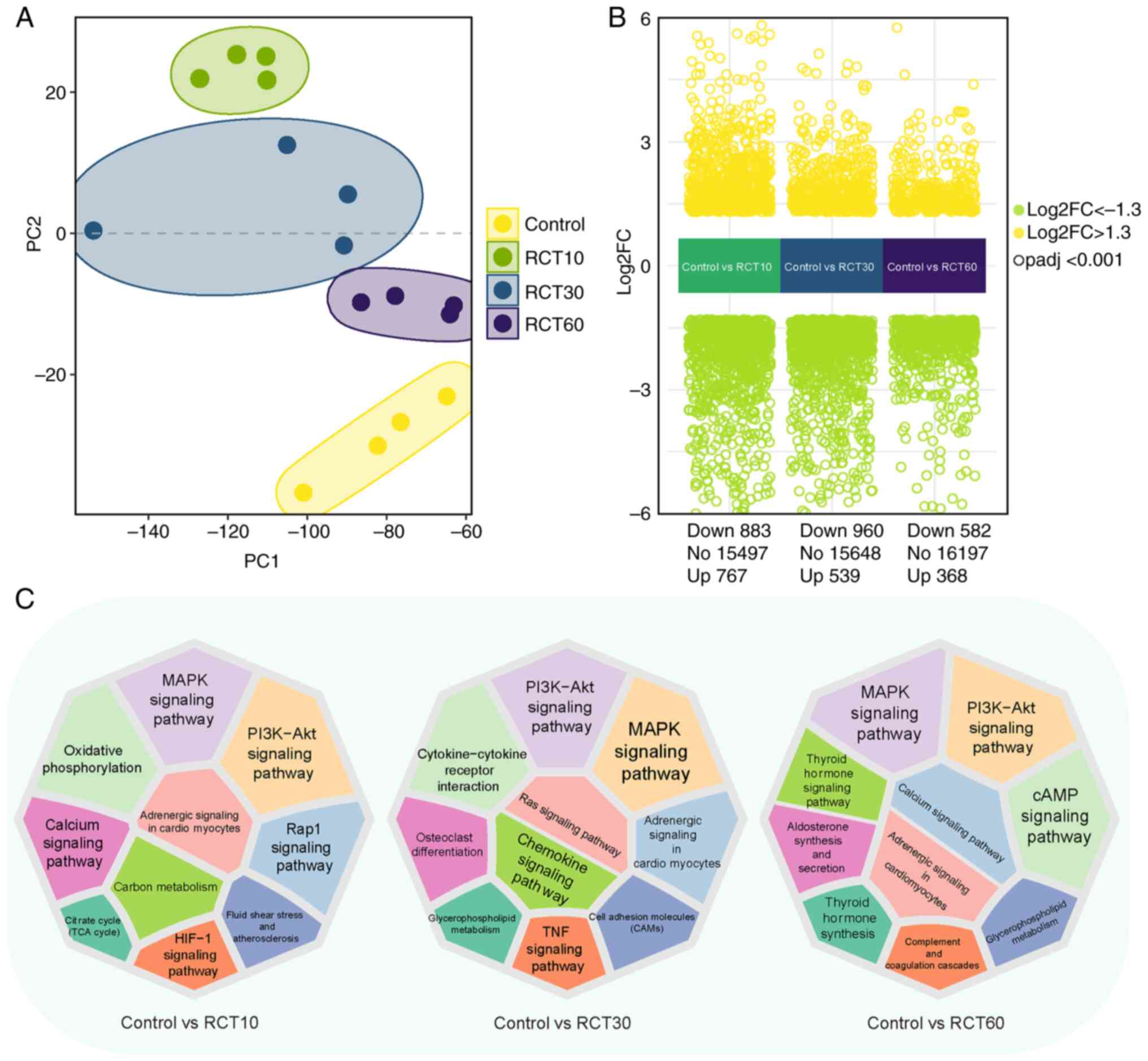
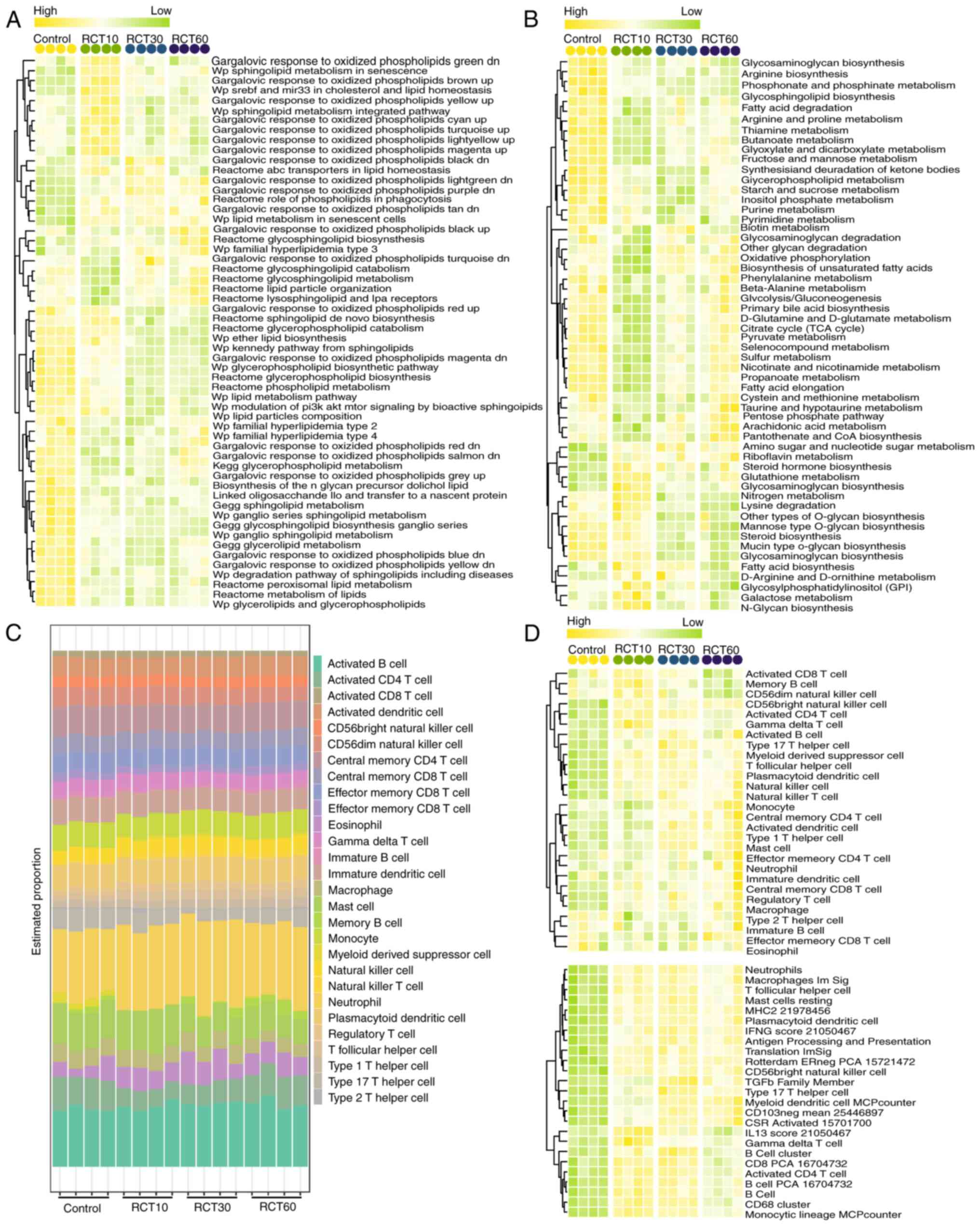
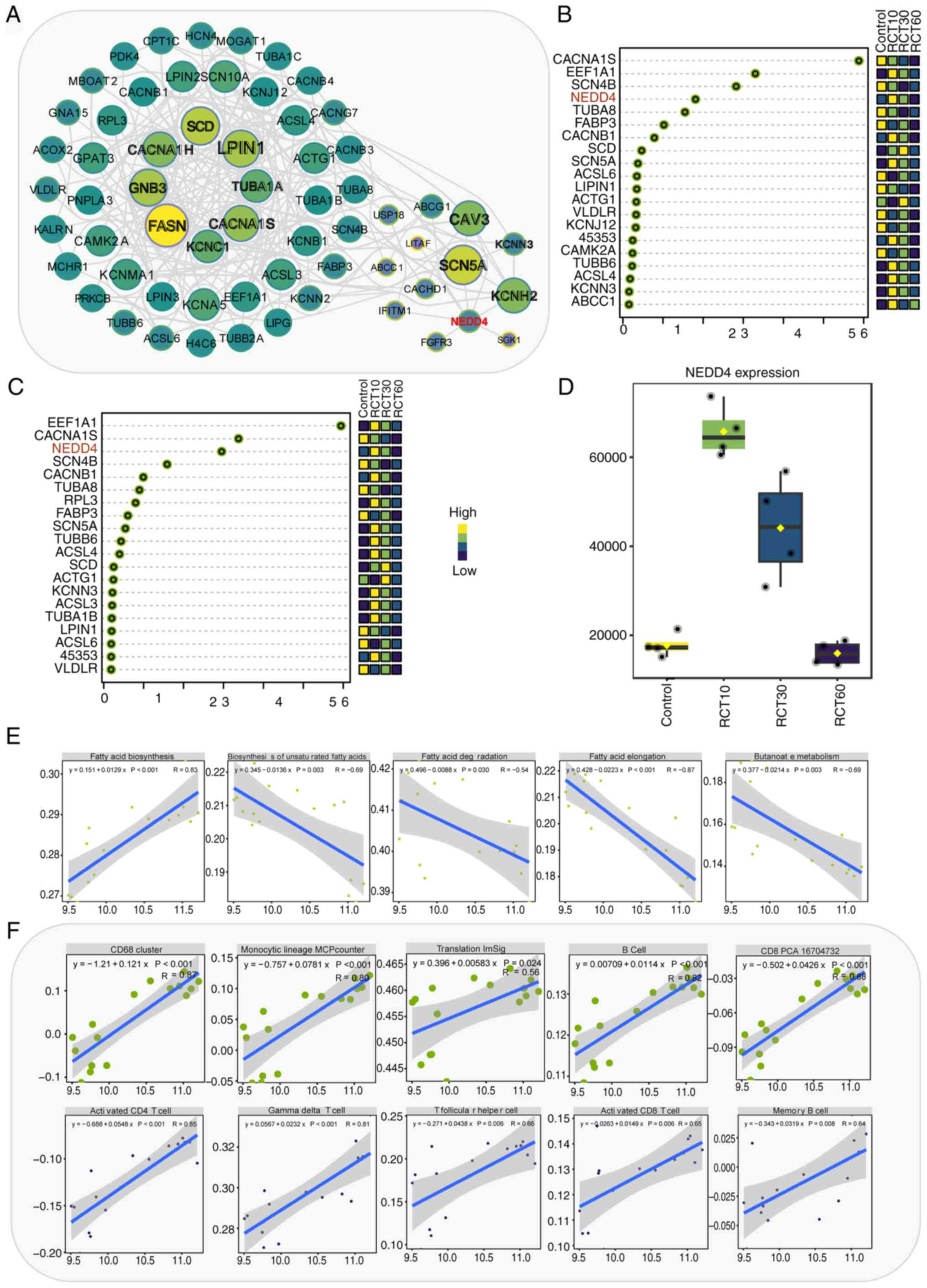
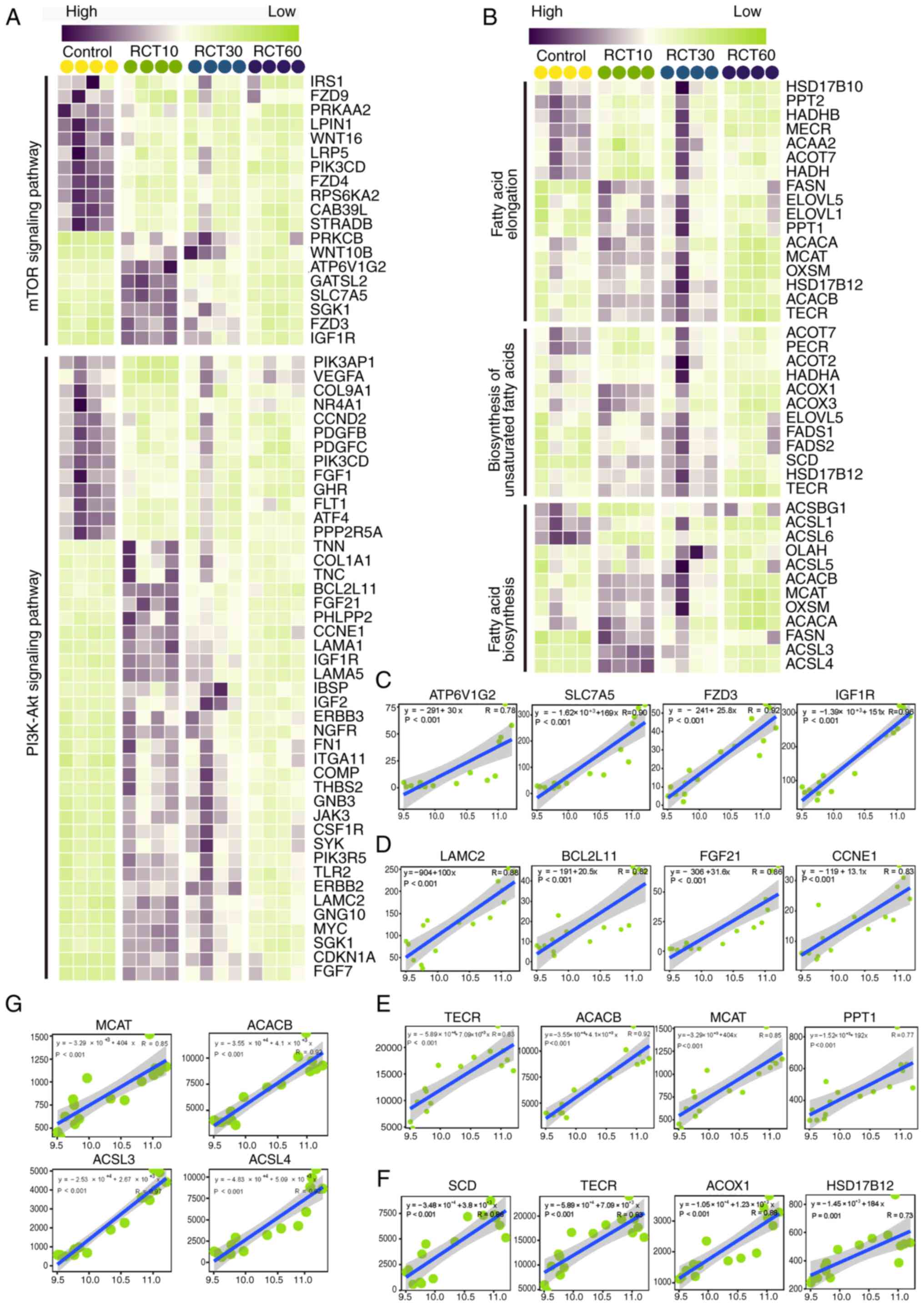
|
1
|
Harada Y, Yokoya S, Sumimoto Y, Iwahori Y,
Kajita Y, Deie M and Adachi N: Prevalence of rotator cuff tears
among older tennis players and its impact on clinical findings and
shoulder function. J Sport Rehabil. 31:849–855. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Merriman MA Jr, Chapman JH, Whitfield T,
Hosseini F, Ghosh D and Laurencin CT: Fat expansion not fat
infiltration of muscle post rotator cuff tendon tears of the
shoulder: Regenerative engineering implications. Regen Eng Transl
Med. 1–14. 2023.
|
|
3
|
Zhu Y, Hu Y, Pan Y, Li M, Niu Y, Zhang T,
Sun H, Zhou S, Liu M, Zhang Y, et al: Fatty infiltration in the
musculoskeletal system: Pathological mechanisms and clinical
implications. Front Endocrinol. 15:14060462024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Alenabi ST: Modifications in early
rehabilitation protocol after rotator cuff repair: EMG Studies
(unpublished PhD thesis). University of Montreal; 2016
|
|
5
|
Fu C, Huang AH, Galatz LM and Han WM:
Cellular and molecular modulation of rotator cuff muscle
pathophysiology. J Orthop Res. 39:2310–2322. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lee S, Park I, Lee HA and Shin SJ: Factors
related to symptomatic failed rotator cuff repair leading to
revision surgeries after primary arthroscopic surgery. Arthroscopy.
36:2080–2088. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Giuliani G, Rosina M and Reggio A:
Signaling pathways regulating the fate of fibro/adipogenic
progenitors (FAPs) in skeletal muscle regeneration and disease.
FEBS J. 289:6484–6517. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Theret M, Rossi FMV and Contreras O:
Evolving roles of muscle-resident fibro-adipogenic progenitors in
health, regeneration, neuromuscular disorders, and aging. Front
Physiol. 12:6734042021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Subhash AK, Davies M, Gatto A, Bogdanov
JM, Lan R, Jensen A, Feeley BT and Petrigliano FA:
Fibro-adipogenesis in injured rotator cuff muscle. Curr Tissue
Microenviron Rep. 3:1–9. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Parker EG: The Role of Fibro-Adipogenic
Progenitor Cells (FAPs) in Muscle Disuse Atrophy. Augusta
University; 2022
|
|
11
|
Bogdanov J, Lan R, Chu TN, Bolia IK, Weber
AE and Petrigliano FA: Fatty degeneration of the rotator cuff:
Pathogenesis, clinical implications, and future treatment. JSES Rev
Rep Tech. 1:301–308. 2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang X, Xu M and Li Y: Adipose tissue
aging and metabolic disorder, and the impact of nutritional
interventions. Nutrients. 14:31342022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chen W, You W, Valencak TG and Shan T:
Bidirectional roles of skeletal muscle fibro-adipogenic progenitors
in homeostasis and disease. Ageing Res Rev. 80:1016822022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Caballero-Sánchez N, Alonso-Alonso S and
Nagy L: Regenerative inflammation: When immune cells help to
re-build tissues. FEBS J. 291:1597–1614. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu GY and Sabatini DM: mTOR at the nexus
of nutrition, growth, ageing and disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
21:183–203. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Querfurth H and Lee HK:
Mammalian/mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) complexes in
neurodegeneration. Mol Neurodegener. 16:442021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Conway JA, Kinsman G and Kramer ER: The
role of NEDD4 E3 ubiquitin-protein ligases in Parkinson's disease.
Genes. 13:5132022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Fitzgerald G: Fibro-adipogenic progenitor
heterogeneity in healthy and diseased skeletal muscle. ETH Zurich.
2022.
|
|
19
|
Szwed A, Kim E and Jacinto E: Regulation
and metabolic functions of mTORC1 and mTORC2. Physiological
reviews. 101:1371–1426. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yue M, Yun Z, Li S, Yan G and Kang Z:
NEDD4 triggers FOXA1 ubiquitination and promotes colon cancer
progression under microRNA-340-5p suppression and ATF1
upregulation. RNA Biology. 18:1981–1995. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Degen RM, Carbone A, Carballo C, Zong J,
Chen T, Lebaschi A, Ying L, Deng XH and Rodeo SA: The effect of
purified human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells on
rotator cuff tendon healing in an athymic rat. ARTHROSCOPY.
32:2435–2443. 1016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Sastourné-Arrey Q, Mathieu M, Contreras X,
Monferran S, Bourlier V, Gil–Ortega M, Murphy E, Laurens C, Varin
A, Guissard C, et al: Adipose tissue is a source of regenerative
cells that augment the repair of skeletal muscle after injury. Nat
Commun. 14:802023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Silva-Vignato B, Coutinho LL, Poleti MD,
Cesar ASM, Moncau CT, Regitano LCA and Balieiro JCC: Gene
co-expression networks associated with carcass traits reveal new
pathways for muscle and fat deposition in Nelore cattle. BMC
Genomics. 20:322019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang L, Qin Y, Wu G, Wang J, Cao J, Wang
Y, Wu D, Yang K, Zhao Z, He L, et al: PRRG4 promotes breast cancer
metastasis through the recruitment of NEDD4 and downregulation of
Robo1. Oncogene. 39:7196–7208. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
King SJ: The role of the energy-sensing
AMP-activated protein kinase in intestinal epithelial physiology
and pathophysiology. University of California; Riverside: 2019
|
|
27
|
Ingham RJ, Gish G and Pawson T: The Nedd4
family of E3 ubiquitin ligases: Functional diversity within a
common modular architecture. Oncogene. 23:1972–1984. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Joe AW, Yi L, Natarajan A, Grand FL, So L,
Wang J, Rudnicki MA and Rossi FMV: Muscle injury activates resident
fibro/adipogenic progenitors that facilitate myogenesis. Nature
Cell Biol. 12:153–163. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Molina T, Fabre P and Dumont NA:
Fibro-adipogenic progenitors in skeletal muscle homeostasis,
regeneration and diseases. Open Biol. 11:2101102021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang N, Wang H, Shen L, Liu X, Ma Y and
Wang C: Aging-related rotator cuff tears: Molecular mechanisms and
implications for clinical management. Adv Biol. 8:e23003312024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Frich LH, Fernandes LR, Schrøder HD,
Hejbøl EK, Nielsen PV, Jørgensen PH, Stensballe A and Lambertsen
KL: The inflammatory response of the supraspinatus muscle in
rotator cuff tear conditions. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 30:e261–e275.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chen W, Chen Y, Liu Y and Wang X:
Autophagy in muscle regeneration: Potential therapies for
myopathies. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 13:1673–1685. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang XX, Zhang B, Xia R and Jia QY:
Inflammation, apoptosis and autophagy as critical players in
vascular dementia. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 24:9601–9614.
2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Boase NA and Kumar S: NEDD4: The founding
member of a family of ubiquitin-protein ligases. Gene. 557:113–122.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Li J: Effect of Nedd4 haploinsufficiency
on insulin sensitivity, adiposity and neuronal behaviors. The
University of Tennessee Health Science Center. 2014.
|
|
36
|
Baloghova N, Lidak T and Cermak L:
Ubiquitin ligases involved in the regulation of Wnt, TGF-β, and
notch signaling pathways and their roles in mouse development and
homeostasis. Genes (Basel). 10:8152019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Sopariwala DH, Yadav V, Badin PM, Likhite
N, Sheth M, Lorca S, Vila IK, Kim ER, Tong Q, Song MS, et al:
Long-term PGC1β overexpression leads to apoptosis, autophagy and
muscle wasting. Sci Rep. 7:102372017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Barthelemy C and André B: Ubiquitylation
and endocytosis of the human LAT1/SLC7A5 amino acid transporter.
Sci Rep. 9:167602019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Nematbakhsh S, Pei Pei C, Selamat J,
Nordin N, Idris LH and Abdull Razis AF: Molecular regulation of
lipogenesis, adipogenesis and fat deposition in chicken. Genes
(Basel). 12:4142021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Salminen A, Kauppinen A and Kaarniranta K:
FGF21 activates AMPK signaling: Impact on metabolic regulation and
the aging process. J Mol Med. 95:123–131. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Babaknejad N, Nayeri H, Hemmati R, Bahrami
S and Esmaillzadeh A: An overview of FGF19 and FGF21: The
therapeutic role in the treatment of the metabolic disorders and
obesity. Horm Metab Res. 50:441–452. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhang M, Zhou W, Cao Y, Kou L, Liu C, Li
X, Zhang B, Guo W, Xu B and Li S: O-GlcNAcylation regulates
long-chain fatty acid metabolism by inhibiting ACOX1
ubiquitination-dependent degradation. Int J Biol Macromol.
266:1311512024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Ndiaye H, Liu JY, Hall A, Minogue S,
Morgan MY and Waugh MG: Immunohistochemical staining reveals
differential expression of ACSL3 and ACSL4 in hepatocellular
carcinoma and hepatic gastrointestinal metastases. Biosci Rep.
40:BSR202002192020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Song F, Li JZ, Wu Y, Wu WY, Wang Y and Li
G: Ubiquitinated ligation protein NEDD4L participates in MiR-30a-5p
attenuated atherosclerosis by regulating macrophage polarization
and lipid metabolism. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 26:1303–1317. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Loix M, Zelcer N, Bogie JF and Hendriks
JJ: The ubiquitous role of ubiquitination in lipid metabolism.
Trends Cell Biol. 34:416–429. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Sciorati C, Clementi E, Manfredi AA and
Rovere-Querini P: Fat deposition and accumulation in the damaged
and inflamed skeletal muscle: Cellular and molecular players. Cell
Mol Life Sci. 72:2135–2156. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Hamrick MW, McGee-Lawrence ME and
Frechette DM: Fatty infiltration of skeletal muscle: Mechanisms and
comparisons with bone marrow adiposity. Front Endocrinol
(Lausanne). 7:692016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Gumucio JP, Qasawa AH, Ferrara PJ, Malik
AN, Funai K, McDonagh B and Mendias CL: Reduced mitochondrial lipid
oxidation leads to fat accumulation in myosteatosis. FASEB J.
33:7863–7881. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Li JJ, Wang R, Lama R, Wang X, Floyd ZE,
Park EA and Liao FF: Ubiquitin ligase NEDD4 regulates PPARγ
stability and adipocyte differentiation in 3T3-L1 cells. Sci Rep.
6:385502016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Chowdhury S, Singh AK, Srivastava S,
Upadhyay V, Sethi A, Siddiqui S and Trivedi AK: AIP4 regulates
adipocyte differentiation by targeting C/EBPα for
ubiquitin-mediated proteasomal degradation. J Cell Biochem.
124:961–973. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Te LJ: Enabling skeletal muscle repair and
functional recovery following denervation-induced injury using
ultrasound mediated gene delivery (UMGD). University of Toronto
(Canada); 2021
|
|
52
|
Parra O and Linos K: Molecular
pathogenesis of soft tissue and bone tumors. Diagn Mol Pathol.
485–551. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Wang K, Liu J, Li YL, Li JP and Zhang R:
Ubiquitination/de-ubiquitination: A promising therapeutic target
for PTEN reactivation in cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer.
1877:1887232022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
D'Cruz R: Identification of PDLIM7 as a
Nedd4-1 substrate in the regulation of skeletal muscle mass.
University of Toronto (Canada); 2016
|
|
55
|
Huang X, Chen J, Cao W, Yang L, Chen Q, He
J, Yi Q, Huang H, Zhang E and Cai Z: The many substrates and
functions of NEDD4-1. Cell Death Dis. 10:9042019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Wang H: Protein degradation pathways in
hepatic ER stress and insulin resistance. RMIT University; 2015
|
|
57
|
Yang B and Kumar S: Nedd4 and Nedd4-2:
Closely related ubiquitin-protein ligases with distinct
physiological functions. Cell Death Differ. 17:68–77. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|