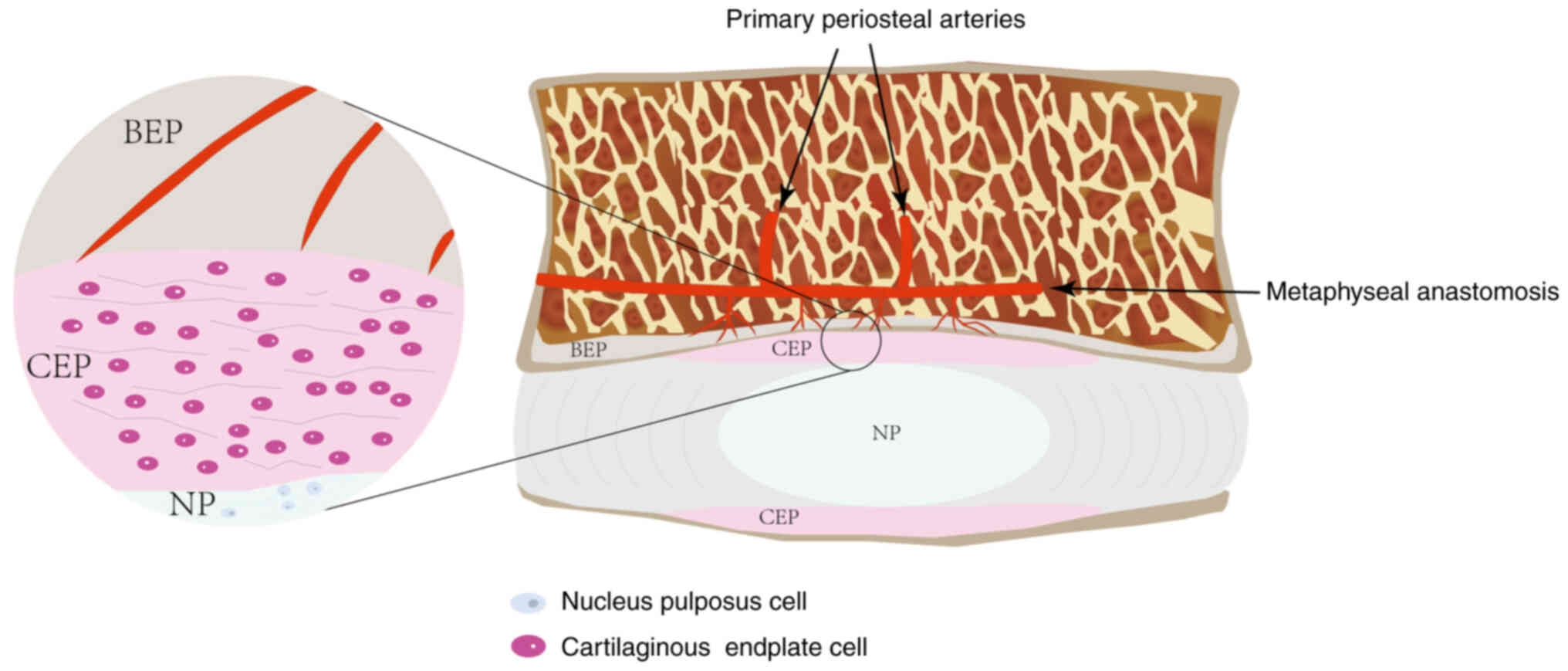
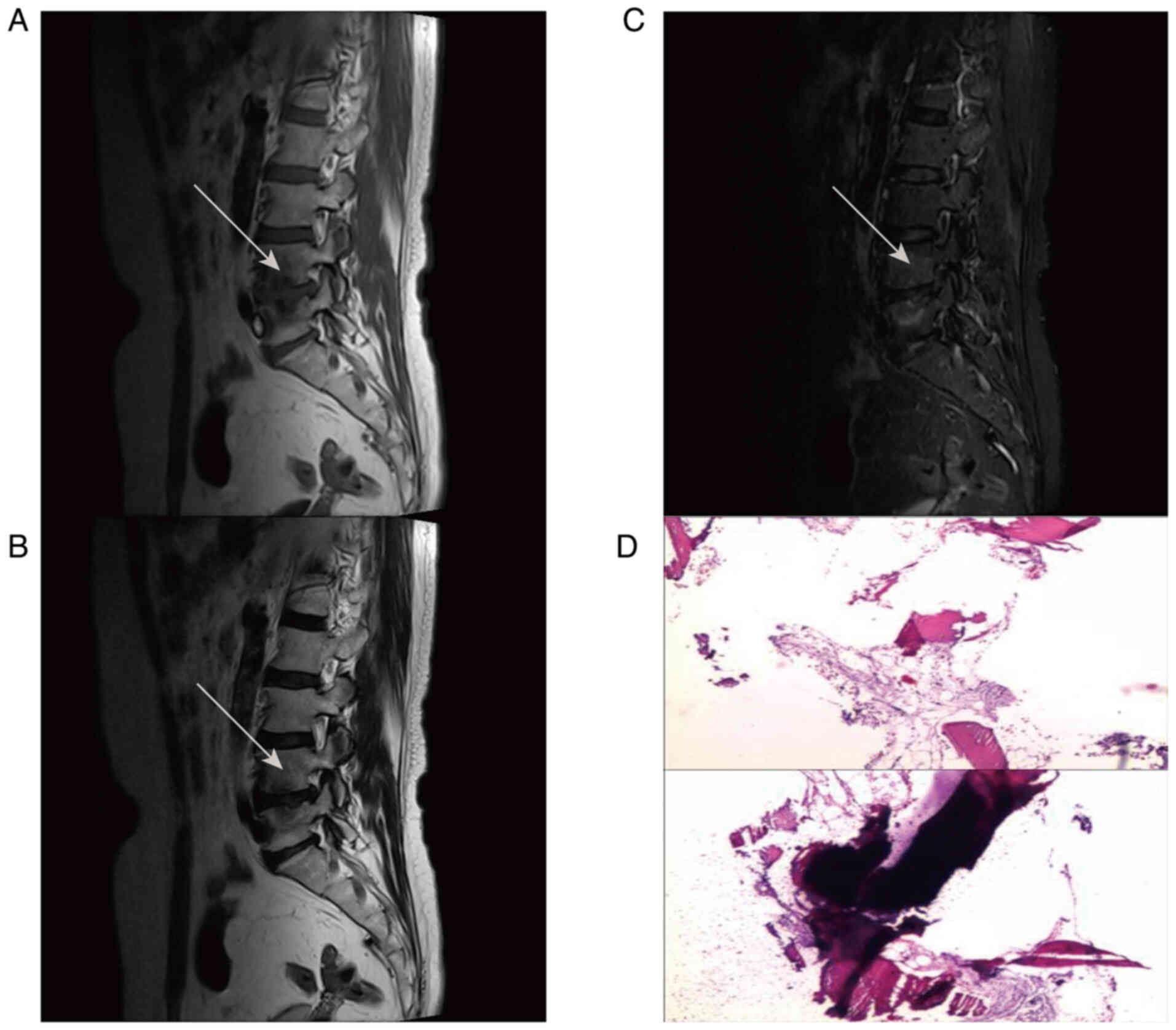
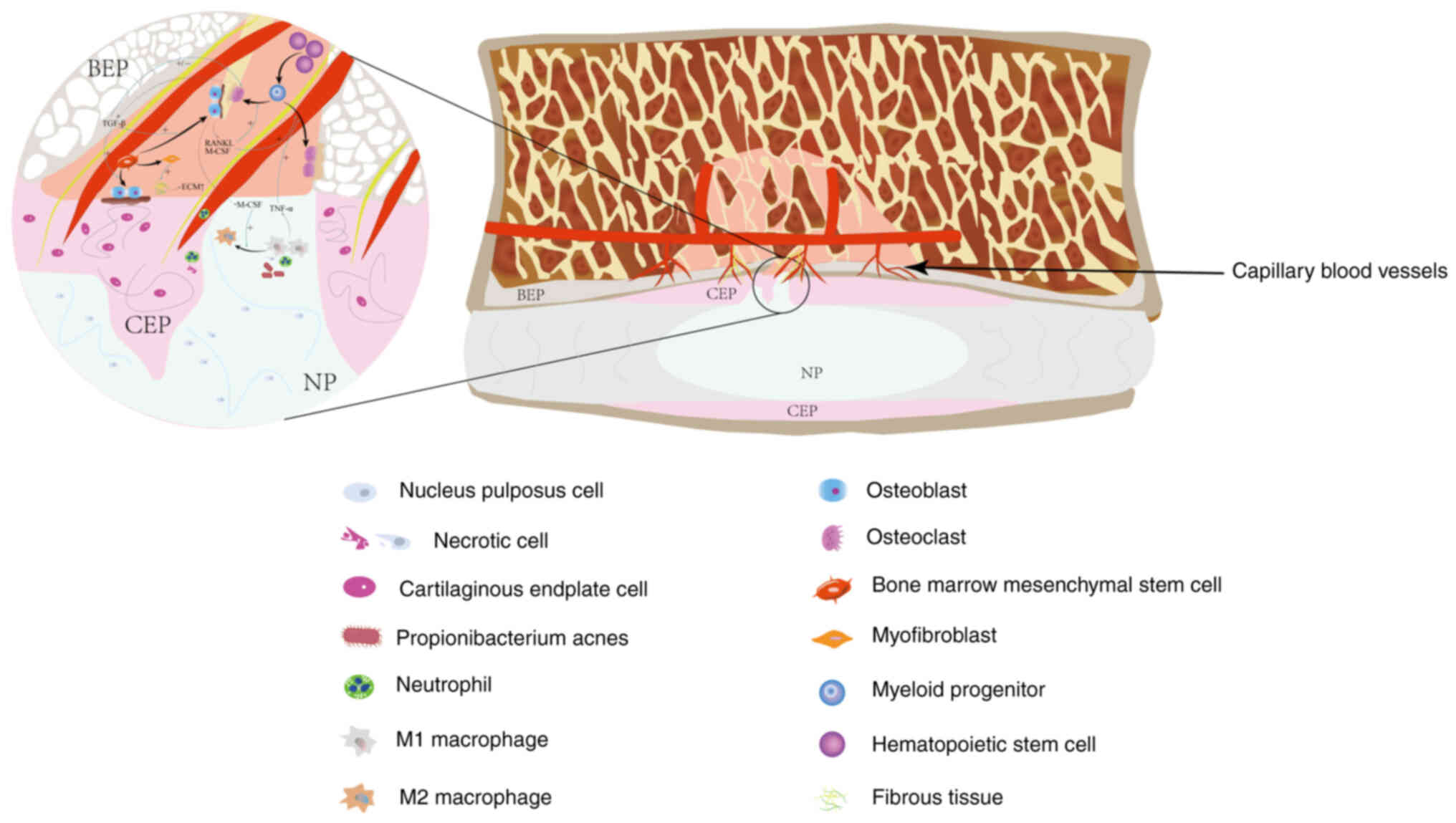
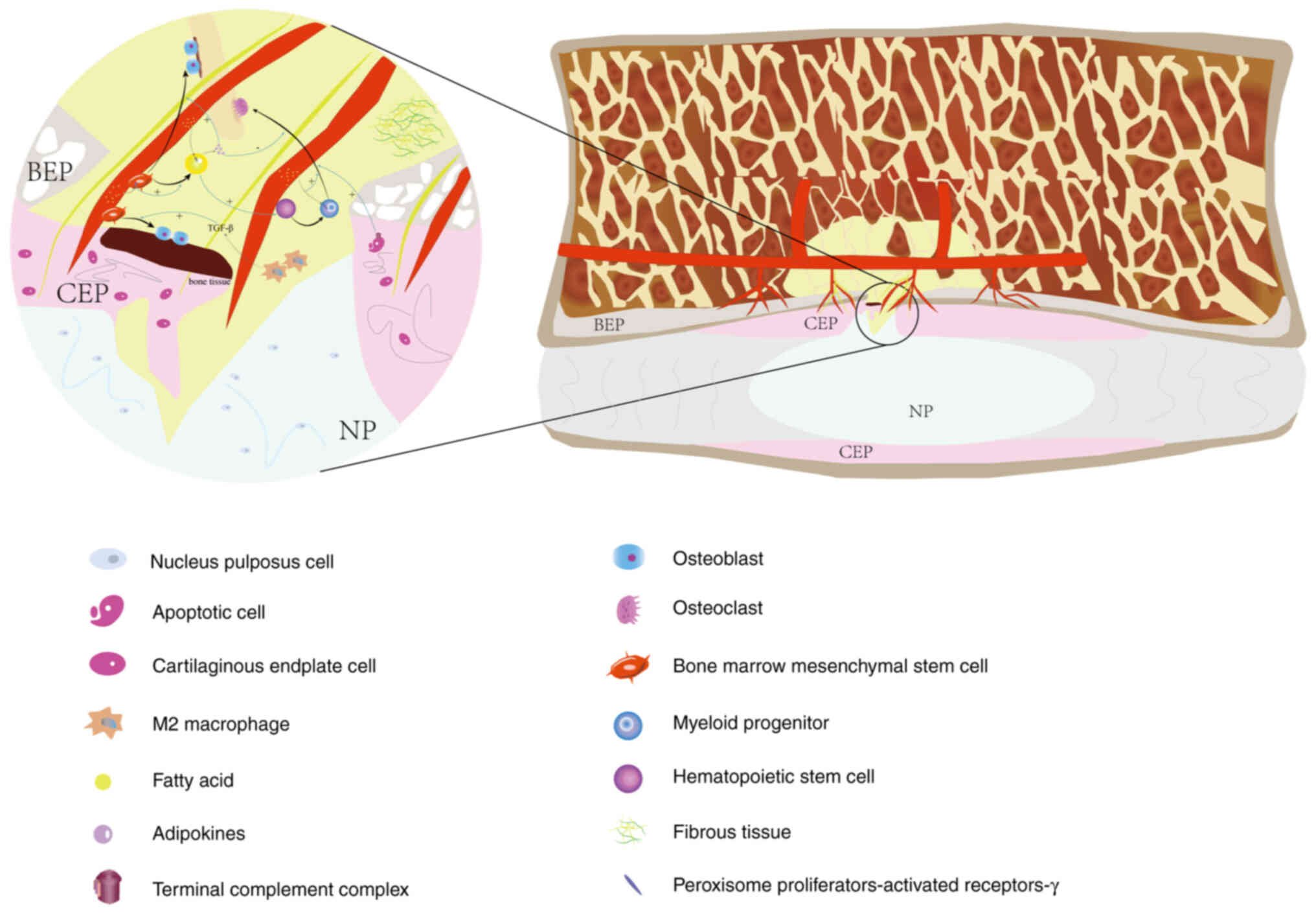
|
1
|
Modic MT, Steinberg PM, Ross JS, Masaryk
TJ and Carter JR: Degenerative disk disease: Assessment of changes
in vertebral body marrow with MR imaging. Radiology. 166((1 Pt 1)):
193–199. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Thompson KJ, Dagher AP, Eckel TS, Clark M
and Reinig JW: Modic changes on MR images as studied with
provocative diskography: Clinical relevance-a retrospective study
of 2457 disks. Radiology. 250:849–855. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Carrino JA, Lurie JD, Tosteson AN,
Tosteson TD, Carragee EJ, Kaiser J, Grove MR, Blood E, Pearson LH,
Weinstein JN and Herzog R: Lumbar spine: Reliability of MR imaging
findings. Radiology. 250:161–170. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Perilli E, Parkinson IH, Truong LH, Chong
KC, Fazzalari NL and Osti OL: Modic (endplate) changes in the
lumbar spine: Bone micro-architecture and remodelling. Eur Spine J.
24:1926–1934. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Tarukado K, Ono T, Tono O, Tanaka H, Ikuta
K, Harimaya K and Doi T: Does modic change progresss with age?
Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 42:1805–1809. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Brinjikji W, Diehn FE, Jarvik JG, Carr CM,
Kallmes DF, Murad MH and Luetmer PH: MRI findings of disc
degeneration are more prevalent in adults with low back pain than
in asymptomatic controls: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 36:2394–2399. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Heggli I, Laux CJ, Mengis T, Karol A,
Cornaz F, Herger N, Aradi-Vegh B, Widmer J, Burkhard MD,
Farshad-Amacker NA, et al: Modic type 2 changes are
fibroinflammatory changes with complement system involvement
adjacent to degenerated vertebral endplates. JOR Spine.
6:e12372022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Heggli I, Epprecht S, Juengel A,
Schuepbach R, Farshad-Amacker N, German C, Mengis T, Herger N,
Straumann L, Baumgartner S, et al: Pro-fibrotic phenotype of bone
marrow stromal cells in Modic type 1 changes. Eur Cell Mater.
41:648–667. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lu X, Zhu Z, Pan J, Feng Z, Lv X, Battié
MC and Wang Y: Traumatic vertebra and endplate fractures promote
adjacent disc degeneration: Evidence from a clinical MR follow-up
study. Skeletal Radiol. 51:1017–1026. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Dudli S, Heggli I, Laux CJ, Spirig JM,
Wanivenhaus F, Betz M, Germann C, Farshad-Amacker NA, Herger N,
Mengis T, et al: Role of C-reactive protein in the bone marrow of
Modic type 1 changes. J Orthop Res. 41:1115–1122. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
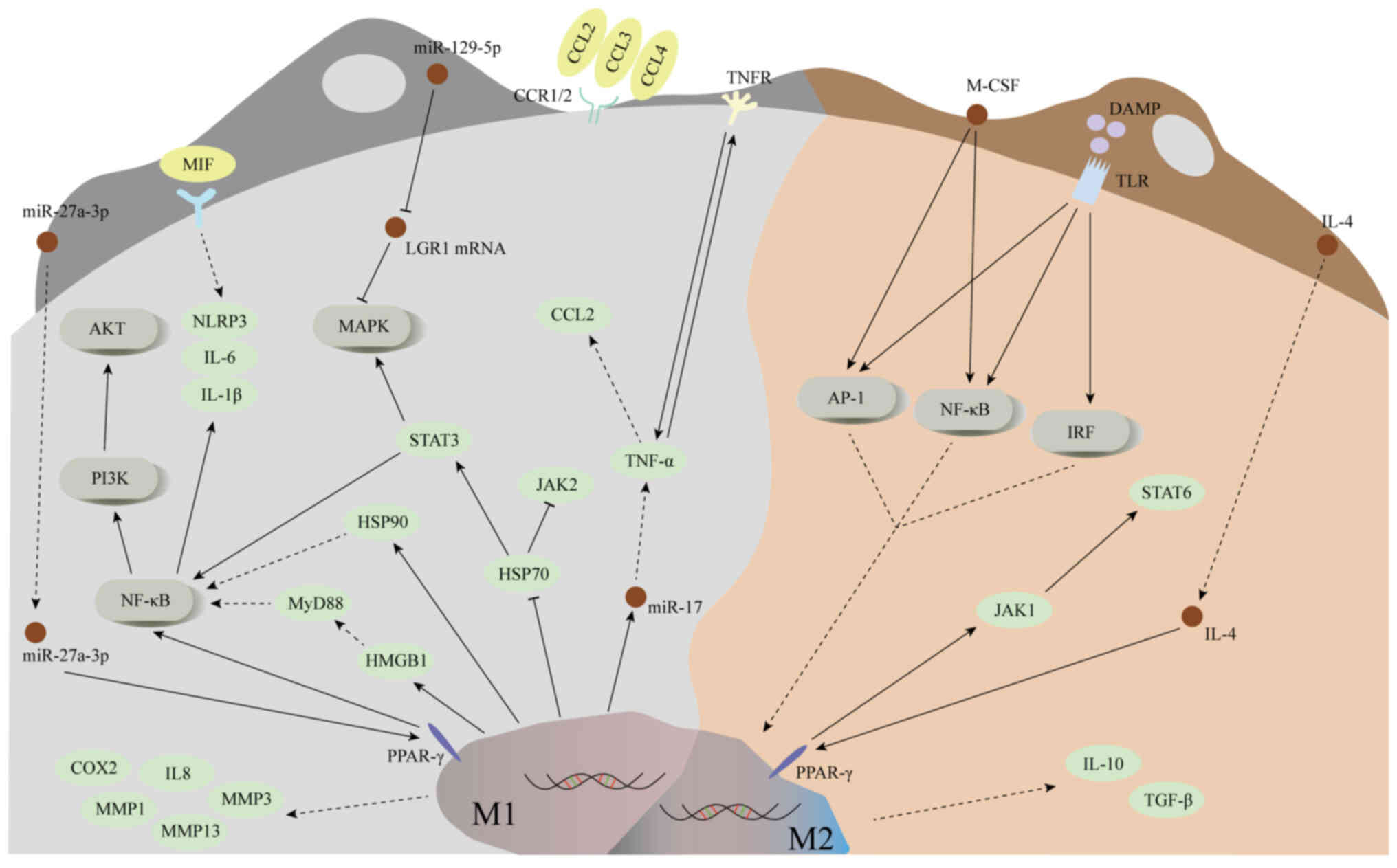
|
11
|
Dudli S, Liebenberg E, Magnitsky S, Miller
S, Demir-Deviren S and Lotz JC: Propionibacterium acnes infected
intervertebral discs cause vertebral bone marrow lesions consistent
with Modic changes. J Orthop Res. 34:1447–1455. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Biczo A, Szita J, McCall I and Varga PP;
Genodisc Consortium; Lazary A, : Association of vitamin D receptor
gene polymorphisms with disc degeneration. Eur Spine J. 29:596–604.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Eksi MS, Kara M, Ozcan-Eksi EE, Aytar MH,
Güngör A, Özgen S and Pamir MN: Is diabetes mellitus a risk factor
for modic changes?: A novel model to understand the association
between intervertebral disc degeneration and end-plate changes. J
Orthop Sci. 25:571–575. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Schmid G, Witteler A, Willburger R, Kuhnen
C, Jergas M and Koester O: Lumbar disk herniation: Correlation of
histologic findings with marrow signal intensity changes in
vertebral endplates at MR imaging. Radiology. 231:352–358. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Roberts S, Evans H, Trivedi J and Menage
J: Histology and pathology of the human intervertebral disc. J Bone
Joint Surg Am. 88 (Suppl 2):S10–S14. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Feng P, Che Y, Gao C, Zhu L, Gao J and Vo
NV: Immune exposure: How macrophages interact with the nucleus
pulposus. Front Immunol. 14:11557462023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Adams MA, Freeman BJ, Morrison HP, Nelson
IW and Dolan P: Mechanical initiation of intervertebral disc
degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 25:1625–1636. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ferguson SJ, Ito K and Nolte LP: Fluid
flow and convective transport of solutes within the intervertebral
disc. J Biomech. 37:213–221. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Torkki M, Majuri ML, Wolff H, Koskelainen
T, Haapea M, Niinimäki J, Alenius H, Lotz J and Karppinen J:
Osteoclast activators are elevated in intervertebral disks with
Modic changes among patients operated for herniated nucleus
pulposus. Eur Spine J. 25:207–216. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Dudli S, Ferguson SJ and Haschtmann D:
Severity and pattern of post-traumatic intervertebral disc
degeneration depend on the type of injury. Spine J. 14:1256–1264.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Dudli S, Haschtmann D and Ferguson SJ:
Fracture of the vertebral endplates, but not equienergetic impact
load, promotes disc degeneration in vitro. J Orthop Res.
30:809–816. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jensen TS, Bendix T, Sorensen JS, Manniche
C, Korsholm L and Kjaer P: Characteristics and natural course of
vertebral endplate signal (Modic) changes in the Danish general
population. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 10:812009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kerttula L, Luoma K, Vehmas T, Gronblad M
and Kaapa E: Modic type I change may predict rapid progressive,
deforming disc degeneration: A prospective 1-year follow-up study.
Eur Spine J. 21:1135–1142. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Dudli S, Sing DC, Hu SS, Berven SH, Burch
S, Deviren V, Cheng I, Tay BKB, Alamin TF, Ith MAM, et al: Issls
prize in basic science 2017: Intervertebral disc/bone marrow
cross-talk with Modic changes. Eur Spine J. 26:1362–1373. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dudli S, Karol A, Giudici L, Heggli I,
Laux CJ, Spirig JM, Wanivenhaus F, Betz M, Germann C,
Farshad-Amacker N, et al: CD90-positive stromal cells associate
with inflammatory and fibrotic changes in modic changes. Osteoarthr
Cartil Open. 4:1002872022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Baum T, Yap SP, Karampinos DC, Nardo L,
Kuo D, Burghardt AJ, Masharani UB, Schwartz AV, Li X and Link TM:
Does vertebral bone marrow fat content correlate with abdominal
adipose tissue, lumbar spine bone mineral density, and blood
biomarkers in women with type 2 diabetes mellitus? J Magn Reson
Imaging. 35:117–124. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Thomas GP, Hemmrich K, Abberton KM,
McCombe D, Penington AJ, Thompson EW and Morrison WA:
Zymosan-induced inflammation stimulates neo-adipogenesis. Int J
Obes (Lond). 32:239–248. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Monden M, Koyama H, Otsuka Y, Morioka T,
Mori K, Shoji T, Mima Y, Motoyama K, Fukumoto S, Shioi A, et al:
Receptor for advanced glycation end products regulates adipocyte
hypertrophy and insulin sensitivity in mice: Involvement of
Toll-like receptor 2. Diabetes. 62:478–489. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Haapasalo K and Meri S: Regulation of the
complement system by pentraxins. Front Immunol. 10:17502019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sjöberg A, Onnerfjord P Mörgelin M,
Heinegård D, Heinegård D and Blom AM: The extracellular matrix and
inflammation: Fibromodulin activates the classical pathway of
complement by directly binding C1q. J Biol Chem. 280:32301–23208.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Webster GF, Leyden JJ and Nilsson UR:
Complement activation in acne vulgaris: Consumption of complement
by comedones. Infect Immun. 26:183–186. 1979. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Piccinini AM and Midwood KS: DAMPening
inflammation by modulating TLR signalling. Mediators Inflamm.
2010:6723952010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ignatius A, Schoengraf P, Kreja L, Liedert
A, Recknagel S, Kandert S, Brenner RE, Schneider M, Lambris JD and
Huber-Lang M: Complement C3a and C5a modulate osteoclast formation
and inflammatory response of osteoblasts in synergism with IL-1β. J
Cell Biochem. 112:2594–2605. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Llorian-Salvador M, Byrne EM, Szczepan M,
Little K, Chen M and Xu H: Complement activation contributes to
subretinal fibrosis through the induction of
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in retinal pigment
epithelial cells. J Neuroinflammation. 19:1822022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Nozaki M, Raisler BJ, Sakurai E, Sarma JV,
Barnum SR, Lambris JD, Chen Y, Zhang K, Ambati BK, Baffi JZ and
Ambati J: Drusen complement components C3a and C5a promote
choroidal neovascularization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
103:2328–2333. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Takahashi K, Miyazaki T, Ohnari H, Takino
T and Tomita K: Schmorl's nodes and low-back pain. Analysis of
magnetic resonance imaging findings in symptomatic and asymptomatic
individuals. Eur Spine J. 4:56–59. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Dudli S, Fields AJ, Samartzis D, Karppinen
J and Lotz JC: Pathobiology of modic changes. Eur Spine J.
25:3723–3734. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Galán-Díez M and Kousteni S: A bone marrow
niche-derived molecular switch between osteogenesis and
hematopoiesis. Genes Dev. 32:324–326. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Zhou BO, Yue R, Murphy MM, Peyer JG and
Morrison SJ: Leptin-receptor-expressing mesenchymal stromal cells
represent the main source of bone formed by adult bone marrow. Cell
Stem Cell. 15:154–168. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Decker M, Martinez-Morentin L, Wang G, Lee
Y, Liu Q, Leslie J and Ding L: Leptin-receptor-expressing bone
marrow stromal cells are myofibroblasts in primary myelofibrosis.
Nat Cell Biol. 19:677–688. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Papayannopoulos V: Neutrophil
extracellular traps in immunity and disease. Nat Rev Immunol.
18:134–147. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Naveiras O, Nardi V, Wenzel PL, Hauschka
PV, Fahey F and Daley GQ: Bone-marrow adipocytes as negative
regulators of the haematopoietic microenvironment. Nature.
460:259–263. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Wan Y, Chong LW and Evans RM: PPAR-gamma
regulates osteoclastogenesis in mice. Nat Med. 13:1496–1503. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
He N, Liu M and Wu Y: Adipose tissue and
hematopoiesis: Friend or foe? J Clin Lab Anal. 37:e248722023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Mattiucci D, Maurizi G, Izzi V, Cenci L,
Ciarlantini M, Mancini S, Mensà E, Pascarella R, Vivarelli M,
Olivieri A, et al: Bone marrow adipocytes support hematopoietic
stem cell survival. J Cell Physiol. 233:1500–1511. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Wilson A, Fu H, Schiffrin M, Winkler C,
Koufany M, Jouzeau JY, Bonnet N, Gilardi F, Renevey F, Luther SA,
et al: Lack of adipocytes alters hematopoiesis in lipodystrophic
mice. Front Immunol. 9:25732018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Kolaczkowska E and Kubes P: Neutrophil
recruitment and function in health and inflammation. Nat Rev
Immunol. 13:159–175. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Borregaard N: Neutrophils, from marrow to
microbes. Immunity. 33:657–670. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Heggli I, Mengis T, Laux CJ, Opitz L,
Herger N, Menghini D, Schuepbach R, Farshad-Amacker NA, Brunner F,
Fields AJ, et al: Low back pain patients with Modic type 1 changes
exhibit distinct bacterial and non-bacterial subtypes. Osteoarthr
Cartil Open. 6:1004342024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Kawai T and Akira S: Toll-like receptors
and their crosstalk with other innate receptors in infection and
immunity. Immunity. 34:637–650. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Fournier BM and Parkos CA: The role of
neutrophils during intestinal inflammation. Mucosal Immunol.
5:354–366. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Thålin C, Hisada Y, Lundström S, Mackman N
and Wallén H: Neutrophil extracellular traps: Villains and targets
in arterial, venous, and cancer-associated thrombosis. Arterioscler
Thromb Vasc Biol. 39:1724–1738. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Wang H, Wang C, Zhao MH and Chen M:
Neutrophil extracellular traps can activate alternative complement
pathways. Clin Exp Immunol. 181:518–527. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Christoffersson G, Vagesjo E, Vandooren J,
Lidén M, Massena S, Reinert RB, Brissova M, Powers AC, Opdenakker G
and Phillipson M: VEGF-A recruits a proangiogenic MMP-9-delivering
neutrophil subset that induces angiogenesis in transplanted hypoxic
tissue. Blood. 120:4653–4662. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Shi J, Gilbert GE, Kokubo Y and Ohashi T:
Role of the liver in regulating numbers of circulating neutrophils.
Blood. 98:1226–1230. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Okabe Y and Medzhitov R: Tissue biology
perspective on macrophages. Nat Immunol. 17:9–17. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Gao J, Liang Y and Wang L: Shaping
polarization of tumor-associated macrophages in cancer
immunotherapy. Front Immunol. 13:8887132022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Nakazawa KR, Walter BA, Laudier DM,
Krishnamoorthy D, Mosley GE, Spiller KL and Iatridis JC:
Accumulation and localization of macrophage phenotypes with human
intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine J. 18:343–356. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Murai K, Sakai D, Nakamura Y, Nakai T,
Igarashi T, Seo N, Murakami T, Kobayashi E and Mochida J: Primary
immune system responders to nucleus pulposus cells: Evidence for
immune response in disc herniation. Eur Cell Mater. 19:13–21. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Daneshvar A, Nemati P, Azadi A, Amid R and
Kadkhodazadeh M: M2 macrophage-derived exosomes for bone
regeneration: A systematic review. Arch Oral Biol. 166:1060342024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Fan S, Zhang C, Sun X, Su C, Xue Y, Song X
and Deng R: Metformin enhances osteogenic differentiation of BMSC
by modulating macrophage M2 polarization. Sci Rep. 14:202672024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Fang C, Zhong R, Lu S, Yu G, Liu Z, Yan C,
Gao J, Tang Y, Wang Y, Zhao Q and Feng X: TREM2 promotes macrophage
polarization from M1 to M2 and suppresses osteoarthritis through
the NF-κB/CXCL3 axis. Int J Biol Sci. 20:1992–2007. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Wang Y, Zhao M, Liu S, Guo J, Lu Y, Cheng
J and Liu J: Macrophage-derived extracellular vesicles: Diverse
mediators of pathology and therapeutics in multiple diseases. Cell
Death Dis. 11:9242020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Häusler KD, Horwood NJ, Chuman Y, Fisher
JL, Ellis J, Martin TJ, Rubin JS and Gillespie MT: Secreted
frizzled-related protein-1 inhibits RANKL-dependent osteoclast
formation. J Bone Miner Res. 19:1873–1881. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Yang Y, Qin J, Lan L, Li N, Wang C, He P,
Liu F, Ni H and Wang Y: M-CSF cooperating with NFκB induces
macrophage transformation from M1 to M2 by upregulating c-Jun.
Cancer Biol Ther. 15:99–107. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Ikebuchi Y, Aoki S, Honma M, Hayashi M,
Sugamori Y, Khan M, Kariya Y, Kato G, Tabata Y, Penninger JM, et
al: Coupling of bone resorption and formation by RANKL reverse
signalling. Nature. 561:195–200. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Pajarinen J, Lin T, Gibon E, Kohno Y,
Maruyama M, Nathan K, Lu L, Yao Z and Goodman SB: Mesenchymal stem
cell-macrophage crosstalk and bone healing. Biomaterials.
196:80–89. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Ni S, Ling Z, Wang X, Cao Y, Wu T, Deng R,
Crane JL, Skolasky R, Demehri S, Zhen G, et al: Sensory innervation
in porous endplates by Netrin-1 from osteoclasts mediates
PGE2-induced spinal hypersensitivity in mice. Nat Commun.
10:56432019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Bachmeier BE, Nerlich AG, Weiler C,
Paesold G, Jochum M and Boos N: Analysis of tissue distribution of
TNF-alpha, TNF-alpha-receptors, and the activating
TNF-alpha-converting enzyme suggests activation of the TNF-alpha
system in the aging intervertebral disc. Ann N Y Acad Sci.
1096:44–54. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Wallach D: The TNF family: Only the
surface has been scratched. Semin Immunol. 26:181–182. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Aggarwal BB, Gupta SC and Kim JH:
Historical perspectives on tumor necrosis factor and its
superfamily: 25 years later, a golden journey. Blood. 119:651–665.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Wang J, Tian Y, Phillips KL, Chiverton N,
Haddock G, Bunning RA, Cross AK, Shapiro IM, Le Maitre CL and
Risbud MV: Tumor necrosis factor alpha- and
interleukin-1beta-dependent induction of CCL3 expression by nucleus
pulposus cells promotes macrophage migration through CCR1.
Arthritis Rheum. 65:832–842. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Nakawaki M, Uchida K, Miyagi M, Inoue G,
Kawakubo A, Kuroda A, Satoh M and Takaso M: Sequential CCL2
expression profile after disc injury in mice. J Orthop Res.
38:895–901. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Chou PH, Chee A, Shi P, Lin CL, Zhao Y,
Zhang L and An HS: Small molecule antagonist of C-C chemokine
receptor 1 (CCR1) reduces disc inflammation in the rabbit model.
Spine J. 20:2025–2036. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Li Z, Wang X, Pan H, Yang H, Li X, Zhang
K, Wang H, Zheng Z, Liu H and Wang J: Resistin promotes CCL4
expression through toll-like receptor-4 and activation of the
p38-MAPK and NF-ĸB signaling pathways: Implications for
intervertebral disc degeneration. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.
25:341–350. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Hwang MH, Son HG, Lee JW, Yoo CM, Shin JH,
Nam HG, Lim HJ, Baek SM, Park JH, Kim JH and Choi H:
Photobiomodulation of extracellular matrix enzymes in human nucleus
pulposus cells as a potential treatment for intervertebral disk
degeneration. Sci Rep. 8:116542018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Abe Y, Akeda K, An HS, Aoki Y, Pichika R,
Muehleman C, Kimura T and Masuda K: Proinflammatory cytokines
stimulate the expression of nerve growth factor by human
intervertebral disc cells. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 32:635–642. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Dudli S, Liebenberg E, Magnitsky S, Lu B,
Lauricella M and Lotz JC: Modic type 1 change is an autoimmune
response that requires a proinflammatory milieu provided by the
‘Modic disc’. Spine J. 18:831–844. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Jia J, Nie L and Liu Y: Butyrate
alleviates inflammatory response and NF-ĸB activation in human
degenerated intervertebral disc tissues. Int Immunopharmacol.
78:1060042020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Ma Z, Tang P, Dong W, Lu Y, Tan B, Zhou N,
Hao J, Shen J and Hu Z: SIRT1 alleviates IL-1β induced nucleus
pulposus cells pyroptosis via mitophagy in intervertebral disc
degeneration. Int Immunopharmacol. 107:1086712022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Zhang K, Ding W, Sun W, Sun XJ, Xie YZ,
Zhao CQ and Zhao J: Beta1 integrin inhibits apoptosis induced by
cyclic stretch in annulus fibrosus cells via ERK1/2 MAPK pathway.
Apoptosis. 21:13–24. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Kang H, Dong Y, Peng R, Liu H, Guo Q, Song
K, Zhu M, Yu K, Wu W and Li F: Inhibition of IRE1 suppresses the
catabolic effect of IL-1β on nucleus pulposus cell and prevents
intervertebral disc degeneration in vivo. Biochem Pharmacol.
197:1149322022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Zhao F, Guo Z, Hou F, Fan W, Wu B and Qian
Z: Magnoflorine alleviates ‘M1’ polarized macrophage-induced
intervertebral disc degeneration through repressing the
HMGB1/Myd88/NF-ĸB pathway and NLRP3 inflammasome. Front Pharmacol.
12:7010872021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Zhang S, Wang P, Hu B, Liu W, Lv X, Chen S
and Shao Z: HSP90 inhibitor 17-AAG attenuates nucleus pulposus
inflammation and catabolism induced by M1-polarized macrophages.
Front Cell Dev Biol. 9:7969742022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Zhang S, Wang P, Hu B, Lv X, Liu W, Chen S
and Shao Z: Inhibiting heat shock protein 90 attenuates nucleus
pulposus fibrosis and pathologic angiogenesis induced by
macrophages via down-regulating cell migration-inducing protein. Am
J Pathol. 193:960–976. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
England H, Summersgill HR, Edye ME,
Rothwell NJ and Brough D: Release of interleukin-1alpha or
interleukin-1beta depends on mechanism of cell death. J Biol Chem.
289:15942–15950. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Phillips KL, Jordan-Mahy N, Nicklin MJ and
Le Maitre CL: Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist deficient mice
provide insights into pathogenesis of human intervertebral disc
degeneration. Ann Rheum Dis. 72:1860–1867. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Hasvik E, Schjolberg T, Jacobsen DP,
Haugen AJ, Grøvle L, Schistad EI and Gjerstad J: Up-regulation of
circulating microRNA-17 is associated with lumbar radicular pain
following disc herniation. Arthritis Res Ther. 21:1862019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Cui S and Zhang L: microRNA-129-5p
shuttled by mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles
alleviates intervertebral disc degeneration via blockade of
LRG1-mediated p38 MAPK activation. J Tissue Eng.
12:204173142110216792021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Zhao X, Sun Z, Xu B, Duan W, Chang L, Lai
K and Ye Z: Degenerated nucleus pulposus cells derived exosome
carrying miR-27a-3p aggravates intervertebral disc degeneration by
inducing M1 polarization of macrophages. J Nanobiotechnology.
21:3172023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Murray PJ: Macrophage polarization. Annu
Rev Physiol. 79:541–566. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Yamamoto Y, Kokubo Y, Nakajima H, Honjoh
K, Watanabe S and Matsumine A: Distribution and polarization of
hematogenous macrophages associated with the progression of
intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).
47:E149–E158. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Greenlee-Wacker MC: Clearance of apoptotic
neutrophils and resolution of inflammation. Immunol Rev.
273:357–370. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Ip WKE, Hoshi N, Shouval DS, Snapper S and
Medzhitov R: Anti-inflammatory effect of IL-10 mediated by
metabolic reprogramming of macrophages. Science. 356:513–519. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Odegaard JI, Ricardo-Gonzalez RR, Goforth
MH, Morel CR, Subramanian V, Mukundan L, Red Eagle A, Vats D,
Brombacher F, Ferrante AW and Chawla A: Macrophage-specific
PPARgamma controls alternative activation and improves insulin
resistance. Nature. 447:1116–1120. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Szanto A, Balint BL, Nagy ZS, Barta E,
Dezso B, Pap A, Szeles L, Poliska S, Oros M, Evans RM, et al: STAT6
transcription factor is a facilitator of the nuclear receptor
PPARγ-Regulated gene expression in macrophages and dendritic cells.
Immunity. 33:699–712. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Kawakubo A, Miyagi M, Yokozeki Y, Nakawaki
M, Takano S, Satoh M, Itakura M, Inoue G, Takaso M and Uchida K:
Origin of M2 Mϕ and its macrophage polarization by TGF-β in a mice
intervertebral injury model. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol.
36:39463202211037922022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Xu YQ, Zhang ZH, Zheng YF and Feng SQ:
Dysregulated miR-133a mediates loss of type II collagen by directly
targeting matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP9) in human intervertebral
disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 41:E717–E724. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Kobayashi T, Kim H, Liu X, Sugiura H,
Kohyama T, Fang Q, Wen FQ, Abe S, Wang X, Atkinson JJ, et al:
Matrix metalloproteinase-9 activates TGF-beta and stimulates
fibroblast contraction of collagen gels. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol
Physiol. 306:L1006–L1015. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
van Caam A, Vonk M, van den Hoogen F, van
Lent P and van der Kraan P: Unraveling SSc Pathophysiology; The
Myofibroblast. Front Immunol. 9:24522018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Abbott RD, Purmessur D, Monsey RD,
Brigstock DR, Laudier DM and Iatridis JC: Degenerative grade
affects the responses of human nucleus pulposus cells to link-N,
CTGF, and TGFβ3. J Spinal Disord Tech. 26:E86–E94. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Wei Q, Liu D, Chu G, Yu Q, Liu Z, Li J,
Meng Q, Wang W, Han F and Li B: TGF-β1-supplemented decellularized
annulus fibrosus matrix hydrogels promote annulus fibrosus repair.
Bioact Mater. 19:581–593. 2022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Zhu L, Yang Y, Yan Z, Zeng J, Weng F, Shi
Y, Shen P, Liu L and Yang H: Controlled release of TGF-β3 for
effective local endogenous repair in IDD using rat model. Int J
Nanomedicine. 17:2079–2096. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Montgomery SR, Nargizyan T, Meliton V,
Nachtergaele S, Rohatgi R, Stappenbeck F, Jung ME, Johnson JS,
Aghdasi B, Tian H, et al: A novel osteogenic oxysterol compound for
therapeutic development to promote bone growth: activation of
hedgehog signaling and osteogenesis through smoothened binding. J
Bone Miner Res. 29:1872–1885. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Jacobsen CM, Schwartz MA, Roberts HJ, Lim
KE, Spevak L, Boskey AL, Zurakowski D, Robling AG and Warman ML:
Enhanced Wnt signaling improves bone mass and strength, but not
brittleness, in the Col1a1(+/mov13) mouse model of type I
Osteogenesis Imperfecta. Bone. 90:127–132. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Ramasamy SK, Kusumbe AP, Wang L and Adams
RH: Endothelial notch activity promotes angiogenesis and
osteogenesis in bone. Nature. 507:376–380. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Heggli I, Teixeira GQ, Iatridis JC,
Neidlinger-Wilke C and Dudli S: The role of the complement system
in disc degeneration and Modic changes. JOR Spine. 7:e13122024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Komori T: Cell death in chondrocytes,
osteoblasts, and osteocytes. Int J Mol Sci. 17:20452016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Albert HB, Lambert P, Rollason J, Sorensen
JS, Worthington T, Pedersen MB, Nørgaard HS, Vernallis A, Busch F,
Manniche C and Elliott T: Does nuclear tissue infected with
bacteria following disc herniations lead to Modic changes in the
adjacent vertebrae? Eur Spine J. 22:690–696. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Riegger J, Huber-Lang M and Brenner RE:
Crucial role of the terminal complement complex in chondrocyte
death and hypertrophy after cartilage trauma. Osteoarthritis
Cartilage. 28:685–697. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Fatoba O, Itokazu T and Yamashita T:
Complement cascade functions during brain development and
neurodegeneration. FEBS J. 289:2085–2109. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Koivisto K, Jarvinen J, Karppinen J,
Haapea M, Paananen M, Kyllönen E, Tervonen O and Niinimäki J: The
effect of zoledronic acid on type and volume of Modic changes among
patients with low back pain. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 18:2742017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Xu L, Chu B, Feng Y, Xu F and Zou YF:
Modic changes in lumbar spine: Prevalence and distribution patterns
of end plate oedema and end plate sclerosis. Br J Radiol.
89:201506502016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Galbusera F, Casaroli G and Bassani T:
Artificial intelligence and machine learning in spine research. JOR
Spine. 2:e10442019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Gao KT, Tibrewala R, Hess M, Bharadwaj UU,
Inamdar G, Link TM, Chin CT, Pedoia V and Majumdar S: Automatic
detection and voxel-wise mapping of lumbar spine Modic changes with
deep learning. JOR Spine. 5:e12042022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Rajasekaran S, Bt P, Murugan C, Mengesha
MG, Easwaran M, Naik AS, Ks SVA, Kanna RM and Shetty AP: The
disc-endplate-bone-marrow complex classification: progress in our
understanding of Modic vertebral endplate changes and their
clinical relevance. Spine J. 24:34–45. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Laustsen AF and Bech-Azeddine R: Do Modic
changes have an impact on clinical outcome in lumbar spine surgery?
A systematic literature review. Eur Spine J. 25:3735–3745. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Määttä JH, Wadge S, MacGregor A, Karppinen
J and Williams FM: ISSLS prize winner: Vertebral endplate (Modic)
change is an independent risk factor for episodes of severe and
disabling low back pain. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 40:1187–1193. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Jensen TS, Karppinen J, Sorensen JS,
Niinimäki J and Leboeuf-Yde C: Vertebral endplate signal changes
(Modic change): A systematic literature review of prevalence and
association with non-specific low back pain. Eur Spine J.
17:1407–1422. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Lambrechts MJ, Brush P, Issa TZ, Toci GR,
Heard JC, Syal A, Schilken MM, Canseco JA, Kepler CK and Vaccaro
AR: Evaluating the impact of modic changes on operative treatment
in the cervical and Lumbar Spine: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 19:101582022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Nian S, Li N, Kong F, Lu S and Chen J: Is
discectomy effective for treating low back pain in patients with
lumbar disc herniation and Modic changes? A systematic review and
meta-analysis of cohort studies. Spine J. 23:533–549. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Conger A, Burnham TR, Clark T, Teramoto M
and McCormick ZL: The effectiveness of intraosseous basivertebral
nerve radiofrequency ablation for the treatment of vertebrogenic
low back pain: An updated systematic review with single-arm
meta-analysis. Pain Med. 23 (Suppl 2):S50–S62. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Ohtori S, Inoue G, Ito T, Koshi T, Ozawa
T, Doya H, Saito T, Moriya H and Takahashi K: Tumor necrosis
factor-immunoreactive cells and PGP 9.5-immunoreactive nerve fibers
in vertebral endplates of patients with discogenic low back pain
and modic type 1 or type 2 changes on MRI. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).
31:1026–1031. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
DePalma MJ, Ketchum JM and Saullo T: What
is the source of chronic low back pain and does age play a role?
Pain Med. 12:224–233. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Depalma MJ, Ketchum JM, Trussell BS,
Saullo TR and Slipman CW: Does the location of low back pain
predict its source? PM R. 3:33–39. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Feng Z, Liu Y, Yang G, Battie MC and Wang
Y: Lumbar vertebral endplate defects on magnetic resonance images:
Classification, distribution patterns, and associations with modic
changes and disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 43:919–927.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Udby PM, Samartzis D, Carreon LY, Andersen
MØ, Karppinen J and Modic M: A definition and clinical grading of
Modic changes. J Orthop Res. 40:301–307. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|