|
1
|
Vorherr H: Breast cancer: epidemiology,
endocrinology, biochemistry, and pathobiology. Urban and
Schwarzenberg; Baltimore: 1980
|
|
2
|
Nilsson S, Makela S, Treuter E, et al:
Mechanisms of estrogen action. Physiol Rev. 81:1535–1565. 2001.
|
|
3
|
Klinge CM: Estrogen receptor interaction
with estrogen response elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 29:2905–2919.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Segars JH and Driggers PH: Estrogen action
and cytoplasmic signaling cascades. Part I: membrane-associated
signaling complexes. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 13:349–354. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Driggers PH and Segars JH: Estrogen action
and cytoplasmic signaling pathways. Part II: the role of growth
factors and phosphorylation in estrogen signaling. Trends
Endocrinol Metab. 13:422–427. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kelly MJ and Levin ER: Rapid actions of
plasma membrane estrogen receptors. Trends Endocrinol Metab.
12:152–156. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang Z, Zhang X, Shen P, Loggie BW, Chang
Y and Deuel TF: Identification, cloning, and expression of human
estrogen receptor-α36, a novel variant of human estrogen
receptor-α66. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 336:1023–1027. 2005.
|
|
8
|
Wang Z, Zhang X, Shen P, Loggie BW, Chang
Y and Deuel TF: A variant of estrogen receptor-{α}, hER-{α}36:
transduction of estrogen- and antiestrogen-dependent
membrane-initiated mitogenic signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
103:9063–9068. 2006.
|
|
9
|
Lin SL, Yan LY, Liang XW, et al: A novel
variant of ER-α, ER-α36, mediates testosterone-stimulated ERK and
Akt activation in endometrial cancer Hec1A cells. Reprod Biol
Endocrinol. 7:1022009.
|
|
10
|
Zou Y, Ding L, Coleman M and Wang Z:
Estrogen receptor-α (ER-α) suppresses expression of its variant
ER-α 36. FEBS Lett. 583:1368–1374. 2009.
|
|
11
|
Lee LM, Cao J, Deng H, Chen P, Gatalica Z
and Wang ZY: ER-α36, a novel variant of ER-α, is expressed in
ER-positive and -negative human breast carcinomas. Anticancer Res.
28:479–483. 2008.
|
|
12
|
Shi L, Dong B, Li Z, et al: Expression of
ER-(α)36, a novel variant of estrogen receptor-(α), and resistance
to tamoxifen treatment in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol.
27:3423–3429. 2009.
|
|
13
|
Bonetta L, Kuehn SE, Huang A, et al: Wilms
tumor locus on 11p13 defined by multiple CpG island-associated
transcripts. Science. 250:994–997. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Call KM, Glaser T, Ito CY, et al:
Isolation and characterization of a zinc finger polypeptide gene at
the human chromosome 11 Wilms’ tumor locus. Cell. 60:509–520.
1990.
|
|
15
|
Gessler M, Poustka A, Cavenee W, Neve RL,
Orkin SH and Bruns GA: Homozygous deletion in Wilms tumours of a
zinc-finger gene identified by chromosome jumping. Nature.
343:774–778. 1990. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Coppes MJ, Campbell CE and Williams BR:
The role of WT1 in Wilms tumorigenesis. FASEB J. 7:886–895.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lee SB and Haber DA: Wilms tumor and the
WT1 gene. Exp Cell Res. 264:74–99. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Little M and Wells C: A clinical overview
of WT1 gene mutations. Hum Mutat. 9:209–225. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Inoue K, Ogawa H, Sonoda Y, et al:
Aberrant overexpression of the Wilms tumor gene (WT1) in human
leukemia. Blood. 89:1405–1412. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Oji Y, Miyoshi S, Maeda H, et al:
Overexpression of the Wilms’ tumor gene WT1 in de novo lung
cancers. Int J Cancer. 100:297–303. 2002.
|
|
21
|
Silberstein GB, Van Horn K, Strickland P,
Roberts CT Jr and Daniel CW: Altered expression of the WT1 wilms
tumor suppressor gene in human breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 94:8132–8137. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Loeb DM, Evron E, Patel CB, et al: Wilms’
tumor suppressor gene (WT1) is expressed in primary breast tumors
despite tumor-specific promoter methylation. Cancer Res.
61:921–925. 2001.
|
|
23
|
Miyoshi Y, Ando A, Egawa C, et al: High
expression of Wilms’ tumor suppressor gene predicts poor prognosis
in breast cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res. 8:1167–1171. 2002.
|
|
24
|
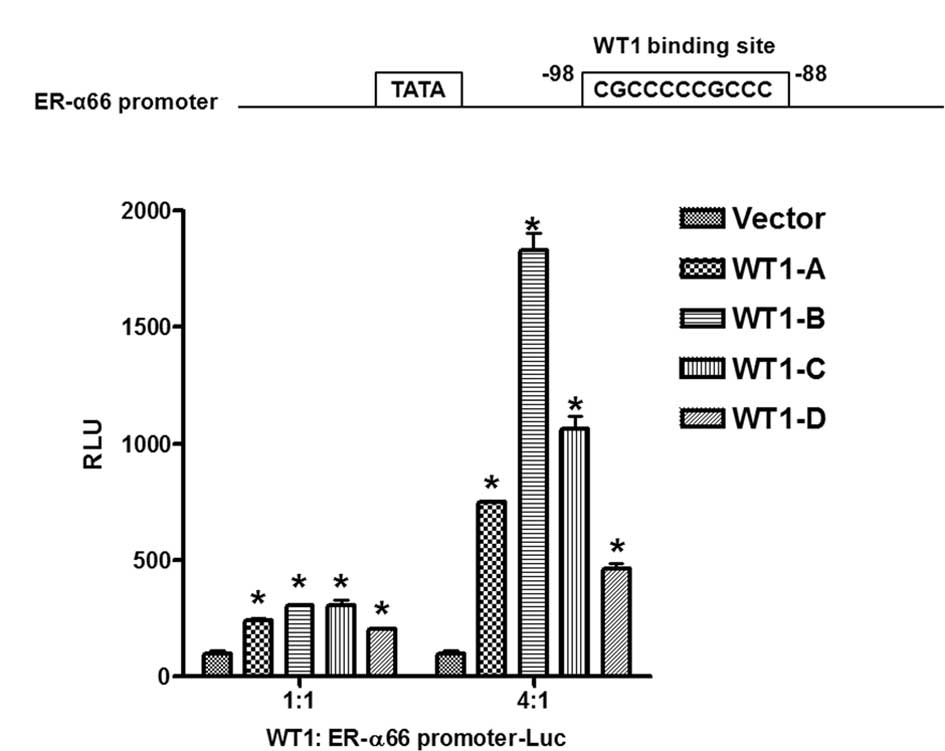
Wang ZY, Qiu QQ and Deuel TF: The Wilms’
tumor gene product WT1 activates or suppresses transcription
through separate functional domains. J Biol Chem. 268:9172–9175.
1993.
|
|
25
|
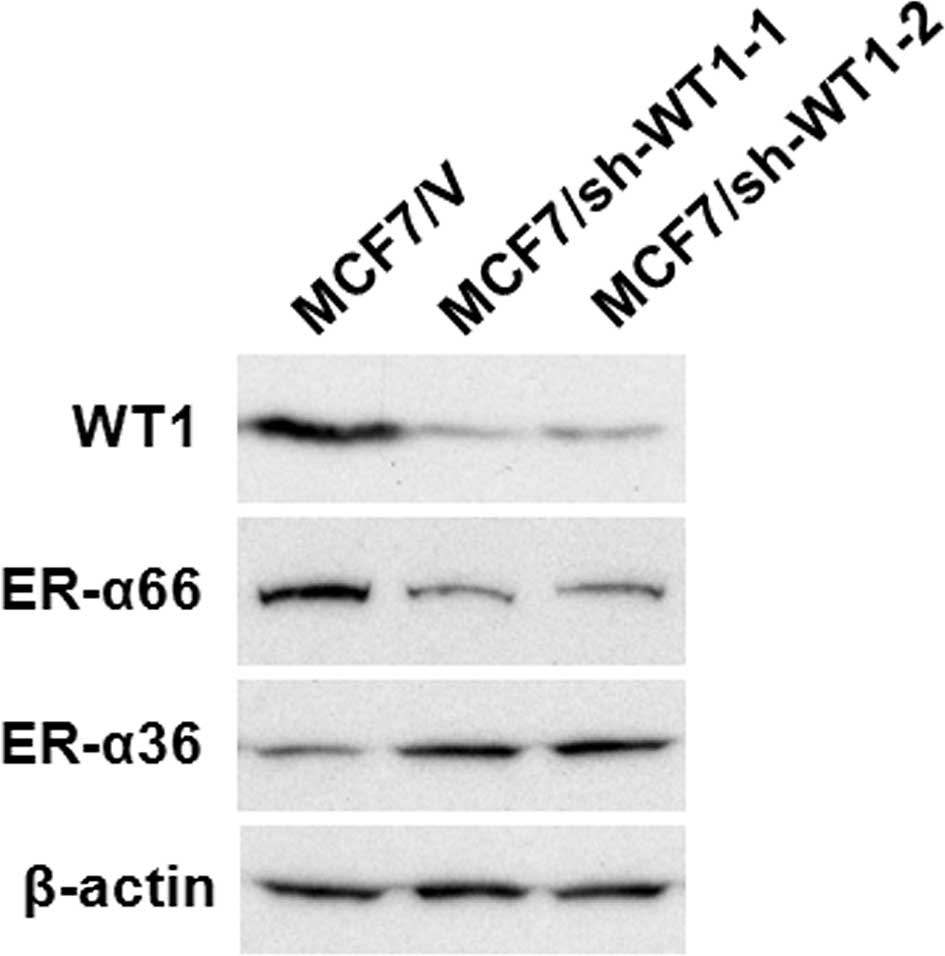
Wang L and Wang ZY: The Wilms’ tumor
suppressor WT1 induces estrogen-independent growth and
anti-estrogen insensitivity in ER-positive breast cancer MCF7
cells. Oncol Rep. 23:1109–1117. 2010.
|
|
26
|
Levin ER: Integration of the extranuclear
and nuclear actions of estrogen. Mol Endocrinol. 19:1951–1959.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Pedram A, Razandi M and Levin ER: Nature
of functional estrogen receptors at the plasma membrane. Mol
Endocrinol. 20:1996–2009. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Yang L, Han Y, Suarez Saiz F and Minden
MD: A tumor suppressor and oncogene: the WT1 story. Leukemia.
21:868–876. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liu XW, Gong LJ, Guo LY, et al: The Wilms’
tumor gene product WT1 mediates the down-regulation of the rat
epidermal growth factor receptor by nerve growth factor in PC12
cells. J Biol Chem. 276:5068–5073. 2001.
|
|
30
|
Han Y, San-Marina S, Liu J and Minden MD:
Transcriptional activation of c-myc proto-oncogene by WT1 protein.
Oncogene. 23:6933–6941. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hewitt SM, Hamada S, McDonnell TJ,
Rauscher FJ III and Saunders GF: Regulation of the proto-oncogenes
bcl-2 and c-myc by the Wilms’ tumor suppressor gene WT1. Cancer
Res. 55:5386–5389. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Englert C, Hou X, Maheswaran S, et al: WT1
suppresses synthesis of the epidermal growth factor receptor and
induces apoptosis. EMBO J. 14:4662–4675. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Han Y, Yang L, Suarez-Saiz F, San-Marina
S, Cui J and Minden MD: Wilms’ tumor 1 suppressor gene mediates
antiestrogen resistance via down-regulation of estrogen receptor-α
expression in breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer Res. 6:1347–1355.
2008.
|
|
34
|
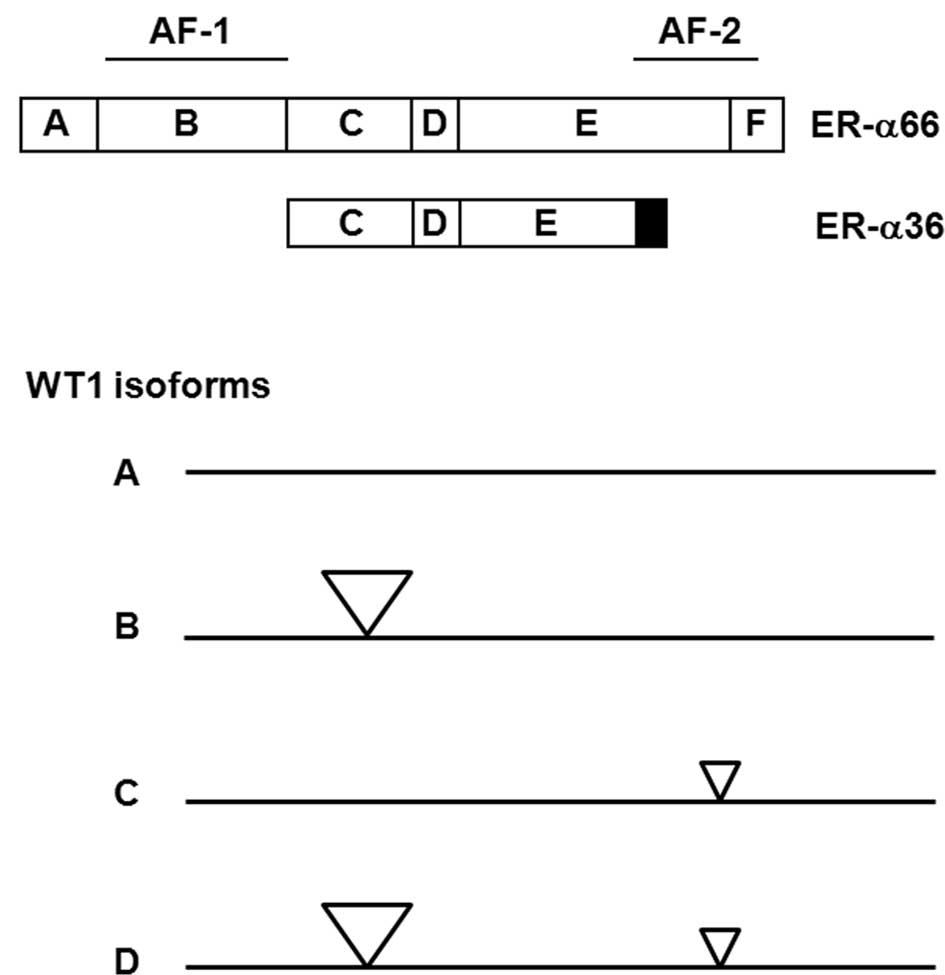
Burwell EA, McCarty GP, Simpson LA,
Thompson KA and Loeb DM: Isoforms of Wilms’ tumor suppressor gene
(WT1) have distinct effects on mammary epithelial cells. Oncogene.
26:3423–3430. 2007.
|