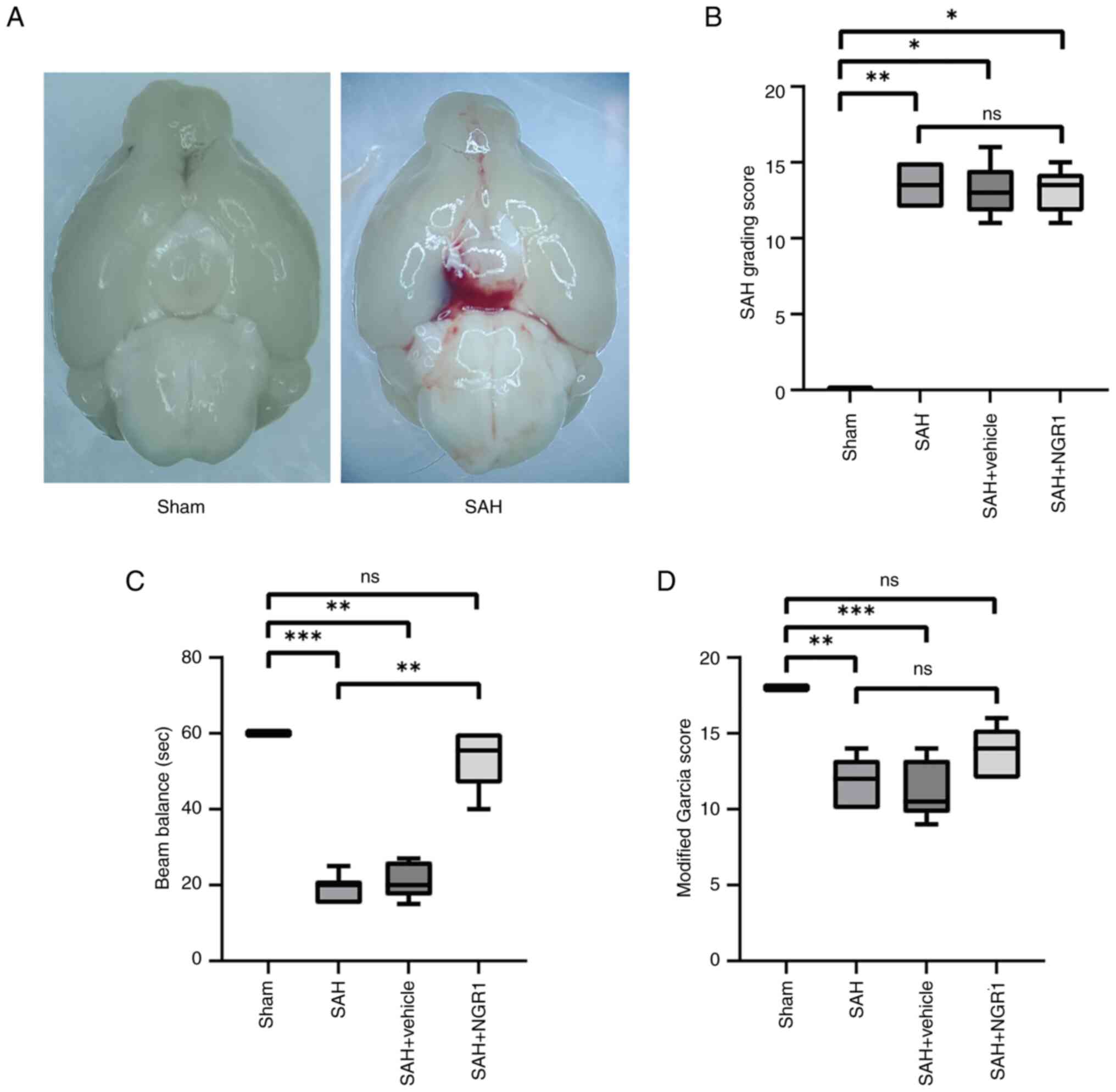
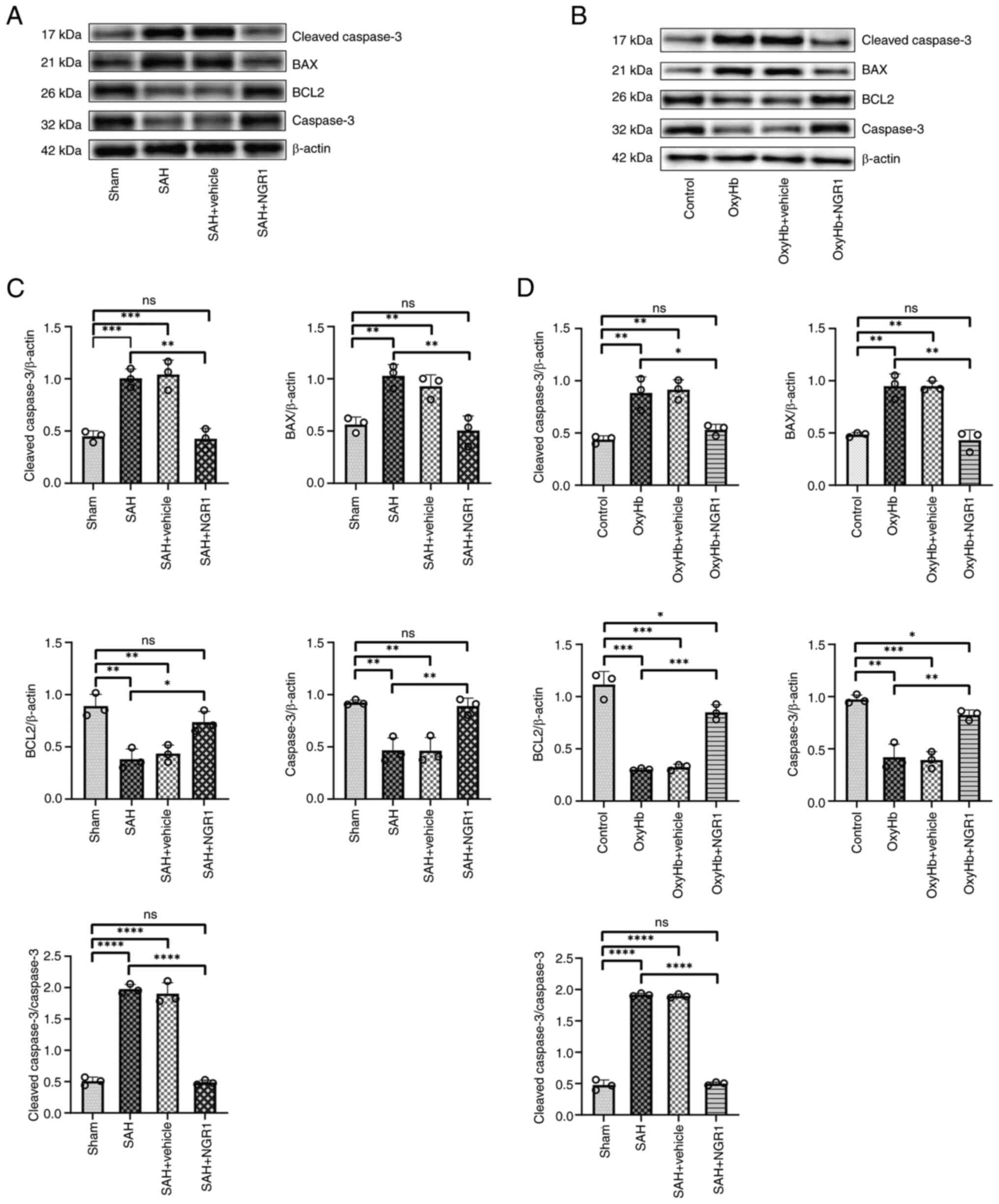
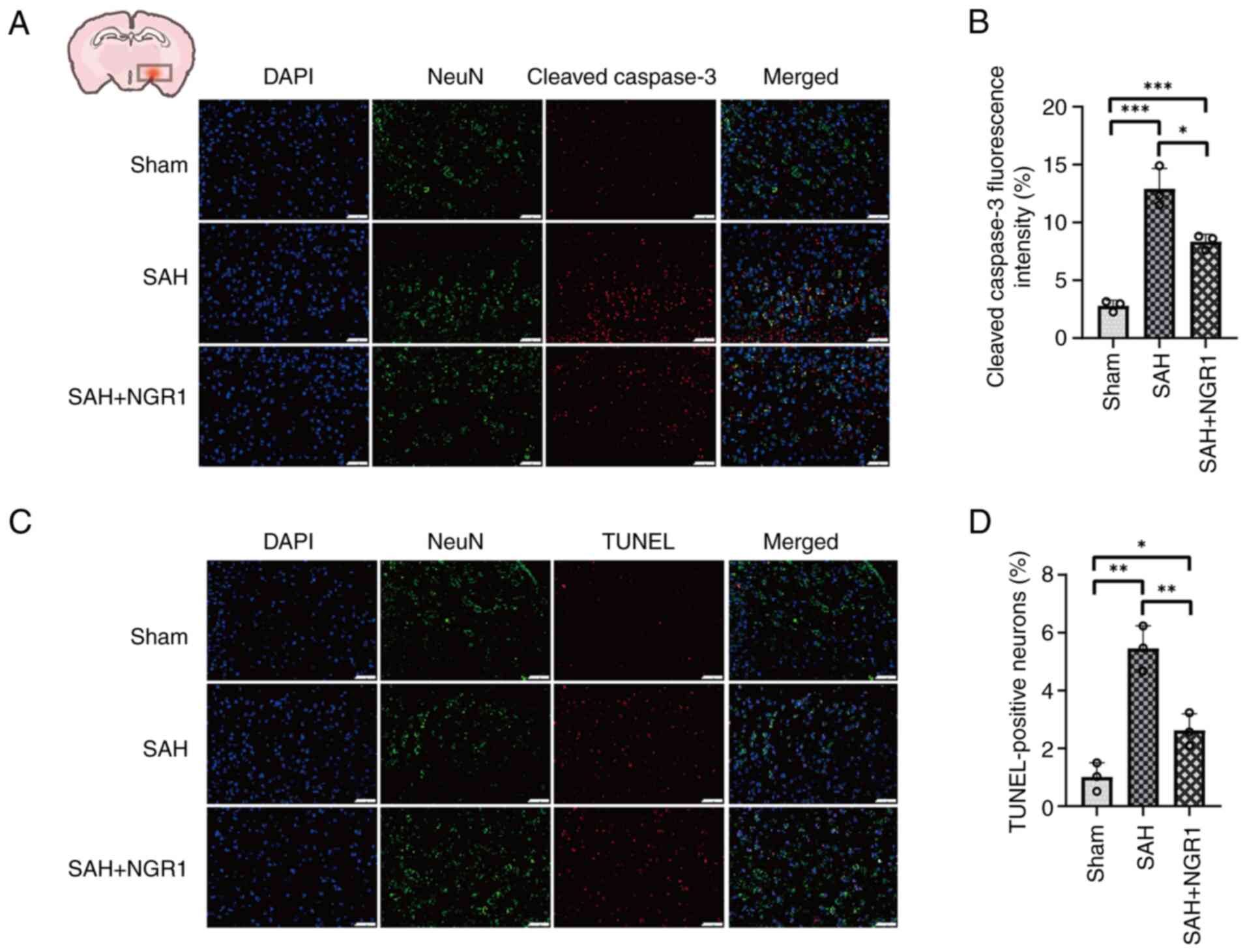
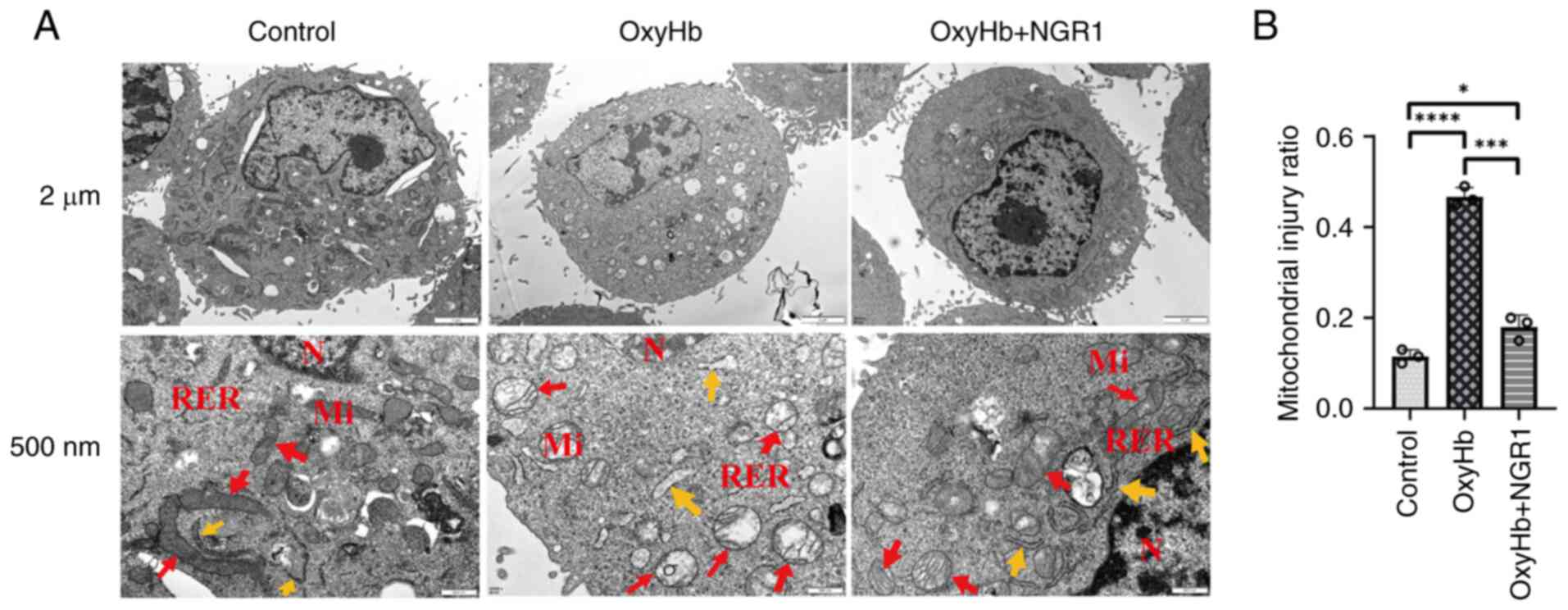
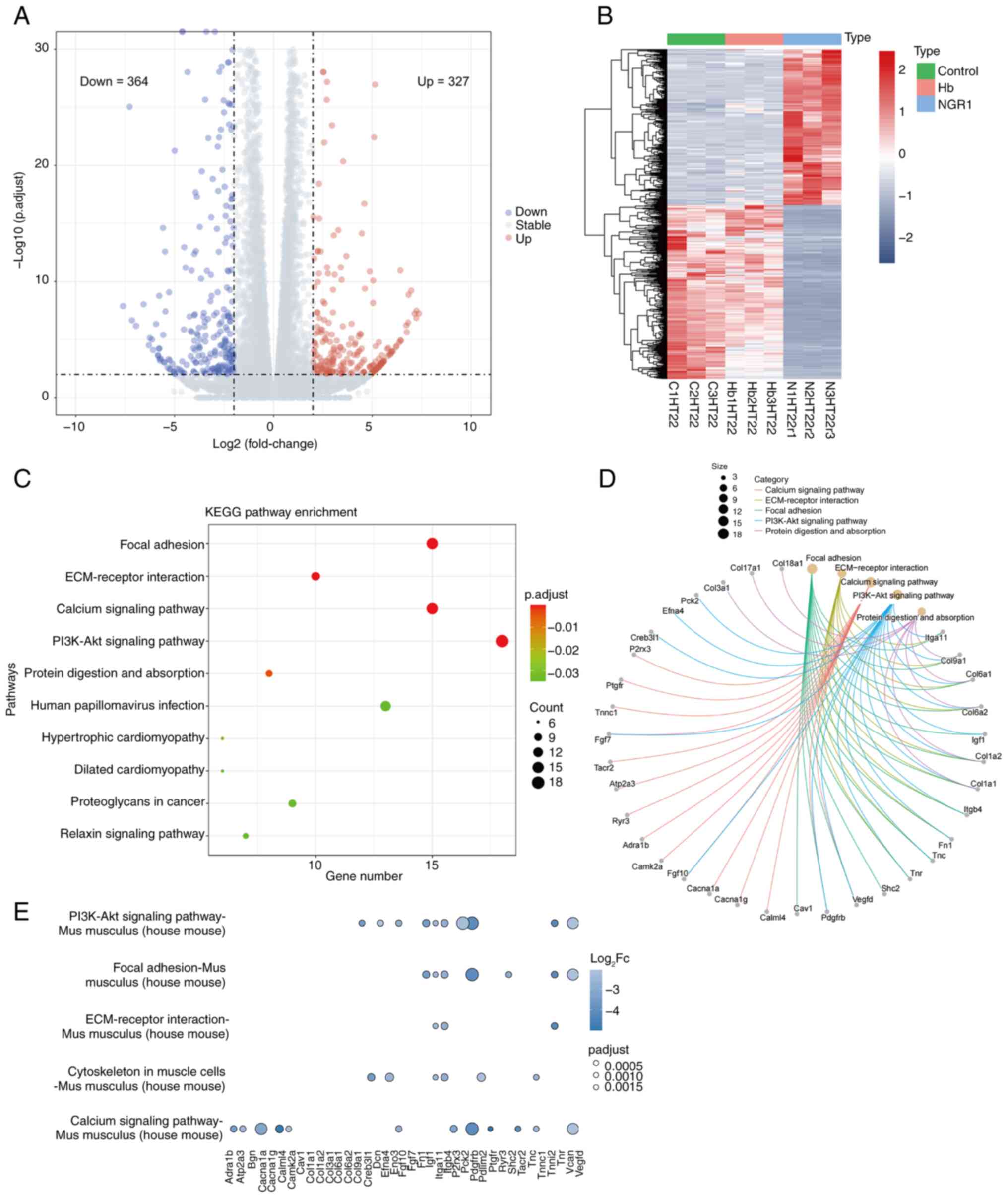
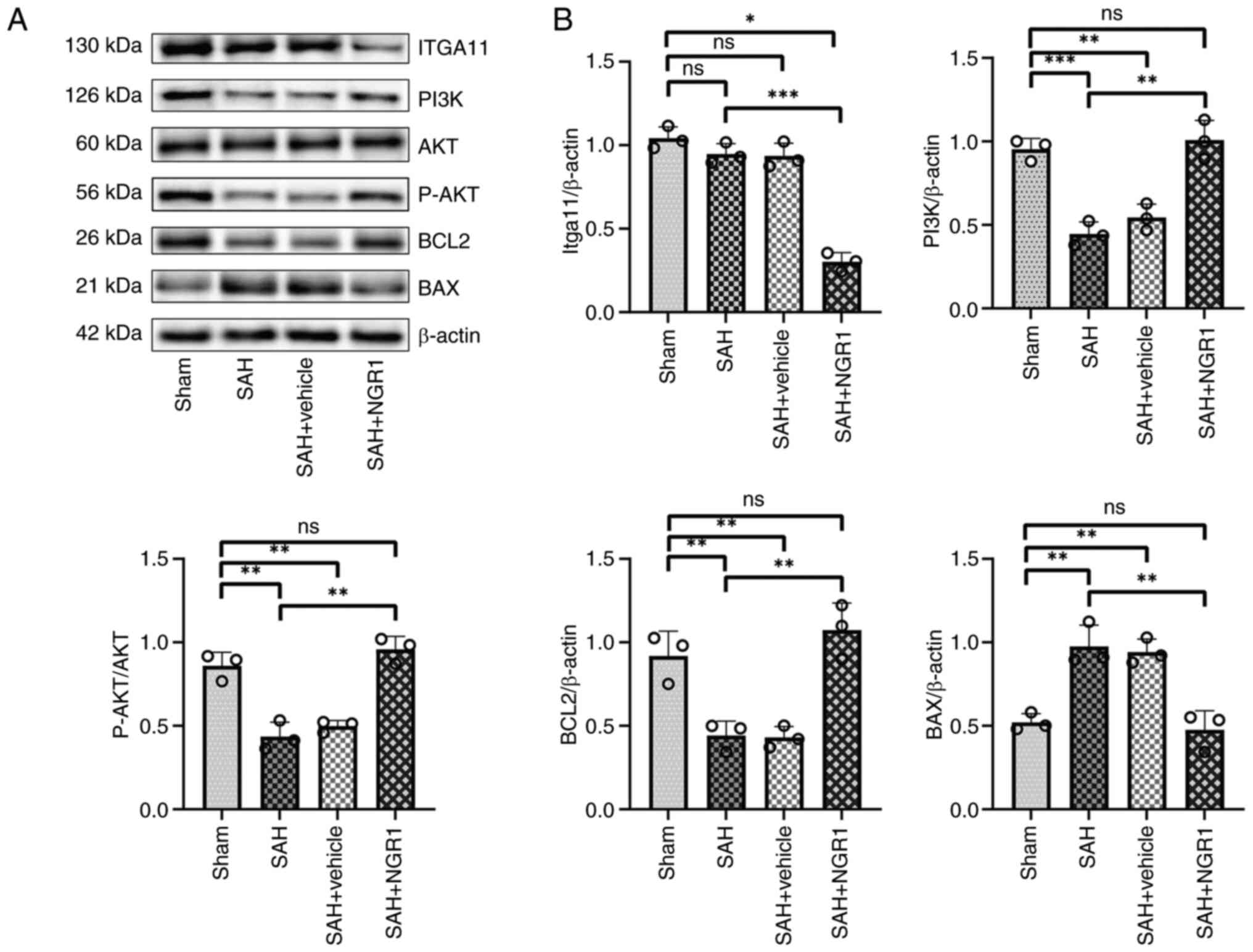
|
1
|
Thilak S, Brown P, Whitehouse T, Gautam N,
Lawrence E, Ahmed Z and Veenith T: Diagnosis and management of
subarachnoid haemorrhage. Nat Commun. 15:18502024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Peng L, Qin H, Liu J, Wu N, Wang X, Han L
and Ding X: Neurosurgical clipping versus endovascular coiling for
patients with ruptured anterior circulation aneurysms: A systematic
review and meta-analysis. Neurosurg Rev. 47:682024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chalet FX, Briasoulis O, Manalastas EJ,
Talbot DA, Thompson JC and Macdonald RL: Clinical burden of
angiographic vasospasm and its complications after aneurysmal
subarachnoid hemorrhage: A systematic review. Neurol Ther.
12:371–390. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cahill J and Zhang JH: Subarachnoid
hemorrhage: Is it time for a new direction? Stroke. 40 (3
Suppl):S86–S87. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Schupper AJ, Hardigan TA, Mehta A, Yim B,
Yaeger KA, De Leacy R, Fifi JT, Mocco J and Majidi S: Sex and
racial disparity in outcome of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage
in the United States: A 20-year analysis. Stroke. 54:1347–1356.
2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lauzier DC, Jayaraman K, Yuan JY, Diwan D,
Vellimana AK, Osbun JW, Chatterjee AR, Athiraman U, Dhar R and
Zipfel GJ: Early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage:
Incidence and mechanisms. Stroke. 54:1426–1440. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Huang H and Lai LT: Incidence and
case-fatality of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage in Australia,
2008–2018. World Neurosurg. 144:e438–e446. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xia C, Hoffman H, Anikpezie N, Philip K,
Wee C, Choudhry R, Albright KC, Masoud H, Beutler T, Schmidt E, et
al: Trends in the incidence of spontaneous subarachnoid hemorrhages
in the United States, 2007–2017. Neurology. 100:e123–e132. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Qureshi AI, Bhatti IA, Gillani SA, Beall
J, Cassarly CN, Gajewski B, Martin RH, Suarez JI and Kwok CS:
Prevalence, trends, and outcomes of cerebral infarction in patients
with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage in the USA. J Neuroimaging.
34:790–798. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Vasconcellos de Oliveira Souza N, Rouanet
C, Fontoura Solla DJ, Barroso de Lima CV, Trevizo J, Rezende F,
Alves MM, de Oliveira Manuel AL, Righy C, Chaddad Neto F, et al:
Impact of medical and neurologic complications on the outcome of
patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage in a middle-income
country. World Neurosurg. 183:e250–e260. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhu W, Ling X, Petersen JD, Liu J, Xiao A
and Huang J: Clipping versus coiling for aneurysmal subarachnoid
hemorrhage: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective
studies. Neurosurg Rev. 45:1291–1302. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
de Liyis BG, Surya SC and Tini K:
Effectivity and safety of endovascular coiling versus microsurgical
clipping for aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: A systematic
review and meta-analysis. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 236:1080582024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Le VT, Nguyen AM and Nguyen PL: Risk
factors for in-hospital seizure and new-onset epilepsy in coiling
and clipping treatment of aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. World
Neurosurg. 184:e460–e467. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Früh A, Wolf S, Wasilewski D, Vajkoczy P
and Truckenmueller P; EARLYDRAIN study group, : Early complications
and outcome after treatment of ruptured aneurysms in patients with
subarachnoid hemorrhage-A post hoc analysis of the EARLYDRAIN
trial. World Neurosurg. 184:e720–e730. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li M, Tian Z, Ru X, Shen J, Chen G, Duan Z
and Cui J: Comparison of endovascular interventional embolization
and microsurgical clipping for ruptured cerebral aneurysms: Impact
on patient outcomes. Int J Neurosci. 1–8. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Hoh BL, Topcuoglu MA, Singhal AB, Pryor
JC, Rabinov JD, Rordorf GA, Carter BS and Ogilvy CS: Effect of
clipping, craniotomy, or intravascular coiling on cerebral
vasospasm and patient outcome after aneurysmal subarachnoid
hemorrhage. Neurosurgery. 55:779–789. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Tawakul A, Alluqmani MM, Badawi AS, Alawfi
AK, Alharbi EK, Aljohani SA, Mogharbel GH, Alahmadi HA and Khawaji
ZY: Risk factors for cerebral vasospasm after subarachnoid
hemorrhage: A systematic review of observational studies. Neurocrit
Care. 41:1081–1099. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lele AV, Fong CT, Walters AM and Souter
MJ: External ventricular drain placement, critical care
utilization, complications, and clinical outcomes after spontaneous
subarachnoid hemorrhage: A single-center retrospective cohort
study. J Clin Med. 13:10322024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kamp MA, Lieshout JHV, Dibué-Adjei M,
Weber JK, Schneider T, Restin T, Fischer I and Steiger HJ: A
systematic and meta-analysis of mortality in experimental mouse
models analyzing delayed cerebral ischemia after subarachnoid
hemorrhage. Transl Stroke Res. 8:206–219. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Dayyani M, Sadeghirad B, Grotta JC,
Zabihyan S, Ahmadvand S, Wang Y, Guyatt GH and Amin-Hanjani S:
Prophylactic therapies for morbidity and mortality after aneurysmal
subarachnoid hemorrhage: A systematic review and network
meta-analysis of randomized trials. Stroke. 53:1993–2005. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sun G: Death and survival from executioner
caspase activation. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 156:66–73. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tan W, Li Y, Ma L, Fu X, Long Q, Yan F, Li
W, Liu X, Ding H, Wang Y and Zhang W: Exosomes of endothelial
progenitor cells repair injured vascular endothelial cells through
the Bcl2/Bax/caspase-3 pathway. Sci Rep. 14:44652024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhu C, Fan F, Li CY, Xiong Y and Liu X:
Caspase-3 promotes oncogene-induced malignant transformation via
EndoG-dependent Src-STAT3 phosphorylation. Cell Death Dis.
15:4862024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hongmei Z: Extrinsic and intrinsic
apoptosis signal pathway review. Ntuli T: Apoptosis and Medicine.
IntechOpen; London, UK: 2012, View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Siddiqui WA, Ahad A and Ahsan H: The
mystery of BCL2 family: Bcl-2 proteins and apoptosis: An update.
Arch Toxicol. 89:289–317. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Pisani C, Ramella M, Boldorini R, Loi G,
Billia M, Boccafoschi F, Volpe A and Krengli M: Apoptotic and
predictive factors by bax, caspases 3/9, Bcl-2, p53 and Ki-67 in
prostate cancer after 12 Gy single-dose. Sci Rep. 10:70502020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Qian S, Wei Z, Yang W, Huang J, Yang Y and
Wang J: The role of BCL-2 family proteins in regulating apoptosis
and cancer therapy. Front Oncol. 12:9853632022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Miller TM, Moulder KL, Knudson CM, Creedon
DJ, Deshmukh M, Korsmeyer SJ and Johnson EM Jr: Bax deletion
further orders the cell death pathway in cerebellar granule cells
and suggests a caspase-independent pathway to cell death. J Cell
Biol. 139:205–217. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chen Q, Huang Z, Chen J, Tian X, Zhang R,
Liang Q, Liu Z and Cheng Y: Notoginsenoside R1 attenuates ischemic
heart failure by modulating MDM2/β arrestin2-mediated β2-adrenergic
receptor ubiquitination. Biomed Pharmacother. 177:1170042024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang S, Chen Q, Jin M, Ren J and Sun X,
Zhang Z, Luo Y and Sun X: Notoginsenoside R1 alleviates cerebral
ischemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB
signaling pathway through microbiota-gut-brain axis. Phytomedicine.
128:1555302024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zeng M, Zhang R, Yang Q, Guo L, Zhang X,
Yu B, Gan J, Yang Z, Li H, Wang Y, et al: Pharmacological therapy
to cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury: Focus on saponins. Biomed
Pharmacother. 155:1136962022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Meng X, Sun G, Ye J, Xu H, Wang H and Sun
X: Notoginsenoside R1-mediated neuroprotection involves estrogen
receptor-dependent crosstalk between Akt and ERK1/2 pathways: A
novel mechanism of Nrf2/ARE signaling activation. Free Radic Res.
48:445–460. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Jiang N, Dai Q, Su X, Fu J, Feng X and
Peng J: Role of PI3K/AKT pathway in cancer: The framework of
malignant behavior. Mol Biol Rep. 47:4587–4629. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Liu R, Chen Y, Liu G, Li C, Song Y, Cao Z,
Li W, Hu J, Lu C and Liu Y: PI3K/AKT pathway as a key link
modulates the multidrug resistance of cancers. Cell Death Dis.
11:7972020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Fresno Vara JA, Casado E, de Castro J,
Cejas P, Belda-Iniesta C and González-Barón M: PI3K/Akt signalling
pathway and cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 30:193–204. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Vasan N and Cantley LC: At a crossroads:
How to translate the roles of PI3K in oncogenic and metabolic
signalling into improvements in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Clin Oncol.
19:471–485. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Barzegar Behrooz A, Talaie Z, Jusheghani
F, Łos MJ, Klonisch T and Ghavami S: Wnt and PI3K/Akt/mTOR survival
pathways as therapeutic targets in glioblastoma. Int J Mol Sci.
23:13532022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
He Y, Sun MM, Zhang GG, Yang J, Chen KS,
Xu WW and Li B: Targeting PI3K/Akt signal transduction for cancer
therapy. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 6:4252021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Manning BD and Cantley LC: AKT/PKB
signaling: Navigating downstream. Cell. 129:1261–1274. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Peng J, Wu Y, Pang J, Sun X, Chen L, Chen
Y, Tang J, Zhang JH and Yong J: Single clip: An improvement of the
filament-perforation mouse subarachnoid haemorrhage model. Brain
Inj. 33:701–711. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Leary S, Underwood W, Anthony R, Cartner
S, Grandin T, Greenacre C, Gwaltney-Brant S, McCrackin MA, Meyer R,
Miller D, et al: AVMA guidelines for the euthanasia of animals:
2020 Edition*. American Veterinary Medical Association 1931; N.
Meacham Road Schaumburg IL 60173: 2020
|
|
42
|
Huang T, Xiao Y, Zhang Y, Wang C, Chen X,
Li Y, Ge Y and Gao J: miR-223 ameliorates thalamus
hemorrhage-induced central poststroke pain via targeting NLRP3 in a
mouse model. Exp Ther Med. 23:3532022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Feng X, Ma W, Zhu J, Jiao W and Wang Y:
Dexmedetomidine alleviates early brain injury following traumatic
brain injury by inhibiting autophagy and neuroinflammation through
the ROS/Nrf2 signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep. 24:6612021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Peng J, Pang J, Huang L, Enkhjargal B,
Zhang T, Mo J, Wu P, Xu W, Zuo Y, Peng J, et al: LRP1 activation
attenuates white matter injury by modulating microglial
polarization through Shc1/PI3K/Akt pathway after subarachnoid
hemorrhage in rats. Redox Biol. 21:1011212019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zhang CS, Han Q, Song ZW, Jia HY, Shao TP
and Chen YP: Hydrogen gas post-conditioning attenuates early
neuronal pyroptosis in a rat model of subarachnoid hemorrhage
through the mitoKATP signaling pathway. Exp Ther Med.
22:8362021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Chen S, Zhou Y, Chen Y and Gu J: fastp: An
ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics.
34:i884–i890. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Kim D, Langmead B and Salzberg SL: HISAT:
A fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat Methods.
12:357–360. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Anders S, Pyl PT and Huber W: HTSeq-a
python framework to work with high-throughput sequencing data.
Bioinformatics. 31:166–169. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Love MI, Huber W and Anders S: Moderated
estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with
DESeq2. Genome Biol. 15:5502014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Robinson MD, McCarthy DJ and Smyth GK:
edgeR: A bioconductor package for differential expression analysis
of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics. 26:139–140. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Yu G, Wang LG, Han Y and He QY:
clusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among
gene clusters. OMICS. 16:284–287. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Team R, . RStudio: Integrated development
for R. Boston, MA: RStudio. Inc.; pp. 700pp. pp8792015
|
|
53
|
Null RCTR, Team R, Null RCT, Core Writing
T, Null R, Team R, Null RDCT, Core R, Team R and Team RDC: R: A
language and environment for statistical computing. Computing.
1:12–21. 2011.
|
|
54
|
Dinh DD, Wan H, Lidington D and Bolz SS:
Female mice display sex-specific differences in cerebrovascular
function and subarachnoid haemorrhage-induced injury. EBioMedicine.
102:1050582024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Kitaeva KV, Rutland CS, Rizvanov AA and
Solovyeva VV: Cell culture based in vitro test systems for
anticancer drug screening. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 8:3222020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Pinto B, Henriques AC, Silva PMA and
Bousbaa H: Three-dimensional spheroids as in vitro preclinical
models for cancer research. Pharmaceutics. 12:11862020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Wu Y, Xu Y, Sun JS, Dai K, Wang Z and
Zhang J: Inhibiting RIPK1-driven neuroinflammation and neuronal
apoptosis mitigates brain injury following experimental
subarachnoid hemorrhage. Exp Neurol. 374:1147052024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Yuan B, Zhao XD, Shen JD, Chen SJ, Huang
HY, Zhou XM, Han YL, Zhou LJ, Lu XJ and Wu Q: Activation of SIRT1
alleviates ferroptosis in the early brain injury after subarachnoid
hemorrhage. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022:90698252022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Tang J, Chen R, Wang L, Yu L, Zuo D, Cui G
and Gong X: Melatonin attenuates thrombin-induced inflammation in
BV2 cells and then protects HT22 cells from apoptosis.
Inflammation. 43:1959–1970. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Richter M, Piwocka O, Musielak M,
Piotrowski I, Suchorska WM and Trzeciak T: From donor to the lab: A
fascinating journey of primary cell lines. Front Cell Dev Biol.
9:7113812021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Helms HC, Abbott NJ, Burek M, Cecchelli R,
Couraud PO, Deli MA, Förster C, Galla HJ, Romero IA, Shusta EV, et
al: In vitro models of the blood-brain barrier: An overview of
commonly used brain endothelial cell culture models and guidelines
for their use. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 36:862–890. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Zhang J, Yang H, Wu J, Zhang D, Wang Y and
Zhai J: Recent progresses in novel in vitro models of primary
neurons: A biomaterial perspective. Front Bioeng Biotechnol.
10:9530312022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Swartzlander DB, Propson NE, Roy ER, Saito
T, Saido T, Wang B and Zheng H: Concurrent cell type-specific
isolation and profiling of mouse brains in inflammation and
Alzheimer's disease. JCI Insight. 3:e1211092018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
El Amki M, Dubois M, Lefevre-Scelles A,
Magne N, Roussel M, Clavier T, Guichet PO, Gérardin E, Compère V
and Castel H: Long-lasting cerebral vasospasm, microthrombosis,
apoptosis and paravascular alterations associated with neurological
deficits in a mouse model of subarachnoid hemorrhage. Mol
Neurobiol. 55:2763–2779. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Fluri F, Schuhmann MK and Kleinschnitz C:
Animal models of ischemic stroke and their application in clinical
research. Drug Des Devel Ther. 9:3445–3454. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Su C, Liu Y, Li R, Wu W, Fawcett JP and Gu
J: Absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion of the
biomaterials used in Nanocarrier drug delivery systems. Adv Drug
Deliv Rev. 143:97–114. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Zhang R, Khan D and Muhammad S:
Establishment of a novel protocol for assessing the severity of
subarachnoid hemorrhage in circle Willis perforation mouse model.
Sci Rep. 14:101472024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Marbacher S, Grüter B, Schöpf S, Croci D,
Nevzati E, D'Alonzo D, Lattmann J, Roth T, Bircher B, Wolfert C, et
al: Systematic review of in vivo animal models of subarachnoid
hemorrhage: Species, standard parameters, and outcomes. Transl
Stroke Res. September 12–2018.(Epub ahead of print). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Shi X, Yu W, Yang T, Liu W, Zhao Y, Sun Y,
Chai L, Gao Y, Dong B and Zhu L: Panax notoginseng saponins
provide neuroprotection by regulating NgR1/RhoA/ROCK2 pathway
expression, in vitro and in vivo. J Ethnopharmacol. 190:301–312.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Pei X, Zhang L, Liu D, Wu Y, Li X, Cao Y
and Du X: Notoginsenoside R1 attenuates brain injury in rats with
traumatic brain injury: Possible mediation of apoptosis via ERK1/2
signaling pathway. PLoS One. 18:e02959032023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Wang D, Gao B, Yang T, Sun H, Ran X and
Lin W: Protective effect of NGR1 against glutamate-induced
cytotoxicity in HT22 hippocampal neuronal cells by upregulating the
SIRT1/Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2021:43581632021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Tu L, Wang Y, Chen D, Xiang P, Shen J, Li
Y and Wang S: Protective effects of notoginsenoside r1 via
regulation of the PI3K-Akt-mTOR/JNK pathway in neonatal cerebral
hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. Neurochem Res. 43:1210–1226. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Zhai Y, Meng X, Luo Y, Wu Y, Ye T, Zhou P,
Ding S, Wang M, Lu SB, Zhu L, et al: Notoginsenoside R1 ameliorates
diabetic encephalopathy by activating the Nrf2 pathway and
inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Oncotarget. 9:9344–9363.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Zhu T and Wan Q: Pharmacological
properties and mechanisms of Notoginsenoside R1 in
ischemia-reperfusion injury. Chin J Traumatol. 26:20–26. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Zhang HB, Tu XK, Chen Q and Shi SS:
Propofol reduces inflammatory brain injury after subarachnoid
hemorrhage: Involvement of PI3K/Akt pathway. J Stroke Cerebrovasc
Dis. 28:1043752019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|