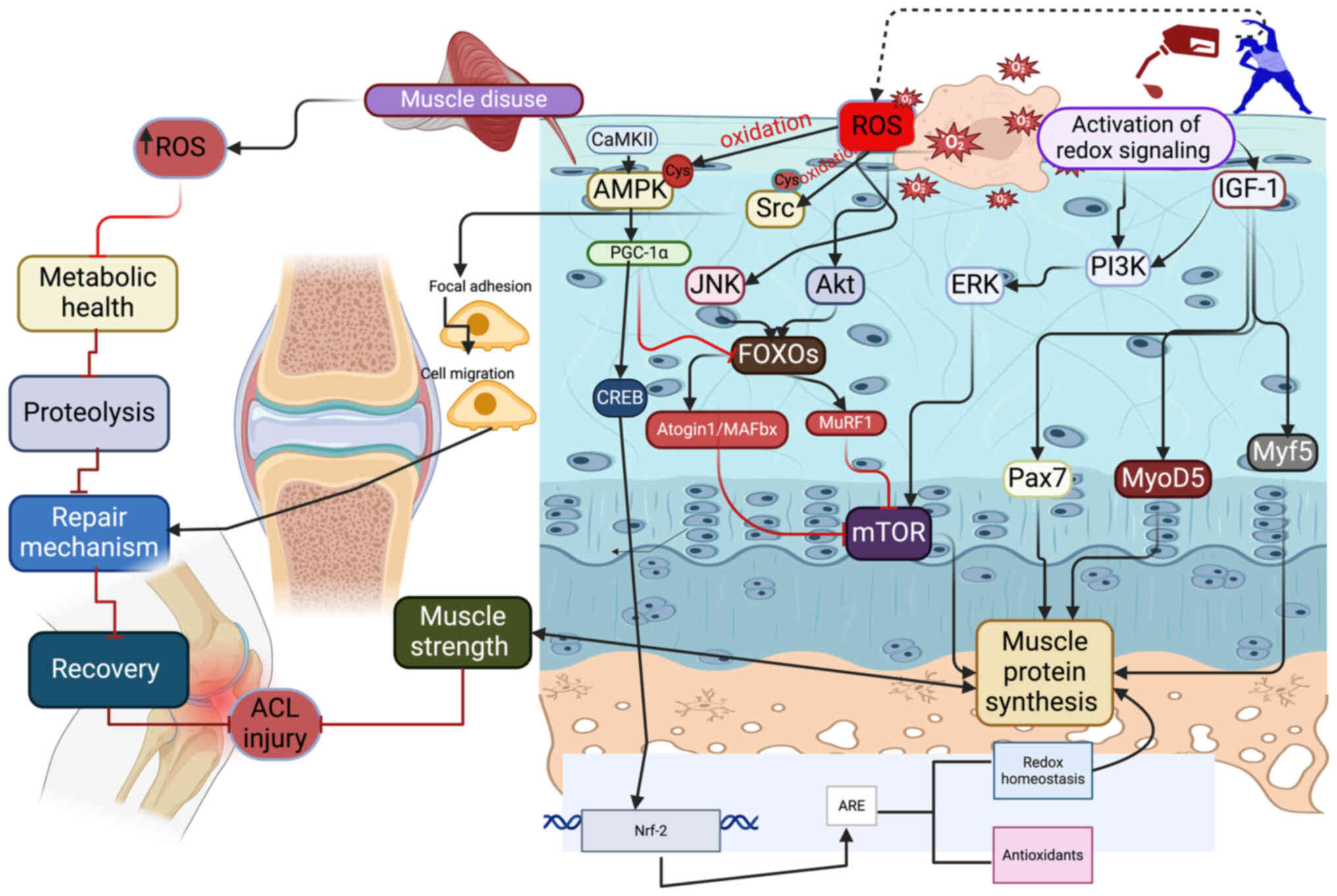
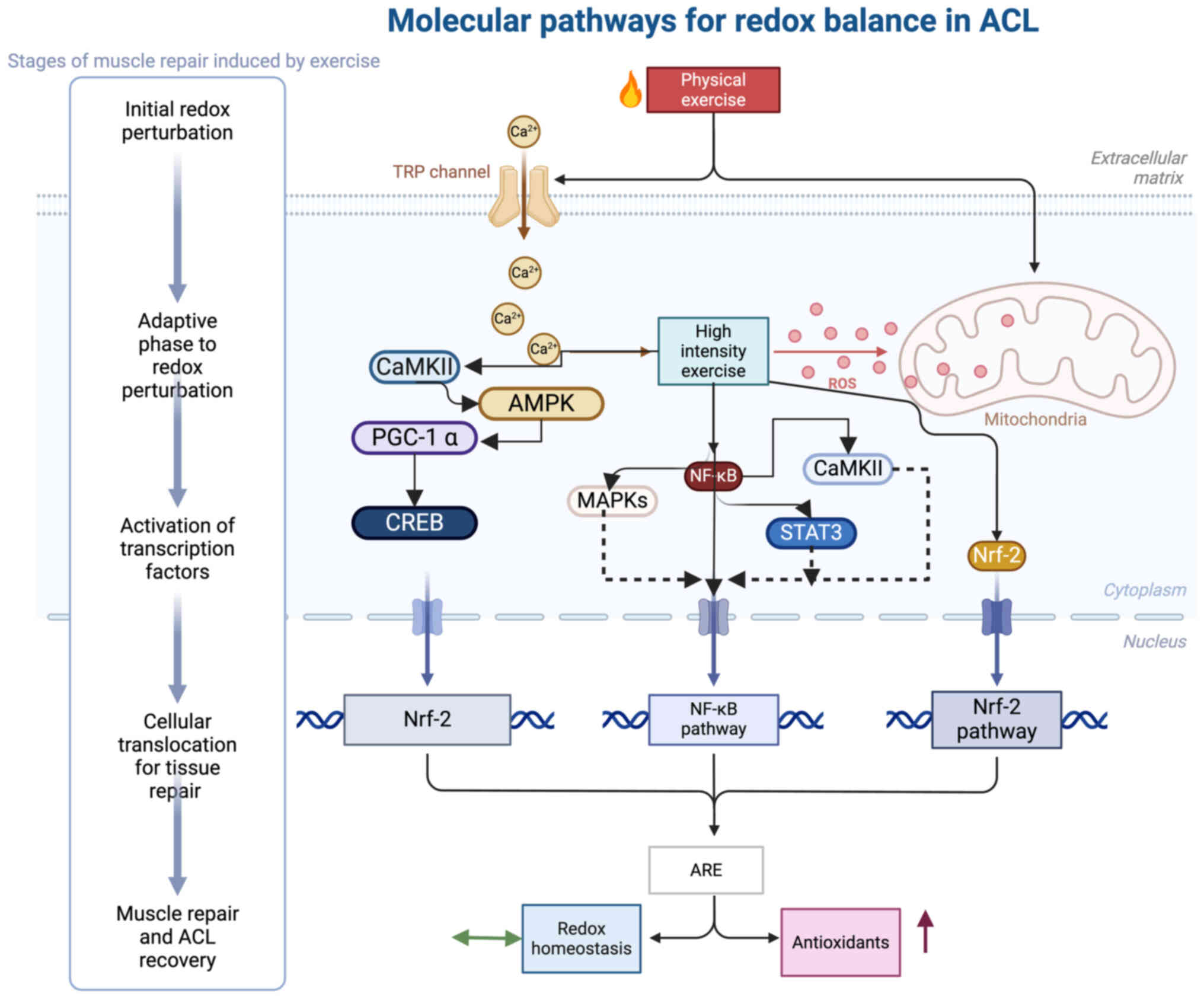
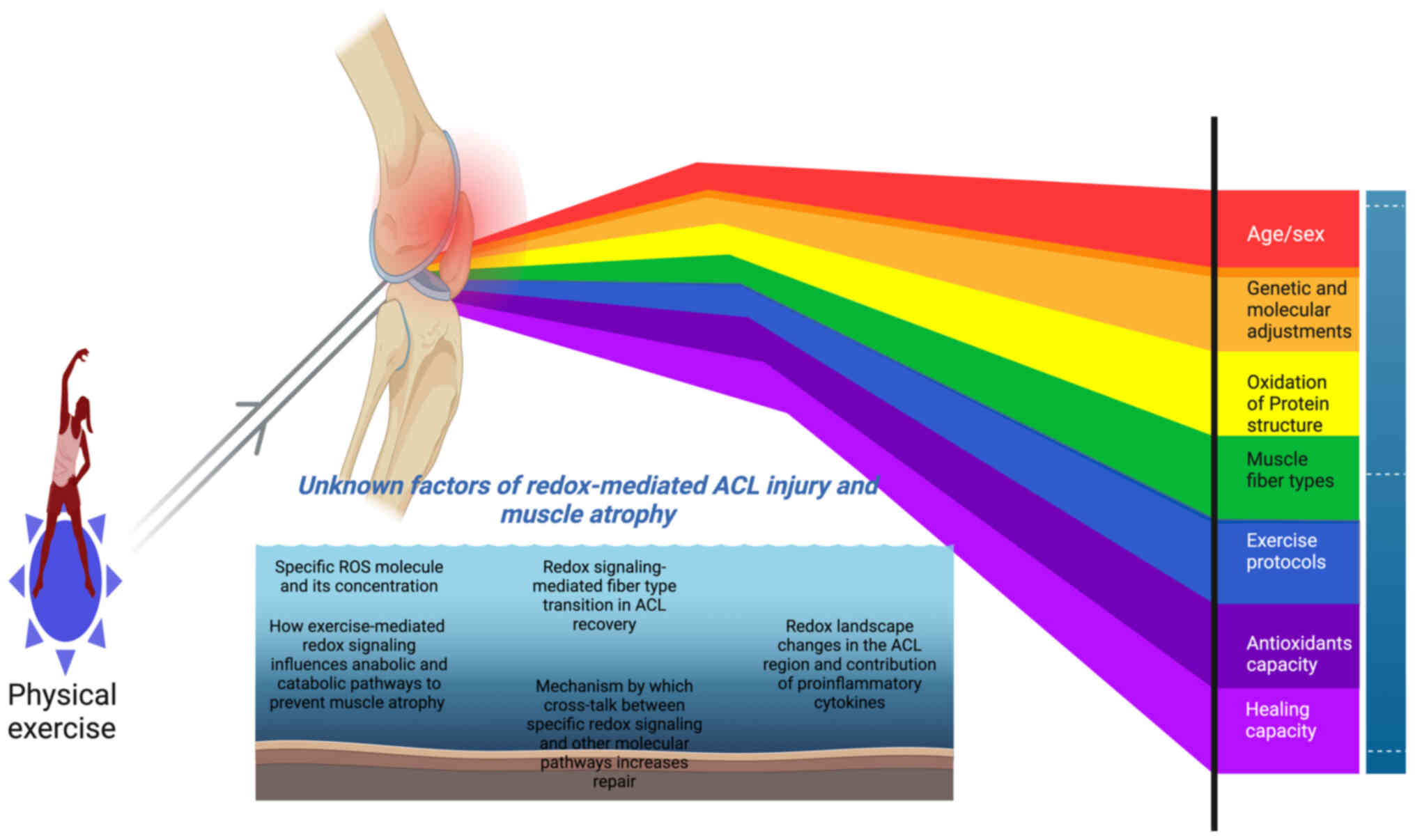
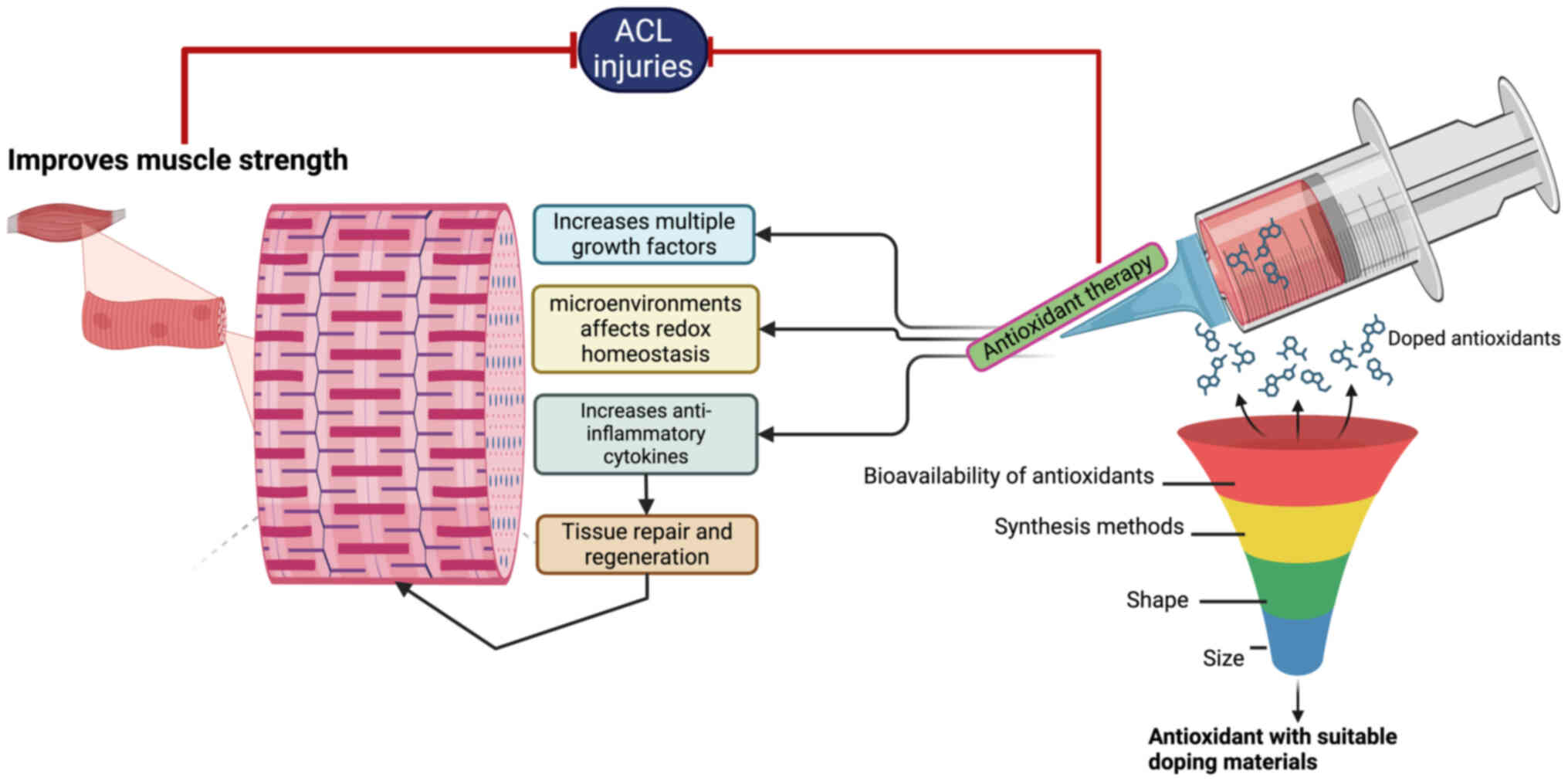
|
1
|
Musahl V and Karlsson J: Anterior cruciate
ligament tear. N Engl J Med. 380:2341–2348. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Arundale AJH, Bizzini M, Giordano A,
Hewett TE, Logerstedt DS, Mandelbaum B, Scalzitti DA,
Silvers-Granelli H and Snyder-Mackler L: Exercise-based knee and
anterior cruciate ligament injury prevention. J Orthop Sports Phys
Ther. 48:A1–A42. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Friel NA and Chu CR: The role of ACL
injury in the development of posttraumatic knee osteoarthritis.
Clin Sports Med. 32:1–12. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mather RC III, Koenig L, Kocher MS, Dall
TM, Gallo P, Scott DJ, Bach BR Jr and Spindler KP; MOON Knee Group,
: Societal and economic impact of anterior cruciate ligament tears.
J Bone Joint Surg Am. 95:1751–1759. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Herzog MM, Marshall SW, Lund JL, Pate V
and Spang JT: Cost of outpatient arthroscopic anterior cruciate
ligament reconstruction among commercially insured patients in the
United States, 2005–2013. Orthop J Sports Med.
27:23259671166847762017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Taylor JB, Waxman JP, Richter SJ and
Shultz SJ: Evaluation of the effectiveness of anterior cruciate
ligament Injury Prevention Programme training components: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Sports Med. 49:79–87.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sugimoto D, Myer GD, Barber Foss KD, Pepin
MJ, Micheli LJ and Hewett TE: Critical components of neuromuscular
training to reduce ACL injury risk in female athletes:
meta-regression analysis. Br J Sports Med. 50:1259–1266. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kwon OS, Davi SM, White MS and Lepley LK:
The role of mitochondrial-derived reactive oxygen species in
non-invasive anterior cruciate ligament injury. FASEB J. 34:1.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Flück M, Viecelli C, Bapst AM, Kasper S,
Valdivieso P, Franchi MV, Ruoss S, Lüthi JM, Bühler M, Claassen H,
et al: Knee extensors muscle plasticity over a 5-years
rehabilitation process after open knee surgery. Front Physiol.
9:13432018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ogata Y, Mabuchi Y, Shinoda K, Horiike Y,
Mizuno M, Otabe K, Suto EG, Suzuki N, Sekiya I and Akazawa C:
Anterior cruciate ligament-derived mesenchymal stromal cells have a
propensity to differentiate into the ligament lineage. Regen Ther.
8:20–28. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Powers SK, Ji LL, Kavazis AN and Jackson
MJ: Reactive oxygen species: Impact on skeletal muscle. Compr
Physiol. 1:941–969. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Powers SK, Deminice R, Ozdemir M,
Yoshihara T, Bomkamp MP and Hyatt H: Exercise-induced oxidative
stress: Friend or foe? J Sport Health Sci. 9:415–425. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jackson MJ, Stretton C and McArdle A:
Hydrogen peroxide as a signal for skeletal muscle adaptations to
exercise: What do concentrations tell us about potential
mechanisms? Redox Biol. 35:1014842020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kehm R, Baldensperger T, Raupbach J and
Höhn A: Protein oxidation-Formation mechanisms, detection and
relevance as biomarkers in human diseases. Redox Biol.
42:1019012021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zmijewski JW, Banerjee S, Bae H, Friggeri
A, Lazarowski ER and Abraham E: Exposure to hydrogen peroxide
induces oxidation and activation of AMP-activated protein kinase. J
Biol Chem. 285:33154–33164. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fang Y, Huang H, Zhou G, Wang Q, Gao F, Li
C, Liu Y and Lin J: An animal model study on the gene expression
profile of meniscal degeneration. Sci Rep. 10:214692020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
LeRoith D, Holly JMP and Forbes BE:
Insulin-like growth factors: Ligands, binding proteins, and
receptors. Mol Metab. 52:1012452021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Katsuragawa Y, Saitoh K, Tanaka N, Wake M,
Ikeda Y, Furukawa H, Tohma S, Sawabe M, Ishiyama M, Yagishita S, et
al: Changes of human menisci in osteoarthritic knee joints.
Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 18:1133–1143. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Heppner DE, Dustin CM, Liao C, Hristova M,
Veith C, Little AC, Ahlers BA, White SL, Deng B, Lam YW, et al:
Direct cysteine sulfenylation drives activation of the Src kinase.
Nat Commun. 9:45222018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Murray MM, Martin SD and Spector M:
Migration of cells from human anterior cruciate ligament explants
into collagen-glycosaminoglycan scaffolds. J Orthop Res.
18:557–564. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Min J, Reznichenko M, Poythress RH,
Gallant CM, Vetterkind S, Li Y and Morgan KG: Src modulates
contractile vascular smooth muscle function via regulation of focal
adhesions. J Cell Physiol. 227:3585–35492. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ellgaard L, Sevier CS and Bulleid NJ: How
are proteins reduced in the endoplasmic reticulum? Trends Biochem
Sci. 43:32–43. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Irrcher I, Ljubicic V and Hood DA:
Interactions between ROS and AMP kinase activity in the regulation
of PGC-1alpha transcription in skeletal muscle cells. Am J Physiol
Cell Physiol. 296:C116–C123. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chen J, Zhou R, Feng Y and Cheng L:
Molecular mechanisms of exercise contributing to tissue
regeneration. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 7:3832022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sanada Y, Tan SJO, Adachi N and Miyaki S:
Pharmacological targeting of heme oxygenase-1 in osteoarthritis.
Antioxidants (Basel). 10:4192021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hu S, Zhang C, Ni L, Huang C, Chen D, Shi
K, Jin H, Zhang K, Li Y, Xie L, et al: Stabilization of HIF-1α
alleviates osteoarthritis via enhancing mitophagy. Cell Death Dis.
11:4812020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhou Y, Zhang X, Baker JS, Davison GW and
Yan X: Redox signaling and skeletal muscle adaptation during
aerobic exercise. iScience. 27:1096432024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hiebert P: The Nrf2 transcription factor:
A multifaceted regulator of the extracellular matrix. Matrix Biol
Plus. 10:1000572021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Morgan MJ and Liu ZG: Crosstalk of
reactive oxygen species and NF-κB signaling. Cell Res. 21:103–115.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gallego-Selles A, Galvan-Alvarez V,
Martinez-Canton M, Garcia-Gonzalez E, Morales-Alamo D, Santana A,
Gonzalez-Henriquez JJ, Dorado C, Calbet JAL and Martin-Rincon M:
Fast regulation of the NF-κB signalling pathway in human skeletal
muscle revealed by high-intensity exercise and ischaemia at
exhaustion: Role of oxygenation and metabolite accumulation. Redox
Biol. 55:1023982022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yang L, Xue R, Tang Z, Zhang J, Wang Y and
Sung KL: Role of NF-κB in the injury induced MMP expression and
activities in ACL. World Congress on Medical Physics and Biomedical
Engineering. Dössel O and Schlegel WC: IFMBE Proceedings Vol 4.
Springer; Berlin: 2009
|
|
32
|
Tierney MT, Aydogdu T, Sala D, Malecova B,
Gatto S, Puri PL, Latella L and Sacco A: STAT3 signaling controls
satellite cell expansion and skeletal muscle repair. Nat Med.
20:1182–1186. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Fang S, Wan X, Zou X, Sun S, Hao X, Liang
C, Zhang Z, Zhang F, Sun B, Li H and Yu B: Arsenic trioxide induces
macrophage autophagy and atheroprotection by regulating
ROS-dependent TFEB nuclear translocation and AKT/mTOR pathway. Cell
Death Dis. 12:882021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Jiang Y, Kou J, Han X, Li X, Zhong Z, Liu
Z, Zheng Y, Tian Y and Yang L: ROS-dependent activation of
autophagy through the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway is induced by
hydroxysafflor yellow A-Sonodynamic therapy in THP-1 macrophages.
Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2017:85191692017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Edström E, Altun M, Hägglund M and Ulfhake
B: Atrogin-1/MAFbx and MuRF1 are downregulated in aging-related
loss of skeletal muscle. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 61:663–674.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Klotz LO, Sánchez-Ramos C, Prieto-Arroyo
I, Urbánek P, Steinbrenner H and Monsalve M: Redox regulation of
FoxO transcription factors. Redox Biol. 6:51–72. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lian D, Chen MM, Wu H, Deng S and Hu X:
The role of oxidative stress in skeletal muscle myogenesis and
muscle disease. Antioxidants (Basel). 11:7552022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Powers SK and Schrager M: Redox signaling
regulates skeletal muscle remodeling in response to exercise and
prolonged inactivity. Redox Biol. 54:1023742022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Keeble AR, Brightwell CR, Latham CM,
Thomas NT, Mobley CB, Murach KA, Johnson DL, Noehren B and Fry CS:
Depressed protein synthesis and anabolic signaling potentiate ACL
tear-resultant quadriceps atrophy. Am J Sports Med. 51:81–96. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Feng L, Li B, Xi Y, Cai M and Tian Z:
Aerobic exercise and resistance exercise alleviate skeletal muscle
atrophy through IGF-1/IGF-1R-PI3K/Akt pathway in mice with
myocardial infarction. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 322:C164–C176.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Tan PL, Shavlakadze T, Grounds MD and
Arthur PG: Differential thiol oxidation of the signaling proteins
Akt, PTEN or PP2A determines whether Akt phosphorylation is
enhanced or inhibited by oxidative stress in C2C12 myotubes derived
from skeletal muscle. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 62:72–79. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Bodine SC and Baehr LM: Skeletal muscle
atrophy and the E3 ubiquitin ligases MuRF1 and MAFbx/atrogin-1. Am
J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 307:E469–E484. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Noehren B, Andersen A, Hardy P, Johnson
DL, Ireland ML, Thompson KL and Damon B: Cellular and morphological
alterations in the vastus lateralis muscle as the result of ACL
injury and reconstruction. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 98:1541–1547.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Latham CM, Balawender PJ, Thomas NT,
Keeble AR, Brightwell CR, Ismaeel A, Wen Y, Fry JL, Sullivan PG,
Johnson DL, et al: Overexpression of manganese superoxide dismutase
mitigates ACL injury-induced muscle atrophy, weakness and oxidative
damage. Free Radic Biol Med. 212:191–198. 2024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Lepley LK, Davi SM, Hunt ER, Burland JP,
White MS, McCormick GY and Butterfield TA: Morphology and anabolic
response of skeletal muscles subjected to eccentrically or
concentrically biased exercise. J Athl Train. 55:336–342. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Lepley LK, Davi SM, Burland JP and Lepley
AS: Muscle atrophy after ACL injury: Implications for clinical
practice. Sports Health. 12:579–586. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Oberhofer K, Hosseini Nasab SH, Schütz P,
Postolka B, Snedeker JG, Taylor W and List R: The influence of
muscle-tendon forces on ACL loading during jump landing: A
systematic review. Muscles Ligaments Tendons J. 7:125–135. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Martin TD, Dennis MD, Gordon BS, Kimball
SR and Jefferson LS: mTORC1 and JNK coordinate phosphorylation of
the p70S6K1 autoinhibitory domain in skeletal muscle following
functional overloading. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab.
306:E1397–E1405. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Jones TW, Eddens L, Kupusarevic J, Simoes
DCM, Furber MJW, van Someren KA and Howatson G: Aerobic exercise
intensity does not affect the anabolic signaling following
resistance exercise in endurance athletes. Sci Rep. 11:107852021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Mitchell CJ, Churchward-Venne TA, Parise
G, Bellamy L, Baker SK, Smith K, Atherton PJ and Phillips SM: Acute
post-exercise myofibrillar protein synthesis is not correlated with
resistance training-induced muscle hypertrophy in young men. PLoS
One. 9:e894312014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Miller BF, Olesen JL, Hansen M, Døssing S,
Crameri RM, Welling RJ, Langberg H, Flyvbjerg A, Kjaer M, Babraj
JA, et al: Coordinated collagen and muscle protein synthesis in
human patella tendon and quadriceps muscle after exercise. J
Physiol. 567:1021–1033. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Kumar V, Atherton P, Smith K and Rennie
MJ: Human muscle protein synthesis and breakdown during and after
exercise. J Appl Physiol (1985). 106:2026–2039. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Plotkin DL, Roberts MD, Haun CT and
Schoenfeld BJ: Muscle fiber type transitions with exercise
training: Shifting perspectives. Sports (Basel). 9:1272021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Meng Q and Su CH: The impact of physical
exercise on oxidative and nitrosative stress: Balancing the
benefits and risks. Antioxidants (Basel). 13:5732024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Nyland J, Pyle B, Krupp R, Kittle G,
Richards J and Brey J: ACL microtrauma: Healing through nutrition,
modified sports training, and increased recovery time. J Exp
Orthop. 9:1212022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Amjad S, Nisar S, Bhat AA, Shah AR,
Frenneaux MP, Fakhro K, Haris M, Reddy R, Patay Z, Baur J and Bagga
P: Role of NAD+in regulating cellular and metabolic
signaling pathways. Mol Metab. 49:1011952021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Shadiow J, Miranda ER, Perkins RK, Mazo
CE, Lin Z, Lewis KN, Mey JT, Solomon TPJ and Haus JM:
Exercise-induced changes to the fiber type-specific redox state in
human skeletal muscle are associated with aerobic capacity. J Appl.
Physiol (1985). 135:508–518. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
de Guia RM, Agerholm M, Nielsen TS,
Consitt LA, Søgaard D, Helge JW, Larsen S, Brandauer J, Houmard JA
and Treebak JT: Aerobic and resistance exercise training reverses
age-dependent decline in NAD+salvage capacity in human
skeletal muscle. Physiol Rep. 7:e141392019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Kuenze CM, Blemker SS and Hart JM:
Quadriceps function relates to muscle size following ACL
reconstruction. J Orthop Res. 34:1656–1662. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Davi SM, Ahn A, White MS, Butterfield TA,
Kosmac K, Kwon OS and Lepley LK: Long-Lasting impairments in
quadriceps mitochondrial health, muscle size, and phenotypic
composition are present after non-invasive anterior cruciate
ligament injury. Front Physiol. 13:8052132022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Mendias CL, Lynch EB, Davis ME, Sibilsky
Enselman ER, Harning JA, Dewolf PD, Makki TA and Bedi A: Changes in
circulating biomarkers of muscle atrophy, inflammation, and
cartilage turnover in patients undergoing anterior cruciate
ligament reconstruction and rehabilitation. Am J Sports Med.
41:1819–1826. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Mittal M, Siddiqui MR, Tran K, Reddy SP
and Malik AB: Reactive oxygen species in inflammation and tissue
injury. Antioxid Redox Signal. 20:1126–1167. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Ismail S, Sturrock A, Wu P, Cahill B,
Norman K, Huecksteadt T, Sanders K, Kennedy T and Hoidal J: NOX4
mediates hypoxia-induced proliferation of human pulmonary artery
smooth muscle cells: the role of autocrine production of
transforming growth factor-{beta}1 and insulin-like growth factor
binding protein-3. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
296:L489–L499. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Barker T, Leonard SW, Trawick RH, Martins
TB, Kjeldsberg CR, Hill HR and Traber MG: Modulation of
inflammation by vitamin E and C supplementation prior to anterior
cruciate ligament surgery. Free Radic Biol Med. 46:599–606. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Barker T, Leonard SW, Trawick RH, Walker
JA and Traber MG: Antioxidant supplementation lowers circulating
IGF-1 but not F(2)-isoprostanes immediately following anterior
cruciate ligament surgery. Redox Rep. 14:221–226. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Fadilah NIM, Phang SJ, Kamaruzaman N,
Salleh A, Zawani M, Sanyal A, Maarof M and Fauzi MB: Antioxidant
biomaterials in cutaneous wound healing and tissue regeneration: A
critical review. Antioxidants (Basel). 12:7872023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Comino-Sanz IM, López-Franco MD, Castro B
and Pancorbo-Hidalgo PL: The role of antioxidants on wound healing:
A review of the current evidence. J Clin Med. 10:35582021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Multisanti CR, Zicarelli G, Caferro A,
Filice M, Faggio C, Vazzana I, Blahova J, Lakdawala P, Cerra MC,
Imbrogno S and Impellitteri F: From personal care to coastal
concerns: Investigating polyethylene glycol impact on Mussel's
antioxidant, physiological, and cellular responses. Antioxidants
(Basel). 13:7342024. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Pinho RA, Haupenthal DPS, Fauser PE,
Thirupathi A and Silveira PCL: Gold nanoparticle-based therapy for
muscle inflammation and oxidative stress. J Inflamm Res.
15:3219–3234. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Thirupathi A, Guzzatti MFM, Corrêa MEAB,
Venturini LM, Casagrande LR, Lima IR, Da Costa C, De Pieri E,
Tietbohl LTW, Feuser PE, et al: Green synthesis of gold
nanoparticles with curcumin or açai in the tissue repair of palatal
wounds. Antioxidants (Basel). 12:15742023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Tellechea E, Asensio AC, Ciaurriz P, Buezo
J, López-Gómez P, Urra M and Moran JF: A study of the interface of
gold nanoparticles conjugated to cowpea fe-superoxide dismutase.
Antioxidants (Basel). 11:20822022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Mongin C, Golden JH and Castellano FN:
Liquid PEG polymers containing antioxidants: A versatile platform
for studying oxygen-sensitive photochemical processes. ACS Appl
Mater Interfaces. 8:24038–24048. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
da Silva BD, do Rosário DKA, Neto LT,
Lelis CA and Conte-Junior CA: Antioxidant, antibacterial and
antibiofilm activity of nanoemulsion-based natural compound
delivery systems compared with non-nanoemulsified versions. Foods.
12:19012023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Timpani CA, Kourakis S, Debruin DA,
Campelj DG, Pompeani N, Dargahi N, Bautista AP, Bagaric RM, Ritenis
EJ, Sahakian L, et al: Dimethyl fumarate modulates the dystrophic
disease program following short-term treatment. JCI Insight.
8:e1659742023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Bernardes D and de Oliveira ALR: Regular
exercise modifies histopathological outcomes of pharmacological
treatment in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Front
Neurol. 9:9502018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Sun C, Yang C, Xue R, Li S, Zhang T, Pan
L, Ma X, Wang L and Li D: Sulforaphane alleviates muscular
dystrophy in mdx mice by activation of Nrf2. J Appl Physiol (1985).
118:224–237. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Pan Y, Chen C, Shen Y, Zhu CH, Wang G,
Wang XC, Chen HQ and Zhu MS: Curcumin alleviates dystrophic muscle
pathology in mdx mice. Mol Cells. 25:531–537. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Bronisz-Budzynska I, Kozakowska M,
Podkalicka P, Kachamakova-Trojanowska N, Łoboda A and Dulak J: The
role of Nrf2 in acute and chronic muscle injury. Skelet Muscle.
10:352020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Baird L and Yamamoto M: The molecular
mechanisms regulating the KEAP1-NRF2 pathway. Mol Cell Biol.
40:e00099–20. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Noguchi N: Ebselen, a useful tool for
understanding cellular redox biology and a promising drug candidate
for use in human diseases. Arch Biochem Biophys. 595:109–112. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Margaritelis NV, Paschalis V, Theodorou
AA, Kyparos A and Nikolaidis MG: Redox basis of exercise
physiology. Redox Biol. 35:1014992020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Sytha SP, Bray JF and Heaps CL: Exercise
induces superoxide and NOX4 contribution in endothelium-dependent
dilation in coronary arterioles from a swine model of chronic
myocardial ischemia. Microvasc Res. 150:1045902023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Szekeres FLM, Walum E, Wikström P and
Arner A: A small molecule inhibitor of Nox2 and Nox4 improves
contractile function after ischemia-reperfusion in the mouse heart.
Sci Rep. 11:119702021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Sanchis-Gomar F, Pareja-Galeano H,
Perez-Quilis C, Santos-Lozano A, Fiuza-Luces C, Garatachea N, Lippi
G and Lucia A: Effects of allopurinol on exercise-induced muscle
damage: new therapeutic approaches? Cell Stress Chaperones.
20:3–13. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Hou M, Hu Q, Chen Y, Zhao L, Zhang J and
Bache RJ: Acute effects of febuxostat, a nonpurine selective
inhibitor of xanthine oxidase, in pacing induced heart failure. J
Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 48:255–263. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Fryburg DA: NG-monomethyl-L-arginine
inhibits the blood flow but not the insulin-like response of
forearm muscle to IGF-I: Possible role of nitric oxide in muscle
protein synthesis. J Clin Invest. 97:1319–1328. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Hickner RC, Fisher JS, Ehsani AA and Kohrt
WM: Role of nitric oxide in skeletal muscle blood flow at rest and
during dynamic exercise in humans. Am J Physiol. 273:H405–H410.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|