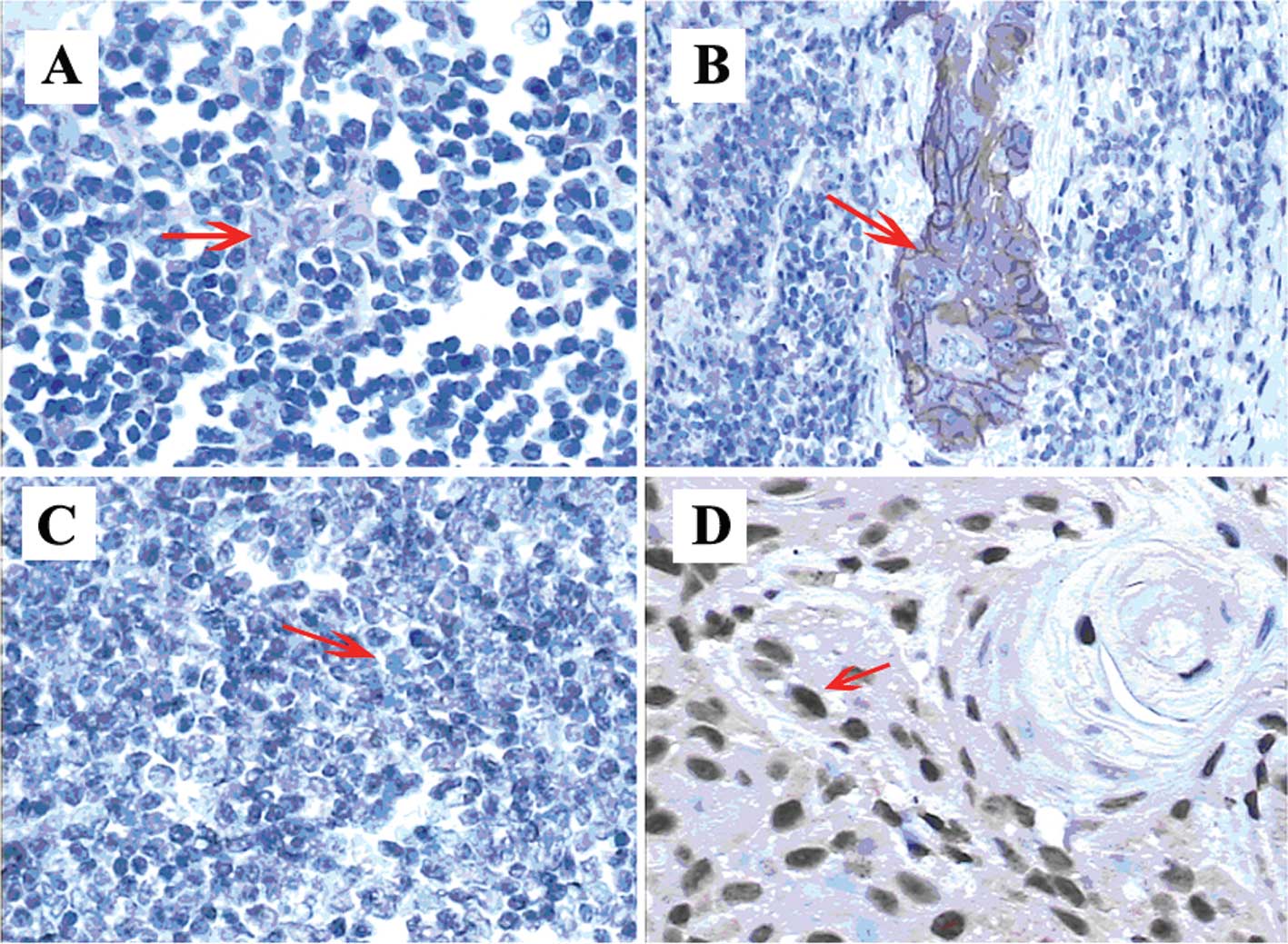
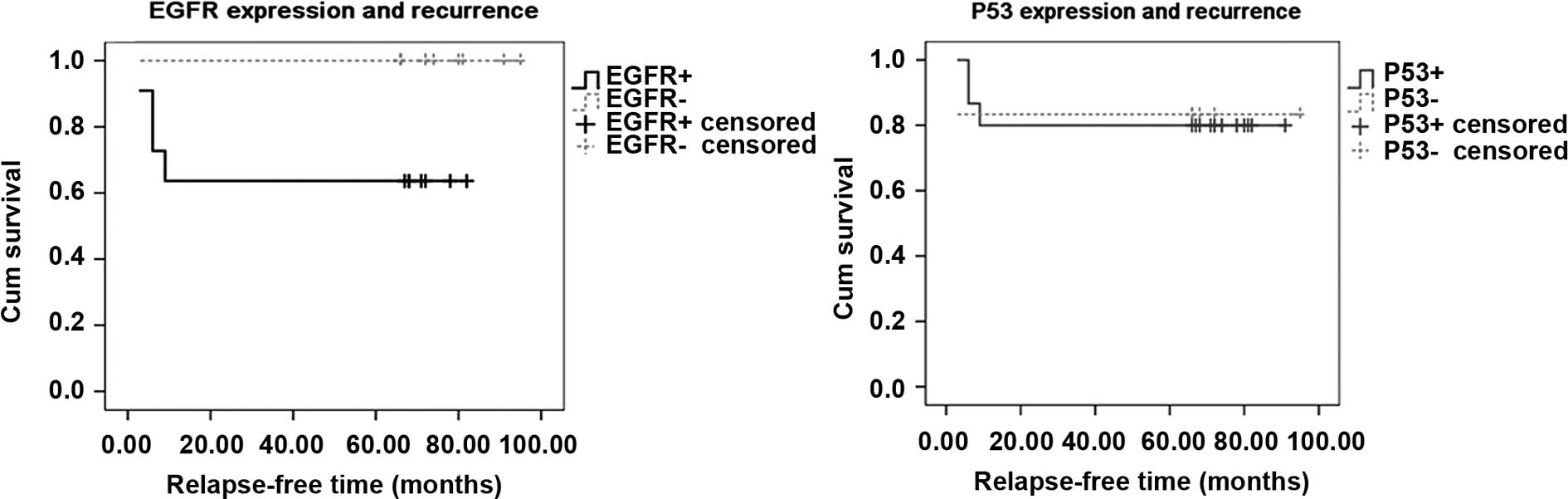
|
1
|
Marx A and Muller-Hermelink H: From basic
immunobiology to the upcoming WHO-classification of tumors of the
thymus. The Second Conference on Biological and Clinical Aspects of
Thymic Epithelial Tumors and related recent developments. Pathol
Res Pract. 195:515–533. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Masaoka A, Monden Y, Nakahara K and
Tanioka T: Follow-up study of thymomas with special reference to
their clinical stages. Cancer. 48:2485–2492. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Suster S: Diagnosis of thymoma. J Clin
Pathol. 59:1238–1244. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Kondo K and Monden Y: Therapy for thymic
epithelial tumors: a clinical study of 1,320 patients from Japan.
Ann Thorac Surg. 76:878–884. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Vousden KH: Outcomes of p53 activation –
spoilt for choice. J Cell Sci. 119:5015–5020. 2006.
|
|
6
|
Tominaga O, Hamelin R, Remvikos Y, Salmon
R and Thomas G: p53 from basic research to clinical applications.
Crit Rev Oncog. 3:257–282. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Shiao YH, Palli D, Caporaso NE, et al:
Genetic and immunohistochemical analyses of p53 independently
predict regional metastasis of gastric cancers. Cancer Epidemiol
Biomarkers Prev. 9:631–633. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Steels E, Paesmans M, Berghmans T, et al:
Role of p53 as a prognostic factor for survival in lung cancer: a
systematic review of the literature with a meta-analysis. Eur
Respir J. 18:705–719. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Pectasides D, Papaxoinis G, Nikolaou M, et
al: Analysis of 7 immunohistochemical markers in male germ cell
tumors demonstrates the prognostic significance of p53 and MIB-1.
Anticancer Res. 29:4151–4156. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Carpenter G and Cohen S: Epidermal growth
factor. J Biol Chem. 265:7709–7712. 1990.
|
|
11
|
Fischer O, Hart S, Gschwind A and Ullrich
A: EGFR signal transactivation in cancer cells. Biochem Soc Trans.
31:1203–1208. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ionescu D, Sasatomi E, Cieply K, Nola M
and Dacic S: Protein expression and gene amplification of epidermal
growth factor receptor in thymomas. Cancer. 103:630–636. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hayashi Y, Ishii N, Obayashi C, et al:
Thymoma: tumour type related to expression of epidermal growth
factor (EGF), EGF-receptor, p53, v-erb B and ras p21. Virchows
Arch. 426:43–50. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sasaki H, Yukiue H, Sekimura A, et al:
Elevated serum epidermal growth factor receptor level in stage IV
thymoma. Surg Today. 34:477–479. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Henley J, Koukoulis G and Loehrer PL Sr:
Epidermal growth factor receptor expression in invasive thymoma. J
Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 167–170. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Aisner SC, Hameed MR, Wang W, et al: EGFR
and C-Kit immuno-staining in advanced or recurrent thymic
epithelial neoplasms staged according to the WHO: an Eastern
Cooperative Oncology Group Study. American Society of Clinical
Oncology. 22:96372004.
|
|
17
|
Girard N, Shen R, Guo T, et al:
Comprehensive genomic analysis reveals clinically relevant
molecular distinctions between thymic carcinomas and thymomas. Clin
Cancer Res. 15:6790–6799. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Suzuki E, Sasaki H, Kawano O, et al:
Expression and mutation statuses of epidermal growth factor
receptor in thymic epithelial tumors. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 36:351–356.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tomita M, Matsuzaki Y and Onitsuka T:
Relationship between expression of cancer-related proteins and
tumor invasiveness in thymoma. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 21:595–598.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Baldi A, Ambrogi V, Mineo D, et al:
Analysis of cell cycle regulator proteins in encapsulated thymomas.
Clin Cancer Res. 11:5078–5083. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Landolfi JA and Terio KA: Transitional
cell carcinoma in fishing cats (Prionailurus viverrinus):
pathology and expression of cyclooxygenase-1, -2 and p53. Vet
Pathol. 43:674–681. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Detterbeck FC: Clinical value of the WHO
classification system of thymoma. Ann Thorac Surg. 81:2328–2334.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Detterbeck FC and Parsons AM: Thymic
tumors. Ann Thorac Surg. 77:1860–1869. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Yin H, Du J, Lu Z, Jiao X, Wang J and Zhou
X: The correlation of the World Health Organization histologic
classification of thymic epithelial tumors and its prognosis: a
clinicopathologic study of 108 patients from China. Int J Surg
Pathol. 17:255–261. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Riedel RF and Burfeind WR Jr: Thymoma:
benign appearance, malignant potential. Oncologist. 11:887–894.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Reddy RHV, Shah R, Kumar B and Thorpe JAC:
Recurrence of stage I thymoma in sternum, 13 years after ‘complete’
excision. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 23:134–135. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shiao Y-H, Palli D, Caporaso NE, et al:
Genetic and immunohistochemical analyses of p53 independently
predict regional metastasis of gastric cancers. Cancer Epidemiol
Biomarkers Prev. 9:631–633. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bedano PM, Perkins S, Burns M, et al: A
phase II trial of erlotinib plus bevacizumab in patients with
recurrent thymoma or thymic carcinoma. American Society of Clinical
Oncology. 26:190872008.
|
|
29
|
Christodoulou C, Murray S, Dahabreh J, et
al: Response of malignant thymoma to erlotinib. Ann Oncol.
19:1361–1362. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|