Introduction
Spinal fusion (SF) involves the surgically joining
of two or more vertebrae to eliminate motion between them and
provide stability. This procedure typically uses bone grafts
alongside hardware such as screws, rods, or plates to aid the
fusion process (1–3). A well-known complication of SF is
adjacent segment disease (ASD), where degeneration occurs in the
spinal segments next to the fused vertebrae. This can present as
disc herniation, spinal stenosis, or facet joint arthritis,
resulting in pain, neurological issues and potentially further
surgeries (1). ASD often arises
due to altered spinal biomechanics following fusion (2). The fused segments cease to bear
mechanical loads, shifting increased stress onto adjacent, unfused
segments, which accelerates degenerative changes in these areas
(3). A number of studies have
confirmed that these mechanical alterations post-fusion contribute
to the degeneration of intervertebral discs and facet joints
adjacent to the fusion site. The increased range of motion and
mechanical load on these segments intensifies degeneration,
particularly in longer fusion constructs (4,5). In
cervical spine surgeries such as anterior cervical discectomy and
fusion (ACDF), altered cervical mechanics influence adjacent
segment degeneration, while lumbar fusion affects spinal alignment
and load distribution (6).
Epidemiological studies report a broad range of ASD
incidence rates, typically between 2–36%, depending on the spinal
region involved (such as lumbar or cervical), the duration of
postoperative follow-up and the surgical technique used (6). Clinically, ASD may manifest as
chronic back pain, radiculopathy, or myelopathy in severe cases,
especially if degeneration results in nerve compression or spinal
canal narrowing (1). Diagnostic
imaging, including magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed
tomography (CT), is commonly employed to identify degenerative
changes in adjacent segments. While spinal fusion remains an
effective treatment for conditions such as degenerative disc
disease, scoliosis and spinal instability, the increasing
prevalence of ASD is a significant concern, particularly as spinal
fusion procedures continue to rise globally (7). In the U.S. alone, >500,000 fusion
surgeries are performed annually, with millions worldwide (8), emphasizing ASD as a critical
postoperative issue (9).
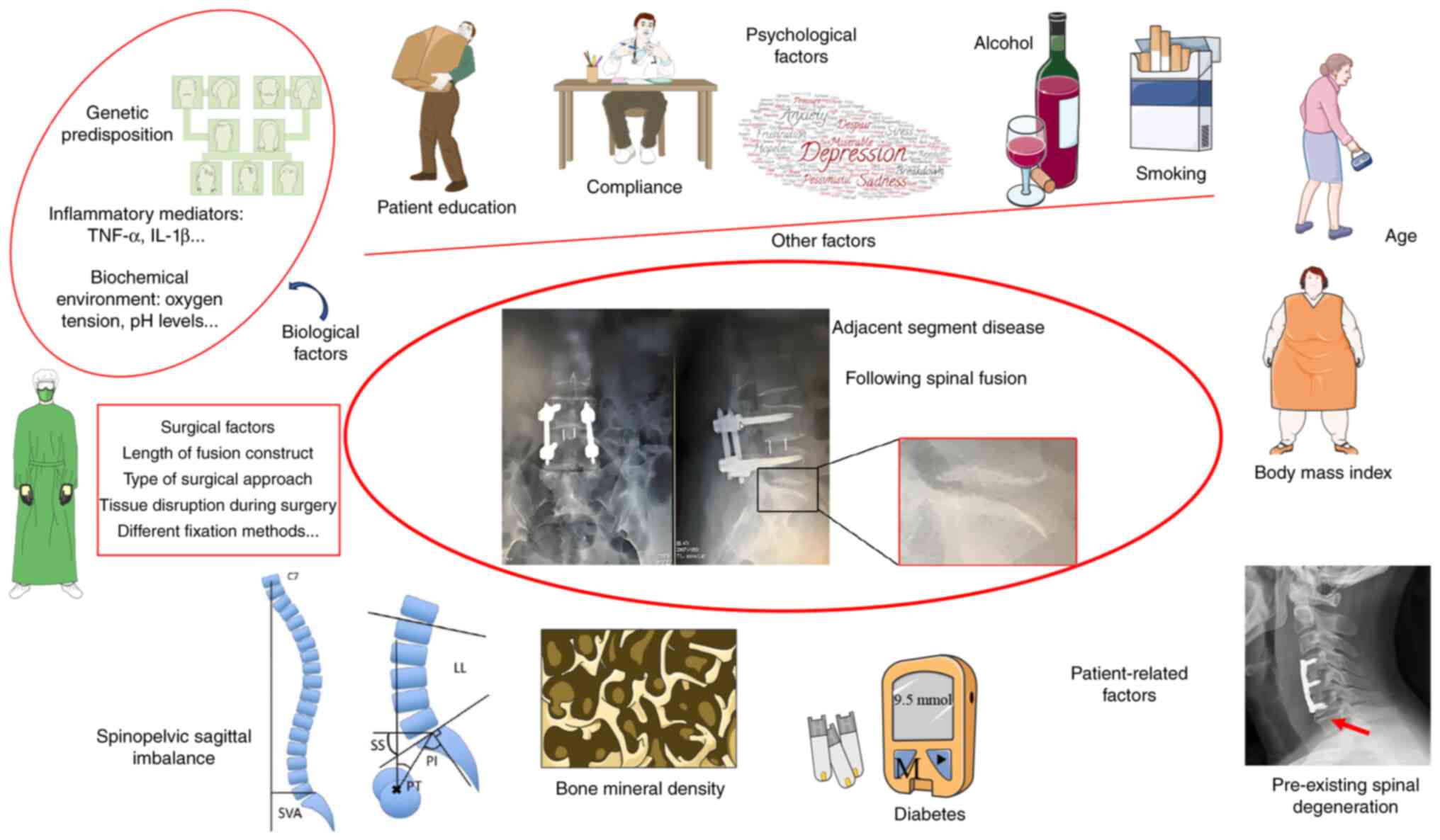
Several factors contribute to the development of
ASD, which can generally be categorized into patient-related and
surgical factors. Patient-related factors include age, body mass
index (BMI), bone mineral density (BMD) and pre-existing spinal
conditions (4,7,10).
Surgical factors, such as the length of the fusion and the
instrumentation used, also play a role. Longer fusion constructs,
for instance, can impose excessive mechanical stress on the
adjacent segments, accelerating degeneration (4,5).
Moreover, studies have investigated the correlation among genetic
predisposition, inflammatory mediators and the local biochemical
environment in the development of ASD-associated adjacent segment
degeneration (7,10). Therefore, understanding these risk
factors is vital for developing strategies to reduce ASD
incidence.
Addressing ASD requires a multifaceted approach
involving both preventive and therapeutic strategies. Surgical
innovations, such as dynamic stabilization devices and total disc
arthroplasty, aim to preserve spinal motion and reduce ASD risk,
though more research is needed to confirm their efficacy (11). Minimally invasive surgical
techniques (MIS), which minimize tissue damage and scar formation,
are associated with lower ASD rates (12). However, the optimal treatment for
ASD remains debated. While conservative management (such as
physical therapy, medications) may relieve symptoms, surgical
intervention may be required for patients with significant
neurological deficits or instability (13).
In summary, the present review specifically focused
on ASD associated with cervical and lumbar spine surgeries, as
these are the most commonly performed fusion procedures (6). ASD continues to present challenges in
the management of patients undergoing spinal fusion. A deeper
understanding of its risk factors, along with advancements in both
surgical techniques and emerging therapies, is essential for
improving patient outcomes and minimizing the need for subsequent
interventions.
Risk factors for ASD
Patient-related factors
Age
Age is a risk factor for ASD following SF surgery,
though findings vary, leading to continuing debate. A 16-year
cohort study reveals that younger patients, particularly those
under 40, who underwent primary ACDF, were more probably to require
subsequent ASD surgery (12).
Other studies, however, report consistent ASD rates across all age
groups (4,14). Similar results were noted in lumbar
fusion cases, with advanced age being emphasized as a risk factor
(15). The overall reoperation
rate due to symptomatic ASD following cervical fusion is 6.57%,
peaking at 8.12% in individuals aged 30–39 and decreasing with age.
Additionally, those under 50 have a higher likelihood of requiring
ASD reoperation (4). Conversely,
for posterior lumbar fusion, patients younger than 45 have a lower
risk of ASD compared with those over 60 (5). Although a meta-analysis revealed a
slight age difference in ASD patients, it was not statistically
significant (16). While
age-related spinal degeneration is well known, it does not fully
explain the higher reoperation rates in younger patients (3). A study has shown that older
individuals exhibit more rapid radiological signs of degeneration
post-fusion (17). This
discrepancy may be linked to differences in physical activity
levels and underlying health conditions. The mixed research
findings suggest that age alone is not the sole risk factor for
ASD, necessitating caution in future studies and clinical care,
especially for younger patients.
BMI
Biomechanically, obesity can overload intervertebral
discs, accelerate cervical disc degeneration and lead to abnormal
stress on surrounding small joints, spinal ligaments and muscles,
causing ASD (14). However, the
relationship between BMI and the development of ASD following
fusion surgery remains debated. Studies by Wei et al
(14) and Zhong et al
(18) demonstrate that elevated
BMI is a risk factor for ASD in patients undergoing cervical ACDF
and minimally invasive lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative
lumbar conditions. Additionally, some investigations have suggested
that a BMI >34 is associated with increased risk following
lumbar fusion procedures (19).
Conversely, certain studies have reported no correlation between
BMI and the risk of ASD following both cervical ACDF (20) and adult lumbar spondylolisthesis
fusion procedures (21). Notably,
this discrepancy is more pronounced in the studies addressing
cervical fusion, without accounting for the potential effect of
postoperative changes in BMI. Therefore, in clinical practice, in
addition to emphasizing preoperative BMI control, it is also
crucial to focus on maintaining BMI within a reasonable range
following fusion surgery for different anatomical regions, which
warrants further in-depth investigation.
BMD
Osteoporosis reduces vertebral hardness, alters
stress distribution and induces significant biomechanical changes
in adjacent segments (22). After
fusion surgery, the BMD of adjacent segments decreases compared
with preoperative levels (23).
Biomechanical studies demonstrate that in lumbar posterior
interbody fusion models with osteoporosis, there is reduced
pressure within adjacent intervertebral discs, decreased shear
stress on fibrous rings and limited range of motion, which
negatively influences ASD progression (24). Studies indicate a higher prevalence
of ASD in postmenopausal women (25), suggesting that osteoporosis is a
risk factor and a predictor of reoperation (19,22).
Patients with low BMD undergoing SF surgery may experience implant
failure, resulting in poor fusion and heightened stress on nearby
vertebrae, worsening ASD onset (26). Studies have demonstrated that
osteoporosis (T-score <-2.5) is associated with the development
of ASD following ACDF (27). Among
patients undergoing fusion for lumbar degenerative conditions,
those with osteoporosis show a higher incidence of ASD (28). However, the reoperation rate in
osteoporotic patients is lower compared with non-osteoporotic
patients (7.4 vs. 13.1%) (28).
Additionally, animal experiments illustrate the effectiveness of
anti-osteoporotic drug therapy in mitigating intervertebral disc
degeneration (IDD) near the lumbar fusion site in rats (29). However, some studies indicate no
direct association between osteoporosis and ASD, possibly due to
significant BMD variations before and after studies or measurement
inaccuracies (19,30). These conflicting findings
underscore the importance of monitoring vertebral BMD pre-fusion,
implementing timely postoperative anti-osteoporosis treatments and
adopting precise BMD measurement methods, including CT scans
alongside the potentially less accurate Dual X-ray Absorptiometry
(DXA) (23).
Diabetes
Research indicates that diabetes alters the
composition and biomechanical properties of intervertebral disc,
contributing to degenerative changes and increased spinal
instability (10). Beyond
microvascular complications, diabetes affects osteoclast and
osteoblast function, leading to the release of pro-inflammatory
cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), interleukin
(IL) 6 and IL-18, which impair bone graft vascularization,
formation and remodeling (10,31).
Diabetic patients undergoing multilevel fusion surgery face higher
complication rates, including non-union and pseudoarthrosis,
compared with non-diabetic individuals (10). Consequently, the risk of revision
surgery for ASD following pseudoarthrosis exceeds the risk of the
initial procedure (10,31). However, the literature indicates
that diabetes is not a risk factor for the development of ASD in
patients undergoing ACDF (20).
While diabetes has no effect on fusion rates in lumbar fusion
surgeries using cellular bone allografts (32), other findings reveal that diabetes
is a significant factor for reoperation following lumbar fusion due
to ASD, with a 44% higher revision rate compared with non-diabetic
patients (10). Therefore, it is
important to note that current literature lacks comprehensive
studies on diabetic patients, particularly regarding preoperative
blood glucose levels and postoperative glycemic control. Further
clinical and animal studies are needed to confirm these
findings.
Pre-existing spinal degeneration
Patients with pre-existing degenerative changes in
the spine, such as disc degeneration, facet joint arthritis,
vertebral slippage and spinal stenosis, face a higher risk of
developing ASD before fusion surgery (33). These degenerative changes reduce
disc height, alter biomechanical and increase pressure on
neighboring segments (34).
Research by Kim et al (35)
found that MRI-detected disc degeneration was a significant
predictor of ASD development. Similarly, one study has suggested
that patients with pre-existing degeneration in adjacent disc
segments are more prone to ASD following SF (2). Degenerative changes in adjacent facet
joints also affect spinal mobility, stability and ASD progression
(2). Research stresses that
preoperative facet joint degeneration is a risk factor for the
development of ASD (2). A study by
Tan et al (36) further
supports this, demonstrating a strong association between facet
joint degeneration and an increased incidence of ASD following
lumbar fusion surgery. Patients with grade III degeneration
[according to the Weishaupt classification (37)] showed a markedly higher risk of
developing ASD compared with those with grade I or II degeneration
(38). Vertebral slippage can also
lead to instability and heightened pressure on neighboring segments
(39). Research indicates that
preoperative vertebral slippage (spondylolisthesis) and spinal
stenosis increase the risk of developing ASD following lumbar
fusion and ACDF (40). Moreover,
as the severity of postoperative spinal stenosis worsens, patients
with ASD show significantly higher Visual Analog Scale scores
(41) for back pain and Oswestry
Disability Index scores (42)
during follow-up compared with those without ASD (43). The current absence of comparative
clinical studies leaves uncertainty regarding whether
degenerative-related ASD results from fusion surgery or natural
degeneration, necessitating further confirmation through animal
experimental studies.
Spinopelvic sagittal imbalance
Spinal and pelvic sagittal parameter imbalance can
result in lumbar spine instability, widely recognized as a risk
factor for postoperative ASD (44). Proper alignment of the spine and
pelvis ensures that the load distribution across the spine is
balanced, minimizing excessive stress on individual segments. When
there is an imbalance in spinopelvic parameters, such as pelvic
incidence (PI), pelvic tilt (PT), sacral slope (SS) and lumbar
lordosis (LL), this balance is disrupted, leading to abnormal
biomechanical forces on the adjacent segments, which accelerates
their degeneration (45). A
mismatch between PI and LL-especially when the difference exceeds
10°-forces adjacent spinal segments to compensate by altering their
alignment. This compensation increases shear forces and mechanical
stress on the adjacent discs and facet joints, leading to premature
degeneration and, ultimately, ASD (44,45).
One study has shown that degenerative changes in neighboring
intervertebral discs are associated with elevated PT and persistent
pelvic tilt mismatch with the PI-LL change, particularly in lower
lumbar fusions (L4-S1) (44). SS
is crucial for sagittal alignment as a compensatory mechanism
(45). Postoperative PI-LL
mismatch increases the risk of ASD 10-fold compared with controls
(34). As PT increases, the center
of gravity shifts forward, raising the spine axis deviation (SVA)
and increasing stress on adjacent segments (46). After posterior lumbar interbody
fusion (PLIF) at L4/5, higher preoperative vertical SVA, vertical
PT angle, reduced LL and PI-LL mismatch are closely associated with
ASD (45). Maintaining a sacral
tilt angle >20° at L4/5 is vital for postoperative ASD
prevention (34,45). Longer fusion segments in patients
with Cobb angle >25° (47) are
more effective in correcting spinal issues, but higher preoperative
Cobb angle may contribute to postoperative ASD (34). Moreover, individuals with a greater
C2-C7 SVA following ACDF are at an increased risk of ASD (20). Despite conflicting evidence,
orthopedic surgeons should carefully consider these parameters
during surgery, especially when feasible intraoperative CT scanning
and measurements are available.
Surgical factors
Length of fusion construct
The length of the fusion construct is a critical in
the development of ASD due to the biomechanical stresses placed on
adjacent segments. Longer fusion constructs, which often span
multiple vertebral levels, restrict spinal mobility and increase
mechanical loads on unfused adjacent segments (34). Mechanistically, this increased
rigidity alters the distribution of forces along the spine, leading
to hypermobility and accelerated degeneration in adjacent segments
(48). Biomechanical models have
shown that the longer the fusion construct, the greater the stress
on adjacent segments, especially in regions near the thoracolumbar
junction, where the transition between mobile and immobile segments
occurs. This change in biomechanics promotes microdamage in
adjacent intervertebral discs and facet joints, leading to their
progressive degeneration (49).
Okuda et al (48) found ASD
rates of 8.6% over 4.6 years post single-segment lumbar PLIF
surgery and 16.4% over 6.0 years post double-segment surgery. Park
et al (46) showed a 2.7
times higher ASD risk in three-segment fusion patients compared
with those with single or two-segment fusions. The key mechanism
here is that long constructs redistribute the load across a smaller
number of remaining mobile segments, leading to biomechanical
overload and subsequent degeneration. These findings emphasize the
need for careful consideration of fusion construct length in
preoperative planning for optimal clinical outcomes.
Type of surgical approach
The incidence of ASD following spinal surgery varies
depending on the surgical approach; however, there is ongoing
debate regarding which technique is most effective in minimizing
postoperative ASD. PLIF, due to its increased rigidity, places
greater mechanical stress on adjacent segments, resulting in a
higher incidence of ASD compared with posterolateral fusion (PLF)
(50). A retrospective study
revealed that the incidence of ASD in PLIF patients is 3.4 times
higher than in PLF patients, with the 10-year ASD-free survival
rate being significantly lower in the PLIF group (51). By contrast, transforaminal lumbar
interbody fusion (TLIF) causes less disruption to posterior spinal
structures, reducing ASD occurrence compared with PLIF (52). Anterior lumbar interbody fusion,
which accesses the spine through the abdomen, avoids posterior
disruption and has been linked to a lower incidence of ASD compared
with both PLIF and TLIF (53).
Furthermore, minimally invasive approaches, such as percutaneous
fixation, cause less damage and significantly reduce ASD risk
(16). Total disc arthroplasty was
developed as an alternative to fusion, aiming to preserve segmental
motion and potentially delay or prevent adjacent-level degeneration
(54). Studies suggest that
patients undergoing ACDF with anterior revision surgeries have
higher rates of recurrent radiculopathy and ASD compared with those
undergoing posterior revisions (55). Additionally, patients who undergo
posterior cervical fusion tend to exhibit higher rates of early ASD
compared with those who opt for anterior approaches (56). While the literature presents mixed
findings regarding the risk of ASD with different surgical
techniques, numerous uncontrollable variables, such as the severity
of the condition, complicate the conclusions. Therefore, careful
consideration of the surgical approach is crucial in planning SF
surgeries to minimize the risk of ASD.
Tissue disruption during surgery
Tissue disruption during surgery, particularly
damage to the paraspinal musculature, ligaments and facet joints,
plays a critical role in ASD development. Surgical techniques that
cause extensive damage to the paraspinal muscles, ligaments and
joints significantly alter spinal biomechanics, thereby increasing
stress on adjacent segments (57).
One study has demonstrated a strong correlation between extensive
joint resection and a higher incidence of ASD (57). Moreover, ASD is more commonly
observed in the intervertebral disc above the fused segment rather
than the segment below, probably due to the biomechanical changes
that increase stress on the superior adjacent segment (3). This stresses the importance of
preserving the superior facet joint capsule during the initial
surgery, as it plays a key role in maintaining the stability and
biomechanics of the adjacent upper segment, potentially preventing
the development of ASD. Additionally, damage to the spinous
processes and surrounding muscles during open surgery can lead to
scar formation and alterations in spinal mechanics, further
contributing to the ASD development (58). Comparative studies have shown that
traditional open surgeries, which involve extensive muscle
dissection, result in higher rates of ASD compared with minimally
invasive surgeries, which improve the preservation of the integrity
of surrounding tissues (57).
Furthermore, research has indicated that minimally invasive
surgeries, which cause less disruption to the paraspinal muscles
and ligaments, are associated with a lower incidence of ASD
(59).
Different fixation methods
It is well known that the primary goal of fusion is
to alleviate pain and prevent further spinal deformity by
stabilizing the affected vertebral segments. Therefore, different
fixation methods aim to achieve physiological spinal motion and a
higher fusion rate, improving biomechanical compatibility and
reducing ASD (60). One study has
shown that the more rigid the instrumentation used, the earlier ASD
tends to develop after fusion (61). Varol et al (60) and Hsiao et al (62) found that, compared with traditional
rigid systems, the Dynesys dynamic system induced less range of
motion in adjacent joints and preserved the intervertebral disc
structure of adjacent segments, thereby reducing the incidence of
ASD. Further biomechanical studies have shown that the hybrid
Dynesys-Transition-Optima system, composed of both dynamic
(flexible and non-fusion) and static (rigid and fusion) components,
can significantly reduce the range of motion at the fusion level
(L4-L5), while improve the preservation of the mobility of stable
segments. This results in a reduced range of motion at the
transitional segments, which may help prevent the occurrence of
adjacent segment degeneration (62). Similarly, research by Guan et
al (63) revealed that
non-fusion techniques incorporating dynamic stabilization not only
reduced the incidence of ASD but also maintained spinal
stability.
Biological factors
Genetic predisposition
Although no direct studies have established a
connection between ASD and genetic predisposition, evidence
suggests a link between genetic factors and IDD, offering insights
into ASD risk factors. A study of 205 Japanese volunteers and
patients aged 20–29 found that the Tt genotype of the Taq I
polymorphism in the vitamin D receptor was more frequently
associated with multilevel disc disease, severe degeneration and
disc herniation compared with the TT genotype, probably due to
changes in the extracellular matrix (ECM) structure of the disc
(7). Research indicates that
cartilage intermediate layer protein (CILP) expression increases as
disc degeneration progresses (64). A recent case-control study
identified an association between degenerative disc disease in a
Japanese cohort and the SNP +1184T→C in exon 8 of CILP. Given that
CILP can bind to transforming growth factor-β or insulin-like
growth factor-1, it may regulate ECM synthesis in the
intervertebral disc, altering the extracellular microenvironment
and promoting IDD (64).
Furthermore, Research has highlighted that gene variations
associated with inflammatory pathways, such as the functional SNP
(+3954C→T) in exon 5 of the IL-1β gene, are linked to IDD and lower
back pain (65).
Inflammatory mediators
Inflammatory cytokines, such as TNF-α and IL-1β, are
also associated with the progression of the IDD (66). These mediators exacerbate
degeneration by promoting catabolic processes within spinal tissues
(66). One study suggested that
targeting these inflammatory pathways may be a viable strategy for
preventing ASD (66). Elevated
levels of IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8 and TNF-α have been observed in
patients with degenerative disc disease (66,67).
Chen et al (67)
demonstrate in an animal model of SF associated with ASD that TNF-α
and IL-1β expression in adjacent segment discs significantly
increases over time. Additionally, research indicates that patients
receiving TNF-α inhibitors preoperatively experienced a markedly
higher rate of reoperation within 1 year due to issues such as
fusion failure and ASD (68).
Additionally, macrophage migration inhibitory factor (MIF) has been
identified as a key factor in spinal degeneration. Research
indicates that MIF may contribute to the hypertrophy of the lumbar
ligamentum flavum in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, which
is closely associated with the development of ASD (69). Furthermore, MIF can directly affect
the vertebral endplates, modulating inflammation and matrix
metabolism in degenerated cartilage endplate chondrocytes through
the activation of the ERK1/2 pathway (70). Thus, more clinical and animal
studies focusing on inflammatory factors could provide new insights
into ASD prevention.
Biochemical environment
The alteration of the local biochemical environment
in the spine is closely associated with IDD, particularly
concerning nutrient supply, oxygen tension and pH levels (71). Adequate nutrient supply is crucial
for maintaining disc cell activity and preventing degeneration
(72). Disruptions in these
factors accelerate disc degeneration, with aging leading to
diminished nutrient supply, reduced oxygen, lower pH and impaired
extracellular matrix synthesis (71). Research indicates that the
functionality of nucleus pulposus cells is affected by the
transport characteristics of the cartilaginous endplate.
Degenerated endplates hinder nutrient transport, worsening IDD
(72,73). Gilbert et al (74) demonstrate that increased acidity
(lower pH) reduces disc cells vitality and enhances
pro-inflammatory cytokines expression. Inhibiting acid-sensing ion
channel-3 may offer therapeutic potential. Recent advances in
understanding the biochemical environment of the spine have
prompted the exploration of novel therapeutic approaches. For
instance, the use of bioactive scaffolds and hydrogels has been
investigated to enhance postoperative nutrient delivery and
maintain intervertebral disc hydration (71,72).
The alterations in the local biochemical environment of the spine,
along with emerging therapeutic strategies, warrant further
exploration for the prevention and management of ASD following SF
surgery.
In addition to patient-related, surgical and
biological factors, other variables such as postoperative
rehabilitation and lifestyle factors play a critical role in the
development and progression of ASD following SF.
Other factors
Patient education, compliance and psychological
factors
Education provided by healthcare professionals on
postoperative health and pain management significantly affects
patient adherence and understanding of their condition (75). Thys et al (75) found that surgeons often impose
stricter postoperative restrictions compared with physical
therapists, some of whom advocate for no restrictions. Mental
health conditions, including anxiety and depression, are risk
factors for ASD following SF surgery (12,76).
Studies found that preoperative and early postoperative fear of
movement significantly influences postoperative pain and functional
rehabilitation in patients undergoing SF (77,78).
Therefore, combining exercise rehabilitation programs with
cognitive behavioral therapy and patient-centered goal-directed
therapies may enhance patient recovery and help prevent
postoperative ASD.
Smoking and alcohol
Alcohol consumption and smoking are potential risk
factors for ASD following SF surgery, though the relationship
remains debated. Smoking has been shown to reduced blood flow,
lower oxygen levels and impair nutrient supply to spinal tissues.
Additionally, smoking can decrease estrogen levels, increasing the
risk of osteoporosis and spinal fractures, as well as the
likelihood of pseudarthrosis in fusion surgery patients (8). One study advocated for mandatory
smoking cessation for at least four weeks postoperatively (8). Evidence shows that smokers have a
significantly higher incidence of ASD following SF compared with
non-smokers (79). While the
direct effect of alcohol on ASD is less studied, it is known to
lower bone density, increase fracture risk and impair bone healing
and regeneration, all of which may indirectly elevate the risk of
ASD (80). However, one study
argued that alcohol consumption and smoking are not risk factors
for ASD, highlighting the limitations of retrospective research
(20). Addressing lifestyle
factors, such as smoking and alcohol consumption, is crucial in the
management of patients undergoing SF surgery. Healthcare providers
should emphasize smoking cessation and reducing alcohol intake to
mitigate the risk of ASD and improve overall surgical outcomes.
In summary, while the role of these factors (patient
education, compliance, psychological health, smoking and alcohol
use) may be under-researched specifically in the context of ASD,
their influence on broader spinal surgery outcomes is
well-established. Thus, they are highlighted as significant
contributors to postoperative success and further investigation is
encouraged to solidify these associations in the context of
ASD.
Treatment strategies for ASD
Diagnosing ASD requires a comprehensive approach,
combining clinical evaluation, imaging studies and patient history.
Clinically, symptoms such as pain and recurrent neurological
deficits are assessed, while imaging (especially MRI and CT) help
detect degenerative changes in adjacent segments, such as disc
herniation and facet joint arthritis. One study indicated that
symptomatic ASD occur in 16.5% of patients at five years and 36.1%
at ten years post-fusion (81),
highlighting the importance of vigilant postoperative monitoring.
Management strategies for ASD include conservative treatments and
surgical interventions. Treatment recommendations should be
individually based on symptom severity, degree of degeneration,
overall health status and patient preferences.
Conservative treatment
Conservative treatments are often the first line of
defense in managing patients with ASD, particularly in those with
mild to moderate symptoms. These treatments aim to relieve
symptoms, improve functional capacity and delay the need for
surgical intervention by addressing the mechanical and inflammatory
aspects of ASD.
Postoperative rehabilitation
therapy
Following SF surgery for degenerative spinal
diseases, patients often experience a protective state in the
spine, making it challenging to full return to normal function
quickly (82). Appropriate
postoperative rehabilitation therapy not only improves functional
capacity but also strengthens the muscles supporting the spine,
helping distribute mechanical loads more evenly and reducing stress
on adjacent segments (83).
Although there is no consensus on the optimal timing, intensity and
duration of rehabilitation after fusion surgery (83), early endurance and muscle
strengthening exercises to restore core balance significantly
enhance back strength, alleviate pain and reduce disability
(83). Changes in paravertebral
muscle size following cervical, lumbar and thoracolumbar fusion
surgeries are significant risk factors for ASD (58,84,85).
For instance, research by Xu et al (58) demonstrate a reduction in the
functional area of the multifidus and erector spinae muscles, along
with an increase in the functional area of the psoas major muscle
following L4-S1 PLIF. Furthermore, Zhou et al (82) reveal that gait alterations (such as
stride length, speed and cadence) and post-minimally invasive
transforaminal interbody fusion may affect spinal-pelvic and lower
limb joint parameters, underscoring the importance of postoperative
rehabilitation in preventing ASD. Research indicates that physical
therapy methods such as flexion-distraction techniques,
high-velocity low-amplitude adjustments and thermotherapy may
effectively relieve pain following fusion surgery (9,86).
Additionally, therapies such as myofascial release and acupuncture,
commonly used by chiropractors, benefit postoperative care
following lumbar fusion surgery (9). Gliedt et al (87) report that stimulating multiple
acupuncture points and auricular therapy effectively reduces
postoperative pain. Compared with traditional rehabilitation,
electroacupuncture demonstrates significant improvements in
functional recovery following lumbar fusion surgery (88). To address ASD risk factors, it is
essential to develop a detailed postoperative rehabilitation
treatment plan that involves collaboration orthopedic and
rehabilitation physicians.
Pharmacological treatment
Similar to the initial treatment for degenerative
disc disease and radiculopathy, ASD can be managed with physical
therapy, rehabilitation therapies such as early back bracing and
lifestyle modifications such as avoiding excessive weight and
bending (89). Medication,
including non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, steroids and
muscle relaxants, can relieve clinical symptoms (90). Recently, small molecule drugs such
as naringin have shown promise in preventing further degeneration
of disc cells and enhancing regeneration, but most are still in
early stages and have not been applied in clinical studies
(91). Non-surgical treatment
should be the first choice for ASD, as long as significant clinical
improvement is observed, regardless of imaging findings (89). However, research comparing
non-surgical and surgical treatments for ASD is lacking,
highlighting the need for more in-depth studies.
Epidural steroid injections
(ESIs)
Research indicates that ~20% of patients experience
pain following surgeries for spinal stenosis or herniated discs,
necessitating additional measures to alleviate this pain (92). When conservative treatments such as
rehabilitation techniques and pharmacotherapy prove ineffective,
ESIs may be used. Corticosteroids reduce inflammatory and edema by
inhibiting inflammatory mediators, resulting in pain relief
(93). Interventional treatments
via different approaches, such as interlaminar, transforaminal and
caudal, demonstrate promising outcomes for various types of chronic
back pain (93). For instance,
Song et al demonstrated that both transforaminal and caudal
ESIs effectively alleviated chronic pain and improved function
following spinal surgery (92).
Additionally, Park et al showed that nerve root blocks and
interlaminar epidural steroid injections were effective in
relieving cervical radicular pain and enhancing function (94). While the relief provided by nerve
root blocks is typically temporary, they can be used as a
diagnostic tool to confirm the source of a patient's symptoms and
guide further treatment decisions. However, the efficacy of ESIs in
the treatment of ASD warrants further clinical investigation to
establish its benefits conclusively.
Facet joint interventions
ASD following SF surgery often involves degeneration
of the facet joints, which can cause referred or radicular pain
(95). Direct injection of
medications into affected facet joints or thermal ablation to
target pain-transmitting nerve fibers are viable treatment options
(95). Evidence-based guidelines
for managing chronic spinal pain recommends various facet joint
interventions, including corticosteroid injections, saline
injections, facet joint nerve blocks and radiofrequency ablation,
depending on the specific spinal segment involved (96). Recently, procedures guided by
ultrasound or CT improved the accuracy, safety and efficacy of
these interventions (97). For
example, Wong and Rajarathinam (97) demonstrate that the accuracy of
ultrasound-guided injections into the cervical facet joints and
their innervating nerves ranged from 78–100%, while the accuracy
for lumbar facet intra-articular injections was between 86–100%.
Compared with fluoroscopy or CT-guided methods, ultrasound guidance
resulted in shorter procedure times with comparable pain relief
outcomes (97). Similarly,
research by Suputtitada et al (98) demonstrate that intra-articular
injections of saline, corticosteroids and anesthetics provide
favorable long-term clinical outcomes for patients with chronic low
back pain. For patients who do not achieve long-term relief from
facet joint injections, radiofrequency ablation (RFA) is a
minimally invasive procedure that targets the nerve fibers
transmitting pain signals from the degenerated facet joints
(99). By using heat to ablate
these nerve fibers, RFA provides longer-lasting pain relief
compared with injections alone (99). A study has shown that RFA can
significantly reduce pain and improve function in patients with
chronic low back pain-related facet joint degeneration, making it a
valuable tool in the interventional management of ASD (99). However, these treatment modalities
are insufficiently emphasized in the management of ASD, with
limited related literature available. Orthopedic surgeons should
not focus solely on surgical interventions for ASD.
Surgical interventions
In cases of ASD following SF, only 6% of patients
with significant clinical symptoms require additional surgical
intervention (90). Surgical
interventions are a crucial treatment option for patients with ASD,
especially when conservative therapies fail to provide adequate
symptom relief or when significant spinal instability and
neurological deficits are present (16). Spinal instability or structural
deformities, such as kyphosis or spondylolisthesis, often require
surgical correction to prevent further degeneration and potential
damage to the spinal cord or nerve roots (16). However, as with any surgical
procedure, there are risks involved, including the potential for
further degeneration at other levels of the spine. Careful
preoperative planning and postoperative rehabilitation are
essential to optimize outcomes and minimize complications. The
choice of surgical procedure depends on the specific pathology and
the patient's overall health status.
Total disc replacement (TDR)
TDR is an alternative to fusion that involves
replacing the degenerated disc with an artificial disc. TDR has
emerged as a significant alternative to traditional fusion
techniques for the treatment of degenerative disc disease and ASD.
The primary advantage of TDR is its ability to preserve motion at
the affected segment, which is in contrast to fusion, where the
vertebrae are permanently immobilized (100). By maintaining the natural
biomechanics of the spine, TDR reduces the mechanical stress placed
on adjacent segments, potentially decreasing the risk of
degeneration at these levels (100). TDR shows favorable outcomes in
selected patients, with improvements in pain, function and range of
motion (100). Rajakumar et
al (100) demonstrate that
cervical TDR surgery effectively alleviates nerve
compression-related symptoms caused by ASD following ACDF.
Additionally, none of the patients required further surgery at the
same vertebral level during the three-year follow-up period. A
study demonstrated that in the treatment of ASD, TDR provided an
improved range of motion at C2-C7 over a follow-up period of more
than one year compared with ACDF (40.2 vs. 35.1°; P=0.001)
(101). Additionally, TDR shows
comparable outcomes in terms of improvement in the neck disability
index, neck visual analog scale and upper limb function (101). However, TDR is not suitable for
all patients, particularly those with pre-existing joint
degeneration. One study showed no difference in the incidence of
ASD between TDR and fusion surgery (102). This finding necessitates more
rigorous evaluation of the efficacy of TDR for treating ASD
post-fusion surgery, including larger sample sizes and longer
follow-up periods. Therefore, careful patient selection is crucial
to ensure the success of the procedure.
Extension of fusion
Extended fusion surgery has been extensively studied
and widely applied as an effective intervention for treating ASD
following SF. This approach aims to reduce degeneration caused by
biomechanical stress transfer by extending the fusion to include
affected adjacent segments (103). It is particularly suitable for
patients with significant ASD and accompanying clinical symptoms,
such as spinal instability (90).
This method involves the addition of instrumentation and performing
fusion at the affected segments to stabilize the spine (104). Research indicates that combining
extended fusion with decompression surgery alleviates symptoms and
reduces the need for subsequent surgeries during long-term
follow-up (104). However,
compared with traditional surgeries, extended fusion is associated
with greater trauma, longer operative times and potential
complications (105). To address
these drawbacks, recent advancements introduced modified
techniques, such as using connectors to extend fixation without
removing the existing hardware, which was showed to significantly
reduce surgical trauma and costs (106). Nonetheless, further randomized
controlled trials are essential to determine the long-term outcomes
of various surgical strategies, particularly in the context of
advancing minimally invasive techniques.
Decompression surgery
Decompression surgery is recommended for patients
with significant nerve root compression, leading to radiculopathy
or myelopathy following SF. However, it is not ideal for patients
with pre-existing spinal kyphosis or instability (90,107). Procedures, such as laminectomy,
laminoplasty and foraminotomy, aim to relieve the spinal cord or
nerve roots pressure, alleviating pain and improving neurological
function (107). Yang et
al (107) found that
laminectomy with instrumentation effectively improves symptoms and
function in ASD patients following anterior cervical corpectomy and
fusion (ACCF), though lordosis gradually declined. He et al
(108) report that in ASD
patients following ACCF or ACDF, laminoplasty provides satisfactory
clinical outcomes when cervical lordosis was <10° and spinal
canal encroachment occupied <50% of the canal's cross-sectional
area. Früh et al (109)
showed that microscopic decompression reduced operative time and
trauma in lumbar ASD. However, microscopic surgery significantly
reduced operative time and surgical trauma.
Minimally invasive surgery (MIS)
MIS has become an essential approach in the
management of ASD due to its numerous benefits over traditional
open surgery (59). MIS
techniques, such as endoscopic decompression, minimally invasive
fusion and robot-assisted cortical bone trajectory (CBT) screw
fixation, aim to minimize the damage to paraspinal muscles,
ligaments and other soft tissues, which are often compromised in
open procedures. The preservation of these structures is critical
for maintaining spinal stability and reducing the risk of further
degeneration in adjacent segments (59). Han et al (110) demonstrate that percutaneous
endoscopic lumbar foraminotomy and interlaminar decompression
effectively alleviate ASD symptoms following lumbar decompression
surgery. Feng et al (111)
report that for elderly patients with ASD following lumbar fusion,
presenting with unilateral radiculopathy or intermittent
claudication and showing radiographic stability, percutaneous
full-endoscopic lumbar discectomy is a viable alternative.
Additionally, one study showed favorable outcomes with the
unilateral biportal endoscopic approach (112). Furthermore, minimally invasive
discectomy, without fusion, proves effective in treating new-onset
cervical disc herniation in patients with previous multilevel
fusion (113). Robot-assisted CBT
screw fixation is identified as an effective salvage strategy for
ASD after lumbar fusion (114).
Moreover, MIS techniques can be combined depending on the disease
characteristics, such as integrating percutaneous spinal endoscopy
with fusion techniques and CBT screw placement (59). However, no standardized criteria
currently exist for selecting surgical methods and further studies
with larger sample sizes and longer follow-up periods are needed to
evaluate the efficacy of these revision surgeries.
OLIF (Oblique lateral interbody
fusion) technique
The OLIF technique accesses the intervertebral disc
via the natural corridor between the peritoneum and the psoas
muscle, minimizing trauma to posterior muscles, ligaments and other
structures (115). This approach
reduces the risks of vascular and nerve plexus injuries, as well as
postoperative low back pain (116). OLIF also facilitates the removal
of substantial disc tissue, increasing the fusion surface area,
which enhances fusion rates (115,116). OLIF alone is an effective option
for symptomatic adult ASD (115).
Compared with PLIF, OLIF demonstrates superior outcomes in terms of
the operative time, blood loss, postoperative complications and
restoration of disc height (116). However, OLIF provides only
indirect decompression, which may be inadequate for patients with
large disc herniations, ossifications, or spinal stenosis (115). One study indicated that
complication rates after lateral approaches (lateral lumbar
interbody fusion, LLIF or OLIF) and posterior approaches (PLIF or
TLIF) are similar when treating ASD. Lateral approaches may
increase the risk of radicular pain due to manipulation of the
psoas muscle (117). Therefore,
surgical decisions must be carefully tailored to the specific
characteristics of the patient's ASD.
Zero-profile (Zero-P) interbody fusion
for cervical ASD
With the increasing clinical application of ACDF
and ACCF and longer follow-up periods, ASD has gained attention
from spine surgeons, with a number of cases requiring surgical
treatment. Scar tissue and prior anterior fixation devices limit
the space for revision surgeries, often necessitating hardware
removal, which prolongs operative time and increases blood loss
(118). The Zero-P system, a
stand-alone device developed for ACDF, reduces complications such
as dysphagia and esophageal injury while providing the benefits of
fusion and anterior plating (119). However, one study suggested that
the Zero-P system is not recommended for single-segment ASD cases
with severe ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament,
osteoporosis, or vertebral fractures (120). Moreover, there is a lack of
prospective studies and long-term follow-up observations on its use
in ASD surgeries, raising concerns about its long-term efficacy and
safety in these specific patient populations.
Emerging treatments and future
directions
Compared with primary lumbar fusion surgery,
revision lumbar fusion is linked to higher rates of reoperation and
subsequent revision surgeries (121). This can lead to a vicious cycle,
particularly in younger patients undergoing SF. Therefore,
innovative treatments for IDD are urgently needed. Recent advances
in biological therapies offer potential solutions in this area,
providing new hope for more effective interventions. Techniques or
materials such as stem cell and exosome therapies, growth factor
injections, annulus fibrosus repair, tissue engineering,
biocompatible interbody cages made from polyetheretherketone
(PEEK), 3D-printed implants and nanoparticle drug delivery systems
were designed to promote the regeneration and repair of
intervertebral discs (122–127). Yu et al (122) demonstrate that transplanting of
menstrual blood-derived stem cells embedded in collagen I gel into
annulus fibrosus defects after discectomy in rats preserves disc
structure and prevents post-discectomy disc degeneration. Jia et
al (123) found that
injecting acellular/drug hydrogels with nucleus pulposus-matched
viscoelasticity maintains the viability of nucleus pulposus cells
under pathological loading conditions, showing potential for
post-discectomy repair. In a study of patients 12 weeks
post-discectomy, autologous disc chondrocyte transplantation
provided long-term pain relief over a two-year follow-up period,
although it did not alter disc height (124). Meng et al (125) developed a high-strength smart
microneedle capable of locally penetrating annulus fibrosus tissue,
with near-infrared remote-controlled drug release to restore the
biomechanical properties of the disc. The studies of Dou et
al (126) and Wang et
al (127) demonstrate that
posterior lumbar decompression, fixation and fusion effectively
reconstructs lumbar stability, with fusion rates for 3D-printed
interbody cages and PEEK cage groups reaching 89.13 and 90.91%,
respectively. Notably, excellent interbody fusion can be achieved
without the need for bone grafting (126,127). Encouragingly, a number of other
biological therapies such as gene editing technologies were
currently under investigation. However, since most of these
therapies remain in the experimental stage (Table I), further research is necessary to
establish their efficacy and safety in clinical practice.
 | Table I.Treatment strategies for adjacent
segment disease. |
Table I.
Treatment strategies for adjacent
segment disease.
| Treatment
strategies | Treatment
method | (Refs.) |
|---|
|
| Postoperative
rehabilitation therapy | (9,57,83–89) |
|
| Pharmacological
treatment | (91,92) |
| Conservative
treatment | Epidural steroid
injections | (93–95) |
|
| Facet joint
interventions | (97–100) |
|
| Total disc
replacement | (101,102) |
|
| Extension of
fusion | (105–107) |
|
| Decompression
surgery | (108–110) |
| Surgical
interventions | Minimally invasive
surgery | (111–115) |
|
| Oblique lateral
interbody fusion | (116–118) |
|
| Zero-profile
interbody fusion | (120,121) |
|
| Stem cell and
exosome therapies | (123,124) |
|
| Annulus fibrosus
repair | (124) |
| Emerging
treatments | Tissue
engineering | (123) |
|
| Nanoparticle drug
delivery systems | (126) |
|
| Growth factor
injections | (126) |
|
| 3D-printed
interbody cages and PEEK cage | (127,128) |
Conclusion and future perspectives
While fusion itself may exacerbate the degeneration
of adjacent spinal levels, the question of whether ASD results from
the natural progression of the disease or the fusion surgery itself
remains contentious (128). The
present review identified several potential risk factors for ASD
following SF, including patient-related variables such as age, BMI,
BMD, diabetes and overall health, as well as surgical factors such
as the length of the fusion segment, the surgical approach and
specific technical choices (Fig.
1).
In conclusion, ASD remains a challenging
complication of spinal fusion surgery, with both mechanical and
biological factors contributing to its development. Current
treatment strategies, including conservative management,
interventional procedures and surgical interventions, provide
varying levels of relief, but the risk of further degeneration
persists. Emerging treatments, such as stem cell therapy,
exosome-based treatments and gene therapy, offer promising new
avenues for addressing the underlying causes of ASD. These
therapies aim to restore the biomechanical and biochemical
environment of the intervertebral disc, potentially reducing the
need for revision surgeries. MIS techniques also show potential in
reducing tissue damage and promoting faster recovery, further
contributing to improved long-term outcomes for ASD patients.
Future research should focus on large-scale
clinical trials to validate the safety and efficacy of these
emerging therapies. Additionally, multidisciplinary approaches that
integrate biological, mechanical and patient-specific factors will
be essential for optimizing treatment strategies and improving
patient outcomes.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
Funding: No funding was received.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Authors' contributions
XH was responsible for reviewing the concept
design, article writing and proofreading. YC, KC, QR, BH, GW, YW
and JL participated in the literature collection, analysis and
summary. JZ was involved in drafting the manuscript and revising it
critically for important intellectual content. Data authentication
is not applicable. All authors read and approved the final
manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
Not applicable.
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
References
|
1
|
Wang K, Wang X, Li Z, Xie T, Wang L, Luo
C, Huang S and Zeng J: The influence of screw positioning on cage
subsidence in patients with oblique lumbar interbody fusion
combined with anterolateral fixation. Orthop Surg. 15:3263–3271.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Nakajima H, Watanabe S, Honjoh K, Kubota A
and Matsumine A: Risk factors for early-onset adjacent segment
degeneration after one-segment posterior lumbar interbody fusion.
Sci Rep. 14:91452024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hilibrand AS and Robbins M: Adjacent
segment degeneration and adjacent segment disease: The consequences
of spinal fusion? Spine J. 4 (Suppl 6):190S–194S. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Shahzad H, Alvarez PM, Pallumeera M,
Bhatti N, Yu E, Phillips FM, Khan SN and Singh VK: Exploring the
incidence and risk factors of reoperation for symptomatic adjacent
segment disease following cervical decompression and fusion. N Am
Spine Soc J. 17:1003052023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sears WR, Sergides IG, Kazemi N, Smith M,
White GJ and Osburg B: Incidence and prevalence of surgery at
segments adjacent to a previous posterior lumbar arthrodesis. Spine
J. 11:11–20. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Helgeson MD, Bevevino AJ and Hilibrand AS:
Update on the evidence for adjacent segment degeneration and
disease. Spine J. 13:342–351. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Pinto EM, Teixeria A, Frada R, Oliveira F,
Atilano P, Veigas T and Miranda A: Patient-related risk factors for
the development of lumbar spine adjacent segment pathology. Orthop
Rev (Pavia). 13:249152021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Berman D, Oren JH, Bendo J and Spivak J:
The effect of smoking on spinal fusion. Int J Spine Surg.
11:292017. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Daniels CJ, Wakefield PJ, Bub GA and
Toombs JD: A narrative review of lumbar fusion surgery with
relevance to chiropractic practice. J Chiropr Med. 15:259–271.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wilson C, Czernik PJ, Elgafy H, Khuder S,
Serdahely K, Rowland A and Lecka-Czernik B: Diabetes increases risk
of lumbar spinal fusion complications: association with altered
structure of newly formed bone at the fusion site. JBMR Plus.
8:ziae0532024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Saghebdous S, Zare R, Chaurasia B,
Vakilzadeh MM, Yousefi O and Boustani MR: Dynamic rod constructs as
the preventive strategy against adjacent segment disease in
degenerative lumbar spinal disorders: A retrospective comparative
cohort study. Arch Bone Jt Surg. 11:404–413. 2023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wu JC, Chang HK, Huang WC and Chen YC:
Risk factors of second surgery for adjacent segment disease
following anterior cervical discectomy and fusion: A 16-year cohort
study. Int J Surg. 68:48–55. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tobert DG, Antoci V, Patel SP, Saadat E
and Bono CM: Adjacent segment disease in the cervical and lumbar
spine. Clin Spine Surg. 30:94–101. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wei Z, Yang S, Zhang Y, Ye J and Chu T:
Prevalence and risk factors for cervical adjacent segment disease
and analysis of the clinical effect of revision surgery: A minimum
of 5 years' follow-up. Global Spine J. Jul 8–2023.(Epub ahead of
print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Mesregah MK, Yoshida B, Lashkari N, Abedi
A, Meisel HJ, Diwan A, Hsieh P, Wang JC, Buser Z and Yoon ST; AO
Spine Knowledge Forum Degenerative, : Demographic, clinical, and
operative risk factors associated with postoperative adjacent
segment disease in patients undergoing lumbar spine fusions: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Spine J. 22:1038–1069. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cannizzaro D, Anania CD, Safa A, Zaed I,
Morenghi M, Riva M, Tomei M, Pessina F, Servadei F, Ortolina A and
Fornari M: Lumbar adjacent segment degeneration after spinal fusion
surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Neurosurg Sci.
67:740–749. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tomé-Bermejo F, Moreno-Mateo F,
Piñera-Parrilla Á, Cervera-Irimia J, Mengis-Palleck CL,
Gallego-Bustos J, Garzón-Márquez F, Rodríguez-Arguisjuela MG,
Sanz-Aguilera S, de la Rosa-Zabala KL, et al: Instrumented lumbar
fusion in patients over 75 years of age: is it worthwhile?-A
comparative study of the improvement in quality of life between
elderly and young patients. J Spine Surg. 9:247–258. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhong ZM, Deviren V, Tay B, Burch S and
Berven SH: Adjacent segment disease after instrumented fusion for
adult lumbar spondylolisthesis: Incidence and risk factors. Clin
Neurol Neurosurg. 156:29–34. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ankrah NK, Eli IM, Magge SN, Whitmore RG
and Yew AY: Age, body mass index, and osteoporosis are more
predictive than imaging for adjacent-segment reoperation after
lumbar fusion. Surg Neurol Int. 12:4532021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Broida SE, Murakami K, Abedi A, Meisel HJ,
Hsieh P, Wang J, Jain A, Buser Z and Yoon ST; AO Spine Knowledge
Forum Degenerative, : Clinical risk factors associated with the
development of adjacent segment disease in patients undergoing
ACDF: A systematic review. Spine J. 23:146–156. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang F, Hou HT, Wang P, Zhang JT and Shen
Y: Symptomatic adjacent segment disease after single-lever anterior
cervical discectomy and fusion: Incidence and risk factors.
Medicine (Baltimore). 96:e86632017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yuan C, Zhou J, Wang L and Deng Z:
Adjacent segment disease after minimally invasive transforaminal
lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar diseases: Incidence
and risk factors. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 23:9822022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Demir Ö, Öksüz E, Deniz FE and Demir O:
Assessing the effects of lumbar posterior stabilization and fusion
to vertebral bone density in stabilized and adjacent segments by
using Hounsfield unit. J Spine Surg. 3:548–553. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhang C, Chang M, Zhang R and Tang S:
Biomechanical effects of osteoporosis on adjacent segments after
posterior lumbar interbody fusion: A finite element study. Pak J
Med Sci. 37:403–408. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dash AS, Billings E, Vlastaris K, Kim HJ,
Cunningham ME, Raphael J, Lovecchio F, Carrino JA, Lebl D, McMahon
D and Stein EM: Pre-operative bone quality deficits and risk of
complications following spine fusion surgery among postmenopausal
women. Osteoporos Int. 35:551–560. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang SK, Wang P, Li XY, Kong C, Niu JY and
Lu SB: Incidence and risk factors for early and late reoperation
following lumbar fusion surgery. J Orthop Surg Res. 17:3852022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Gong DC, Baumann AN, Muralidharan A, Piche
JD, Anderson PA and Aleem I: The association of preoperative bone
mineral density and outcomes after anterior cervical discectomy and
fusion: A systematic review. Clin Spine Surg. Jul 23–2024.(Epub
ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Lechtholz-Zey EA, Ayad M, Gettleman BS,
Mills ES, Shelby H, Ton AT, Shah I, Wang JC, Hah RJ and Alluri RK:
Systematic review and meta-analysis of the effect of osteoporosis
on reoperation rates and complications after surgical management of
lumbar degenerative disease. J Bone Metab. 31:114–131. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhou Z, Tian FM, Wang P, Gou Y, Zhang H,
Song HP, Wang WY and Zhang L: Alendronate prevents intervertebral
disc degeneration adjacent to a lumbar fusion in ovariectomized
rats. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 40:E1073–E1083. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bagheri SR, Alimohammadi E, Zamani
Froushani A and Abdi A: Adjacent segment disease after posterior
lumbar instrumentation surgery for degenerative disease: Incidence
and risk factors. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong).
27:23094990198423782019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Thever Y, Han Lincoln LM, Gatot C and Chee
Cheong RS: Do diabetic patients have poorer clinical and
radiological outcomes following minimally invasive transforaminal
lumbar interbody fusion? Int J Spine Surg. 17:708–714. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Russo A, Park DK, Lansford T, Nunley P,
Peppers TA, Wind JJ, Hassanzadeh H, Sembrano J, Yoo J and Sales J:
Impact of surgical risk factors for non-union on lumbar spinal
fusion outcomes using cellular bone allograft at 24-months
follow-up. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 25:3512024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lee CS, Hwang CJ, Lee SW, Ahn YJ, Kim YT,
Lee DH and Lee MY: Risk factors for adjacent segment disease after
lumbar fusion. Eur Spine J. 18:1637–1643. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Pang L, Gao Z, Ma L, Li Y, Lu Z, Zhang L,
Li P and Wu L: Comparison of short-segment and long-segment
fixation in treatment of degenerative scoliosis and analysis of
factors associated with adjacent spondylolisthesis. Open Med
(Wars). 19:202409832024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kim JY, Ryu DS, Paik HK, Ahn SS, Kang MS,
Kim KH, Park JY, Chin DK, Kim KS, Cho YE and Kuh SU: Paraspinal
muscle, facet joint, and disc problems: Risk factors for adjacent
segment degeneration after lumbar fusion. Spine J. 16:867–875.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Tan L, Du X, Tang R, Rong L and Zhang L:
Preoperative adjacent facet joint osteoarthritis is associated with
the incidence of adjacent segment degeneration and low back pain
after lumbar interbody fusion. Asian Spine J. 18:21–31. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Weishaupt D, Zanetti M, Boos N and Hodler
J: MR imaging and CT in osteoarthritis of the lumbar facet joints.
Skeletal Radiol. 28:215–219. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Mu YZ, Chen X and Zhao B: Effect of
adjacent segmental facet joint degeneration on adjacent segment
disease after lumbar fusion and fixation. Zhongguo Gu Shang.
36:428–431. 2023.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ekman P, Möller H, Shalabi A, Yu YX and
Hedlund R: A prospective randomised study on the long-term effect
of lumbar fusion on adjacent disc degeneration. Eur Spine J.
18:1175–1186. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhu Q, Li N, Ding Y, Zhang Z, Jiang W,
Jiang T, Qiao Q, Qian Y and Cheng H: Incidence of adjacent segment
degeneration and its associated risk factors following anterior
cervical discectomy and fusion: A meta-analysis. World Neurosurg.
183:e153–e172. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Todd KH, Funk KG, Funk JP and Bonacci R:
Clinical significance of reported changes in pain severity. Ann
Emerg Med. 27:485–489. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Fairbank JC, Couper J, Davies JB and
O'Brien JP: The Oswestry low back pain disability questionnaire.
Physiotherapy. 66:271–273. 1980.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Sun Z, Li W, Guo Y, Zhou S, Xu F, Chen Z,
Qi Q, Guo Z, Zeng Y and Sun C: Effect of pre-existing adjacent
segment degeneration on short-term effectiveness after lumbar
fusion surgery. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi.
33:837–844. 2019.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Matsumoto T, Okuda S, Nagamoto Y,
Takahashi Y, Furuya M and Iwasaki M: Spinopelvic sagittal
realignment and incidence of adjacent segment disease after
single-segment posterior lumbar inter-body fusion using 12°
lordotic cages-a 2-year prospective cohort study. J Spine Surg.
9:269–277. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Tartara F, Garbossa D, Armocida D, Di
Perna G, Ajello M, Marengo N, Bozzaro M, Petrone S, Giorgi PD,
Schirò GR, et al: Relationship between lumbar lordosis, pelvic
parameters, PI-LL mismatch and outcome after short fusion surgery
for lumbar degenerative disease. Literature review, rational and
presentation of public study protocol: RELApSE study (registry for
evaluation of lumbar artrodesis sagittal alignEment). World
Neurosurg X. 18:1001622023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Park JS, Shim KD, Song YS and Park YS:
Risk factor analysis of adjacent segment disease requiring surgery
after short lumbar fusion: The influence of rheumatoid arthritis.
Spine J. 18:1578–1583. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Loder RT, Urquhart A, Steen H, Graziano G,
Hensinger RN, Schlesinger A, Schork MA and Shyr Y: Variability in
Cobb angle measurements in children with congenital scoliosis. J
Bone Joint Surg Br. 77:768–770. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Okuda S, Yamashita T, Matsumoto T,
Nagamoto Y, Sugiura T, Takahashi Y, Maeno T and Iwasaki M: Adjacent
segment disease after posterior lumbar interbody fusion: A case
series of 1000 patients. Global Spine J. 8:722–727. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Burch MB, Wiegers NW, Patil S and
Nourbakhsh A: Incidence and risk factors of reoperation in patients
with adjacent segment disease: A meta-analysis. J Craniovertebr
Junction Spine. 11:9–16. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Zhang C, Berven SH, Fortin M and Weber MH:
Adjacent segment degeneration versus disease after lumbar spine
fusion for degenerative pathology: A systematic review with
meta-analysis of the literature. Clin Spine Surg. 29:21–29. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Alentado VJ, Lubelski D, Healy AT, Orr RD,
Steinmetz MP, Benzel EC and Mroz TE: Predisposing characteristics
of adjacent segment disease after lumbar fusion. Spine (Phila Pa
1976). 41:1167–1172. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Wang T and Ding W: Risk factors for
adjacent segment degeneration after posterior lumbar fusion surgery
in treatment for degenerative lumbar disorders: A meta-analysis. J
Orthop Surg Res. 15:5822020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Ke W, Chen C, Wang B, Hua W, Lu S, Song Y,
Luo R, Liao Z, Li G, Ma L, et al: Biomechanical evaluation of
different surgical approaches for the treatment of adjacent segment
diseases after primary anterior cervical discectomy and fusion: A
finite element analysis. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 9:7189962021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Epstein NE and Agulnick MA: Cervical disc
arthroplasty (CDA)/total disc replacement (TDR) vs. anterior
cervical diskectomy/fusion (ACDF): A review. Surg Neurol Int.
13:5652022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Bydon M, Xu R, De la Garza-Ramos R, Macki
M, Sciubba DM, Wolinsky JP, Witham TF, Gokaslan ZL and Bydon A:
Adjacent segment disease after anterior cervical discectomy and
fusion: Incidence and clinical outcomes of patients requiring
anterior versus posterior repeat cervical fusion. Surg Neurol Int.
5 (Suppl 3):S74–S78. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Liu WJ, Hu L, Chou PH, Wang JW and Kan WS:
Comparison of anterior cervical discectomy and fusion versus
posterior cervical foraminotomy in the treatment of cervical
radiculopathy: A systematic review. Orthop Surg. 8:425–431. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Jeong TS, Son S, Lee SG, Ahn Y, Jung JM
and Yoo BR: Comparison of adjacent segment disease after minimally
invasive versus open lumbar fusion: A minimum 10-year follow-up. J
Neurosurg Spine. 36:525–533. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Xu F, Zhou S, Sun Z, Jiang S, Han G and Li
W: Relationship between the postoperative variations of paraspinal
muscles and adjacent-segment degeneration in patients with
degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis after posterior instrumented
lumbar fusion. J Neurosurg Spine. 40:551–561. 2024.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Liu DS, Wang YX and Rexiti P: Progress in
minimally invasive surgery for adjacent segment disease after
lumbar fusion. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi. 61:722–727. 2023.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Varol E, Etli MU, Avci F, Yaltirik CK,
Ramazanoglu AF, Onen MR and Naderi S: Comparison of clinical and
radiological results of dynamic and rigid instrumentation in
degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis. J Craniovertebr Junction
Spine. 13:350–356. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Kim CH, Chung CK and Jahng TA: Comparisons
of outcomes after single or multilevel dynamic stabilization:
Effects on adjacent segment. J Spinal Disord Tech. 24:60–67. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Hsiao CK, Tsai YJ, Yen CY, Li YC, Hsiao HY
and Tu YK: Biomechanical effect of hybrid dynamic stabilization
implant on the segmental motion and intradiscal pressure in human
lumbar spine. Bioengineering (Basel). 10:312022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Guan J, Liu T, Yu X, Li W, Feng N, Jiang
G, Zhao H and Yang Y: Biomechanical and clinical research of Isobar
semi-rigid stabilization devices for lumbar degenerative diseases:
A systematic review. Biomed Eng Online. 22:952023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Liu L, He J, Liu C, Yang M, Fu J, Yi J, Ai
X, Liu M, Zhuang Y, Zhang Y, et al: Cartilage intermediate layer
protein affects the progression of intervertebral disc degeneration
by regulating the extracellular microenvironment (review). Int J
Mol Med. 47:475–484. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Chan D, Song Y, Sham P and Cheung KMC:
Genetics of disc degeneration. Eur Spine J. 15 (Suppl 3):S317–S325.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Johnson ZI, Schoepflin ZR, Choi H, Shapiro
IM and Risbud MV: Disc in flames: Roles of TNF-α and IL-1β in
intervertebral disc degeneration. Eur Cell Mater. 30:104–117. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Chen S, Suo S, Xie Z, He J, Li J, Duan D,
Qiao G and Zhang W: Establishment of an animal model of adjacent
segment degeneration after interbody fusion and related
experimental studies. J Orthop Surg Res. 18:6662023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Gaudiani MA, Winkelman RD, Ravishankar P,
Rabah NM, Mroz TE and Coughlin DJ: The association of preoperative
TNF-alpha inhibitor use and reoperation rates in spinal fusion
surgery. Spine J. 21:972–979. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Lu QL, Wang XZ, Xie W, Chen XW, Zhu YL and
Li XG: Macrophage migration inhibitory factor may contribute to
hypertrophy of lumbar ligamentum flavum in type 2 diabetes
mellitus. Chin Med J (Engl). 133:623–625. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Xiong C, Huang Y, Kang H, Zhang T, Xu F
and Cai X: Macrophage inhibition factor-mediated CD74 signal
modulate inflammation and matrix metabolism in the degenerated
cartilage endplate chondrocytes by activating extracellular signal
regulated kinase 1/2. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 42:E61–E70. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Ying Y, Cai K, Cai X, Zhang K, Qiu R,
Jiang G and Luo K: Recent advances in the repair of degenerative
intervertebral disc for preclinical applications. Front Bioeng
Biotechnol. 11:12597312023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Wong J, Sampson SL, Bell-Briones H, Ouyang
A, Lazar AA, Lotz JC and Fields AJ: Nutrient supply and nucleus
pulposus cell function: Effects of the transport properties of the
cartilage endplate and potential implications for intradiscal
biologic therapy. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 27:956–964. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Xiang P, Luo ZP and Che YJ: Insights into
the mechanical microenvironment within the cartilaginous endplate:
An emerging role in maintaining disc homeostasis and normal
function. Heliyon. 10:e311622024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Gilbert HTJ, Hodson N, Baird P, Richardson
SM and Hoyland JA: Acidic pH promotes intervertebral disc
degeneration: Acid-sensing ion channel-3 as a potential therapeutic
target. Sci Rep. 6:373602016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Thys T, Bogaert L, Dankaerts W, Depreitere
B, Van Wambeke P, Brumangne S, Bultheel M, Vanden Abeele V, Moke L,
Spriet A, et al: Qualitative study exploring the views of patients
and healthcare providers on current rehabilitation practices after
lumbar fusion surgery. BMJ Open. 14:e0777862024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Adogwa O, Verla T, Thompson P, Penumaka A,
Kudyba K, Johnson K, Fulchiero E, Miller T Jr, Hoang KB, Cheng J
and Bagley CA: Affective disorders influence clinical outcomes
after revision lumbar surgery in elderly patients with symptomatic
adjacent-segment disease, recurrent stenosis, or pseudarthrosis:
Clinical article. J Neurosurg Spine. 21:153–159. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Archer KR, Seebach CL, Mathis SL, Riley LH
and Wegener ST: Early postoperative fear of movement predicts pain,
disability, and physical health six months after spinal surgery for
degenerative conditions. Spine J. 14:759–767. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Jakobsson M, Hagströmer M, Lotzke H, von
Rosen P and Lundberg M: Fear of movement was associated with
sedentary behaviour 12 months after lumbar fusion surgery in
patients with low back pain and degenerative disc disorder. BMC
Musculoskelet Disord. 24:8742023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Glassman SD, Anagnost SC, Parker A, Burke
D, Johnson JR and Dimar JR: The effect of cigarette smoking and
smoking cessation on spinal fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).
25:2608–2615. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Maurel DB, Boisseau N, Benhamou CL and
Jaffre C: Alcohol and bone: Review of dose effects and mechanisms.
Osteoporos Int. 23:1–16. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Chou PH, Lin HH, An HS, Liu KY, Su WR and
Lin CL: Could the topping-off technique be the preventive strategy
against adjacent segment disease after pedicle screw-based fusion
in lumbar degenerative diseases? A systematic review. Biomed Res
Int. 2017:43856202017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Zhou C, Zhou N, Zheng Y, Si H, Wang Y and
Yin J: The efficacy of 3D gait analysis to evaluate surgical (and
rehabilitation) outcome after degenerative lumbar surgery. BMC
Surg. 24:1972024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Barbosa TP, Raposo AR, Cunha PD, Cruz
Oliveira N, Lobarinhas A, Varanda P and Direito-Santos B:
Rehabilitation after cervical and lumbar spine surgery. EFORT Open
Rev. 8:626–638. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Pennington Z, Cottrill E, Ahmed AK,
Passias P, Protopsaltis T, Neuman B, Kebaish KM, Ehresman J,
Westbroek EM, Goodwin ML and Sciubba DM: Paraspinal muscle size as
an independent risk factor for proximal junctional kyphosis in
patients undergoing thoracolumbar fusion. J Neurosurg Spine.
31:380–388. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Kwok WCH, Wong CYY, Law JHW, Tsang VWT,
Tong LWL, Samartzis D, An HS and Wong AYL: Risk factors for
adjacent segment disease following anterior cervical discectomy and
fusion with plate fixation: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
J Bone Joint Surg Am. 104:1915–1945. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Beyerman KL, Palmerino MB, Zohn LE, Kane
GM and Foster KA: Efficacy of treating low back pain and
dysfunction secondary to osteoarthritis: Chiropractic care compared
with moist heat alone. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 29:107–114.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Gliedt JA, Daniels CJ and Wuollet A:
Narrative review of perioperative acupuncture for clinicians. J
Acupunct Meridian Stud. 8:264–269. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Zhao B, Wang K, Zhao JX, Wang C, Huang X,
Shu-qiang M and Qiang H: Clinical effects of acupuncture after
surgical operation in patients with prolapse of the lumbar
intervertebral disc. J Tradit Chin Med. 28:250–254. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Chou D, Dekutoski M, Hermsmeyer J and
Norvell DC: The treatment of lumbar adjacent segment pathology
after a previous lumbar surgery: A systematic review. Spine (Phila
Pa 1976). 37 (22 Suppl):S180–S188. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
McDonald CL, Alsoof D, Glueck J, Osorio C,
Stone B, McCluskey L, Diebo BG, Daniels AH and Basques BA: Adjacent
segment disease after spinal fusion. JBJS Rev. 11:2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
91
|
Kamali A, Ziadlou R, Lang G, Pfannkuche J,
Cui S, Li Z, Richards RG, Alini M and Grad S: Small molecule-based
treatment approaches for intervertebral disc degeneration: Current
options and future directions. Theranostics. 11:27–47. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Song JH, Lee WY, Cho KR, Nam SH, Park KD
and Park Y: Fluoroscopy-guided transforaminal versus caudal
epidural steroid injection for chronic pain after spinal surgery: A
retrospective mid-term comparative study. J Pain Res. 14:2129–2138.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Kvasnitskyi M: Epidural injections in the
treatment of radicular syndrome and chronic lower back pain in
degenerative-dystrophic spine damage. Georgian Med News. 109–115.
2022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Park KD, Lee WY, Nam SH, Kim M and Park Y:
Ultrasound-guided selective nerve root block versus
fluoroscopy-guided interlaminar epidural block for the treatment of
radicular pain in the lower cervical spine: A retrospective
comparative study. J Ultrasound. 22:167–177. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Yoo YM and Kim KH: Facet joint disorders:
From diagnosis to treatment. Korean J Pain. 37:3–12. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Manchikanti L, Kaye AD, Soin A, Albers SL,
Beall D, Latchaw R, Sanapati MR, Shah S, Atluri S, Abd-Elsayed A,
et al: Comprehensive evidence-based guidelines for facet joint
interventions in the management of chronic spinal pain: American
society of interventional pain physicians (ASIPP) guidelines facet
joint interventions 2020 guidelines. Pain Physician. 23 (Suppl
3):S1–S127. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Wong MJ and Rajarathinam M:
Ultrasound-guided axial facet joint interventions for chronic
spinal pain: A narrative review. Can J Pain. 7:21936172023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Suputtitada A, Nopsopon T, Rittiphairoj T
and Pongpirul K: Intra-articular facet joint injection of normal
saline for chronic low back pain: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Medicina (Kaunas). 59:10382023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Láinez Ramos-Bossini AJ, Jiménez Gutiérrez
PM and Ruiz Santiago F: Efficacy of radiofrequency in lumbar facet
joint pain: A systematic review and meta-analysis of
placebo-controlled randomized controlled trials. Radiol Med.
129:794–806. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Rajakumar DV, Hari A, Krishna M, Konar S
and Sharma A: Adjacent-level arthroplasty following cervical
fusion. Neurosurg Focus. 42:E52017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Lu VM, Mobbs RJ and Phan K: Clinical
outcomes of treating cervical adjacent segment disease by anterior
cervical discectomy and fusion versus total disc replacement: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Global Spine J. 9:559–567.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Parish JM, Asher AM and Coric D:
Adjacent-segment disease following spinal arthroplasty. Neurosurg
Clin N Am. 32:505–510. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Drysch A, Ajiboye RM, Sharma A, Li J, Reza
T, Harley D, Park DY and Pourtaheri S: Effectiveness of
reoperations for adjacent segment disease following lumbar spinal
fusion. Orthopedics. 41:e161–e167. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Chen WJ, Lai PL, Niu CC, Chen LH, Fu TS
and Wong CB: Surgical treatment of adjacent instability after
lumbar spine fusion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 26:E519–E524. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Louie PK, Haws BE, Khan JM, Markowitz J,
Movassaghi K, Ferguson J, Lopez GD, An HS and Phillips FM:
Comparison of stand-alone lateral lumbar interbody fusion versus
open laminectomy and posterolateral instrumented fusion in the
treatment of adjacent segment disease following previous lumbar
fusion surgery. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 44:E1461–E1469. 2019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Turel MK, Kerolus MG, David BT and Fessler
RG: Minimally invasive options for surgical management of adjacent
segment disease of the lumbar spine. Neurol India. 66:755–762.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Yang S, Yang D, Ma L, Wang H and Ding W:
Clinical efficacy of laminectomy with instrumented fixation in
treatment of adjacent segmental disease following ACCF surgery: A
retrospective observational study of 48 patients. Sci Rep.
9:65512019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
He W, He D, Wang QL, Tian W, Liu B, Liu
YJ, Sun YQ, Xing YG, Yuan N, Yuan Q, et al: Longitudinal
spinous-splitting laminoplasty with coral bone for the treatment of
cervical adjacent segment degenerative disease: A 5-year follow-up
study. Orthop Surg. 14:435–442. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Früh A, Leißa P, Tkatschenko D,
Truckenmüller P, Wessels L, Vajkoczy P and Bayerl S: Decompression
with or without fusion in degenerative adjacent segment stenosis
after lumbar fusions. Neurosurg Rev. 45:3739–3748. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Han J, Tang W, Li G, Ji X, Wu X, Zhu K,
Zhang G, Zhou C, Ma X and Guo J: Comparison of percutaneous
endoscopic transforaminal and interlaminar approaches in treating
adjacent segment disease following lumbar decompression surgery: A
clinical retrospective study. Pain Physician. 26:E833–E842. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Feng P, Kong Q, Zhang B, Liu J, Ma J and
Hu Y: Percutaneous full endoscopic lumbar discectomy for
symptomatic adjacent segment disease after lumbar fusion in elderly
patients. Orthop Surg. 15:1749–1755. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Sakhrekar R, Ha JS, Han HD, Kim DH, Kim CW
and Kulkarni S: Unilateral biportal endoscopic approach for
symptomatic adjacent segment disease: Case report and technical
note. J Orthop Case Rep. 13:172–177. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Jacobson RE, Granville M and Berti A:
Minimally invasive anterior cervical discectomy without fusion to
treat cervical disc herniations in patients with previous cervical
fusions. Cureus. 9:e11312017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Han J, Guo J, Ma X, Zhang G, Han S, Zhang
H, Liu H, Chen M and Wang Y: The cortical bone trajectory screw
technique assisted by the mazor renaissance robotic system as a
salvage strategy for failed lumbar spine surgery: Technical note
and case series. J Pain Res. 16:2971–2980. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Zhang B, Hu Y, Kong Q, Feng P, Liu J and
Ma J: Comparison of oblique lumbar interbody fusion combined with
posterior decompression (OLIF-PD) and posterior lumbar interbody
fusion (PLIF) in the treatment of adjacent segmental disease (ASD).
J Pers Med. 13:3682023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Miscusi M, Trungu S, Ricciardi L, Forcato
S, Piazza A, Ramieri A and Raco A: Stand-alone oblique lumbar
interbody fusion (OLIF) for the treatment of adjacent segment
disease (ASD) after previous posterior lumbar fusion: Clinical and
radiological outcomes and comparison with posterior revision
surgery. J Clin Med. 12:29852023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Rajan PV, Megerian M, Desai A, Halkiadakis
PN, Rabah N, Shost MD, Butt B, Showery JE, Grabel Z, Pelle DW and
Savage JW: Transforaminal versus lateral interbody fusions for
treatment of adjacent segment disease in the lumbar spine. Clin
Spine Surg. Sep 12–2024.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Shen Y, Du W, Wang LF, Dong Z and Wang F:
Comparison of zero-profile device versus plate-and-cage implant in
the treatment of symptomatic adjacent segment disease after
anterior cervical discectomy and fusion: A minimum 2-year follow-up
study. World Neurosurg. 115:e226–e232. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Wang F, Wang P, Miao DC, Du W and Shen Y:
Different surgical approaches for the treatment of adjacent segment
diseases after anterior cervical fusion: A retrospective study of
49 patients. Medicine (Baltimore). 96:e70422017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Tu Q, Sun H, Chen H and Zhu C: The
surgical treatment strategy for adjacent segment disease after
anterior cervical discectomy and fusion of multi-segments. Chin J
Clin Anat. 41:218–223. 2023.
|
|
121
|
Lambrechts MJ, Toci GR, Siegel N, Karamian
BA, Canseco JA, Hilibrand AS, Schroeder GD, Vaccaro AR and Kepler
CK: Revision lumbar fusions have higher rates of reoperation and
result in worse clinical outcomes compared to primary lumbar
fusions. Spine J. 23:105–115. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Yu L, Wu H, Zeng S, Hu X, Wu Y, Zhou J,
Yuan L, Zhang Q, Xiang C and Feng Z: Menstrual blood-derived
mesenchymal stem cells combined with collagen I gel as a
regenerative therapeutic strategy for degenerated disc after
discectomy in rats. Stem Cell Res Ther. 15:752024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Jia H, Lin X, Wang D, Wang J, Shang Q, He
X, Wu K, Zhao B, Peng P, Wang H, et al: Injectable hydrogel with
nucleus pulposus-matched viscoelastic property prevents
intervertebral disc degeneration. J Orthop Translat. 33:162–173.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Krut Z, Pelled G, Gazit D and Gazit Z:
Stem cells and exosomes: New therapies for intervertebral disc
degeneration. Cells. 10:22412021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Meng Q, Xie E, Sun H, Wang H, Li J, Liu Z,
Li K, Hu J, Chen Q, Liu C, et al: High-strength smart microneedles
with ‘offensive and defensive’ effects for intervertebral disc
repair. Adv Mater. 36:e23054682024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Dou X, Liu X, Liu Y, Wang L, Jia F, Shen
F, Ma Y, Liang C, Jin G, Wang M, et al: Biomimetic porous Ti6Al4V
implants: A novel interbody fusion cage via gel-casting technique
to promote spine fusion. Adv Healthc Mater. 13:e24005502024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Wang Z, Zhang D, Zhang Z and Miao J: The
postoperative clinical effects of utilizing 3D printed (Ti6Al4V)
interbody fusion cages in posterior lumbar fusion: A retrospective
cohort study. Medicine (Baltimore). 103:e384312024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Song KJ, Choi BW, Jeon TS, Lee KB and
Chang H: Adjacent segment degenerative disease: is it due to
disease progression or a fusion-associated phenomenon? Comparison
between segments adjacent to the fused and non-fused segments. Eur
Spine J. 20:1940–1945. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|