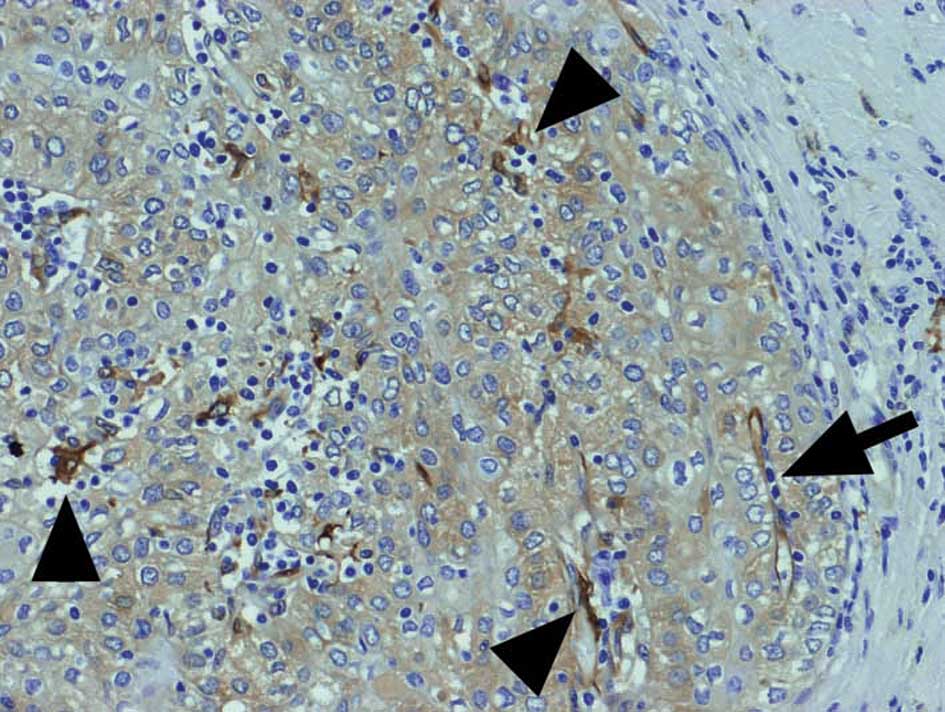
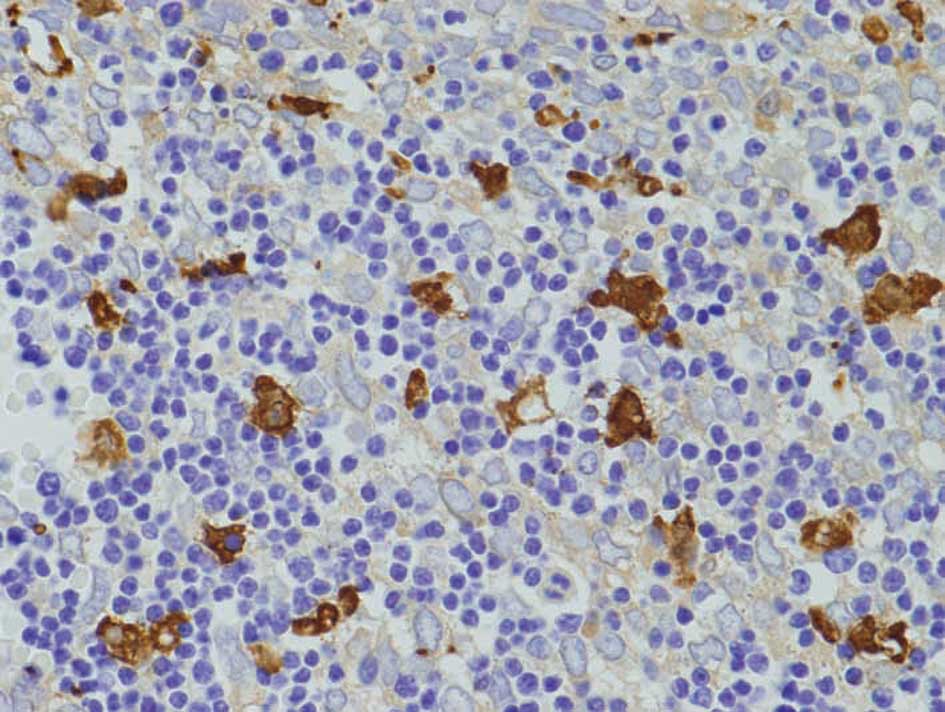
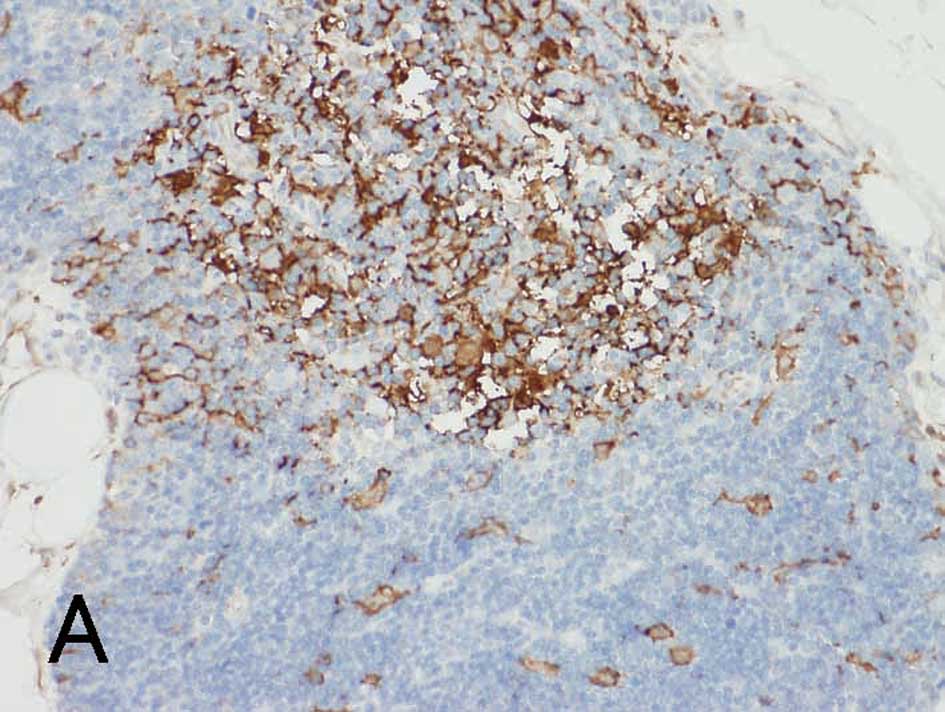
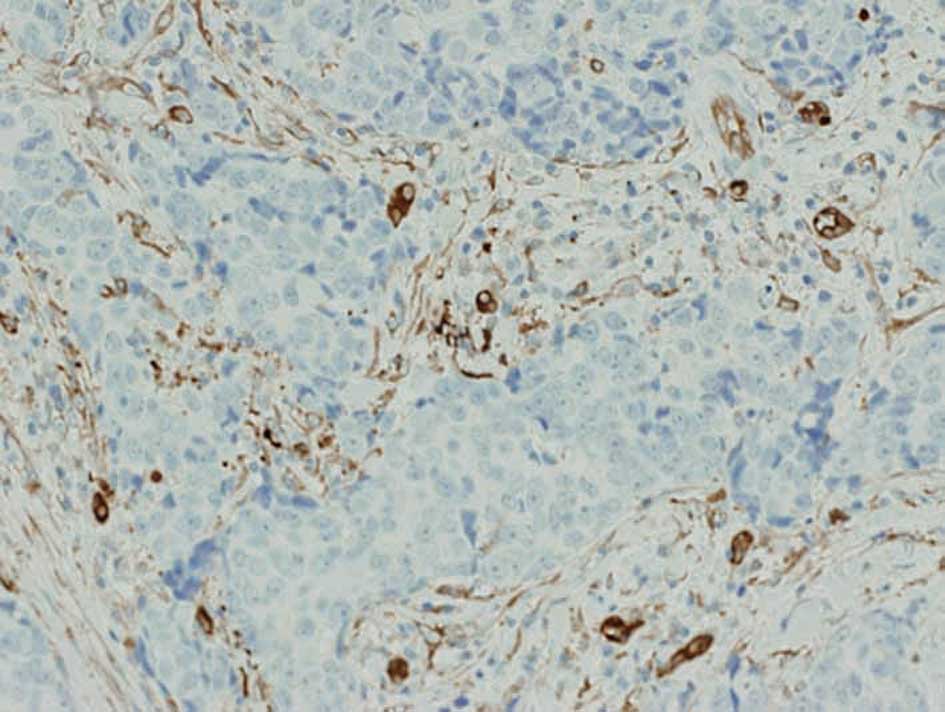
|
1
|
Kurup A and Loehrer PJ Sr: Thymoma and
thymic carcinoma: therapeutic approaches. Clin Lung Cancer.
6:28–32. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Duwe BV, Sterman DH and Musani AI: Tumors
of the mediastinum. Chest. 128:2893–2909. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Marx A, Ströbel P, Zettl A, Chan JKC,
Müller-Hermelink HK, Harris NL, Kuo TT, Shimosato Y and Engel P:
Thymomas. Pathology and Genetics of Tumours of the Lung, Pleura,
Thymus and Heart (WHO classification of tumors series). Travis WD,
Brambilla E, Müller-Helmelink HK and Harris CC: IARC Press; Lyon,
France: pp. 152–171. 2004
|
|
4
|
Margaritora S, Cesario A, Cusumano G,
Meacci E, D’Angelillo R, Bonassi S, Carnassale G, Porziella V,
Tessitore A, Vita ML, Lauriola L, Evoli A and Granone P:
Thirty-five-year follow-up analysis of clinical and pathologic
outcomes of thymoma surgery. Ann Thorac Surg. 89:245–252.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Masaoka A, Monden Y, Nakahara K and
Tanioka T: Follow-up study of thymomas with special reference to
their clinical stages. Cancer. 48:2485–2492. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Okumura M, Miyoshi S, Takeuchi Y, Yoon HE,
Minami M, Takeda SI, Fujii Y, Nakahara K and Matsuda H: Results of
surgical treatment of thymomas with special reference to the
involved organs. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 117:605–613. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gerner MY and Mescher MF: Antigen
processing and MHC-II presentation by dermal and tumor-infiltrating
dendritic cells. J Immunol. 182:2726–2737. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kornstein MJ, Hoxie JA, Levinson AI and
Brooks JJ: Immunohistology of human thymomas. Arch Pathol Lab Med.
109:460–463. 1985.
|
|
9
|
Pomplun S, Wotherspoon AC, Shah G,
Goldstraw P, Ladas G and Nicholson AG: Immunohistochemical markers
in the differentiation of thymic and pulmonary neoplasms.
Histopathology. 40:152–158. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lee D and Wright DH: Immunohistochemical
study of 22 cases of thymoma. J Clin Pathol. 41:1297–1304. 1988.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Pinkus GS, Pinkus JL, Langhoff E,
Matsumura F, Yamashiro S, Mosialos G and Said JW: Fascin, a
sensitive new marker for Reed-Sternberg cells of hodgkin’s disease.
Evidence for a dendritic or B cell derivation? Am J Pathol.
150:543–562. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kurata A, Terado Y, Schulz A, Fujioka Y
and Franke FE: Inflammatory cells in the formation of tumor-related
sarcoid reactions. Hum Pathol. 36:546–554. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Machesky LM and Li A: Fascin: invasive
filopodia promoting metastasis. Commun Integr Biol. 3:263–270.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Darnel AD, Behmoaram E, Vollmer RT, Corcos
J, Bijian K, Sircar K, Su J, Jiao J, Alaoui-Jamali MA and Bismar
TA: Fascin regulates prostate cancer cell invasion and is
associated with metastasis and biochemical failure in prostate
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 15:1376–1383. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Iguchi T, Aishima S, Umeda K, Sanefuji K,
Fujita N, Sugimachi K, Gion T, Taketomi A, Maehara Y and Tsuneyoshi
M: zFascin expression in progression and prognosis of
hepatocellular carcinoma. J Surg Oncol. 100:575–579. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yildiz L, Kefeli M, Aydin O and Kandemir
B: Fascin expression in melanocytic lesions of the skin. Eur J
Dermatol. 19:445–450. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang FR, Tao LH, Shen ZY, Lv Z, Xu LY and
Li EM: Fascin expression in human embryonic, fetal, and normal
adult tissue. J Histochem Cytochem. 56:193–199. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Brunhuber T, Haybaeck J, Schäfer G, Mikuz
G, Langhoff E, Saeland S, Lebecque S, Romani N and Obrist P:
Immunohistochemical tracking of an immune response in mammary
Paget’s disease. Cancer Lett. 272:206–220. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ozerhan IH, Ersoz N, Onguru O, Ozturk M,
Kurt B and Cetiner S: Fascin expression in colorectal carcinomas.
Clinics. 65:157–164. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Onodera M, Zen Y, Harada K, Sato Y, Ikeda
H, Itatsu K, Sato H, Ohta T, Asaka M and Nakanuma Y: Fascin is
involved in tumor necrosis factor-alpha-dependent production of
MMP9 in cholangiocarcinoma. Lab Invest. 89:1261–1274. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Xie JJ, Xu LY, Wu JY, Shen ZY, Zhao Q, Du
ZP, Lv Z, Gu W, Pan F, Xu XE, Xie D and Li EM: Involvement of CYR61
and CTGF in the fascin-mediated proliferation and invasiveness of
esophageal squamous cell carcinomas cells. Am J Pathol.
176:939–951. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kefeli M, Yildiz L, Kaya FC, Aydin O and
Kandemir B: Fascin expression in uterine smooth muscle tumors. Int
J Gynecol Pathol. 28:328–333. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Durmaz A, Kurt B, Ongoru O, Karahatay S,
Gerek M and Yalcin S: Significance of fascin expression in
laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. J Laryngol Otol. 124:194–198.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Marchevsky AM, Gupta R, McKenna RJ, Wick
M, Moran C, Zakowski MF and Suster S: Evidence-based pathology and
the pathologic evaluation of thymomas: the World Health
Organization classification can be simplified into only 3
categories other than thymic carcinoma. Cancer. 112:2780–2788.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Kondo K, Mukai K, Sato Y, Matsuno Y,
Shimosato Y and Monden Y: An immunohistochemical study of thymic
epithelial tumors. III. The distribution of interdigitating
reticulum cells and S-100 beta-positive small lymphocytes. Am J
Surg Pathol. 14:1139–1147. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Rouse RV and Weiss LM: Human thymomas:
evidence of immunohistologically defined normal and abnormal
microenvironmental differentiation. Cell Immunol. 111:94–106. 1988.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Kurata A, Terado Y, Izumi M, Fujioka Y and
Franke FE: Where does the antigen of cutaneous sarcoidosis come
from? J Cutan Pathol. 37:211–221. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wakimoto T, Tomisaka R, Nishikawa Y, Sato
H, Yoshino T and Takahashi K: Identification and characterization
of human thymic cortical dendritic macrophages that may act as
professional scavengers of apoptotic thymocytes. Immunobiology.
213:837–847. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ambe K, Mori M and Enjoji M: S-100
protein-positive dendritic cells in colorectal adenocarcinomas.
Distribution and relation to the clinical prognosis. Cancer.
63:496–503. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Becker Y: Anticancer role of dendritic
cells (DC) in human and experimental cancers – a review. Anticancer
Res. 12:511–520. 1992.
|
|
31
|
Müller-Hermelink HK, Möller P, Engel P,
Menestrina F, Kuo TT, Shimosato Y, Ströbel PH, Asamura H, Marx A,
Masaoka A, Harris NL and Sobin LH: Tumours of the thymus. Pathology
and Genetics of Tumours of the Lung, Pleura, Thymus and Heart (WHO
classification of tumors series). Travis WD, Brambilla E,
Müller-Helmelink HK and Harris CC: IARC Press; Lyon, France: pp.
145–151. 2004
|
|
32
|
Vignjevic D, Schoumacher M, Gavert N,
Janssen KP, Jih G, Laé M, Louvard D, Ben-Ze’ev A and Robine S:
Fascin, a novel target of beta-catenin-TCF signaling, is expressed
at the invasive front of human colon cancer. Cancer Res.
67:6844–6853. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|