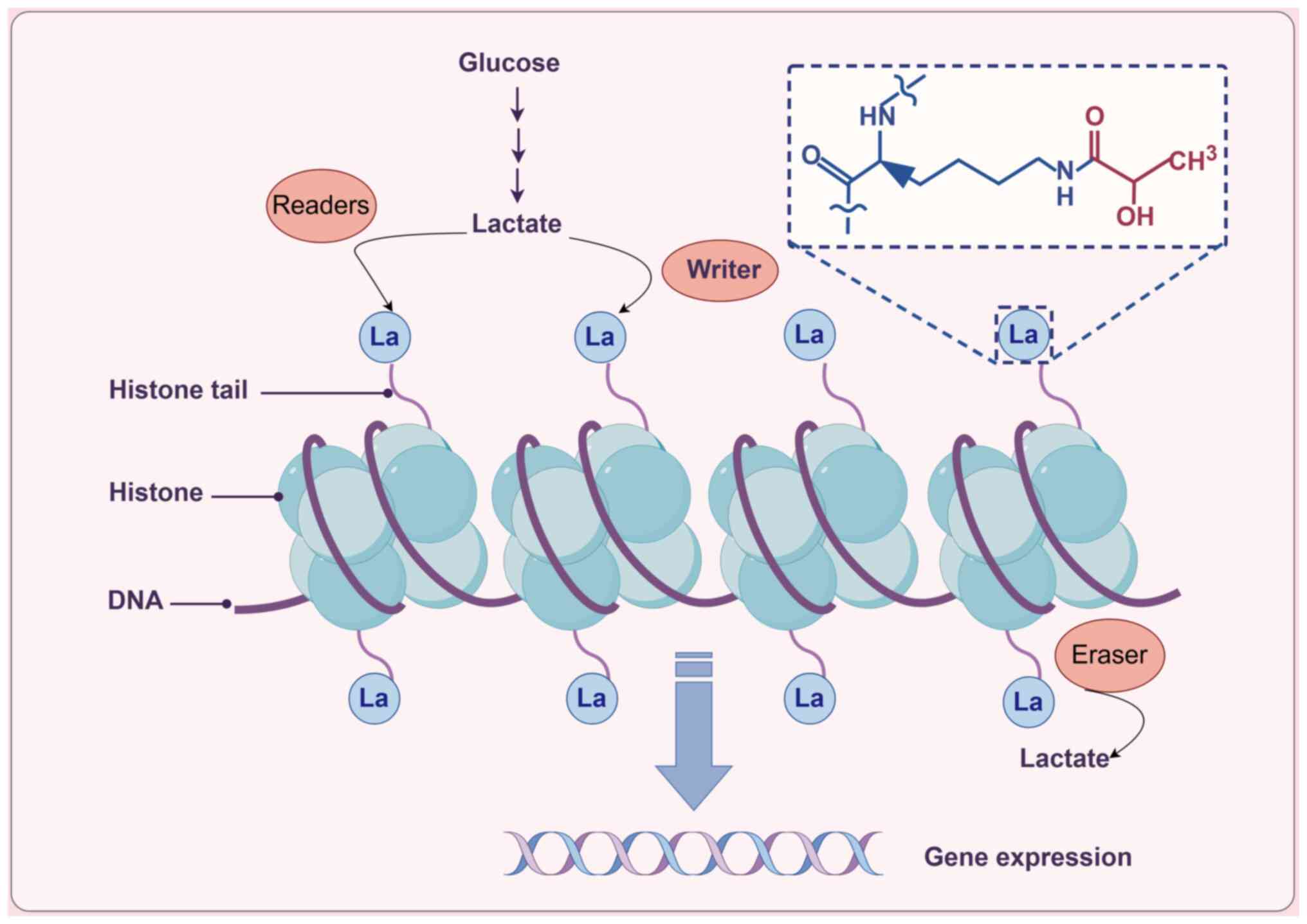
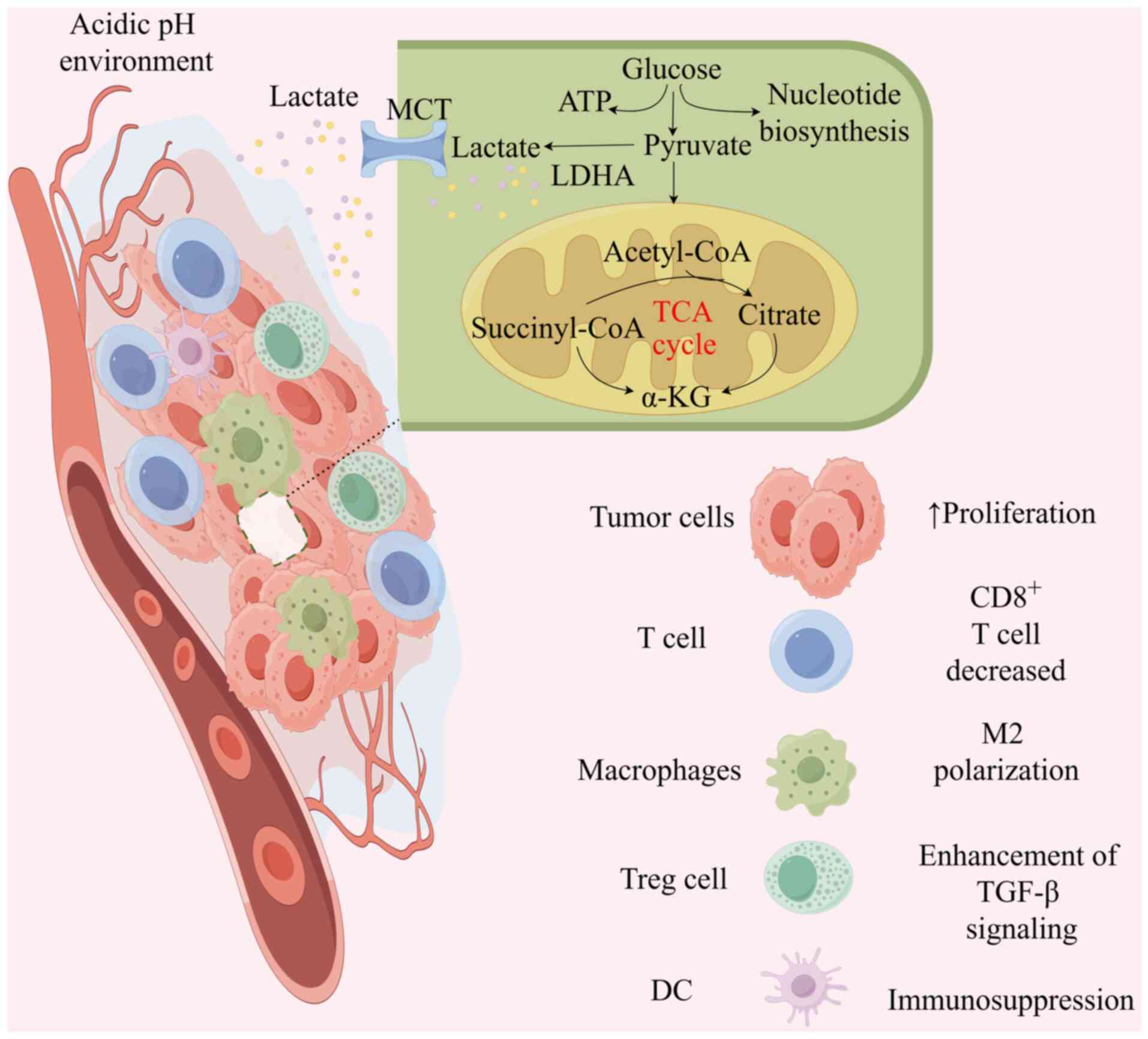
|
1
|
Doyle HA and Mamula MJ: Post-translational
protein modifications in antigen recognition and autoimmunity.
Trends Immunol. 22:443–449. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ramazi S and Zahiri J: Posttranslational
modifications in proteins: Resources, tools and prediction methods.
Database (Oxford). 2021:baab0122021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wang H, Yang L, Liu M and Luo J: Protein
post-translational modifications in the regulation of cancer
hallmarks. Cancer Gene Ther. 30:529–547. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhang H and Han W: Protein
post-translational modifications in head and neck cancer. Front
Oncol. 10:5719442020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Visconti A and Qiu H: Recent advances in
serum response factor posttranslational modifications and their
therapeutic potential in cardiovascular and neurological diseases.
Vascul Pharmacol. 156:1074212024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang Z, Li M, Jiang H, Luo S, Shao F, Xia
Y, Yang M, Ren X, Liu T, Yan M, et al: Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase
1 functions as a protein phosphatase to dephosphorylate histone H3
and suppresses PPARα-regulated gene transcription and tumour
growth. Nat Cell Biol. 24:1655–1665. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhong Q, Xiao X, Qiu Y, Xu Z, Chen C,
Chong B, Zhao X, Hai S, Li S, An Z and Dai L: Protein
posttranslational modifications in health and diseases: Functions,
regulatory mechanisms, and therapeutic implications. MedComm
(2020). 4:e2612023. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yu T, Wang Y, Fan Y, Fang N, Wang T, Xu T
and Shu Y: CircRNAs in cancer metabolism: A review. J Hematol
Oncol. 12:902019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
San-Millan I, Sparagna GC, Chapman HL,
Warkins VL, Chatfield KC, Shuff SR, Martinez JL and Brooks GA:
Chronic lactate exposure decreases mitochondrial function by
inhibition of fatty acid uptake and cardiolipin alterations in
neonatal rat cardiomyocytes. Front Nutr. 9:8094852022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Brooks GA: Lactate as a fulcrum of
metabolism. Redox Biol. 35:1014542020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhu W, Guo S, Sun J, Zhao Y and Liu C:
Lactate and lactylation in cardiovascular diseases: Current
progress and future perspectives. Metabolism. 158:1559572024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang D, Tang Z, Huang H, Zhou G, Cui C,
Weng Y, Liu W, Kim S, Lee S, Perez-Neut M, et al: Metabolic
regulation of gene expression by histone lactylation. Nature.
574:575–580. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Pérez-Tomás R and Pérez-Guillén I: Lactate
in the tumor microenvironment: An essential molecule in cancer
progression and treatment. Cancers (Basel). 12:32442020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yu X, Yang J, Xu J, Pan H, Wang W, Yu X
and Shi S: Histone lactylation: From tumor lactate metabolism to
epigenetic regulation. Int J Biol Sci. 20:1833–1854. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Heydari Z, Moeinvaziri F, Mirazimi SMA,
Dashti F, Smirnova O, Shpichka A, Mirzaei H, Timashev P and Vosough
M: Alteration in DNA methylation patterns: Epigenetic signatures in
gastrointestinal cancers. Eur J Pharmacol. 973:1765632024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Rungratanawanich W, Ballway JW, Wang X,
Won KJ, Hardwick JP and Song BJ: Post-translational modifications
of histone and non-histone proteins in epigenetic regulation and
translational applications in alcohol-associated liver disease:
Challenges and research opportunities. Pharmacol Ther.
251:1085472023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang J, Wang Z, Wang Q, Li X and Guo Y:
Ubiquitous protein lactylation in health and diseases. Cell Mol
Biol Lett. 29:232024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Xu X, Zhang DD, Kong P, Gao YK, Huang XF,
Song Y, Zhang WD, Guo RJ, Li CL, Chen BW, et al: Sox10 escalates
vascular inflammation by mediating vascular smooth muscle cell
transdifferentiation and pyroptosis in neointimal hyperplasia. Cell
Rep. 42:1128692023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yang D, Yin J, Shan L, Yi X, Zhang W and
Ding Y: Identification of lysine-lactylated substrates in gastric
cancer cells. iScience. 25:1046302022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chen M, Cen K, Song Y, Zhang X, Liou YC,
Liu P, Huang J, Ruan J, He J, Ye W, et al:
NUSAP1-LDHA-glycolysis-lactate feedforward loop promotes Warburg
effect and metastasis in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cancer
Lett. 567:2162852023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Meng Q, Sun H, Zhang Y, Yang X, Hao S, Liu
B, Zhou H, Xu ZX and Wang Y: Lactylation stabilizes DCBLD1
activating the pentose phosphate pathway to promote cervical cancer
progression. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 43:362024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chu YD, Cheng LC, Lim SN, Lai MW, Yeh CT
and Lin WR: Aldolase B-driven lactagenesis and CEACAM6 activation
promote cell renewal and chemoresistance in colorectal cancer
through the Warburg effect. Cell Death Dis. 14:6602023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gu X, Zhuang A, Yu J, Yang L, Ge S, Ruan
J, Jia R, Fan X and Chai P: Histone lactylation-boosted ALKBH3
potentiates tumor progression and diminished promyelocytic leukemia
protein nuclear condensates by m1A demethylation of SP100A. Nucleic
Acids Res. 52:2273–2289. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Liu R, Wu J, Guo H, Yao W, Li S, Lu Y, Jia
Y, Liang X, Tang J and Zhang H: Post-translational modifications of
histones: Mechanisms, biological functions, and therapeutic
targets. MedComm (2020). 4:e2922023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Pan RY, He L, Zhang J, Liu X, Liao Y, Gao
J, Liao Y, Yan Y, Li Q, Zhou X, et al: Positive feedback regulation
of microglial glucose metabolism by histone H4 lysine 12
lactylation in Alzheimer's disease. Cell Metab. 34:634–648.e6.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Levine AJ and Puzio-Kuter AM: The control
of the metabolic switch in cancers by oncogenes and tumor
suppressor genes. Science. 330:1340–1344. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang Y, Song H, Li M and Lu P: Histone
lactylation bridges metabolic reprogramming and epigenetic rewiring
in driving carcinogenesis: Oncometabolite fuels oncogenic
transcription. Clin Transl Med. 14:e16142024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hu Y, He Z, Li Z, Wang Y, Wu N, Sun H,
Zhou Z, Hu Q and Cong X: Lactylation: The novel histone
modification influence on gene expression, protein function, and
disease. Clin Epigenetics. 16:722024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wu D, Spencer CB, Ortoga L, Zhang H and
Miao C: Histone lactylation-regulated METTL3 promotes ferroptosis
via m6A-modification on ACSL4 in sepsis-associated lung injury.
Redox Biol. 74:1031942024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wu F, Hua Y, Kaochar S, Nie S, Lin YL, Yao
Y, Wu J, Wu X, Fu X, Schiff R, et al: Discovery, structure-activity
relationship, and biological activity of histone-competitive
inhibitors of histone acetyltransferases P300/CBP. J Med Chem.
63:4716–4731. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Antika TR, Chrestella DJ, Tseng YK, Yeh
YH, Hsiao CD and Wang CC: A naturally occurring mini-alanyl-tRNA
synthetase. Commun Biol. 6:3142023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zong Z, Xie F, Wang S, Wu X, Zhang Z, Yang
B and Zhou F: Alanyl-tRNA synthetase, AARS1, is a lactate sensor
and lactyltransferase that lactylates p53 and contributes to
tumorigenesis. Cell. 187:2375–2392.e33. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ju J, Zhang H, Lin M, Yan Z, An L, Cao Z,
Geng D, Yue J, Tang Y, Tian L, et al: The alanyl-tRNA synthetase
AARS1 moonlights as a lactyltransferase to promote YAP signaling in
gastric cancer. J Clin Invest. 134:e1745872024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yoo L, Mendoza D, Richard AJ and Stephens
JM: KAT8 beyond acetylation: A survey of its epigenetic regulation,
genetic variability, and implications for human health. Genes
(Basel). 15:6392024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Xie B, Zhang M, Li J, Cui J, Zhang P, Liu
F, Wu Y, Deng W, Ma J, Li X, et al: KAT8-catalyzed lactylation
promotes eEF1A2-mediated protein synthesis and colorectal
carcinogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 121:e23141281212024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Dong H, Zhang J, Zhang H, Han Y, Lu C,
Chen C, Tan X, Wang S, Bai X, Zhai G, et al: YiaC and CobB regulate
lysine lactylation in Escherichia coli. Nat Commun.
13:66282022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Parks AR and Escalante-Semerena JC:
Modulation of the bacterial CobB sirtuin deacylase activity by
N-terminal acetylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 117:15895–15901.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Mutlu B and Puigserver P: GCN5
acetyltransferase in cellular energetic and metabolic processes.
Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 1864:1946262021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yang K, Fan M, Wang X, Xu J, Wang Y, Tu F,
Gill PS, Ha T, Liu L, Williams DL and Li C: Lactate promotes
macrophage HMGB1 lactylation, acetylation, and exosomal release in
polymicrobial sepsis. Cell Death Differ. 29:133–146. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Moreno-Yruela C, Zhang D, Wei W, Bæk M,
Liu W, Gao J, Danková D, Nielsen AL, Bolding JE, Yang L, et al:
Class I histone deacetylases (HDAC1-3) are histone lysine
delactylases. Sci Adv. 8:eabi66962022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Micelli C and Rastelli G: Histone
deacetylases: Structural determinants of inhibitor selectivity.
Drug Discov Today. 20:718–735. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Fan Z, Liu Z, Zhang N, Wei W, Cheng K, Sun
H and Hao Q: Identification of SIRT3 as an eraser of H4K16la.
iScience. 26:1077572023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Tao Z, Jin Z, Wu J, Cai G and Yu X:
Sirtuin family in autoimmune diseases. Front Immunol.
14:11862312023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Hagihara H, Shoji H, Otabi H, Toyoda A,
Katoh K, Namihira M and Miyakawa T: Protein lactylation induced by
neural excitation. Cell Rep. 37:1098202021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Rho H, Terry AR, Chronis C and Hay N:
Hexokinase 2-mediated gene expression via histone lactylation is
required for hepatic stellate cell activation and liver fibrosis.
Cell Metab. 35:1406–1423.e8. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Gaffney DO, Jennings EQ, Anderson CC,
Marentette JO, Shi T, Schou Oxvig AM, Streeter MD, Johannsen M,
Spiegel DA, Chapman E, et al: Non-enzymatic lysine lactoylation of
glycolytic enzymes. Cell Chem Biol. 27:206–213.e6. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Kiri S and Ryba T: Cancer, metastasis, and
the epigenome. Mol Cancer. 23:1542024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Lv X, Lv Y and Dai X: Lactate, histone
lactylation and cancer hallmarks. Expert Rev Mol. 25:e72023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Yan F, Teng Y, Li X, Zhong Y, Li C, Yan F
and He X: Hypoxia promotes non-small cell lung cancer cell
stemness, migration, and invasion via promoting glycolysis by
lactylation of SOX9. Cancer Biol Ther. 25:23041612024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Zhang C, Zhou L, Zhang M, Du Y, Li C, Ren
H and Zheng L: H3K18 lactylation potentiates immune escape of
non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 84:3589–3601. 2024.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Qiao Z, Li Y, Li S, Liu S and Cheng Y:
Hypoxia-induced SHMT2 protein lactylation facilitates glycolysis
and stemness of esophageal cancer cells. Mol Cell Biochem.
479:3063–3076. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Miao Z, Zhao X and Liu X: Hypoxia induced
β-catenin lactylation promotes the cell proliferation and stemness
of colorectal cancer through the wnt signaling pathway. Exp Cell
Res. 422:1134392023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Yu J, Chai P, Xie M, Ge S, Ruan J, Fan X
and Jia R: Histone lactylation drives oncogenesis by facilitating
m6A reader protein YTHDF2 expression in ocular melanoma.
Genome Biol. 22:852021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Huang Y, Luo G, Peng K, Song Y, Wang Y,
Zhang H, Li J, Qiu X, Pu M, Liu X, et al: Lactylation stabilizes
TFEB to elevate autophagy and lysosomal activity. J Cell Biol.
223:e2023080992024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Yang Z, Yan C, Ma J, Peng P, Ren X, Cai S,
Shen X, Wu Y, Zhang S, Wang X, et al: Lactylome analysis suggests
lactylation-dependent mechanisms of metabolic adaptation in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Metab. 5:61–79. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Yang J, Luo L, Zhao C, Li X, Wang Z, Zeng
Z, Yang X, Zheng X, Jie H, Kang L, et al: A positive feedback loop
between inactive VHL-triggered histone lactylation and PDGFRβ
signaling drives clear cell renal cell carcinoma progression. Int J
Biol Sci. 18:3470–3483. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Hou X, Ouyang J, Tang L, Wu P, Deng X, Yan
Q, Shi L, Fan S, Fan C, Guo C, et al: KCNK1 promotes proliferation
and metastasis of breast cancer cells by activating lactate
dehydrogenase A (LDHA) and up-regulating H3K18 lactylation. PLoS
Biol. 22:e30026662024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Sun L, Zhang Y, Yang B, Sun S, Zhang P,
Luo Z, Feng T, Cui Z, Zhu T, Li Y, et al: Lactylation of METTL16
promotes cuproptosis via m6A-modification on FDX1 mRNA
in gastric cancer. Nat Commun. 14:65232023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Xie B, Lin J, Chen X, Zhou X, Zhang Y, Fan
M, Xiang J, He N, Hu Z and Wang F: CircXRN2 suppresses tumor
progression driven by histone lactylation through activating the
Hippo pathway in human bladder cancer. Mol Cancer. 22:1512023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Wang X, Ying T, Yuan J, Wang Y, Su X, Chen
S, Zhao Y, Zhao Y, Sheng J, Teng L, et al: BRAFV600E restructures
cellular lactylation to promote anaplastic thyroid cancer
proliferation. Endocr Relat Cancer. 30:e2203442023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Dai E, Wang W and Li Y, Ye D and Li Y:
Lactate and lactylation: Behind the development of tumors. Cancer
Lett. 591:2168962024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Li F, Si W, Xia L, Yin D, Wei T, Tao M,
Cui X, Yang J, Hong T and Wei R: Positive feedback regulation
between glycolysis and histone lactylation drives oncogenesis in
pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Mol Cancer. 23:902024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Jing F, Zhang J, Zhang H and Li T:
Unlocking the multifaceted molecular functions and diverse disease
implications of lactylation. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 100:172–189.
2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Xia Y, Sun M, Huang H and Jin WL: Drug
repurposing for cancer therapy. Signal Transduct Target Ther.
9:922024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Chen H, Li Y, Li H, Chen X, Fu H, Mao D,
Chen W, Lan L, Wang C, Hu K, et al: NBS1 lactylation is required
for efficient DNA repair and chemotherapy resistance. Nature.
631:663–669. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Chen Y, Wu J, Zhai L, Zhang T, Yin H, Gao
H, Zhao F, Wang Z, Yang X, Jin M, et al: Metabolic regulation of
homologous recombination repair by MRE11 lactylation. Cell.
187:294–311.e21. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Li G, Wang D, Zhai Y, Pan C, Zhang J, Wang
C, Huang R, Yu M, Li Y, Liu X, et al: Glycometabolic
reprogramming-induced XRCC1 lactylation confers therapeutic
resistance in ALDH1A3-overexpressing glioblastoma. Cell Metab.
36:1696–1710.e10. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Yue Q, Wang Z, Shen Y, Lan Y, Zhong X, Luo
X, Yang T, Zhang M, Zuo B, Zeng T, et al: Histone H3K9 lactylation
confers temozolomide resistance in glioblastoma via LUC7L2-mediated
MLH1 intron retention. Adv Sci (Weinh). 11:e23092902024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Li F, Zhang H, Huang Y, Li D, Zheng Z, Xie
K, Cao C, Wang Q, Zhao X, Huang Z, et al: Single-cell transcriptome
analysis reveals the association between histone lactylation and
cisplatin resistance in bladder cancer. Drug Resist Updat.
73:1010592024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Li W, Zhou C, Yu L, Hou Z, Liu H, Kong L,
Xu Y, He J, Lan J, Ou Q, et al: Tumor-derived lactate promotes
resistance to bevacizumab treatment by facilitating autophagy
enhancer protein RUBCNL expression through histone H3 lysine 18
lactylation (H3K18la) in colorectal cancer. Autophagy. 20:114–130.
2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Komedchikova EN, Kolesnikova OA, Syuy AV,
Volkov VS, Deyev SM, Nikitin MP and Shipunova VO: Targosomes:
Anti-HER2 PLGA nanocarriers for bioimaging, chemotherapy and local
photothermal treatment of tumors and remote metastases. J Control
Release. 365:317–330. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Chen S, Xu Y, Zhuo W and Zhang L: The
emerging role of lactate in tumor microenvironment and its clinical
relevance. Cancer Lett. 590:2168372024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Wang S, Qi X, Liu D, Xie D, Jiang B, Wang
J, Wang X and Wu G: The implications for urological malignancies of
non-coding RNAs in the the tumor microenvironment. Comput Struct
Biotechnol J. 23:491–505. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Li Y, Cao Q, Hu Y, He B, Cao T, Tang Y,
Zhou XP, Lan XP and Liu SQ: Advances in the interaction of
glycolytic reprogramming with lactylation. Biomed Pharmacother.
177:1169822024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Li X, Yang Y, Zhang B, Lin X, Fu X, An Y,
Zou Y, Wang JX, Wang Z and Yu T: Lactate metabolism in human health
and disease. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 7:3052022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Wang JX, Choi SYC, Niu X, Kang N, Xue H,
Killam J and Wang Y: Lactic acid and an acidic tumor
microenvironment suppress anticancer immunity. Int J Mol Sci.
21:83632020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Huber V, Camisaschi C, Berzi A, Ferro S,
Lugini L, Triulzi T, Tuccitto A, Tagliabue E, Castelli C and
Rivoltini L: Cancer acidity: An ultimate frontier of tumor immune
escape and a novel target of immunomodulation. Semin Cancer Biol.
43:74–89. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Qu J, Li P and Sun Z: Histone lactylation
regulates cancer progression by reshaping the tumor
microenvironment. Front Immunol. 14:12843442023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Xiong J, He J, Zhu J, Pan J, Liao W, Ye H,
Wang H, Song Y, Du Y, Cui B, et al: Lactylation-driven
METTL3-mediated RNA m6A modification promotes
immunosuppression of tumor-infiltrating myeloid cells. Mol Cell.
82:1660–1677.e10. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Gu J, Zhou J, Chen Q, Xu X, Gao J, Li X,
Shao Q, Zhou B, Zhou H, Wei S, et al: Tumor metabolite lactate
promotes tumorigenesis by modulating MOESIN lactylation and
enhancing TGF-β signaling in regulatory T cells. Cell Rep.
40:1111222022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Chevrier S, Levine JH, Zanotelli VRT,
Silina K, Schulz D, Bacac M, Ries CH, Ailles L, Jewett MAS, Moch H,
et al: An immune atlas of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Cell.
169:736–749.e18. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Cai J, Song L, Zhang F, Wu S, Zhu G, Zhang
P, Chen S, Du J, Wang B, Cai Y, et al: Targeting SRSF10 might
inhibit M2 macrophage polarization and potentiate anti-PD-1 therapy
in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Commun (Lond). 44:1231–1260.
2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Chaudagar K, Hieromnimon HM, Khurana R,
Labadie B, Hirz T, Mei S, Hasan R, Shafran J, Kelley A, Apostolov
E, et al: Reversal of lactate and PD-1-mediated macrophage
immunosuppression controls growth of PTEN/p53-deficient prostate
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 29:1952–1968. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Sun L, Zhang H and Gao P: Metabolic
reprogramming and epigenetic modifications on the path to cancer.
Protein Cell. 13:877–919. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Jiang SS, Kang ZR, Chen YX and Fang JY:
The gut microbiome modulate response to immunotherapy in cancer.
Sci China Life Sci. 68:381–396. 2025. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Xie Y, Xie F, Zhou X, Zhang L, Yang B,
Huang J, Wang F, Yan H, Zeng L, Zhang L and Zhou F: Microbiota in
tumors: From understanding to application. Adv Sci (Weinh).
9:e22004702022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Sepich-Poore GD, Zitvogel L, Straussman R,
Hasty J, Wargo JA and Knight R: The microbiome and human cancer.
Science. 371:eabc45522021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Mischke M and Plösch T: The gut microbiota
and their metabolites: Potential implications for the host
epigenome. Adv Exp Med Biol. 902:33–44. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Woo V and Alenghat T: Epigenetic
regulation by gut microbiota. Gut Microbes. 14:20224072022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Shock T, Badang L, Ferguson B and
Martinez-Guryn K: The interplay between diet, gut microbes, and
host epigenetics in health and disease. J Nutr Biochem.
95:1086312021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Zhang Z, Chen Y, Zheng Y, Wang L, Shen S,
Yang G, Yang Y and Wang T: Quxie capsule alleviates
colitis-associated colorectal cancer through modulating the gut
microbiota and suppressing A. fumigatus-induced aerobic glycolysis.
Integr Cancer Ther. 21:153473542211385342022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Sun S, Xu X, Liang L, Wang X, Bai X, Zhu
L, He Q, Liang H, Xin X, Wang L, et al: Lactic acid-producing
probiotic saccharomyces cerevisiae attenuates ulcerative colitis
via suppressing macrophage pyroptosis and modulating gut
microbiota. Front Immunol. 12:7776652021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Wang J, Liu Z, Xu Y, Wang Y, Wang F, Zhang
Q, Ni C, Zhen Y, Xu R, Liu Q, et al: Enterobacterial LPS-inducible
LINC00152 is regulated by histone lactylation and promotes cancer
cells invasion and migration. Front Cell Infect Microbiol.
12:9138152022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Wang SP, Rubio LA, Duncan SH, Donachie GE,
Holtrop G, Lo G, Farquharson FM, Wagner J, Parkhill J, Louis P, et
al: Pivotal roles for pH, lactate, and lactate-utilizing bacteria
in the stability of a human colonic microbial ecosystem. mSystems.
5:e00645–20. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Koh A, De Vadder F, Kovatcheva-Datchary P
and Bäckhed F: From dietary fiber to host physiology: Short-chain
fatty acids as key bacterial metabolites. Cell. 165:1332–1345.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Li Z, Gong T, Wu Q, Zhang Y, Zheng X, Li
Y, Ren B, Peng X and Zhou X: Lysine lactylation regulates metabolic
pathways and biofilm formation in streptococcus mutans. Sci Signal.
16:eadg18492023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Wang Y, Liu Y, Xiang G, Jian Y, Yang Z,
Chen T, Ma X, Zhao N, Dai Y, Lv Y, et al: Post-translational toxin
modification by lactate controls staphylococcus aureus virulence.
Nat Commun. 15:98352024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Lin J, Liu G, Chen L, Kwok HF and Lin Y:
Targeting lactate-related cell cycle activities for cancer therapy.
Semin Cancer Biol. 86:1231–1243. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Fan H, Yang F, Xiao Z, Luo H, Chen H, Chen
Z, Liu Q and Xiao Y: Lactylation: Novel epigenetic regulatory and
therapeutic opportunities. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab.
324:E330–E338. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Zhang Q, Cao L and Xu K: Role and
mechanism of lactylation in cancer. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi.
27:471–479. 2024.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
De Cesare M, Pratesi G, Giusti A, Polizzi
D and Zunino F: Stimulation of the apoptotic response as a basis
for the therapeutic synergism of lonidamine and cisplatin in
combination in human tumour xenografts. Br J Cancer. 77:434–439.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Shu Y, Yue J, Li Y, Yin Y, Wang J, Li T,
He X, Liang S, Zhang G, Liu Z and Wang Y: Development of human
lactate dehydrogenase a inhibitors: High-throughput screening,
molecular dynamics simulation and enzyme activity assay. J Comput
Aided Mol Des. 38:282024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Pan L, Feng F, Wu J, Fan S, Han J, Wang S,
Yang L, Liu W, Wang C and Xu K: Demethylzeylasteral targets lactate
by inhibiting histone lactylation to suppress the tumorigenicity of
liver cancer stem cells. Pharmacol Res. 181:1062702022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Su J, Zheng Z, Bian C, Chang S, Bao J, Yu
H, Xin Y and Jiang X: Functions and mechanisms of lactylation in
carcinogenesis and immunosuppression. Front Immunol.
14:12530642023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Smith LE and Rogowska-Wrzesinska A: The
challenge of detecting modifications on proteins. Essays Biochem.
64:135–153. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Hao Y, Gu C, Luo W, Shen J, Xie F, Zhao Y,
Song X, Han Z and He J: The role of protein post-translational
modifications in prostate cancer. PeerJ. 12:e177682024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Xin Q, Wang H, Li Q, Liu S, Qu K, Liu C
and Zhang J: Lactylation: A passing fad or the future of
posttranslational modification. Inflammation. 45:1419–1429. 2022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Gao X, Pang C, Fan Z, Wang Y, Duan Y and
Zhan H: Regulation of newly identified lysine lactylation in
cancer. Cancer Lett. 587:2166802024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Vétizou M, Pitt JM, Daillère R, Lepage P,
Waldschmitt N, Flament C, Rusakiewicz S, Routy B, Roberti MP, Duong
CPM, et al: Anticancer immunotherapy by CTLA-4 blockade relies on
the gut microbiota. Science. 350:1079–1084. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Gori S, Inno A, Belluomini L, Bocus P,
Bisoffi Z, Russo A and Arcaro G: Gut microbiota and cancer: How gut
microbiota modulates activity, efficacy and toxicity of antitumoral
therapy. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 143:139–147. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Wu Z, Huang R and Yuan L: Crosstalk of
intracellular post-translational modifications in cancer. Arch
Biochem Biophys. 676:1081382019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Tomasi ML and Ramani K: SUMOylation and
phosphorylation cross-talk in hepatocellular carcinoma. Transl
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 3:202018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|