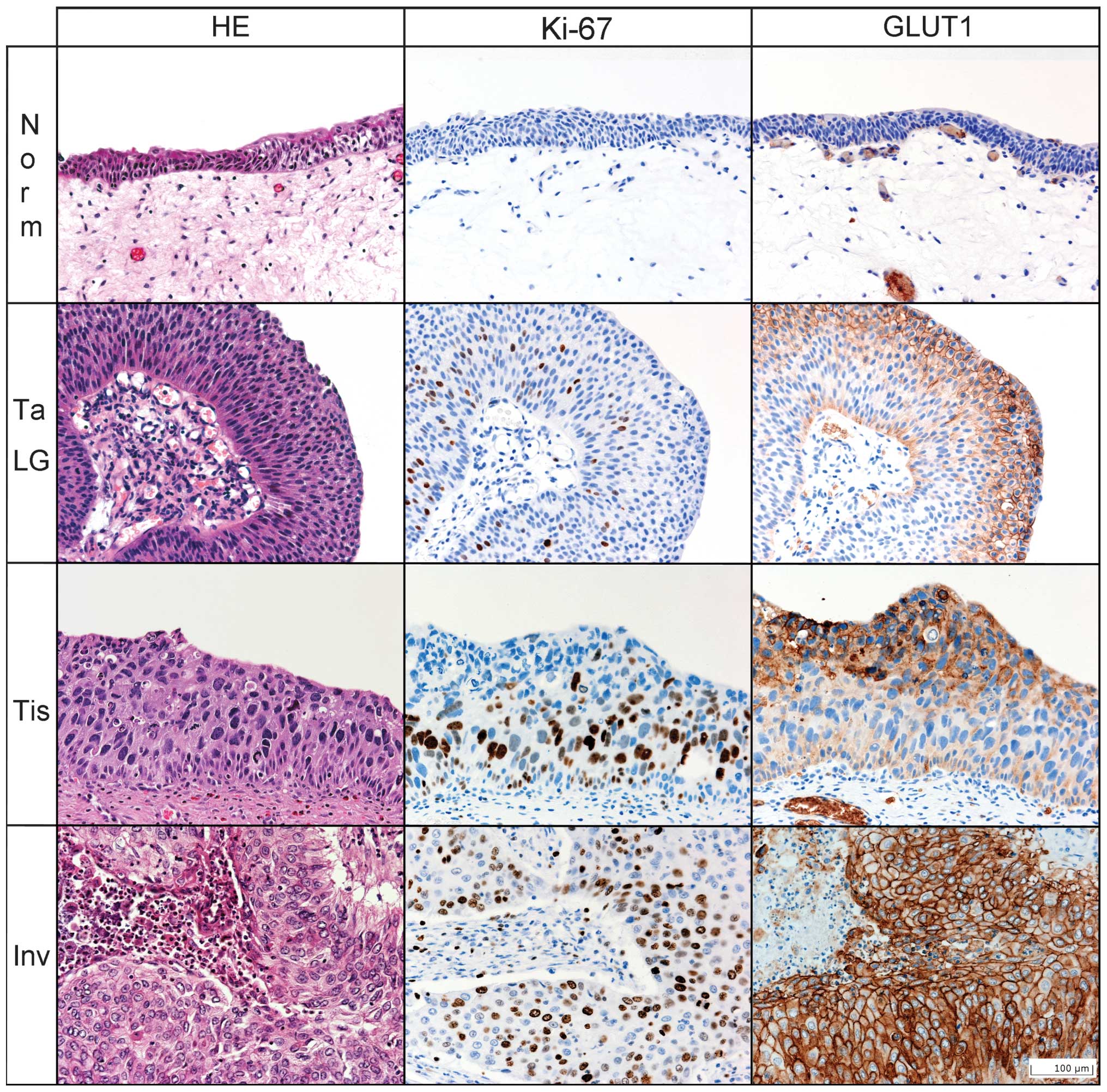
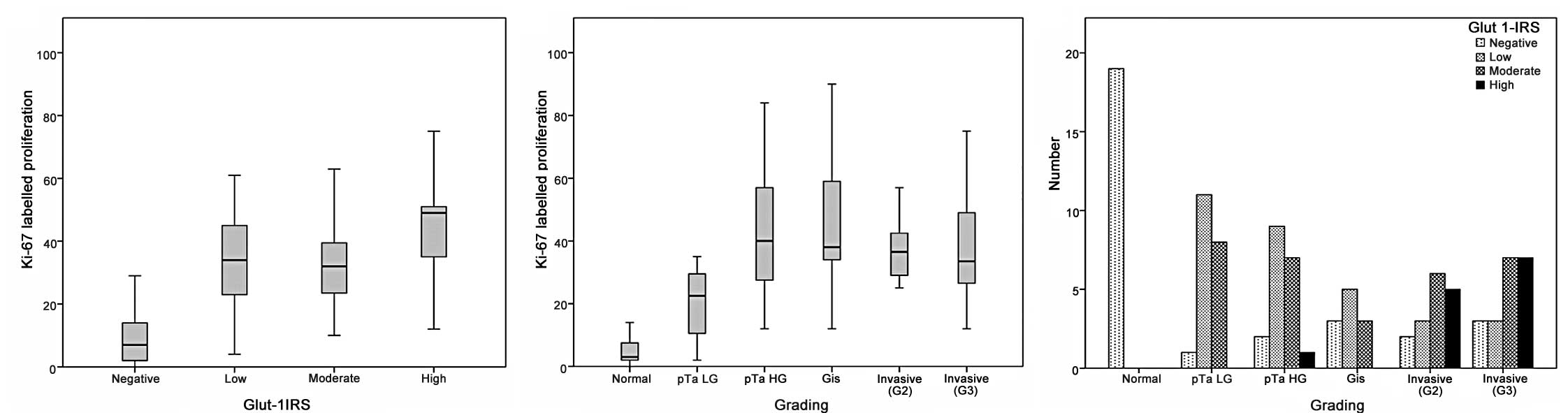
|
1
|
Lopez-Beltran A and Sauter G: Infiltrating
urothelial carcinoma. World Health Organization Classification of
Tumours – Tumours of the Urinary System and Male Genital Organs.
Eble N: IARC Press; Lyon: pp. 93–109. 2004
|
|
2
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J and Ward E: Cancer
Statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 60:277–300. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Husmann G, Kaatsch P, Katalinic A, Bertz
J, Haberland J, Kraywinkel K and Wolf U: 3.17 Bladder. Cancer in
Germany 2005/2006 Incidence and Trends. Robert Koch Institute (ed.)
and Association of Population-based Cancer Registries in Germany
(ed). Robert-Koch-Institut; Berlin: pp. 84–87. 2010
|
|
4
|
Boyle P and Levin B: Bladder cancer. World
Health Organization-World Cancer Report 2008. Boyle P and Levin B:
IARC Press; Lyon: pp. 444–449. 2008
|
|
5
|
Kaufman DS, Shipley WU and Feldman AS:
Bladder cancer. Lancet. 374:239–249. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Macheda ML, Rogers S and Best JD:
Molecular and cellular regulation of glucose transporter (GLUT)
proteins in cancer. J Cell Physiol. 202:654–662. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Agus DB, Gambhir SS, Pardridge WM,
Spielholz C, Baselga J, Vera JC and Golde DW: Vitamin C crosses the
blood-brain barrier in the oxidized form through the glucose
transporters. J Clin Invest. 100:2842–2848. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gould GW and Holman GD: The glucose
transporter family: structure, function and tissue-specific
expression. Biochem J. 295:329–341. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Harik SI, Kalaria RN, Whitney PM,
Andersson L, Lundahl P, Ledbetter SR and Perry G: Glucose
transporters are abundant in cells with ‘occluding’ junctions at
the blood-eye barriers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 87:4261–4264.
1990.
|
|
10
|
Younes M, Lechago LV, Somoano JR, Mosharaf
M and Lechago J: Wide expression of the human erythrocyte glucose
transporter Glut1 in human cancers. Cancer Res. 56:1164–1167.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yamamoto T, Seino Y, Fukumoto H, Koh G,
Yano H, Inagaki N, Yamada Y, Inoue K, Manabe T and Imura H:
Over-expression of facilitative glucose transporter genes in human
cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 170:223–230. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Brown RS and Wahl RL: Overexpression of
Glut-1 glucose transporter in human breast cancer. An
immunohistochemical study. Cancer. 72:2979–2985. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Nagase Y, Takata K, Moriyama N, Aso Y,
Murakami T and Hirano H: Immunohistochemical localization of
glucose transporters in human renal cell carcinoma. J Urol.
153:798–801. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Mellanen P, Minn H, Grenman R and Harkonen
P: Expression of glucose transporters in head-and-neck tumors. Int
J Cancer. 56:622–629. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chang S, Lee S, Lee C, Kim JI and Kim Y:
Expression of the human erythrocyte glucose transporter in
transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder. Urology. 55:448–452.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lee JH, Kim YW and Chang SG: Glucose
transporter-1 expression in urothelial papilloma of the bladder.
Urol Int. 74:268–271. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
O’Keeffe MB, Devlin AH, Burns AJ, Gardiner
TA, Logan ID, Hirst DG and McKeown SR: Investigation of pericytes,
hypoxia, and vascularity in bladder tumors: association with
clinical outcomes. Oncol Res. 17:93–101. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhou JT, Cai ZM, Li NC and Na YQ:
Expression of hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha and glucose
transporter protein 1 in renal and bladder cancers and the clinical
significance thereof. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 86:1970–1974.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hoskin PJ, Sibtain A, Daley FM and Wilson
GD: GLUT1 and CAIX as intrinsic markers of hypoxia in bladder
cancer: relationship with vascularity and proliferation as
predictors of outcome of ARCON. Br J Cancer. 89:1290–1297. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Visca P, Sebastiani V, Pizer ES, Botti C,
de Carli P, Filippi S, Monaco S and Alo PL: Immunohistochemical
expression and prognostic significance of FAS and GLUT1 in bladder
carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 23:335–339. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Younes M, Juarez D, Lechago LV and Lerner
SP: Glut 1 expression in transitional cell carcinoma of the urinary
bladder is associated with poor patient survival. Anticancer Res.
21:575–578. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cheng L, Montironi R, Davidson DD and
Lopez-Beltran A: Staging and reporting of urothelial carcinoma of
the urinary bladder. Mod Pathol. 22:S70–S95. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wu XR: Biology of urothelial
tumorigenesis: insights from genetically engineered mice. Cancer
Metastasis Rev. 28:281–290. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lindemann-Docter K and Knuchel R: Update
on urothelial carcinoma histopathology. Pathologe. 29:331–338.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Patil VV, Wang ZJ, Sollitto RA, Chuang KW,
Konety BR, Hawkins RA and Coakley FV: 18F-FDG PET/CT of
transitional cell carcinoma. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 193:W497–W504.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hiyoshi Y, Watanabe M, Imamura Y, Nagai Y,
Baba Y, Yoshida N, Toyama E, Hayashi N and Baba H: The relationship
between the glucose transporter type 1 expression and
F-fluorodeoxyglucose uptake in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Oncology. 76:286–292. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Usuda K, Sagawa M, Aikawa H, Ueno M,
Tanaka M, Machida Y, Zhao XT, Ueda Y, Higashi K and Sakuma T:
Correlation between glucose transporter-1 expression and
(18)F-fluoro-2-deoxyglucose uptake on positron emission tomography
in lung cancer. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 58:405–410. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|