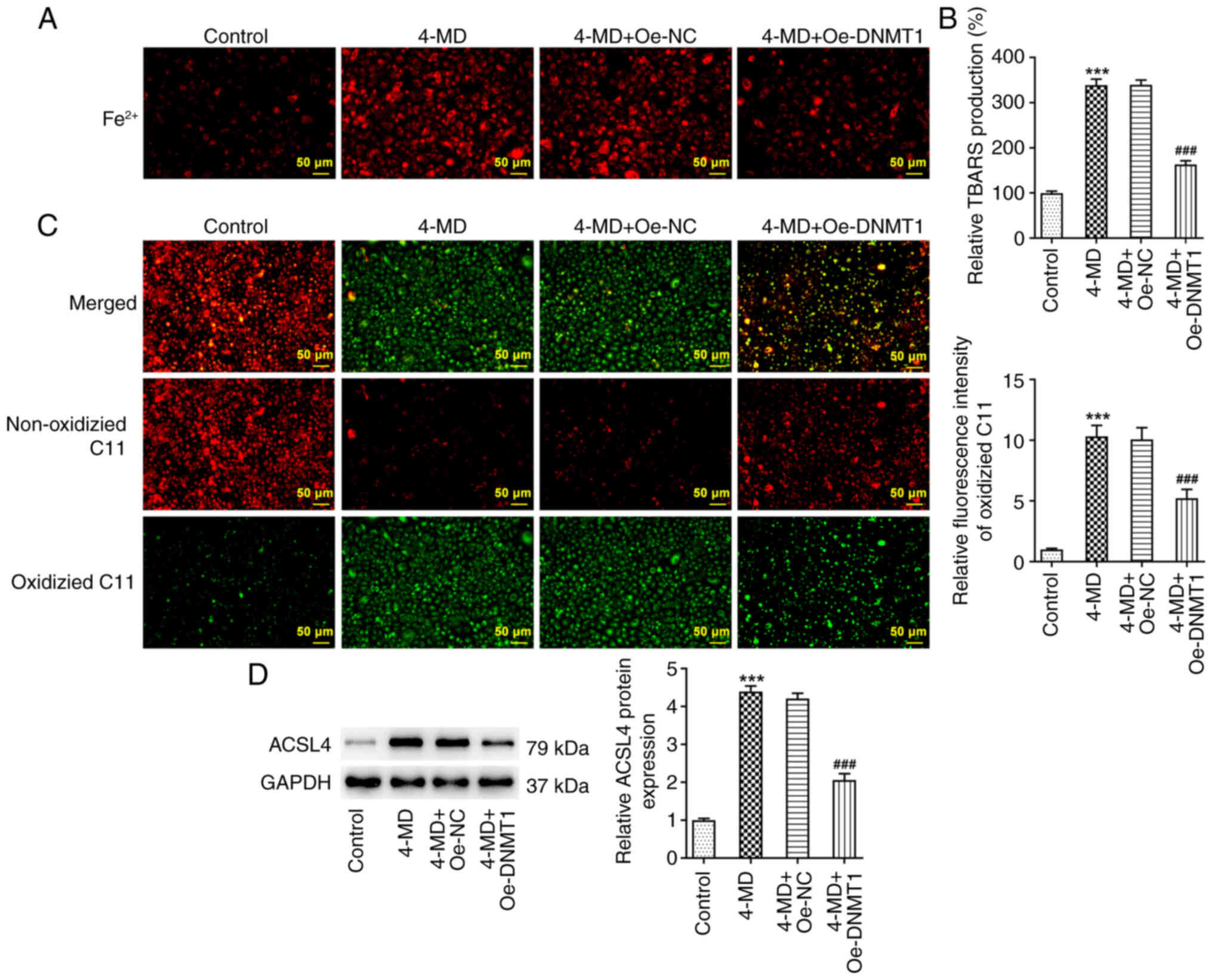
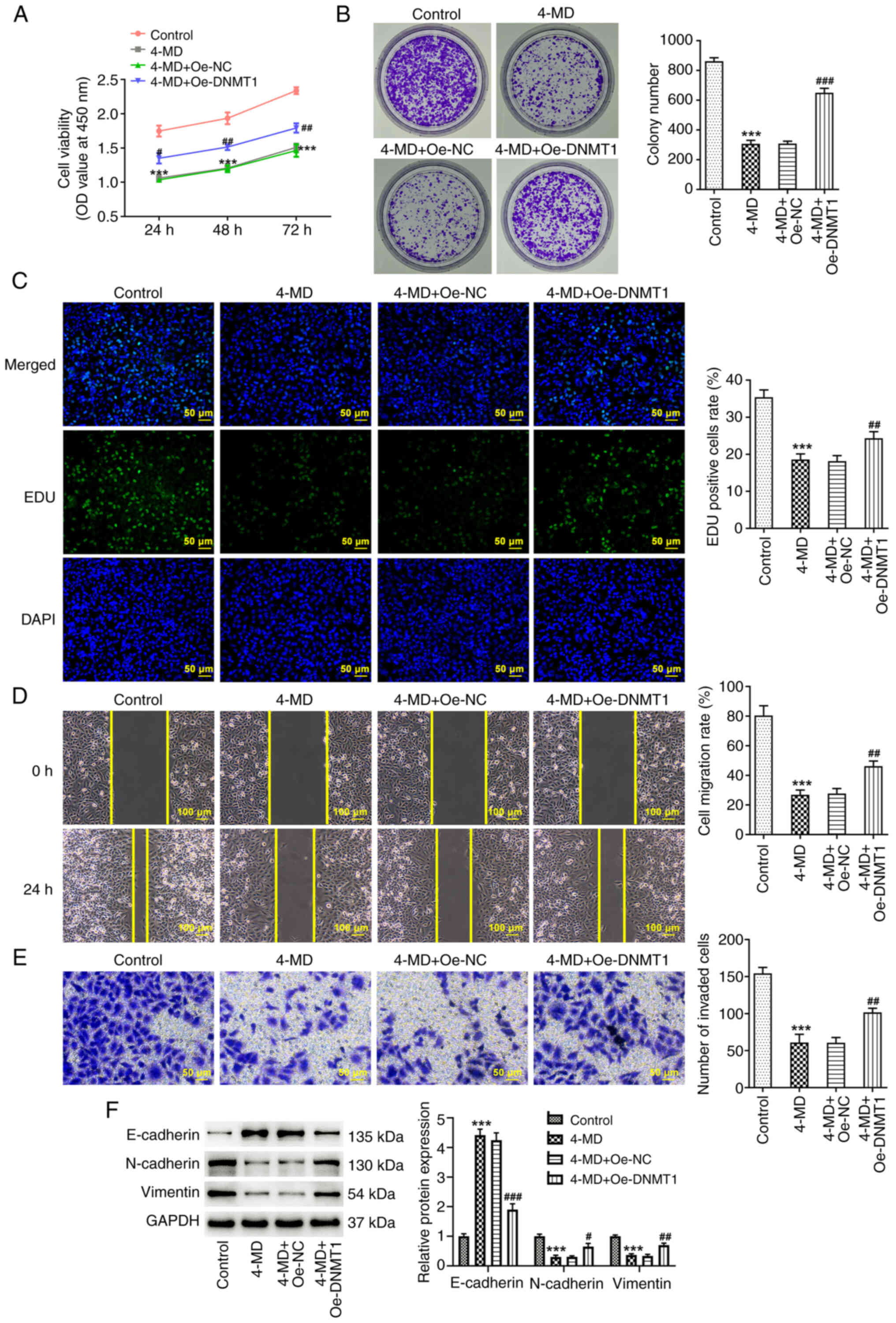
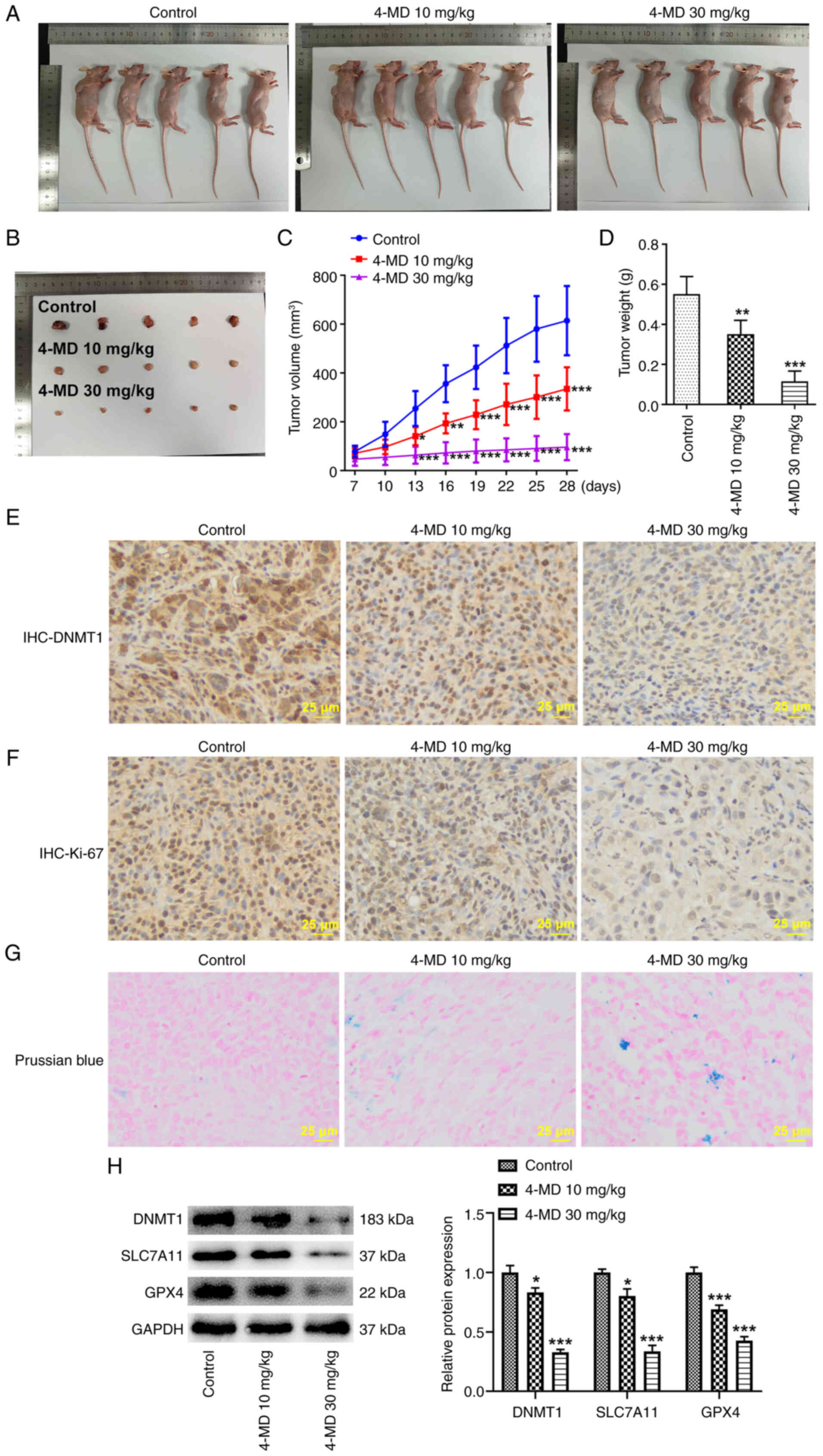
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Wagle NS and Jemal
A: Cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin. 73:17–48. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 69:7–34. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kim N, Kim HK, Lee K, Hong Y, Cho JH, Choi
JW, Lee JI, Suh YL, Ku BM, Eum HH, et al: Single-cell RNA
sequencing demonstrates the molecular and cellular reprogramming of
metastatic lung adenocarcinoma. Nat Commun. 11:22852020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lambert AW, Pattabiraman DR and Weinberg
RA: Emerging biological principles of metastasis. Cell.
168:670–691. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Luo H, Vong CT, Chen H, Gao Y, Lyu P, Qiu
L, Zhao M, Liu Q, Cheng Z, Zou J, et al: Naturally occurring
anti-cancer compounds: Shining from Chinese herbal medicine. Chin
Med. 14:482019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chan SC, Chang YS, Wang JP, Chen SC and
Kuo SC: Three new flavonoids and antiallergic, anti-inflammatory
constituents from the heartwood of Dalbergia odorifera. Planta Med.
64:153–158. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kim DC, Lee DS, Ko W, Kim KW, Kim HJ, Yoon
CS, Oh H and Kim YC: Heme Oxygenase-1-Inducing Activity of
4-Methoxydalbergione and 4′-Hydroxy-4-methoxydalbergione from
Dalbergia odorifera and Their Anti-inflammatory and Cytoprotective
Effects in Murine Hippocampal and BV2 microglial cell line and
primary rat microglial cells. Neurotox Res. 33:337–352. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Du H, Tao T, Xu S, Xu C, Li S, Su Q, Yan
J, Liu B and Li R: 4-Methoxydalbergione Inhibits Bladder Cancer
Cell Growth via Inducing Autophagy and Inhibiting Akt/ERK Signaling
Pathway. Front Mol Biosci. 8:7896582022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zeng L, Qin Y, Lu X, Fang X, Huang J, Yu C
and Feng ZB: 4-Methoxydalbergione Elicits Anticancer Effects by
Upregulation of GADD45G in Human Liver Cancer Cells. J Healthc Eng.
2023:67108802023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li M, Xiao Y, Liu P, Wei L, Zhang T, Xiang
Z, Liu X, Zhang K, Zhong Q and Chen F: 4-Methoxydalbergione
inhibits esophageal carcinoma cell proliferation and migration by
inactivating NF-ĸB. Oncol Rep. 49:422023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li R, Xu CQ, Shen JX, Ren QY, Chen DL, Lin
MJ, Huang RN, Li CH, Zhong RT, Luo ZH, et al: 4-Methoxydalbergione
is a potent inhibitor of human astroglioma U87 cells in vitro and
in vivo. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 42:1507–1515. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Park KR, Yun HM, Quang TH, Oh H, Lee DS,
Auh QS and Kim EC: 4-Methoxydalbergione suppresses growth and
induces apoptosis in human osteosarcoma cells in vitro and in vivo
xenograft model through down-regulation of the JAK2/STAT3 pathway.
Oncotarget. 7:6960–6971. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yan HF, Zou T, Tuo QZ, Xu S, Li H, Belaidi
AA and Lei P: Ferroptosis: Mechanisms and links with diseases.
Signal Transduct Target Ther. 6:492021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hassannia B, Vandenabeele P and Vanden
Berghe T: Targeting ferroptosis to iron out cancer. Cancer Cell.
35:830–849. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liang C, Zhang X, Yang M and Dong X:
Recent progress in ferroptosis inducers for cancer therapy. Adv
Mater. 31:e19041972019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Percie du Sert N, Hurst V, Ahluwalia A,
Alam S, Avey MT, Baker M, Browne WJ, Clark A, Cuthill IC, Dirnagl
U, et al: The ARRIVE guidelines 2.0: Updated guidelines for
reporting animal research. PLoS Biol. 18:e30004102020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Pritt SL and Smith TM: Institutional
animal care and use committee postapproval monitoring programs: A
proposed comprehensive classification scheme. J Am Assoc Lab Anim
Sci. 59:127–131. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang X, Wang R, Piotrowski M, Zhang H and
Leach KL: Intracellular concentrations determine the cytotoxicity
of adefovir, cidofovir and tenofovir. Toxicol In Vitro. 29:251–258.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang J, Gao M, Niu Y and Sun J: From
DNMT1 degrader to ferroptosis promoter: Drug repositioning of
6-Thioguanine as a ferroptosis inducer in gastric cancer. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 603:75–81. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zeng J, Li X, Liang L, Duan H, Xie S and
Wang C: Phosphorylation of CAP1 regulates lung cancer
proliferation, migration, and invasion. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
148:137–153. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global Cancer Statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Muthusamy B, Patil PD and Pennell NA:
Perioperative systemic therapy for resectable non-small cell lung
cancer. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 20:953–961. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Xie S, Wu Z, Qi Y, Wu B and Zhu X: The
metastasizing mechanisms of lung cancer: Recent advances and
therapeutic challenges. Biomed Pharmacother. 138:1114502021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bakir B, Chiarella AM, Pitarresi JR and
Rustgi AK: EMT, MET, plasticity, and tumor metastasis. Trends Cell
Biol. 30:764–776. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chanvorachote P, Petsri K and Thongsom S:
Epithelial to mesenchymal transition in lung cancer: Potential
EMT-Targeting natural product-derived compounds. Anticancer Res.
42:4237–4246. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Menju T and Date H: Lung cancer and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg.
69:781–789. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ye J, Zhang R, Wu F, Zhai L, Wang K, Xiao
M, Xie T and Sui X: Non-apoptotic cell death in malignant tumor
cells and natural compounds. Cancer Lett. 420:210–227. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Xu R, Wu J, Luo Y, Wang Y, Tian J, Teng W,
Zhang B, Fang Z and Li Y: Sanguinarine represses the growth and
metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer by facilitating
ferroptosis. Curr Pharm Des. 28:760–768. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Qian X, Zhu L, Xu M, Liu H, Yu X, Shao Q
and Qin J: Shikonin suppresses small cell lung cancer growth via
inducing ATF3-mediated ferroptosis to promote ROS accumulation.
Chem Biol Interact. 382:1105882023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yang WS and Stockwell BR: Ferroptosis:
Death by lipid peroxidation. Trends Cell Biol. 26:165–176. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yao ZJ, Dong J, Che YJ, Zhu MF, Wen M,
Wang NN, Wang S, Lu AP and Cao DS: TargetNet: A web service for
predicting potential drug-target interaction profiling via
multi-target SAR models. J Comput Aided Mol Des. 30:413–424. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wu XY, Chen HC, Li WW, Yan JD and Lv RY:
DNMT1 promotes cell proliferation via methylating hMLH1 and hMSH2
promoters in EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer. J Biochem.
168:151–157. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ma F, Lei YY, Ding MG, Luo LH, Xie YC and
Liu XL: LncRNA NEAT1 Interacted With DNMT1 to regulate malignant
phenotype of cancer cell and cytotoxic T Cell Infiltration via
Epigenetic Inhibition of p53, cGAS, and STING in Lung Cancer. Front
Genet. 11:2502020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zou P, Chen Z, He Q and Zhuo Y:
Polyphyllin I induces ferroptosis in castration-resistant prostate
cancer cells through the ERK/DNMT1/ACSL4 axis. Prostate. 84:64–73.
2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|