P, et al: Distinct
regulatory programs control the latent regenerative potential of
dermal fibroblasts during wound healing. Cell Stem Cell.
28:581–583. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Foster DS, Januszyk M, Yost KE, Chinta MS,
Gulati GS, Nguyen AT, Burcham AR, Salhotra A, Ransom RC, Henn D, et
al: Integrated spatial multiomics reveals fibroblast fate during
tissue repair. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 118:e21100251182021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Cai F, Wang P, Chen W, Zhao R and Liu Y:
The physiological phenomenon and regulation of macrophage
polarization in diabetic wound. Mol Biol Rep. 50:9469–9477. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Krzyszczyk P, Schloss R, Palmer A and
Berthiaume F: The role of macrophages in acute and chronic wound
healing and interventions to promote pro-wound healing phenotypes.
Front Physiol. 9:4192018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Vannella KM and Wynn TA: Mechanisms of
organ injury and repair by macrophages. Annu Rev Physiol.
79:593–617. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Boniakowski AE, Kimball AS, Jacobs BN,
Kunkel SL and Gallagher KA: Macrophage-Mediated Inflammation in
normal and diabetic wound healing. J Immunol. 199:17–24. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Lurier EB, Dalton D, Dampier W, Raman P,
Nassiri S, Ferraro NM, Rajagopalan R, Sarmady M and Spiller KL:
Transcriptome analysis of IL-10-stimulated (M2c) macrophages by
next-generation sequencing. Immunobiology. 222:847–856. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Jetten N, Verbruggen S, Gijbels MJ, Post
MJ, De Winther MPJ and Donners MM: Anti-inflammatory M2, but not
pro-inflammatory M1 macrophages promote angiogenesis in vivo.
Angiogenesis. 17:109–118. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Lolmede K, Campana L, Vezzoli M, Bosurgi
L, Tonlorenzi R, Clementi E, Bianchi ME, Cossu G, Manfredi AA,
Brunelli S and Rovere-Querini P: Inflammatory and alternatively
activated human macrophages attract vessel-associated stem cells,
relying on separate HMGB1- and MMP-9-dependent pathways. J Leukoc
Biol. 85:779–787. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
El Ayadi A, Jay JW and Prasai A: Current
approaches targeting the wound healing phases to attenuate fibrosis
and scarring. Int J Mol Sci. 21:11052020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Gosain A and DiPietro LA: Aging and wound
healing. World J Surg. 28:321–326. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Cui N, Hu M and Khalil RA: Biochemical and
biological attributes of matrix metalloproteinases. Prog Mol Biol
Transl Sci. 147:1–73. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Ogle ME, Segar CE, Sridhar S and Botchwey
EA: Monocytes and macrophages in tissue repair: Implications for
immunoregenerative biomaterial design. Exp Biol Med (Maywood).
241:1084–1097. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Madsen DH, Leonard D, Masedunskas A, Moyer
A, Jürgensen HJ, Peters DE, Amornphimoltham P, Selvaraj A, Yamada
SS, Brenner DA, et al: M2-like macrophages are responsible for
collagen degradation through a mannose receptor-mediated pathway. J
Cell Biol. 202:951–966. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Kimball A, Schaller M, Joshi A, Davis FM,
denDekker A, Boniakowski A, Bermick J, Obi A, Moore B, Henke PK, et
al: Ly6CHi blood monocyte/macrophage drive chronic inflammation and
impair wound healing in diabetes mellitus. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc
Biol. 38:1102–1114. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Barman PK, Urao N and Koh TJ: Diabetes
induces myeloid bias in bone marrow progenitors associated with
enhanced wound macrophage accumulation and impaired healing. J
Pathol. 249:435–446. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Dasu MR, Thangappan RK, Bourgette A,
DiPietro LA, Isseroff R and Jialal I: TLR2 expression and
signaling-dependent inflammation impair wound healing in diabetic
mice. Lab Investig J Tech Methods Pathol. 90:1628–1636. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Davis FM, denDekker A, Kimball A, Joshi
AD, El Azzouny M, Wolf SJ, Obi AT, Lipinski J, Gudjonsson JE, Xing
X, et al: Epigenetic Regulation of TLR4 in Diabetic Macrophages
Modulates Immunometabolism and Wound Repair. J Immunol.
204:2503–2513. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Dasu MR and Martin SJ: Toll-like receptor
expression and signaling in human diabetic wounds. World J
Diabetes. 5:219–223. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Bannon P, Wood S, Restivo T, Campbell L,
Hardman MJ and Mace KA: Diabetes induces stable intrinsic changes
to myeloid cells that contribute to chronic inflammation during
wound healing in mice. Dis Model Mech. 6:1434–1447. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Mirza RE, Fang MM, Ennis WJ and Koh TJ:
Blocking interleukin-1β induces a healing-associated wound
macrophage phenotype and improves healing in type 2 diabetes.
Diabetes. 62:2579–2587. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Gallagher KA, Joshi A, Carson WF, Schaller
M, Allen R, Mukerjee S, Kittan N, Feldman EL, Henke PK, Hogaboam C,
et al: Epigenetic changes in bone marrow progenitor cells influence
the inflammatory phenotype and alter wound healing in type 2
diabetes. Diabetes. 64:1420–1430. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Lin CW, Hung CM, Chen WJ, Chen JC, Huang
WY, Lu CS, Kuo ML and Chen SG: New horizons of macrophage
immunomodulation in the healing of diabetic foot ulcers.
Pharmaceutics. 14:20652022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Gu XY, Shen SE, Huang CF, Liu YN, Chen YC,
Luo L, Zeng Y and Wang AP: Effect of activated autologous
monocytes/macrophages on wound healing in a rodent model of
experimental diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 102:53–59. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Chen C, Liu T, Tang Y, Luo G, Liang G and
He W: Epigenetic regulation of macrophage polarization in wound
healing. Burns Trauma. 11:tkac0572023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Pradhan L, Cai X, Wu S, Andersen ND,
Martin M, Malek J, Guthrie P, Veves A and Logerfo FW: Gene
expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and neuropeptides in
diabetic wound healing. J Surg Res. 167:336–342. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Theocharidis G and Veves A: Autonomic
nerve dysfunction and impaired diabetic wound healing; the role of
neuropeptides. Auton Neurosci Basic Clin. 223:1026102020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Lu YZ, Nayer B, Singh SK, Alshoubaki YK,
Yuan E, Park AJ, Maruyama K, Akira S and Martino MM: CGRP sensory
neurons promote tissue healing via neutrophils and macrophages.
Nature. 628:604–611. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Kim H, Wang SY, Kwak G, Yang Y, Kwon IC
and Kim SH: Exosome-Guided Phenotypic Switch of M1 to M2
Macrophages for Cutaneous Wound Healing. Adv Sci (Weinh).
6:19005132019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Spampinato SF, Caruso GI, De Pasquale R,
Sortino MA and Merlo S: The treatment of impaired wound healing in
diabetes: looking among old drugs. Pharm (Basel). 13:602020.
|
|
87
|
Mirza R and Koh TJ: Dysregulation of
monocyte/macrophage phenotype in wounds of diabetic mice. Cytokine.
56:256–264. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Gurevich DB, Severn CE, Twomey C,
Greenhough A, Cash J, Toye AM, Mellor H and Martin P: Live imaging
of wound angiogenesis reveals macrophage orchestrated vessel
sprouting and regression. EMBO J. 37:e977862018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Okonkwo UA, Chen L, Ma D, Haywood VA,
Barakat M, Urao N and DiPietro LA: Compromised angiogenesis and
vascular Integrity in impaired diabetic wound healing. PLoS One.
15:e02319622020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Al Sadoun H: Macrophage phenotypes in
normal and diabetic wound healing and therapeutic interventions.
Cells. 11:24302022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Nacev BA, Jones KB, Intlekofer AM, Yu JSE,
Allis CD, Tap WD, Ladanyi M and Nielsen TO: The epigenomics of
sarcoma. Nat Rev Cancer. 20:608–623. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Ma X, Mei S, Wuyun Q, Zhou L, Sun D and
Yan J: Epigenetics in diabetic cardiomyopathy. Clin Epigenetics.
16:522024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Ahmed M, de Winther MPJ and Van den
Bossche J: Epigenetic mechanisms of macrophage activation in type 2
diabetes. Immunobiology. 222:937–943. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Davis FM and Gallagher KA: Epigenetic
mechanisms in monocytes/macrophages regulate inflammation in
cardiometabolic and vascular disease. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc
Biol. 39:623–634. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Yassi M, Chatterjee A and Parry M:
Application of deep learning in cancer epigenetics through DNA
methylation analysis. Brief Bioinform. 24:bbad4112023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Wong WK, Yin B, Lam CYK, Huang Y, Yan J,
Tan Z and Wong SHD: The Interplay Between Epigenetic Regulation and
CD8+ T Cell Differentiation/Exhaustion for T Cell Immunotherapy.
Front Cell Dev Biol. 9:7832272022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Xu F, Mao C, Ding Y, Rui C, Wu L, Shi A,
Zhang H, Zhang L and Xu Z: Molecular and enzymatic profiles of
mammalian DNA methyltransferases: structures and targets for drugs.
Curr Med Chem. 17:4052–4071. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Rabkin SW and Wong CN: Epigenetics in
Heart Failure: Role of DNA methylation in potential pathways
leading to heart failure with preserved ejection fraction.
Biomedicines. 11:28152023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Moore LD, Le T and Fan G: DNA methylation
and its basic function. Neuropsychopharmacology. 38:23–38. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Hamidi T, Singh AK and Chen T: Genetic
alterations of DNA methylation machinery in human diseases.
Epigenomics. 7:247–265. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Vatanmakanian M, Steffan JJ, Koul S, Ochoa
AC, Chaturvedi LS and Koul HK: Regulation of SPDEF expression by
DNA methylation in advanced prostate cancer. Front Endocrinol
(Lausanne). 14:11561202023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
De Marco K, Sanese P, Simone C and Grossi
V: Histone and DNA methylation as epigenetic regulators of DNA
damage repair in gastric cancer and emerging therapeutic
opportunities. Cancers (Basel). 15:49762023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Zeng Y, Rong H, Xu J, Cao R, Li S, Gao Y,
Cheng B and Zhou T: DNA Methylation: An Important Biomarker and
Therapeutic Target for Gastric Cancer. Front Genet. 13:8239052022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Adam S, Klingel V, Radde NE, Bashtrykov P
and Jeltsch A: On the accuracy of the epigenetic copy machine:
Comprehensive specificity analysis of the DNMT1 DNA
methyltransferase. Nucleic Acids Res. 51:6622–6633. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Smith ZD and Meissner A: DNA methylation:
Roles in mammalian development. Nat Rev Genet. 14:204–220. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Topriceanu CC, Dev E, Ahmad M, Hughes R,
Shiwani H, Webber M, Direk K, Wong A, Ugander M, Moon JC, et al:
Accelerated DNA methylation age plays a role in the impact of
cardiovascular risk factors on the human heart. Clin Epigenetics.
15:1642023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Chen ZX and Riggs AD: DNA methylation and
demethylation in mammals. J Biol Chem. 286:18347–18353. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Ren L, Chang YF, Jiang SH, Li XH and Cheng
HP: DNA methylation modification in Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.
Front Cell Dev Biol. 12:14163252024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Yano N and Fedulov AV: Targeted DNA
Demethylation: Vectors, Effectors and Perspectives. Biomedicines.
11:13342023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Guo F, Li X, Liang D, Li T, Zhu P, Guo H,
Wu X, Wen L, Gu TP, Hu B, et al: Active and passive demethylation
of male and female pronuclear DNA in the mammalian zygote. Cell
Stem Cell. 15:447–459. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Ravichandran M, Jurkowska RZ and Jurkowski
TP: Target specificity of mammalian DNA methylation and
demethylation machinery. Org Biomol Chem. 16:1419–1435. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Yan J, Tie G, Wang S, Tutto A, DeMarco N,
Khair L, Fazzio TG and Messina LM: Diabetes impairs wound healing
by Dnmt1-dependent dysregulation of hematopoietic stem cells
differentiation towards macrophages. Nat Commun. 9:332018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Babu M, Durga Devi T, Mäkinen P, Kaikkonen
M, Lesch HP, Junttila S, Laiho A, Ghimire B, Gyenesei A and
Ylä-Herttuala S: Differential promoter methylation of macrophage
genes is associated with impaired vascular growth in ischemic
muscles of hyperlipidemic and type 2 diabetic Mice: Genome-Wide
Promoter Methylation Study. Circ Res. 117:289–299. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Davis FM, Tsoi LC, Wasikowski R, denDekker
A, Joshi A, Wilke C, Deng H, Wolf S, Obi A, Huang S, et al:
Epigenetic regulation of the PGE2 pathway modulates macrophage
phenotype in normal and pathologic wound repair. JCI Insight.
5:e1384432020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Park J, Lee K, Kim K and Yi SJ: The role
of histone modifications: From neurodevelopment to neurodiseases.
Signal Transduct Target Ther. 7:2172022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Li Y, Hu M, Xie J, Li S and Dai L:
Dysregulation of histone modifications in bone marrow mesenchymal
stem cells during skeletal ageing: Roles and therapeutic prospects.
Stem Cell Res Ther. 14:1662023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Fulton MD, Zhang J, He M, Ho MC and Zheng
YG: Intricate Effects of α-Amino and Lysine Modifications on
Arginine Methylation of the N-Terminal Tail of Histone H4.
Biochemistry. 56:3539–3548. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Jambhekar A, Dhall A and Shi Y: Roles and
regulation of histone methylation in animal development. Nat Rev
Mol Cell Biol. 20:625–641. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Shvedunova M and Akhtar A: Modulation of
cellular processes by histone and non-histone protein acetylation.
Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 23:329–349. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Allis CD and Jenuwein T: The molecular
hallmarks of epigenetic control. Nat Rev Genet. 17:487–500. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Zhu W, Liu L, Wu J, Gao R, Fu L, Yang X,
Zou Y, Zhang S and Luo D: SMYD3 activates the TCA cycle to promote
M1-M2 conversion in macrophages. Int Immunopharmacol.
127:1113292024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Chi G, Pei JH and Li XQ: EZH2-mediated
H3K27me3 promotes autoimmune hepatitis progression by regulating
macrophage polarization. Int Immunopharmacol. 106:1086122022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Schaller MA: MLL1 is central to
macrophage-mediated inflammation. Blood. 141:687–689. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Kimball AS, Joshi A, Carson WF IV,
Boniakowski AE, Schaller M, Allen R, Bermick J, Davis FM, Henke PK,
Burant CF, et al: The Histone Methyltransferase MLL1 directs
macrophage-mediated inflammation in wound healing and is altered in
a murine model of obesity and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes.
66:2459–2471. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Schliehe C, Flynn EK, Vilagos B, et al:
The methyltransferase Setdb2 mediates virus-induced susceptibility
to bacterial superinfection. Nat Immunol. 16:67–74. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Kimball AS, Davis FM, denDekker A, Joshi
AD, Schaller MA, Bermick J, Xing X, Burant CF, Obi AT, Nysz D, et
al: The Histone Methyltransferase Setdb2 Modulates Macrophage
Phenotype and Uric Acid Production in Diabetic Wound Repair.
Immunity. 51:258–271.e5. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Davis FM, denDekker A, Joshi AD, Wolf SJ,
Audu C, Melvin WJ, Mangum K, Riordan MO, Kunkel SL and Gallagher
KA: Palmitate-TLR4 signaling regulates the histone demethylase,
JMJD3, in macrophages and impairs diabetic wound healing. Eur J
Immunol. 50:1929–1940. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Taipale M, Rea S, Richter K, Vilar A,
Lichter P, Imhof A and Akhtar A: hMOF histone acetyltransferase is
required for histone H4 lysine 16 acetylation in mammalian cells.
Mol Cell Biol. 25:6798–6810. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
129
|
Rea S, Xouri G and Akhtar A: Males absent
on the first (MOF): From flies to humans. Oncogene. 26:5385–5394.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
denDekker AD, Davis FM, Joshi AD, Wolf SJ,
Allen R, Lipinski J, Nguyen B, Kirma J, Nycz D, Bermick J, et al:
TNF-α regulates diabetic macrophage function through the histone
acetyltransferase MOF. JCI Insight. 5:e1323062020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Mullican SE, Gaddis CA, Alenghat T, Nair
MG, Giacomin PR, Everett LJ, Feng D, Steger DJ, Schug J, Artis D
and Lazar MA: Histone deacetylase 3 is an epigenomic brake in
macrophage alternative activation. Genes Dev. 25:2480–2488. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
132
|
Shakespear MR, Halili MA, Irvine KM,
Fairlie DP and Sweet MJ: Histone deacetylases as regulators of
inflammation and immunity. Trends Immunol. 32:335–343. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Chen X, Barozzi I, Termanini A, Prosperini
E, Recchiuti A, Dalli J, Mietton F, Matteoli G, Hiebert S and
Natoli G: Requirement for the histone deacetylase Hdac3 for the
inflammatory gene expression program in macrophages. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 109:E2865–E2874. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Teena R, Dhamodharan U, Ali D, Rajesh K
and Ramkumar KM: Gene expression profiling of multiple histone
deacetylases (HDAC) and Its Correlation with NRF2-Mediated redox
regulation in the pathogenesis of diabetic foot ulcers.
Biomolecules. 10:14662020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Cabanel M, da Costa TP, El-Cheikh MC and
Carneiro K: The epigenome as a putative target for skin repair: the
HDAC inhibitor Trichostatin A modulates myeloid progenitor
plasticity and behavior and improves wound healing. J Transl Med.
17:2472019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
136
|
Karnam K, Sedmaki K, Sharma P, Mahale A,
Ghosh B and Kulkarni OP: Pharmacological blockade of HDAC3
accelerates diabetic wound healing by regulating macrophage
activation. Life Sci. 321:1215742023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
137
|
Djebali S, Davis CA, Merkel A, Dobin A,
Lassmann T, Mortazavi A, Tanzer A, Lagarde J, Lin W, Schlesinger F,
et al: Landscape of transcription in human cells. Nature.
489:101–108. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Tang YB, Uwimana MMP, Zhu SQ, Zhang LX, Wu
Q and Liang ZX: Non-coding RNAs: Role in diabetic foot and wound
healing. World J Diabetes. 13:1001–1013. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Maciak P, Suder A, Wadas J, Aronimo F,
Maiuri P, Bochenek M, Pyrc K, Kula-Pacurar A and Pabis M: Dynamic
changes in LINC00458/HBL1 lncRNA expression during hiPSC
differentiation to cardiomyocytes. Sci Rep. 14:1092024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
140
|
Zhang P, Wu S, He Y, Li X, Zhu Y, Lin X,
Chen L, Zhao Y, Niu L, Zhang S, et al: LncRNA-Mediated adipogenesis
in different adipocytes. Int J Mol Sci. 23:74882022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Zaki A, Ali MS, Hadda V, Ali SM, Chopra A
and Fatma T: Long non-coding RNA (lncRNA): A potential therapeutic
target in acute lung injury. Genes Dis. 9:1258–1268. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
142
|
Hussein RM: Long non-coding RNAs: The
hidden players in diabetes mellitus-related complications. Diabetes
Metab Syndr. 17:1028722023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Hu J, Zhang L, Liechty C, Zgheib C, Hodges
MM, Liechty KW and Xu J: Long Noncoding RNA GAS5 regulates
macrophage polarization and diabetic wound healing. J Invest
Dermatol. 140:1629–1638. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Kuang L, Zhang C, Li B, Deng H, Chen R and
Li G: Human Keratinocyte-Derived Exosomal MALAT1 promotes diabetic
wound healing by upregulating MFGE8 via microRNA-1914-3p. Int J
Nanomedicine. 18:949–970. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Saliminejad K, Khorram Khorshid HR,
Soleymani Fard S and Ghaffari SH: An overview of microRNAs:
Biology, functions, therapeutics, and analysis methods. J Cell
Physiol. 234:5451–5465. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
146
|
Kmiołek T, Rzeszotarska E, Wajda A,
Walczuk E, Kuca-Warnawin E, Romanowska-Próchnicka K, Stypinska B,
Majewski D, Jagodzinski PP, Pawlik A and Paradowska-Gorycka A: The
Interplay between Transcriptional Factors and MicroRNAs as an
Important Factor for Th17/Treg Balance in RA Patients. Int J Mol
Sci. 21:71692020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Self-Fordham JB, Naqvi AR, Uttamani JR,
Kulkarni V and Nares S: MicroRNA: Dynamic regulators of macrophage
polarization and plasticity. Front Immunol. 8:10622017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
Pasca S, Jurj A, Petrushev B, Tomuleasa C
and Matei D: MicroRNA-155 Implication in M1 polarization and the
impact in inflammatory diseases. Front Immunol. 11:6252020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Moura J, Sørensen A, Leal EC, Svendsen R,
Carvalho L, Willemoes RJ, Jørgensen PT, Jenssen H, Wengel J,
Dalgaard LT and Carvalho E: microRNA-155 inhibition restores
Fibroblast Growth Factor 7 expression in diabetic skin and
decreases wound inflammation. Sci Rep. 9:58362019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Ye J, Kang Y, Sun X, Ni P, Wu M and Lu S:
MicroRNA-155 inhibition promoted wound healing in diabetic rats.
Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 16:74–84. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
Peng X, He F, Mao Y, Lin Y, Fang J, Chen
Y, Sun Z, Zhuo Y and Jiang J: miR-146a promotes M2 macrophage
polarization and accelerates diabetic wound healing by inhibiting
the TLR4/NF-κB axis. J Mol Endocrinol. 69:315–327. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
152
|
Hao Y, Yang L, Liu Y, Ye Y, Wang J, Yu C,
Yan H, Xing Y, Jia Z, Hu C, et al: mmu-miR-145a-5p accelerates
diabetic wound healing by promoting macrophage polarization toward
the M2 Phenotype. Front Med. 8:7755232021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
153
|
Liechty C, Hu J, Zhang L, Liechty KW and
Xu J: Role of microRNA-21 and its underlying mechanisms in
inflammatory responses in diabetic wounds. Int J Mol Sci.
21:33282020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
154
|
Meng Z, Zhou D, Gao Y, Zeng M and Wang W:
miRNA delivery for skin wound healing. Adv Drug Deliv Rev.
129:308–318. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Boca S, Gulei D, Zimta AA, Onaciu A, Magdo
L, Tigu AB, Ionescu C, Irimie A, Buiga R and Berindan-Neagoe I:
Nanoscale delivery systems for microRNAs in cancer therapy. Cell
Mol Life Sci. 77:1059–1086. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
Tang XH, Guo T, Gao XY, Wu XL, Xing XF, Ji
JF and Li ZY: Exosome-derived noncoding RNAs in gastric cancer:
functions and clinical applications. Mol Cancer. 20:992021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
Yang Q, Luo Y, Ge P, Lan B, Liu J, Wen H,
Cao Y, Sun Z, Zhang G, Yuan H, et al: Emodin ameliorates severe
acute pancreatitis-associated acute lung injury in rats by
modulating exosome-specific miRNA Expression Profiles. Int J
Nanomedicine. 18:6743–6761. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
158
|
Ye H, Wang F, Xu G, Shu F, Fan K and Wang
D: Advancements in engineered exosomes for wound repair: Current
research and future perspectives. Front Bioeng Biotechnol.
11:13013622023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
159
|
Khalaj K, Figueira RL, Antounians L,
Lauriti G and Zani A: Systematic review of extracellular
vesicle-based treatments for lung injury: are EVs a potential
therapy for COVID-19? J Extracell Vesicles. 9:17953652020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
160
|
Zhao H, Shang Q, Pan Z, Bai Y, Li Z, Zhang
H, Zhang Q, Guo C, Zhang L and Wang Q: Exosomes from
adipose-derived stem cells attenuate adipose inflammation and
obesity through polarizing M2 macrophages and beiging in white
adipose tissue. Diabetes. 67:235–247. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
161
|
Xia W, Liu Y, Jiang X, Li M, Zheng S,
Zhang Z, Huang X, Luo S, Khoong Y, Hou M and Zan T: Lean adipose
tissue macrophage derived exosome confers immunoregulation to
improve wound healing in diabetes. J Nanobiotechnology. 21:1282023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Blanpain C and Fuchs E: Epidermal stem
cells of the skin. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 22:339–373. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
163
|
Ma T, Zhao Y, Shen G, Chai B, Wang W, Li
X, Zhang Z and Meng Q: Novel bilayer cell patch combining epidermal
stem cells and angiogenic adipose stem cells for diabetic wound
healing. J Control Release. 359:315–325. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
164
|
Yang RH, Qi SH, Shu B, Ruan SB, Lin ZP,
Lin Y, Shen R, Zhang FG, Chen XD and Xie JL: Epidermal stem cells
(ESCs) accelerate diabetic wound healing via the Notch signalling
pathway. Biosci Rep. 36:e003642016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
165
|
Xu H, Yang H, Wang Z, Tang Q, Cao X, Chen
C, Dong Y, Xu Z, Lv D, Rong Y, et al: Epidermal stem cell derived
exosomes alleviate excessive autophagy induced endothelial cell
apoptosis by delivering miR200b-3p to Diabetic Wounds. J Invest
Dermatol. 144:1134–1147.e2. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
166
|
Yang H, Xu H, Wang Z, Li X, Wang P, Cao X,
Xu Z, Lv D, Rong Y, Chen M, et al: Analysis of
miR-203a-3p/SOCS3-mediated induction of M2 macrophage polarization
to promote diabetic wound healing based on epidermal stem
cell-derived exosomes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 197:1105732023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
167
|
Hassan WU, Greiser U and Wang W: Role of
adipose-derived stem cells in wound healing. Wound Repair Regen.
22:313–325. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
168
|
Markov A, Thangavelu L, Aravindhan S,
Zekiy AO, Jarahian M, Chartrand MS, Pathak Y, Marofi F, Shamlou S
and Hassanzadeh A: Mesenchymal stem/stromal cells as a valuable
source for the treatment of immune-mediated disorders. Stem Cell
Res Ther. 12:1922021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
169
|
Zou JP, Huang S, Peng Y, Liu HW, Cheng B,
Fu XB and Xiang XF: Mesenchymal stem cells/multipotent mesenchymal
stromal cells (MSCs): Potential role in healing cutaneous chronic
wounds. Int J Low Extrem Wounds. 11:244–253. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
170
|
Mahjoor M, Fakouri A, Farokhi S, Nazari H,
Afkhami H and Heidari F: Regenerative potential of mesenchymal
stromal cells in wound healing: Unveiling the influence of normoxic
and hypoxic environments. Front Cell Dev Biol. 11:12458722023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
171
|
Ti D, Hao H, Tong C, Liu J, Dong L, Zheng
J, Zhao Y, Liu H, Fu X and Han W: LPS-preconditioned mesenchymal
stromal cells modify macrophage polarization for resolution of
chronic inflammation via exosome-shuttled let-7b. J Transl Med.
13:3082015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
172
|
Shi Y, Wang S, Zhang W, Zhu Y, Fan Z,
Huang Y, Li F and Yang R: Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
facilitate diabetic wound healing through the restoration of
epidermal cell autophagy via the HIF-1α/TGF-β1/SMAD pathway. Stem
Cell Res Ther. 13:3142022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
173
|
Li L, Chen X, Wang WE and Zeng C: How to
improve the survival of transplanted mesenchymal stem cell in
ischemic heart? Stem Cells Int. 2016:96827572016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
174
|
Zhou X, Ye C, Jiang L, Zhu X, Zhou F, Xia
M and Chen Y: The bone mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal
miR-146a-5p promotes diabetic wound healing in mice via macrophage
M1/M2 polarization. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 579:1120892024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
175
|
Sun Y, Zhou Y, Shi Y, Zhang Y, Liu K,
Liang R, Sun P, Chang X, Tang W, Zhang Y, et al: Expression of
miRNA-29 in Pancreatic β Cells Promotes Inflammation and Diabetes
via TRAF3. Cell Rep. 34:1085762021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
176
|
Zeng X, Chen B, Wang L, Sun Y, Jin Z, Liu
X, Ouyang L and Liao Y: Chitosan@Puerarin hydrogel for accelerated
wound healing in diabetic subjects by miR-29ab1 mediated
inflammatory axis suppression. Bioact Mater. 19:653–665.
2022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
177
|
Reda El Sayed S, Cristante J, Guyon L,
Denis J, Chabre O and Cherradi N: MicroRNA therapeutics in cancer:
Current advances and challenges. Cancers (Basel). 13:26802021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
178
|
Bhatnagar D, Ladhe S and Kumar D:
Discerning the Prospects of miRNAs as a Multi-Target Therapeutic
and Diagnostic for Alzheimer's Disease. Mol Neurobiol.
60:5954–5974. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
179
|
Huang S, Zhou Y, Zhang Y, Liu N, Liu J,
Liu L and Fan C: Advances in MicroRNA therapy for heart failure:
Clinical trials, preclinical studies, and controversies. Cardiovasc
Drugs Ther. Jul 28–2023.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
180
|
Amina SJ, Azam T, Dagher F and Guo B: A
review on the use of extracellular vesicles for the delivery of
drugs and biological therapeutics. Expert Opin Drug Deliv.
21:45–70. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
181
|
Yin W, Ma H, Qu Y, Wang S, Zhao R, Yang Y
and Guo ZN: Targeted exosome-based nanoplatform for new-generation
therapeutic strategies. Biomed Mater. 19:2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
182
|
Li X, Yang L and Chen LL: The biogenesis,
functions, and challenges of circular RNAs. Mol Cell. 71:428–442.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
183
|
Zhang W, He Y and Zhang Y: CircRNA in
ocular neovascular diseases: Fundamental mechanism and clinical
potential. Pharmacol Res. 197:1069462023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
184
|
Moallemi Rad L, Sadoughi MM, Nicknam A,
Colagar AH, Hussen BM, Taheri M and Ghafouri-Fard S: The impact of
non-coding RNAs in the pathobiology of eye disorders. Int J Biol
Macromol. 239:1242452023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
185
|
Titze-de-Almeida SS and Titze-de-Almeida
R: Progress in circRNA-Targeted Therapy in Experimental Parkinson's
Disease. Pharmaceutics. 15:20352023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
186
|
Liu J, Duan P, Xu C, Xu D, Liu Y and Jiang
J: CircRNA circ-ITCH improves renal inflammation and fibrosis in
streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice by regulating the
miR-33a-5p/SIRT6 axis. Inflamm Res. 70:835–846. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
187
|
Shang B, Xu T, Hu N, Mao Y and Du X:
Circ-Klhl8 overexpression increased the therapeutic effect of EPCs
in diabetic wound healing via the miR-212-3p/SIRT5 axis. J Diabetes
Complications. 35:1080202021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
188
|
Lareyre F, Clément M, Moratal C, Loyer X,
Jean-Baptiste E, Hassen-Khodja R, Chinetti G, Mallat Z and Raffort
J: Differential micro-RNA expression in diabetic patients with
abdominal aortic aneurysm. Biochimie. 162:1–7. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
189
|
Hu L, Wang J, Zhou X, Xiong Z, Zhao J, Yu
R, Huang F, Zhang H and Chen L: Exosomes derived from human adipose
mensenchymal stem cells accelerates cutaneous wound healing via
optimizing the characteristics of fibroblasts. Sci Rep.
6:329932016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
190
|
Shi R, Jin Y, Zhao S, Yuan H, Shi J and
Zhao H: Hypoxic ADSC-derived exosomes enhance wound healing in
diabetic mice via delivery of circ-Snhg11 and induction of M2-like
macrophage polarization. Biomed Pharmacother. 153:1134632022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
191
|
Li Y, Luo Q, Li Z, Wang Y, Zhu C, Li T and
Li X: Long Non-coding RNA IRAIN Inhibits VEGFA Expression via
Enhancing Its DNA methylation leading to tumor suppression in renal
carcinoma. Front Oncol. 10:10822020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
192
|
Wen J, Wu Y and Luo Q: DNA
methyltransferases-associated long non-coding RNA PRKCQ-AS1
regulate DNA methylation in myelodysplastic syndrome. Int J Lab
Hematol. Apr 28–2024.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
193
|
Sun SC: The non-canonical NF-κB pathway in
immunity and inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol. 17:545–558. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
194
|
Xia T, Fu S, Yang R, Yang K, Lei W, Yang
Y, Zhang Q, Zhao Y, Yu J, Yu L and Zhang T: Advances in the study
of macrophage polarization in inflammatory immune skin diseases. J
Inflamm (Lond). 20:332023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
195
|
Zhang Q, Lenardo MJ and Baltimore D: 30
Years of NF-κB: A blossoming of relevance to human pathobiology.
Cell. 168:37–57. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
196
|
Gao S, Mao F, Zhang B, Zhang L, Zhang X,
Wang M, Yan Y, Yang T, Zhang J, Zhu W, et al: Mouse bone
marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells induce macrophage M2
polarization through the nuclear factor-κB and signal transducer
and activator of transcription 3 pathways. Exp Biol Med (Maywood).
239:366–375. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
197
|
Deng L, Du C, Song P, Chen T, Rui S,
Armstrong DG and Deng W: The role of oxidative stress and
antioxidants in diabetic wound healing. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2021:88527592021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
198
|
Dunnill C, Patton T, Brennan J, Barrett J,
Dryden M, Cooke J, Leaper D and Georgopoulos NT: Reactive oxygen
species (ROS) and wound healing: the functional role of ROS and
emerging ROS-modulating technologies for augmentation of the
healing process. Int Wound J. 14:89–96. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
199
|
Wan L, Bai X, Zhou Q, Chen C, Wang H, Liu
T, Xue J, Wei C and Xie L: The advanced glycation end-products
(AGEs)/ROS/NLRP3 inflammasome axis contributes to delayed diabetic
corneal wound healing and nerve regeneration. Int J Biol Sci.
18:809–825. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
200
|
Kang HJ, Kumar S, D'Elia A, Dash B, Nanda
V, Hsia HC, Yarmush ML and Berthiaume F: Self-assembled
elastin-like polypeptide fusion protein coacervates as competitive
inhibitors of advanced glycation end-products enhance diabetic
wound healing. J Control Release. 333:176–187. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
201
|
O'Shea JJ, Schwartz DM, Villarino AV,
Gadina M, McInnes IB and Laurence A: The JAK-STAT pathway: impact
on human disease and therapeutic intervention. Annu Rev Med.
66:311–328. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
202
|
Liu Y, Liu Z, Tang H, Shen Y, Gong Z, Xie
N, Zhang X, Wang W, Kong W, Zhou Y and Fu Y: The N6-methyladenosine
(m6A)-forming enzyme METTL3 facilitates M1 macrophage polarization
through the methylation of STAT1 mRNA. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
317:C762–C775. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
203
|
Zhang MZ, Wang X, Wang Y, Niu A, Wang S,
Zou C and Harris RC: IL-4/IL-13-mediated polarization of renal
macrophages/dendritic cells to an M2a phenotype is essential for
recovery from acute kidney injury. Kidney Int. 91:375–386. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
204
|
Degboé Y, Rauwel B, Baron M, Boyer JF,
Ruyssen-Witrand A, Constantin A and Davignon JL: Polarization of
Rheumatoid Macrophages by TNF Targeting Through an IL-10/STAT3
Mechanism. Front Immunol. 10:32019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
205
|
Liu Y, Stewart KN, Bishop E, Marek CJ,
Kluth DC, Rees AJ and Wilson HM: Unique expression of suppressor of
cytokine signaling 3 is essential for classical macrophage
activation in rodents in vitro and in vivo. J Immunol.
180:6270–6278. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
206
|
Tsogbadrakh B, Ryu H, Ju KD, Lee J, Yun S,
Yu KS, Kim HJ, Ahn C and Oh KH: AICAR, an AMPK activator, protects
against cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury through the
JAK/STAT/SOCS pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 509:680–686.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
207
|
Feng L, Sun Y, Song P, Xu L, Wu X, Wu X,
Shen Y, Sun Y, Kong L, Wu X and Xu Q: Seselin ameliorates
inflammation via targeting Jak2 to suppress the proinflammatory
phenotype of macrophages. Br J Pharmacol. 176:317–333. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
208
|
Suzuki K, Meguro K, Nakagomi D and
Nakajima H: Roles of alternatively activated M2 macrophages in
allergic contact dermatitis. Allergol Int. 66:392–397. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
209
|
Bai JW, Wei M, Li JW and Zhang GJ: Notch
signaling pathway and endocrine resistance in breast cancer. Front
Pharmacol. 11:9242020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
210
|
Singla RD, Wang J and Singla DK:
Regulation of Notch 1 signaling in THP-1 cells enhances M2
macrophage differentiation. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
307:H1634–H1642. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
211
|
Lamouille S, Xu J and Derynck R: Molecular
mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Rev Mol Cell
Biol. 15:178–196. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
212
|
Chen G, Deng C and Li YP: TGF-β and BMP
signaling in osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. Int J
Biol Sci. 8:272–288. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
213
|
Perez LG, Kempski J, McGee HM, Pelzcar P,
Agalioti T, Giannou A, Konczalla L, Brockmann L, Wahib R, Xu H, et
al: TGF-β signaling in Th17 cells promotes IL-22 production and
colitis-associated colon cancer. Nat Commun. 11:26082020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
214
|
Wang L, Li Y, Wang X, Wang P, Essandoh K,
Cui S, Huang W, Mu X, Liu Z, Wang Y, et al: GDF3 protects mice
against sepsis-induced cardiac dysfunction and mortality by
suppression of macrophage pro-inflammatory phenotype. Cells.
9:1202020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
215
|
Louiselle AE, Niemiec SM, Zgheib C and
Liechty KW: Macrophage polarization and diabetic wound healing.
Transl Res. 236:109–116. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|