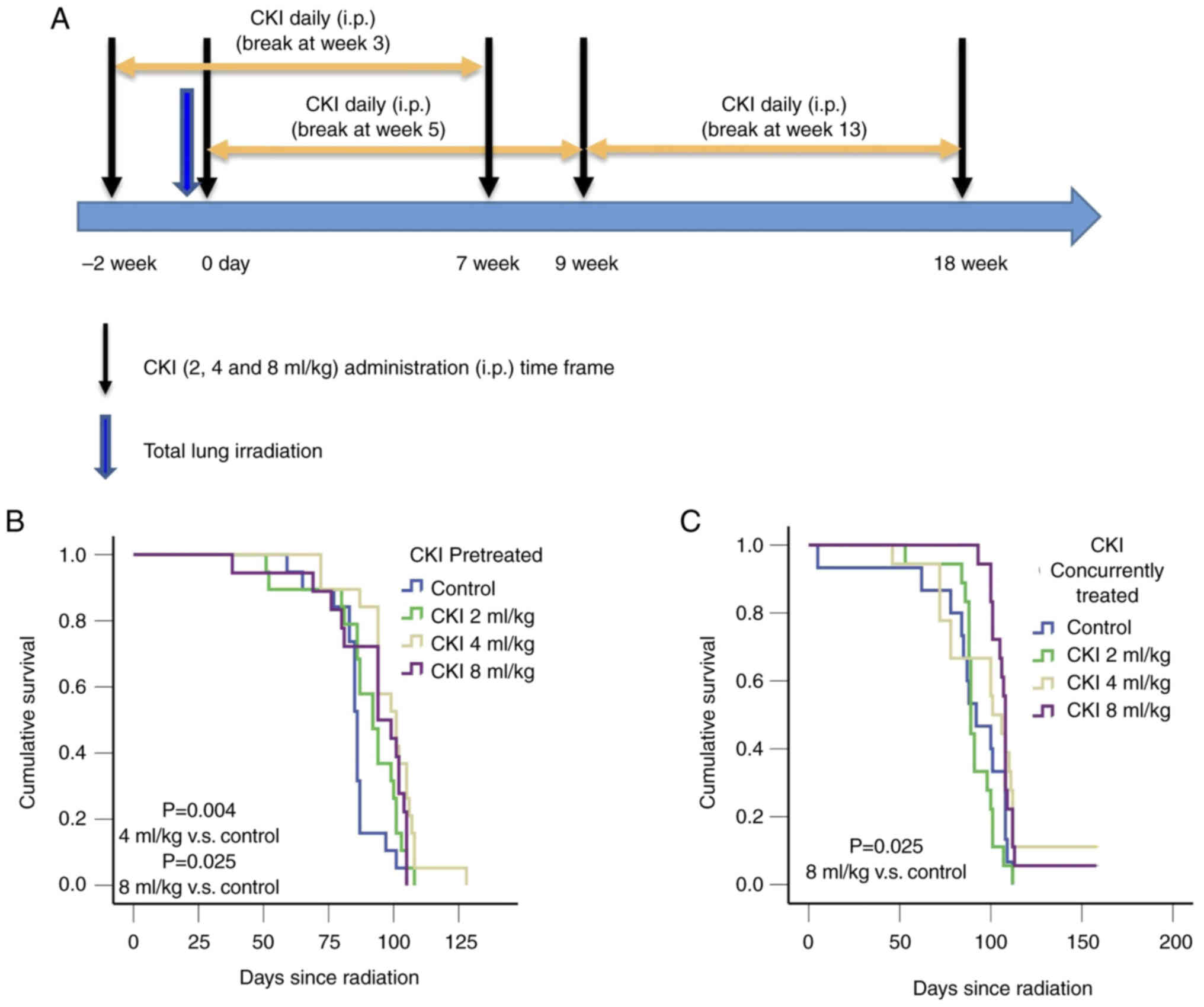
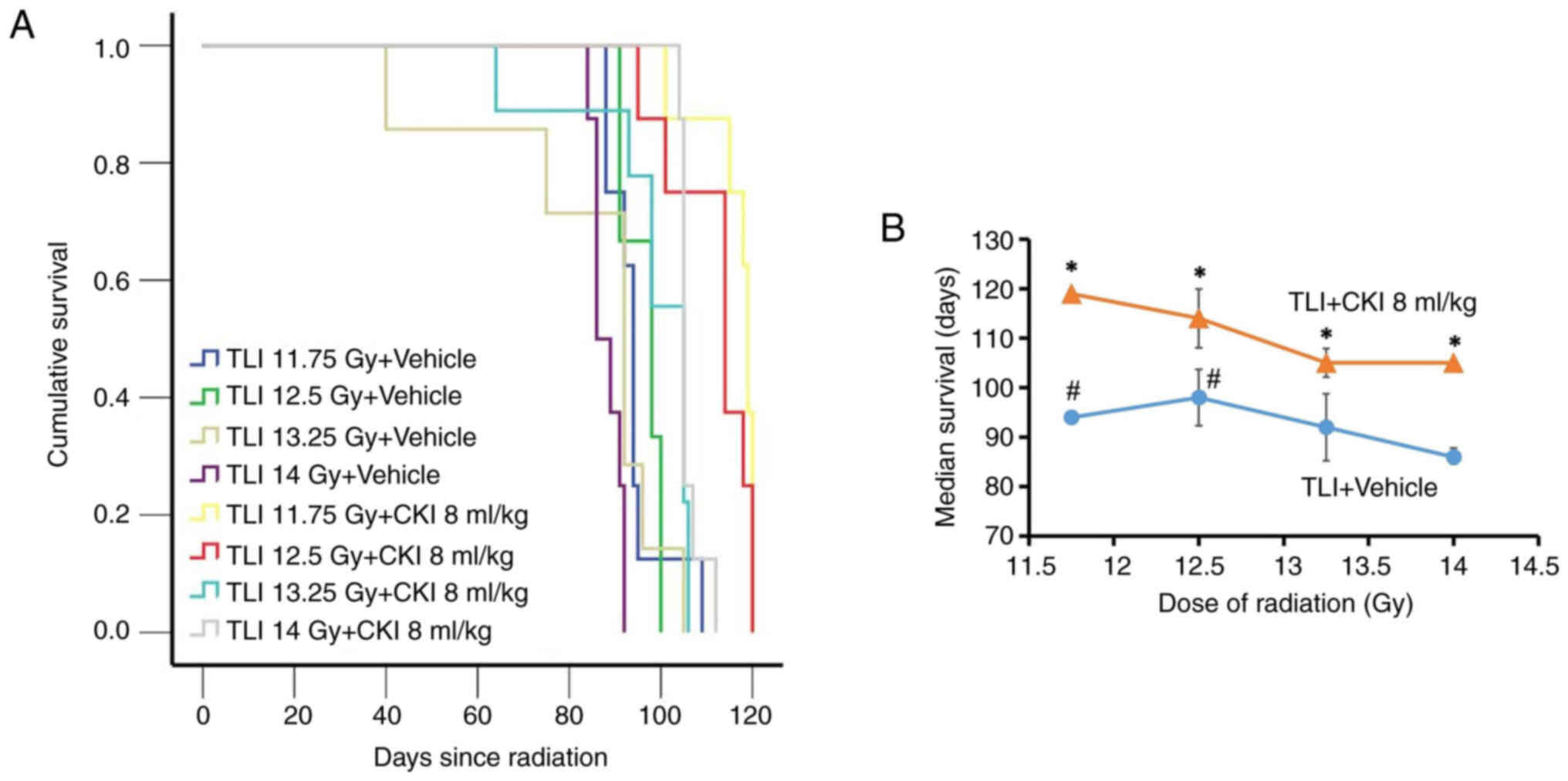
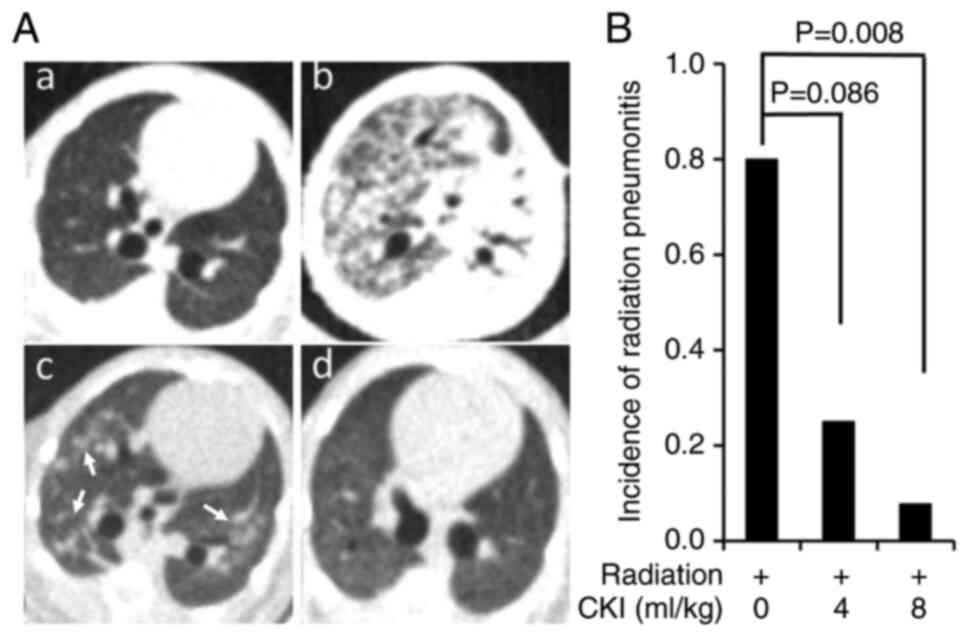
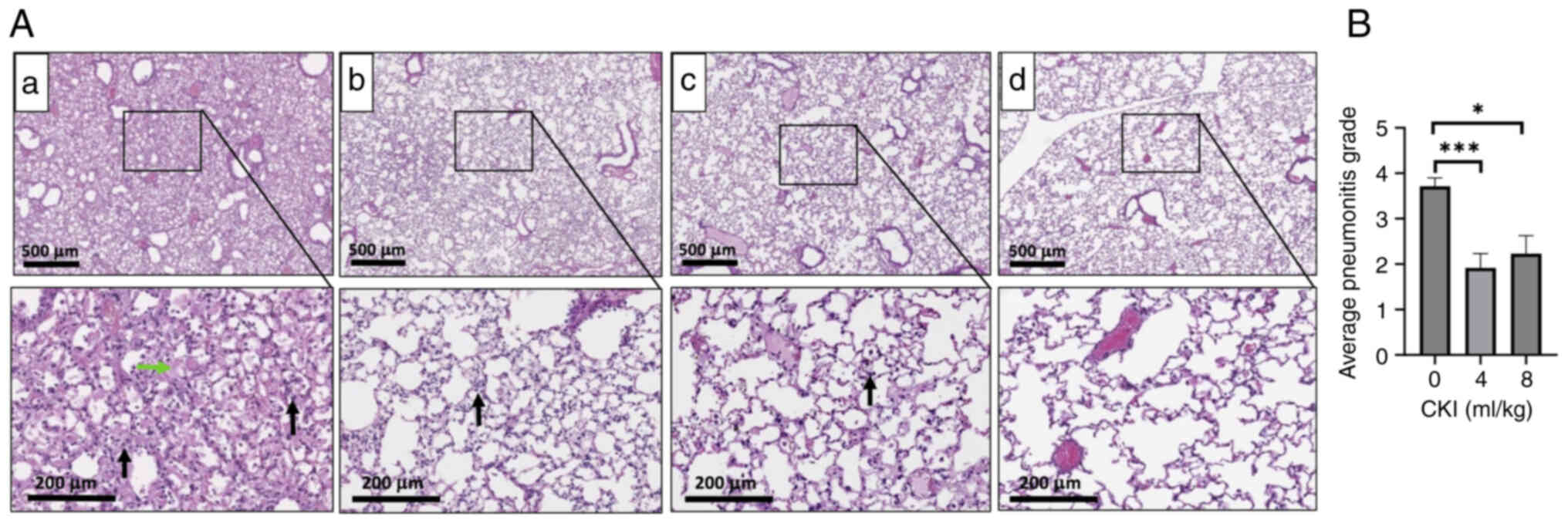
|
1
|
Jain V and Berman AT: Radiation
pneumonitis: Old problem, new tricks. Cancers (Basel). 10:2222018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rodrigues G, Lock M, D'Souza D, Yu E and
Van Dyk J: Prediction of radiation pneumonitis by dose-volume
histogram parameters in lung cancer-a systematic review. Radiother
Oncol. 71:127–138. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yan Y, Fu J, Kowalchuk RO, Wright CM,
Zhang R, Li X and Xu Y: Exploration of radiation-induced lung
injury, from mechanism to treatment: a narrative review. Transl
Lung Cancer Res. 11:307–322. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Arroyo-Hernández M, Maldonado F,
Lozano-Ruiz F, Muñoz-Montaño W, Nuñez-Baez M and Arrieta O:
Radiation-induced lung injury: Current evidence. BMC Pulm Med.
21:92021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yue J, Shi Q, Xu T, Jeter M, Chen TY,
Komaki R, Gomez DR, Pan T, Cleeland CS, Liao Z and Wang XS:
Patient-reported lung symptoms as an early signal of impending
radiation pneumonitis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer
treated with chemoradiation: An observational study. Qual Life Res.
27:1563–1570. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
King TE Jr: Clinical advances in the
diagnosis and therapy of the interstitial lung diseases. Am J
Respir Crit Care Med. 172:268–279. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Trott KR, Herrmann T and Kasper M: Target
cells in radiation pneumopathy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.
58:463–469. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tsoutsou PG and Koukourakis MI: Radiation
pneumonitis and fibrosis: Mechanisms underlying its pathogenesis
and implications for future research. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.
66:1281–1293. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jin H, Yoo Y, Kim Y, Kim Y, Cho J and Lee
YS: Radiation-induced lung fibrosis: preclinical animal models and
therapeutic strategies. Cancers (Basel). 12:15612020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Rades D, Fehlauer F, Bajrovic A, Mahlmann
B, Richter E and Alberti W: Serious adverse effects of amifostine
during radiotherapy in head and neck cancer patients. Radiother
Oncol. 70:261–264. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Devine A and Marignol L: Potential of
amifostine for chemoradiotherapy and radiotherapy-associated
toxicity reduction in advanced NSCLC: A meta-analysis. Anticancer
Res. 36:5–12. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Roy S, Salerno KE and Citrin DE: Biology
of radiation-induced lung injury. Semin Radiat Oncol. 31:155–161.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu XJ and Chen ZH: The pathophysiological
role of mitochondrial oxidative stress in lung diseases. J Transl
Med. 15:2072017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Schieber M and Chandel NS: ROS function in
redox signaling and oxidative stress. Curr Biol. 24:R453–R462.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Giuranno L, Ient J, De Ruysscher D and
Vooijs MA: Radiation-induced lung injury (RILI). Front Oncol.
9:8772019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lierova A, Jelicova M, Nemcova M, Proksova
M, Pejchal J, Zarybnicka L and Sinkorova Z: Cytokines and
radiation-induced pulmonary injuries. J Radiat Res. 59:709–753.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ao X, Zhao L, Davis MA, Lubman DM,
Lawrence TS and Kong FM: Radiation produces differential changes in
cytokine profiles in radiation lung fibrosis sensitive and
resistant mice. J Hematol Oncol. 2:62009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hong JH, Chiang CS, Tsao CY, Lin PY,
McBride WH and Wu CJ: Rapid induction of cytokine gene expression
in the lung after single and fractionated doses of radiation. Int J
Radiat Biol. 75:1421–1427. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Rübe CE, Wilfert F, Palm J, König J,
Burdak-Rothkamm S, Liu L, Schuck A, Willich N and Rübe C:
Irradiation induces a biphasic expression of pro-inflammatory
cytokines in the lung. Strahlenther Onkol. 180:442–448. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Szabo S, Ghosh SN, Fish BL, Bodiga S,
Tomic R, Kumar G, Morrow NV, Moulder JE, Jacobs ER and Medhora M:
Cellular inflammatory infiltrate in pneumonitis induced by a single
moderate dose of thoracic × radiation in rats. Radiat Res.
173:545–556. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhao L, Wang L, Ji W, Wang X, Zhu X,
Hayman JA, Kalemkerian GP, Yang W, Brenner D, Lawrence TS and Kong
FM: Elevation of plasma TGF-beta1 during radiation therapy predicts
radiation-induced lung toxicity in patients with non-small-cell
lung cancer: A combined analysis from Beijing and Michigan. Int J
Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 74:1385–1390. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Rube CE, Uthe D, Schmid KW, Richter KD,
Wessel J, Schuck A, Willich N and Rube C: Dose-dependent induction
of transforming growth factor beta (TGF-beta) in the lung tissue of
fibrosis-prone mice after thoracic irradiation. Int J Radiat Oncol
Biol Phys. 47:1033–1042. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chen Y, Rubin P, Williams J, Hernady E,
Smudzin T and Okunieff P: Circulating IL-6 as a predictor of
radiation pneumonitis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 49:641–648.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chen Y, Williams J, Ding I, Hernady E, Liu
W, Smudzin T, Finkelstein JN, Rubin P and Okunieff P: Radiation
pneumonitis and early circulatory cytokine markers. Semin Radiat
Oncol. 12 (1 Suppl 1):S26–S33. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shaikh SB, Prabhu A and Bhandary YP:
Interleukin-17A: A potential therapeutic target in chronic lung
diseases. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 19:921–928.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Baindara P: Targeting interleukin-17 in
radiation-induced toxicity and cancer progression. Cytokine Growth
Factor Rev. 75:31–39. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Paun A, Bergeron ME and Haston CK: The
Th1/Th17 balance dictates the fibrosis response in murine
radiation-induced lung disease. Sci Rep. 7:115862017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hunter NR, Valdecanas D, Liao Z, Milas L,
Thames HD and Mason KA: Mitigation and treatment of
radiation-induced thoracic injury with a cyclooxygenase-2
inhibitor, celecoxib. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 85:472–476.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yang HJ, Youn H, Seong KM, Yun YJ, Kim W,
Kim YH, Lee JY, Kim CS, Jin YW and Youn B: Psoralidin, a dual
inhibitor of COX-2 and 5-LOX, regulates ionizing radiation
(IR)-induced pulmonary inflammation. Biochem Pharmacol. 82:524–534.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yang S: Ku Shen (Radix Sophorae
Flavescentis). The Divine Farmer's Materia Medica: A Translation of
the Shen Nong Ben Cao Jing. Yang Shou-zhong. Blue Poppy Press,
Inc.; Boulder, CO, USA: pp. 561998
|
|
31
|
Zhou W, Wu J, Zhu Y, Meng Z, Liu X, Liu S,
Ni M, Jia S, Zhang J and Guo S: Study on the mechanisms of compound
Kushen injection for the treatment of gastric cancer based on
network pharmacology. BMC Complement Med Ther. 20:62020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang S, Lian X, Sun M, Luo L and Guo L:
Efficacy of compound Kushen injection plus radiotherapy on
nonsmall-cell lungcancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J
Cancer Res Ther. 12:1298–1306. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ao M, Xiao X and Li Q: Efficacy and safety
of compound Kushen injection combined with chemotherapy on
postoperative Patients with breast cancer: A meta-analysis of
randomized controlled trials. Medicine (Baltimore). 98:e140242019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Aung TN, Qu ZP, Kortschak RD and Adelson
DL: Understanding the effectiveness of natural compound mixtures in
cancer through their molecular mode of action. Int J Mol Sci.
18:6562017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Deng B, Deng C and Cheng ZQ: Chinese
herbal extractions for relieving radiation induced lung injury: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Evid Based Complement Alternat
Med. 2017:21416452017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Liu J, Yu Q, Wang XS, Shi Q, Wang J, Wang
F, Ren S, Jin J, Han B, Zhang W, et al: Compound kushen injection
reduces severe toxicity and symptom burden associated with curative
radiotherapy in patients with lung cancer. J Natl Compr Canc Netw.
21:821–830.e3. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhang J, Qu Z, Yao H, Sun L, Harata-Lee Y,
Cui J, Aung TN, Liu X, You R, Wang W, et al: An effective drug
sensitizing agent increases gefitinib treatment by down regulating
PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway and up regulating autophagy in non-small cell
lung cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. 118:1091692019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhang B, Liu ZY, Li YY, Luo Y, Liu ML,
Dong HY, Wang YX, Liu Y, Zhao PT, Jin FG and Li ZC:
Antiinflammatory effects of matrine in LPS-induced acute lung
injury in mice. Eur J Pharm Sci. 44:573–579. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Cui J, Qu Z, Harata-Lee Y, Shen H, Aung
TN, Wang W, Kortschak RD and Adelson DL: The effect of compound
kushen injection on cancer cells: Integrated identification of
candidate molecular mechanisms. PLoS One. 15:e02363952020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Zhao Z, Fan H, Higgins T, Qi J, Haines D,
Trivett A, Oppenheim JJ, Wei H, Li J, Lin H and Howard OM: Fufang
Kushen injection inhibits sarcoma growth and tumor-induced
hyperalgesia via TRPV1 signaling pathways. Cancer Lett.
355:232–241. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Williams JP, Brown SL, Georges GE,
Hauer-Jensen M, Hill RP, Huser AK, Kirsch DG, Macvittie TJ, Mason
KA, Medhora MM, et al: Animal models for medical countermeasures to
radiation exposure. Radiat Res. 173:557–578. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Liao ZX, Travis EL and Tucker SL: Damage
and morbidity from pneumonitis after irradiation of partial volumes
of mouse lung. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 32:1359–1370. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Travis EL: Relative radiosensitivity of
the human lung. Adv Radiat Biol. 12:205–238. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Yang PY, Jiang Y, Rhea PR, Coway T, Chen
D, Gagea M, Harribance SL and Cohen L: Human biofield therapy and
the growth of mouse lung carcinoma. Integr Cancer Ther.
18:15347354198407972019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Yang PY, Chan D, Felix E, Madden T, Klein
RD, Shureiqi I, Chen X, Dannenberg AJ and Newman RA: Determination
of endogenous tissue inflammation profiles by LC/MS/MS: COX- and
LOX-derived bioactive lipids. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty
Acids. 75:385–395. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Dileto CL and Travis EL: Fibroblast
radiosensitivity in vitro and lung fibrosis in vivo: Comparison
between a fibrosis-prone and fibrosis-resistant mouse strain.
Radiat Res. 146:61–67. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Finkelstein JN, Johnston CJ, Baggs R and
Rubin P: Early alterations in extracellular matrix and transforming
growth factor beta gene expression in mouse lung indicative of late
radiation fibrosis. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 28:621–631. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Wang LP, Wang YW, Wang BZ, Sun GM, Wang XY
and Xu JL: Expression of interleukin-17A in lung tissues of
irradiated mice and the influence of dexamethasone.
ScientificWorldJournal. 2014:2510672014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Wang BZ, Wang LP, Han H, Cao FL, Li GY, Xu
JL, Wang XW and Wang LX: Interleukin-17A antagonist attenuates
radiation-induced lung injuries in mice. Exp Lung Res. 40:77–85.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Yang Y, Sun M, Li W, Liu C, Jiang Z, Gu P,
Li J, Wang W, You R, Ba Q, et al: Rebalancing TGF-β/Smad7 signaling
via Compound kushen injection in hepatic stellate cells protects
against liver fibrosis and hepatocarcinogenesis. Clin Transl Med.
11:e4102021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Howe LR, Subbaramaiah K, Brown AM and
Dannenberg AJ: Cyclooxygenase-2: A target for the prevention and
treatment of breast cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. 8:97–114. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Yang P, Chan D, Felix E, Cartwright C,
Menter DG, Madden T, Klein RD, Fischer SM and Newman RA: Formation
and antiproliferative effect of prostaglandin E(3) from
eicosapentaenoic acid in human lung cancer cells. J Lipid Res.
45:1030–1039. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Lee SJ, Yi CO, Heo RW, Song DH, Cho YJ,
Jeong YY, Kang KM, Roh GS and Lee JD: Clarithromycin attenuates
radiation-induced lung injury in mice. PLoS One. 10:e01316712015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Smith JNP, Witkin MD, Jogasuria AP,
Christo KF, Raffay TM, Markowitz SD and Desai AB: Therapeutic
targeting of 15-PGDH in murine pulmonary fibrosis. Sci Rep.
10:116572020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Myung SJ, Rerko RM, Yan M, Platzer P, Guda
K, Dotson A, Lawrence E, Dannenberg AJ, Lovgren AK, Luo G, et al:
15-Hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase is an in vivo suppressor of
colon tumorigenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:12098–12102. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Tai HH, Tong M and Ding Y:
15-Hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase (15-PGDH) and lung cancer.
Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 83:203–208. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Ding Y, Tong M, Liu S, Moscow JA and Tai
HH: NAD+-linked 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase (15-PGDH)
behaves as a tumor suppressor in lung cancer. Carcinogenesis.
26:65–72. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Yan M, Rerko RM, Platzer P, Dawson D,
Willis J, Tong M, Lawrence E, Lutterbaugh J, Lu S, Willson JK, et
al: 15-Hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase, a COX-2 oncogene
antagonist, is a TGF-beta-induced suppressor of human
gastrointestinal cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:17468–17473.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Chai Y, Lam RKK, Calaf GM, Zhou H,
Amundson S and Hei TK: Radiation-induced non-targeted response in
vivo: Role of the TGFβ-TGFBR1-COX-2 signalling pathway. Br J
Cancer. 108:1106–1112. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Fang L, Chang HM, Cheng JC, Leung PCK and
Sun YP: TGF-β1 induces COX-2 expression and PGE2 production in
human granulosa cells through Smad signaling pathways. J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 99:E1217–E1226. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Farhood B, Khodamoradi E,
Hoseini-Ghahfarokhi M, Motevaseli E, Mirtavoos-Mahyari H, Eleojo
Musa A and Najafi M: TGF-β in radiotherapy: Mechanisms of tumor
resistance and normal tissues injury. Pharmacol Res.
155:1047452020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Lee S, Shin S, Kim H, Han S and Kim K,
Kwon J, Kwak JH, Lee CK, Ha NJ, Yim D and Kim K: Anti-inflammatory
function of arctiin by inhibiting COX-2 expression via NF-κB
pathways. J Inflamm (Lond). 8:162011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Liou CJ, Lai YR, Chen YL, Chang YH, Li ZY
and Huang WC: Matrine attenuates COX-2 and ICAM-1 expressions in
human lung epithelial cells and prevents acute lung injury in
LPS-induced mice. Mediators Inflamm. 2016:36304852016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Aung TN, Nourmohammadi S, Qu Z, Harata-Lee
Y, Cui J, Shen HY, Yool AJ, Pukala T, Du H, Kortschak RD, et al:
Fractional deletion of compound kushen injection indicates cytokine
signaling pathways are critical for its perturbation of the cell
cycle. Sci Rep. 9:142002019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Xu GL, Yao L, Rao SY, Gong ZN, Zhang SQ
and Yu SQ: Attenuation of acute lung injury in mice by oxymatrine
is associated with inhibition of phosphorylated p38
mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Ethnopharmacol. 98:177–183.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Jin JH, Kim JS, Kang SS, Son KH, Chang HW
and Kim HP: Anti-inflammatory and anti-arthritic activity of total
flavonoids of the roots of Sophora flavescens. J Ethnopharmacol.
127:589–595. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Saito S and Murase K: Detection and early
phase assessment of radiation-induced lung injury in mice using
micro-CT. PLoS One. 7:e459602012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Plathow C, Li M, Gong P, Zieher H,
Kiessling F, Peschke P, Kauczor HU, Abdollahi A and Huber PE:
Computed tomography monitoring of radiation-induced lung fibrosis
in mice. Invest Radiol. 39:600–609. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Yang Y, Sun M, Yao W, Wang F, Li X, Wang
W, Li J, Gao Z, Qiu L, You R, et al: Compound kushen injection
relieves tumor-associated macrophage-mediated immunosuppression
through TNFR1 and sensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma to sorafenib.
J Immunother Cancer. 8:e0003172020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Liu X, Bai M, Li H, Ye P, Duan X, Wu C,
Huang Z, Lu S, Zhang J, Zhao Z, et al: Single-cell RNA-sequencing
uncovers compound kushen injection synergistically improves the
efficacy of chemotherapy by modulating the tumor environment of
breast cancer. Front Immunol. 13:9653422022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|