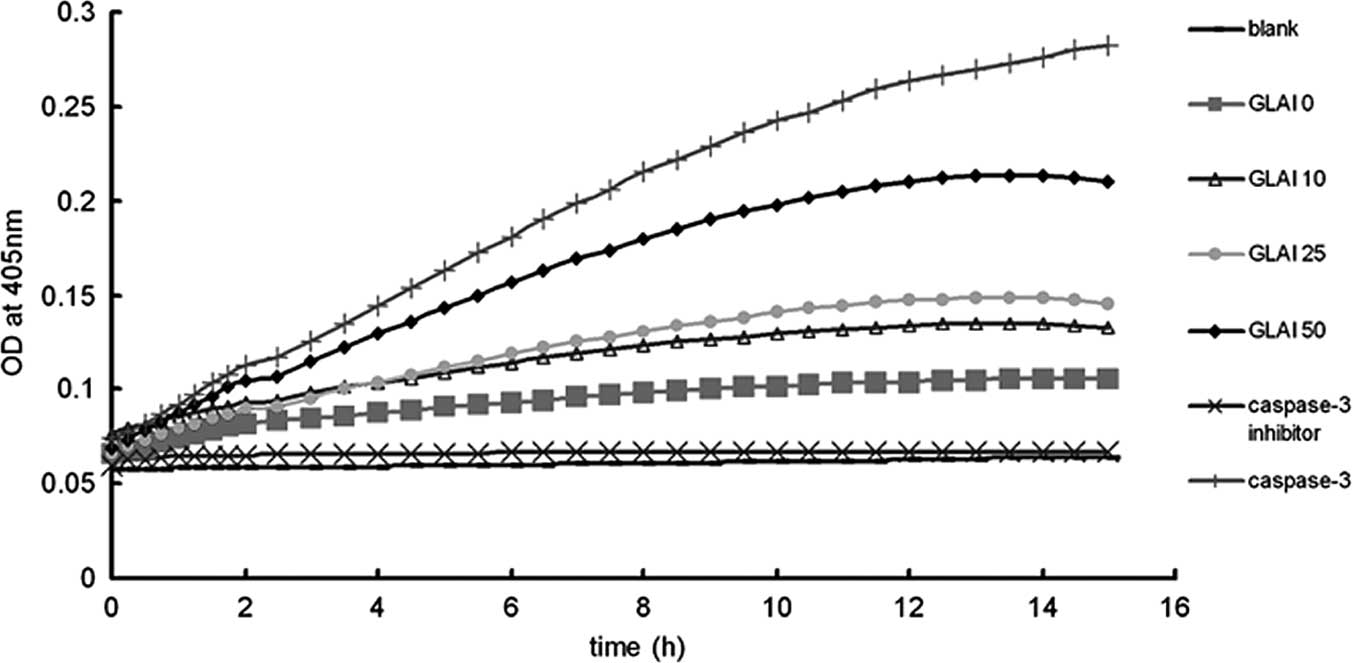
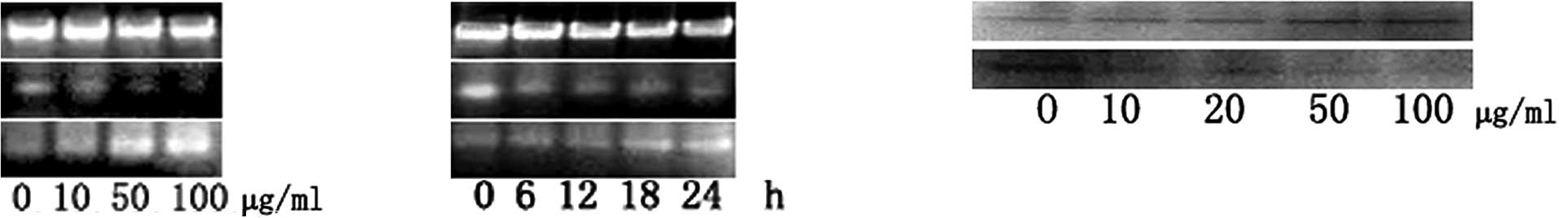
|
1
|
Wasson RG: Soma-Divine Mushroom of
Immortality. Harcourt, Brace & World; New York: pp. 3811968
|
|
2
|
Chang ST and Buswell JA: Ganoderma
lucidum (Curt.:Fr) P. Karst. (Aphyllophoromycetideae) –
a mushrooming medicinal mushroom. International Journal of
Medicinal Mushrooms. 1:139–146. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Wachtel-Galor S, Benzie IFF, Tomlinson B
and Buswell JA: Lingzhi (Ganoderma lucidum): molecular
aspects of health effects. Herbal Medicines. Packer L, Halliwell B
and Ong CN: Marcel Dekker Inc; New York: pp. 179–228. 2004
|
|
4
|
Furusawa E, Chou SC, Furusawa S, Hirazumi
A and Dang Y: Antitumor activity of Ganoderma lucidum, an
edible mushroom, on intraperitoneal implanted Lewis lung carcinoma
in syngeneic mice. Phytotherapy Research. 6:300–304. 1992.
|
|
5
|
Lieu CW, Lee SS and Wang SY: The effect of
Ganoderma lucidum on induction of differentiation in
leukemic U937 cells. Anticancer Res. 12:1211–1215. 1992.
|
|
6
|
Wang SY, Hsu ML, Hsu HC, et al: The
anti-tumor effect of Ganoderma lucidum is mediated by
cytokines released from activated macrophages and T lymphocytes.
Int J Cancer. 70:699–705. 1997.
|
|
7
|
Zhu M, Chang Q, Wong LK, Chong FS and Li
RC: Triterpene antioxidants from ganoderma lucidum.
Phytother Res. 13:529–531. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Kim DH, Shim SB, Kim NJ and Jang IS:
Beta-glucuronidase-inhibitory activity and hepatoprotective effect
of Ganoderma lucidum. Biol Pharm Bull. 22:162–164. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Komoda Y, Shimizu M, Sonoda Y and Sato Y:
Ganoderic acid and its derivatives as cholesterol synthesis
inhibitors. Chem Pharma Bull. 37:531–533. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kabir Y, Kimura S and Tamura T: Dietary
effect of Ganoderma lucidum mushroom on blood pressure and
lipid levels in spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR). J Nutr Sci
Vitaminol. 34:433–438. 1988.
|
|
11
|
Lee SY and Rhee HM: Cardiovascular effects
of mycelium extract of Ganoderma lucidum: inhibition of
sympathetic outflow as a mechanism of its hypotensive action. Chem
Pharma Bull. 38:1359–1364. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Su CY, Shiao MS and Wang CT: Differential
effects of ganodermic acid S on the thromboxane A2-signaling
pathways in human platelets. Biochem Pharmacol. 58:587–595. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gan KH, Fann YF, Hsu SH, Kuo KW and Lin
CN: Mediation of the cytotoxicity of lanostanoids and steroids of
Ganoderma tsugae through apoptosis and cell cycle. J Nat
Prod. 61:485–487. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Min BS, Gao JJ, Nakamura N and Hattori M:
Triterpenes from the spores of Ganoderma lucidum and their
cytotoxicity against meth-A and LLC tumor cells. Chem Pharma Bull.
48:1026–1033. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Noda Y, Kaiya T, Kohda K and Kawazoe Y:
Enhanced cytotoxicity of some triterpenes toward leukemia L1210
cells cultured in low pH media: possibility of a new mode of cell
killing. Chem Pharma Bull. 45:1665–1670. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wu TS, Shi LS and Kuo SC: Cytotoxicity of
Ganoderma lucidum triterpenes. J Nat Prod. 64:1121–1122.
2001.
|
|
17
|
Beauparlant P and Shore GC: Therapeutic
activation of caspases in cancer: a question of selectivity. Curr
Opin Drug Discov Devel. 6:179–187. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Thorburn A: Death receptor-induced cell
killing. Cell Signal. 16:139–144. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Qi SN, Yoshida A, Wang ZR and Ueda T: GP7
can induce apoptotic DNA fragmentation of human leukemia cells
through caspase-3-dependent and -independent pathways. Int J Mol
Med. 13:163–167. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang JF, Liu JJ, Liu PQ, Lin DJ, Li XD
and Chen GH: Oridonin inhibits cell growth by induction of
apoptosis on human hepatocelluar carcinoma BEL-7402 cells. Hepatol
Res. 35:104–110. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Thornberry NA and Lazebnik Y: Caspases:
enemies within. Science. 281:1312–1316. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Subramaniam V, Vincent IR and Jothy S:
Upregulation and dephosphorylation of cofilin: modulation by CD44
variant isoform in human colon cancer cells. Exp Mol Pathol.
79:187–193. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Martin SJ, Reutelingsperger CP, McGahon
AJ, et al: Early redistribution of plasma membrane
phosphatidylserine is a general feature of apoptosis regardless of
the initiating stimulus: inhibition by overexpression of Bcl-2 and
Abl. J Exp Med. 182:1545–1556. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Donepudi M and Grutter MG: Structure and
zymogen activation of caspases. Biophys Chem. 101–102:145–153.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Denault JB and Salvesen GS: Caspases: keys
in the ignition of cell death. Chem Rev. 102:4489–4500. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Boatright KM and Salvesen GS: Caspase
activation. Biochem Soc Symp. 233–242. 2003.
|
|
27
|
Philchenkov AA: Caspases as regulators of
apoptosis and other cell functions. Biochemistry. 68:365–376.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Huether A, Hopfner M, Sutter AP, Schuppan
D and Scherubl H: Erlotinib induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis
in hepatocellular cancer cells and enhances chemosensitivity
towards cytostatics. J Hepatol. 43:661–669. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Nagata S: Apoptosis by death factor. Cell.
88:355–365. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Srinivasan A, Roth KA, Sayers RO, et al:
In situ immunodetection of activated caspase-3 in apoptotic neurons
in the developing nervous system. Cell Death Differ. 5:1004–1016.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tanabe H, Eguchi Y, Shimizu S, Martinou JC
and Tsujimoto Y: Death-signalling cascade in mouse cerebellar
granule neurons. Eur J Neurosci. 10:1403–1411. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Bhathena SJ and Velasquez MT: Beneficial
role of dietary phytoestrogens in obesity and diabetes. Am J Clin
Nutr. 76:1191–1201. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Gross A, McDonnell JM and Korsmeyer SJ:
BCL-2 family members and the mitochondria in apoptosis. Genes Dev.
13:1899–1911. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Oltvai ZN, Milliman CL and Korsmeyer SJ:
Bcl-2 heterodimerizes in vivo with a conserved homolog, Bax, that
accelerates programmed cell death. Cell. 74:609–619. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Choi YH, Kong KR, Kim YA, et al: Induction
of Bax and activation of caspases during β-sitosterol-mediated
apoptosis in human colon cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 23:1657–1662.
2003.
|
|
36
|
Levy P, Robin H, Bertrand F, Kornprobst M
and Capeau J: Butyrate-treated colonic Caco-2 cells exhibit
defective integrin-mediated signaling together with increased
apoptosis and differentiation. J Cell Physiol. 197:336–347. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
White E: Life, death, and the pursuit of
apoptosis. Genes Dev. 10:1–15. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|