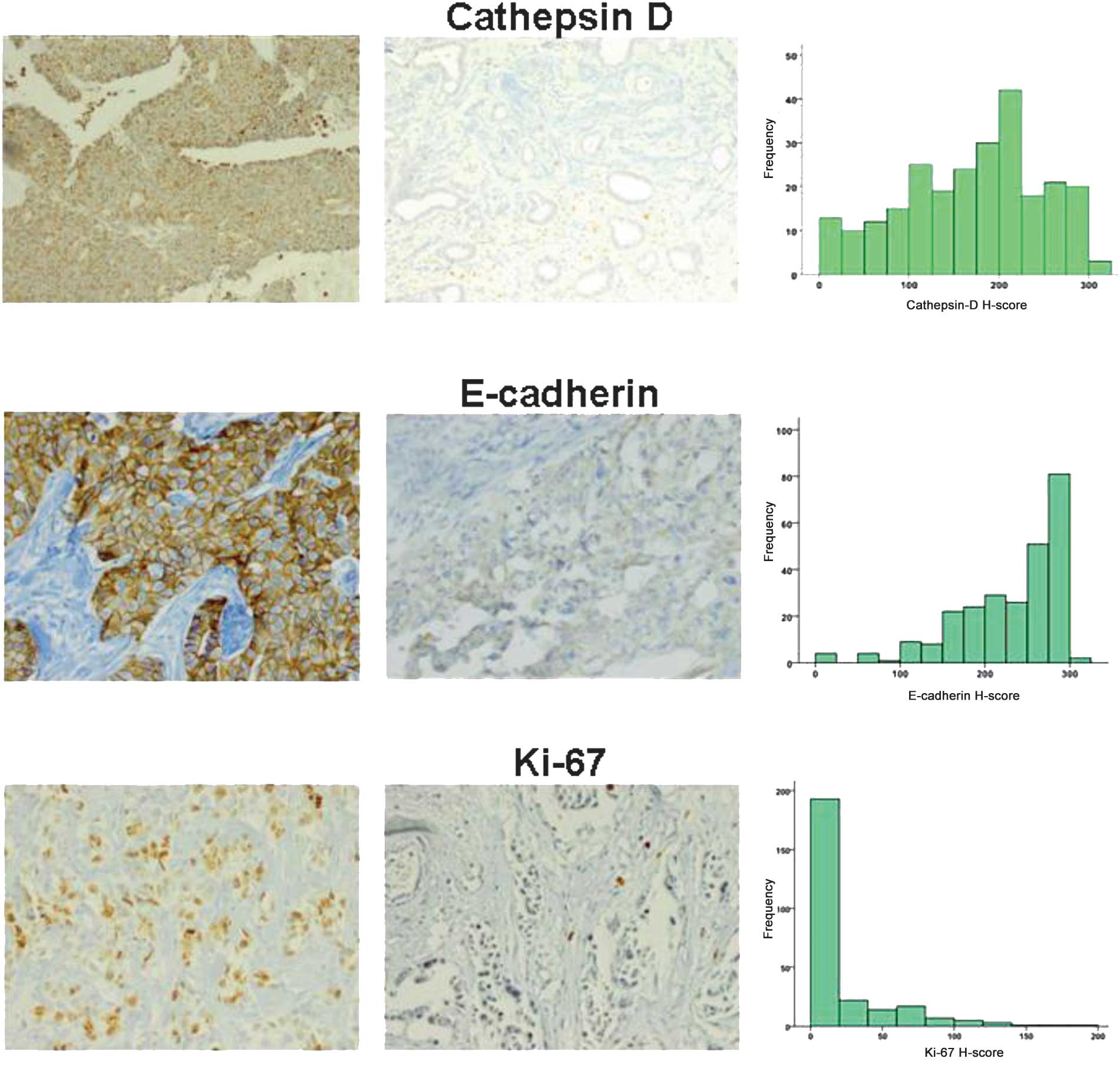
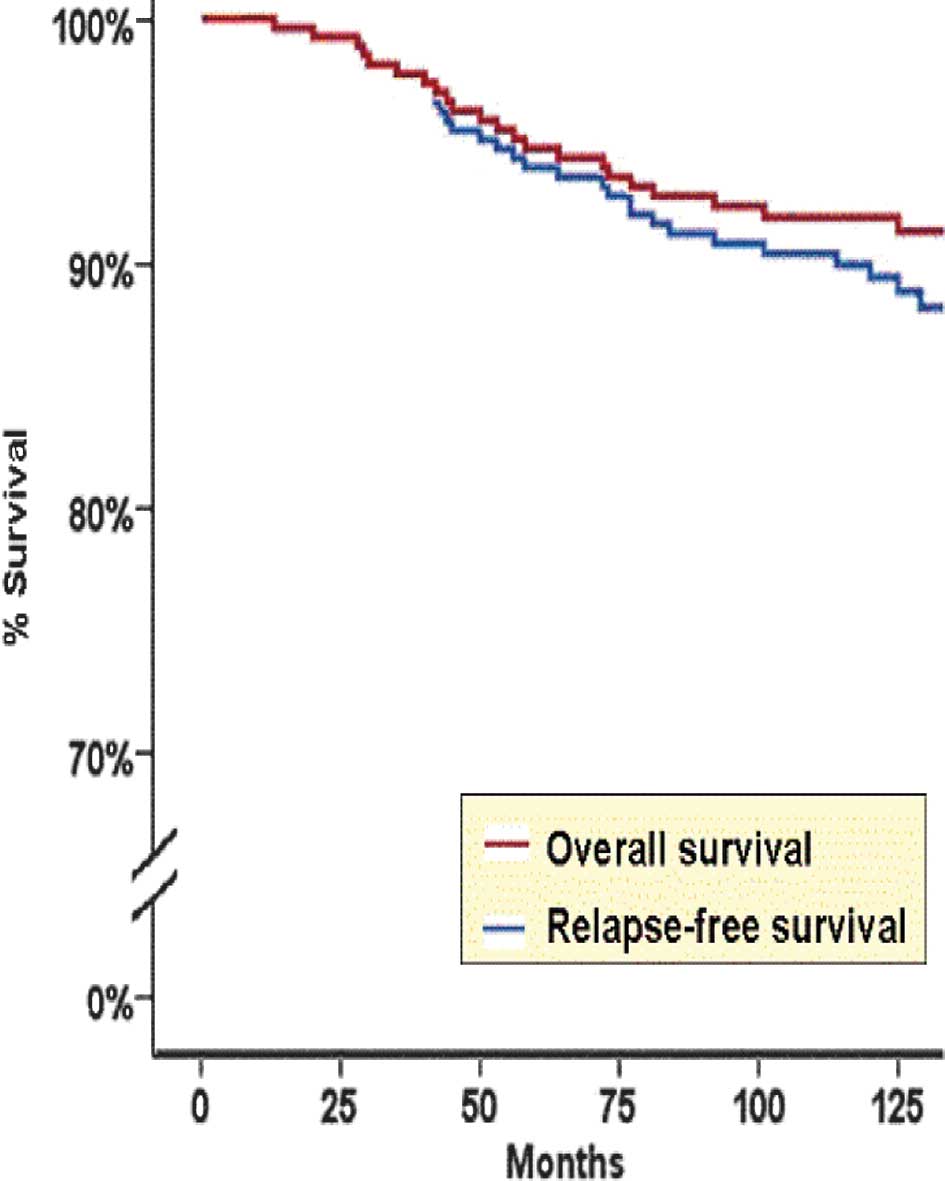
|
1
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, et al: Cancer
statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 60:277–300. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Burstein HJ, Harris JR and Morrow M:
Malignant tumors of the breast. Cancer: Principles and Practice of
Oncology. DeVita VT, Hellman S and Rosenberg SA: 8th edition.
Lippincot Williams & Wilkins; Philadelphia: pp. 1606–1654.
2008
|
|
3
|
Van Belle V, van Calster B, Brouckaert O,
et al: Qualitative assessment of the progesterone receptor and Her2
improves the Nottingham Prognostic Index up to 5 years after breast
cancer diagnosis. J Clin Oncol. 28:4129–4134. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Goldhirsch A, Ingle JN, Gelber RD, et al:
Panel members. Thresholds for therapies: highlights of the St
Gallen International Expert Consensus on the primary therapy of
early breast cancer 2009. Ann Oncol. 20:1319–1329. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
National Institutes of Health. Consensus
Development Conference Statement adjuvant therapy for breast
cancer, November 1–3, 2000. J Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 5–15.
2001.
|
|
6
|
Adjuvant! Onlinehttp://www.adjuvantonline.com/index.jsp.
|
|
7
|
Wang Y, Klijn JG, Zhang Y, et al:
Gene-expression profiles to predict distant metastasis of
lymph-node-negative primary breast cancer. Lancet. 365:671–679.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Paik S, Shak S, Tang G, et al: A multigene
assay to predict recurrence of tamoxifen-treated, node-negative
breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 351:2817–2826. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Singletary SE, Allred C, Ashley P, et al:
Revision of the American Joint Committee on Cancer staging system
for breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 20:3628–3636. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Elston CW and Ellis IO: Pathological
prognostic factors in breast cancer. I The value of histological
grade in breast cancer: experience from a large study with
long-term follow-up. Histopathology. 19:403–410. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Pauletti G, Dandekar S, Rong H, et al:
Assessment of methods for tissue-based detection of the HER-2/neu
alteration in human breast cancer: a direct comparison of
fluorescence in situ hybridization and immunohistochemistry. J Clin
Oncol. 18:3651–3664. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Detere S, Saccani G, Jotti L, et al: A
‘quickscore’ method for immunohistochemical semiquantitation:
validation for oestrogen receptor in breast carcinomas. J Clin
Pathol. 48:876–879. 1995.
|
|
13
|
McShane LM, Altman DG, Sauerbrei W, et al:
Reporting recommendations for tumor MARKer prognostic studies
(REMARK). Nat Clin Pract Oncol. 2:416–422. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Foekens JA, Look MP, Bolt-de Vries J, et
al: Cathepsin-D in primary breast cancer: prognostic evaluation
involving 2810 patients. Br J Cancer. 79:300–307. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ohri SS, Vashishta A, Proctor M, et al:
The propeptide of cathepsin D increases proliferation, invasion and
metastasis of breast cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 32:491–498.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sagulenko V, Muth D, Sagulenko E, et al:
Cathepsin D protects human neuroblastoma cells from
doxorubicin-induced cell death. Carcinogenesis. 29:1869–1877. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Prasad CP, Rath G, Mathur S, et al:
Expression analysis of E-cadherin, Slug and GSK3beta in invasive
ductal carcinoma of breast. BMC Cancer. 9:3252009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Frixen UH, Behrens J, Sachs M, et al:
E-cadherin-mediated cell-cell adhesion prevents invasiveness of
human carcinoma cells. J Cell Biol. 113:173–185. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Goodwin M and Yap AS: Classical cadherin
adhesion molecules: coordinating cell adhesion, signaling and the
cytoskeleton. J Mol Histol. 35:839–844. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Nelson WJ and Nusse R: Convergence of Wnt,
β-catenin, and cadherin pathways. Science. 303:1483–1487. 2004.
|
|
21
|
Roarty K and Rosen JM: Wnt and mammary
stem cells: hormones cannot fly wingless. Curr Opin Pharmacol.
10:643–649. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Van Diest PJ, van der Wall E and Baak JP:
Prognostic value of proliferation in invasive breast cancer: a
review. J Clin Pathol. 57:675–681. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Albain KS, Paik S and van’t Veer L:
Prediction of adjuvant chemotherapy benefit in endocrine
responsive, early breast cancer using multigene assays. Breast.
18(Suppl 3): 141–145. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Geffen DB, Abu-Ghanem S, Sion-Vardy N, et
al: The impact of the 21-gene recurrence score assay on decision
making about adjuvant chemotherapy in early-stage
estrogen-receptor-positive breast cancer in an oncology practice
with a unified treatment policy. Ann Oncol. March;2011.(E-pub ahead
of print).
|
|
25
|
Soerjomataram I, Louwman MW, Ribot JG, et
al: An overview of prognostic factors for long-term survivors of
breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 107:309–330. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Payne SJ, Bowen RL, Jones JL, et al:
Predictive markers in breast cancer – the present. Histopathology.
52:82–90. 2008.
|