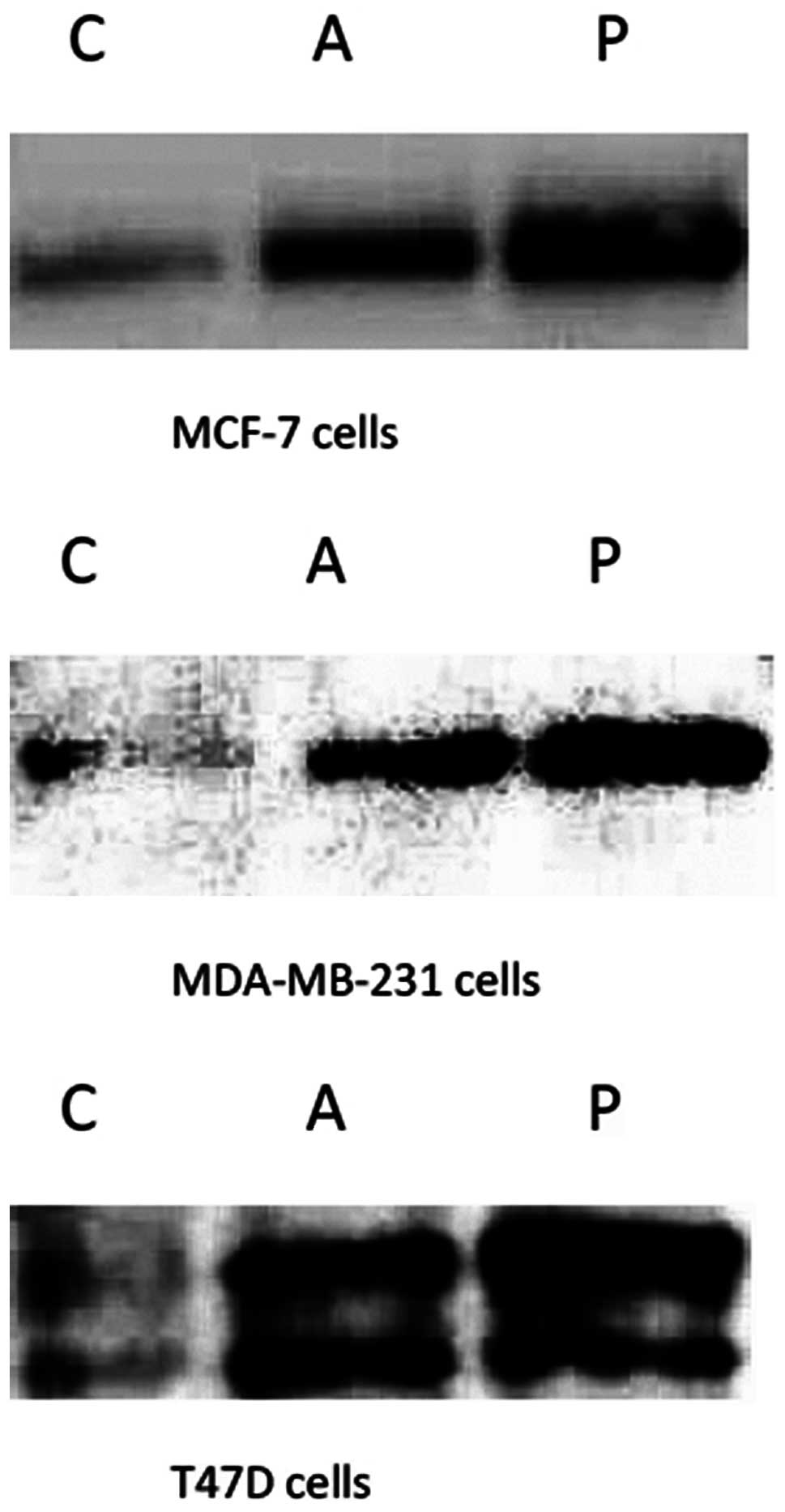
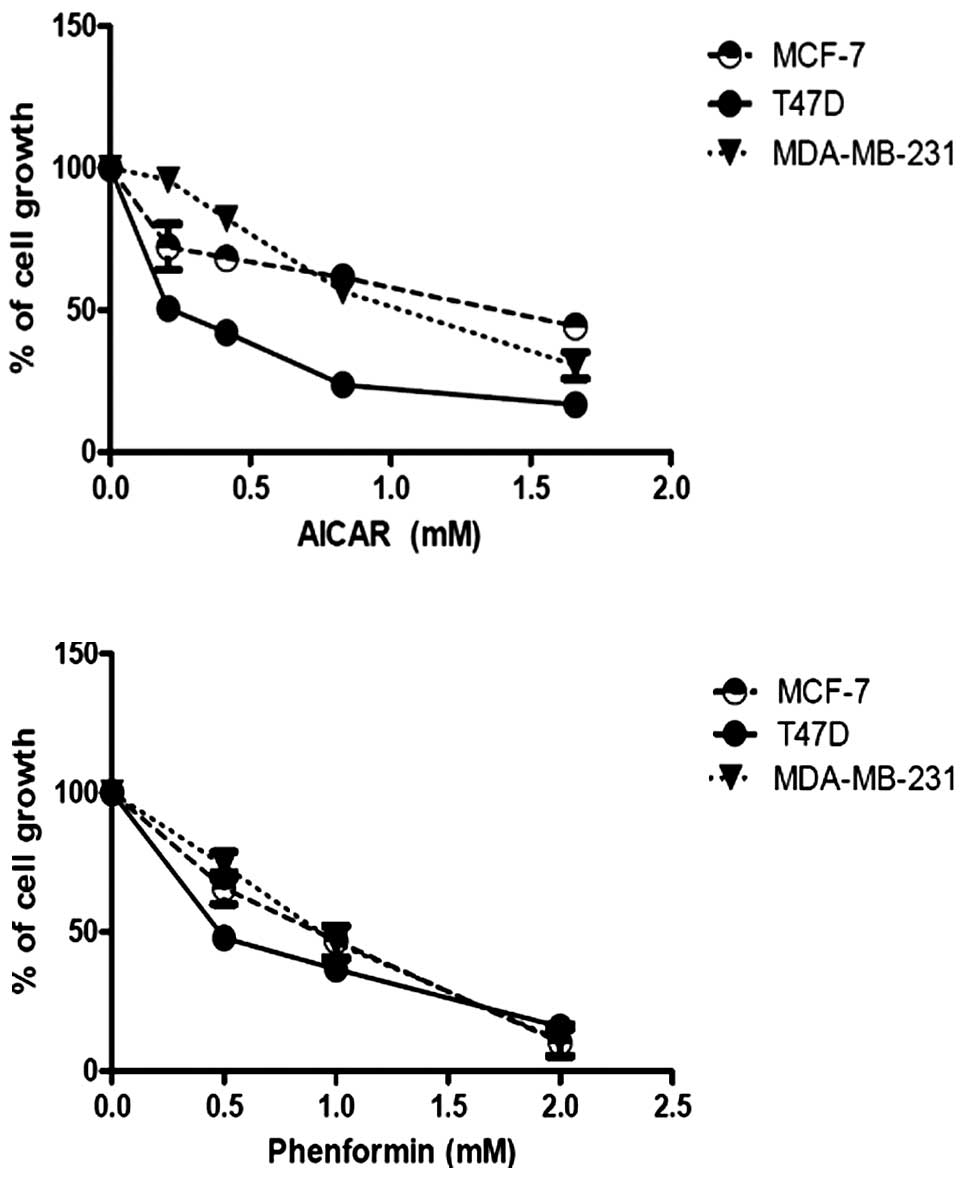
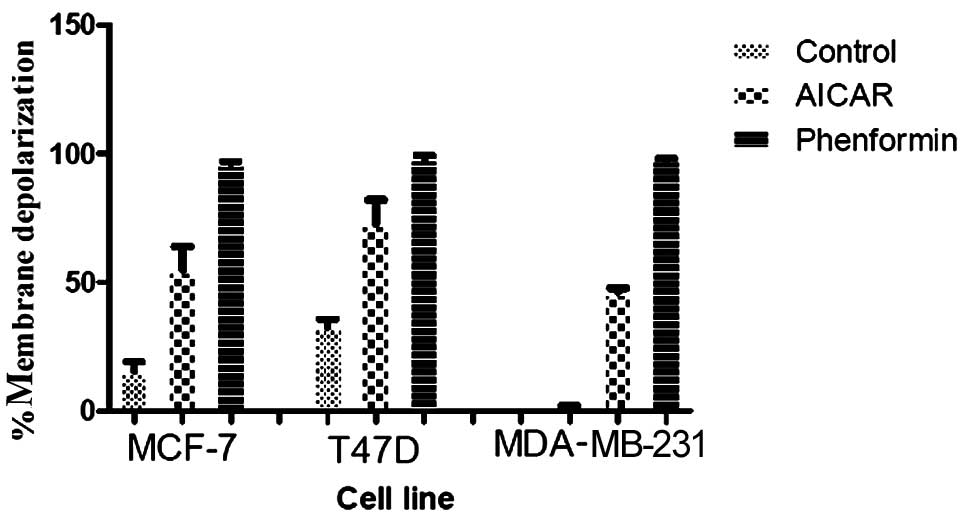
|
1
|
Evans DG and Howell A: Breast cancer
risk-assessment models. Breast Cancer Res. 9:2132007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lorincz AM and Sukumar S: Molecular links
between obesity and breast cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer. 13:279–292.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Todorov PT, McDevitt TM, Meyer DJ, Ueyama
H, Ohkubo I and Tisdale MJ: Purification and characterization of a
tumor lipid-mobilizing factor. Cancer Res. 58:2353–2358.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Katajisto P, Vallenius T, Vaahtomeri K,
Ekman N, Udd L, Tiainen M and Makela TP: The LKB1 tumor suppressor
kinase in human disease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1775:63–75.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lizcano JM, Goransson O, Toth R, Deak M,
Morrice NA, Boudeau J, Hawley SA, Udd L, Makela TP, Hardie DG and
Alessi DR: LKB1 is a master kinase that activates 13 kinases of the
AMPK subfamily, including MARK/PAR-1. EMBO J. 23:833–843. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Viollet B, Athea Y, Mounier R, Guigas B,
Zarrinpashneh E, Horman S, Lantier L, Hebrard S, Devin-Leclerc J,
Beauloye C, Foretz M, Andreelli F, Ventura-Clapier R and Bertrand
L: AMPK: Lessons from transgenic and knockout animals. Front
Biosci. 14:19–44. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bode AM and Dong Z: Post-translational
modification of p53 in tumorigenesis. Nat Rev Cancer. 4:793–805.
2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Caraci F, Chisari M, Frasca G, Chiechio S,
Salomone S, Pinto A, Sortino MA and Bianchi A: Effects of
phenformin on the proliferation of human tumor cell lines. Life
Sci. 74:643–650. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Luo Z, Saha AK, Xiang X and Ruderman NB:
AMPK, the metabolic syndrome and cancer. Trends Pharmacol Sci.
26:69–76. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Xiang X, Saha AK, Wen R, Ruderman NB and
Luo Z: AMP-activated protein kinase activators can inhibit the
growth of prostate cancer cells by multiple mechanisms. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 321:161–167. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Rattan R, Giri S, Singh AK and Singh I:
5-Aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide-1-beta-D-ribofuranoside inhibits
cancer cell proliferation in vitro and in vivo via AMP-activated
protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 280:39582–39593. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yang L, Cao Z, Yan H and Wood WC:
Coexistence of high levels of apoptotic signaling and inhibitor of
apoptosis proteins in human tumor cells: implication for cancer
specific therapy. Cancer Res. 63:6815–6824. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Butler H and Korbonits M: Cannabinoids for
clinicians: the rise and fall of the cannabinoid antagonists. Eur J
Endocrinol. 161:655–662. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sengupta TK, Leclerc GM, Hsieh-Kinser TT,
Leclerc GJ, Singh I and Barredo JC: Cytotoxic effect of
5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide-1-beta-4-ribofuranoside (AICAR) on
childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) cells: implication for
targeted therapy. Mol Cancer. 6:462007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mukherjee P, Mulrooney TJ, Marsh J, Blair
D, Chiles TC and Seyfried TN: Differential effects of energy stress
on AMPK phosphorylation and apoptosis in experimental brain tumor
and normal brain. Mol Cancer. 7:372008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Elmore S: Apoptosis: a review of
programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol. 35:495–516. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhou G, Myers R, Li Y, Chen Y, Shen X,
Fenyk-Melody J, Wu M, Ventre J, Doebber T, Fujii N, Musi N,
Hirshman MF, Goodyear LJ and Moller DE: Role of AMP-activated
protein kinase in mechanism of metformin action. J Clin Invest.
108:1167–1174. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|