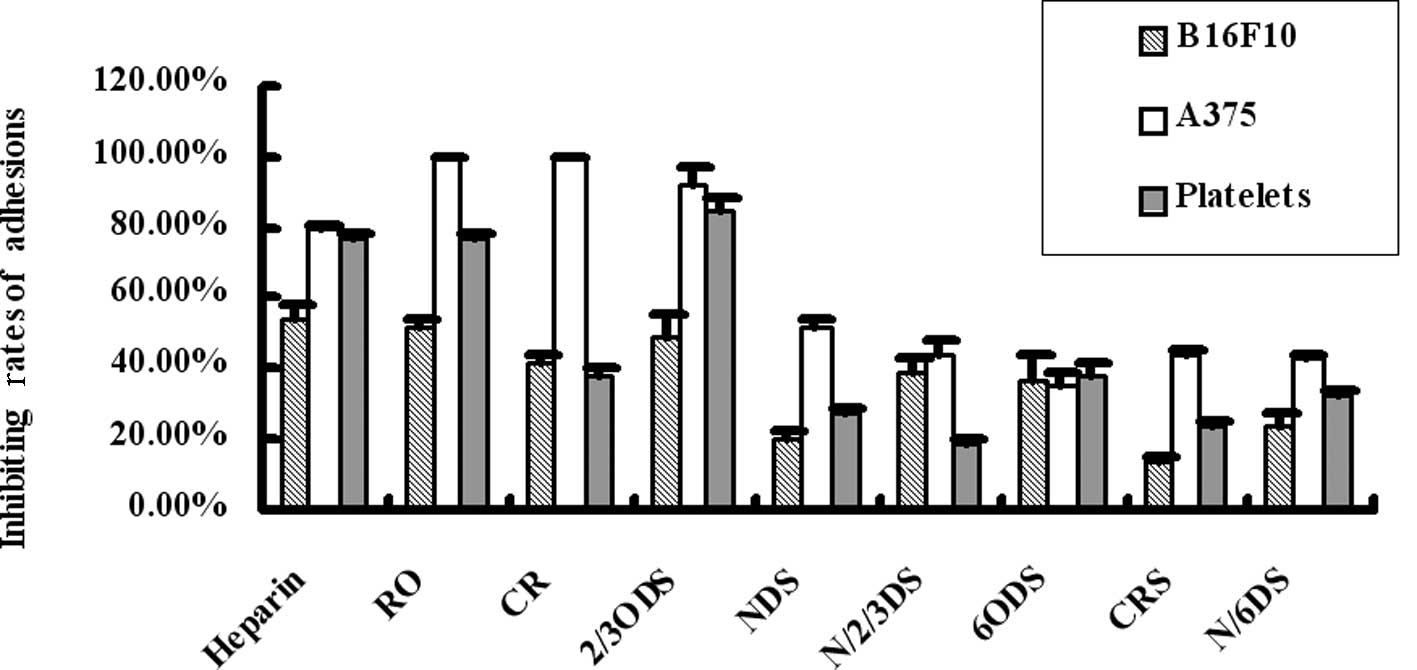
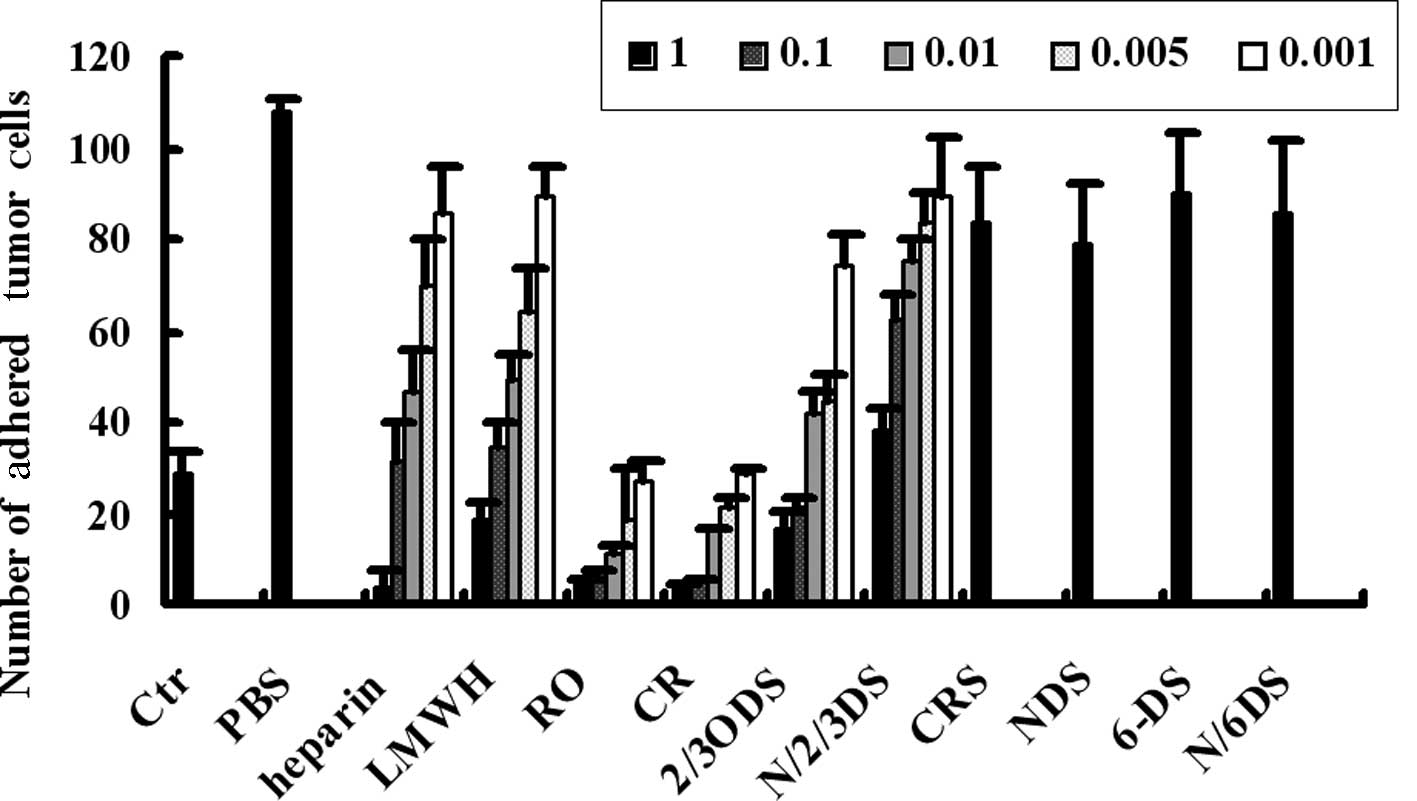
|
1
|
Weiler H: A platelet cloak for tumor
cells. Blood. 105:5–6. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Nieswandt B, Hafner M, Echtenacher B and
Männel DN: Lysis of tumor cells by natural killer cells in mice is
impeded by platelets. Cancer Res. 59:1295–1300. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Montrucchio G, Sapino A, Bussolati B,
Ghisolfi G, Rizea-Savu S, Silvestro L, Lupia E and Camussi G:
Potential angiogenic role of platelet-activating factor in human
breast cancer. Am J Pathol. 153:1589–1596. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Manegold PC, Hutter J, Pahernik SA,
Messmer K and Dellian M: Platelet-endothelial interaction in tumor
angiogenesis and microcirculation. Blood. 101:1970–1976. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Trikha M and Nakada MT: Platelets and
cancer: implications for antiangiogenic therapy. Semin Thromb
Hemost. 28:39–44. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
McCarty OJ, Mousa SA, Bray PF and
Konstantopoulos K: Immobilized platelets support human colon
carcinoma cell tethering, rolling, and firm adhesion under dynamic
flow conditions. Blood. 96:1789–1797. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ishai-Michaeli R, Eldor A and Vlodavsky I:
Heparanase activity expressed by platelets, neutrophils, and
lymphoma cells releases active fibroblast growth factor from
extracellular matrix. Cell Regul. 11:833–842. 1990.
|
|
8
|
Suzuki K, Aiura K, Ueda M and Kitajima M:
The influence of platelets on the promotion of invasion by tumor
cells and inhibition by anti-platelet agents. Pancreas. 29:132–140.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jurasz P, Alonso-Escolano D and Radomski
MW: Platelet-cancer interactions: mechanisms and pharmacology of
tumour cell- induced platelet aggregation. Br J Pharmacol.
143:819–826. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ma YQ and Geng JG: Heparan sulfate-like
proteoglycans mediate adhesion of human malignant melanoma A375
cells to P-selectin under flow. J Immunol. 165:558–565. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Felding-Habermann B, Habermann R, Saldívar
E and Ruggeri ZM: Role of beta3 integrins in melanoma cell adhesion
to activated platelets under flow. J Biol Chem. 271:5892–5900.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Karpatkin S, Pearlstein E, Ambrogio C and
Coller BS: Role of adhesive proteins in platelet tumor interaction
in vitro and metastasis formation in vivo. J Clin Invest.
81:1012–1019. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Cominetti MR, Martin AC, Ribeiro JU,
Djaafri I, Fauvel-Lafève F, Crépin M and Selistre-de-Araujo HS:
Inhibition of platelets and tumor cell adhesion by the disintegrin
domain of human ADAM9 to collagen I under dynamic flow conditions.
Biochimie. 91:1045–1052. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li F, Yu G, Li S, Peng S and Fu J:
Antimetastatic effect of integrin IIb/IIIa inhibitors on salivary
adenoid cystic carcinoma. Chin J Cancer Res. 13:198–201. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Varki NM and Varki A: Heparin inhibition
of selectin-mediated interactions during the hemorrhagic phase of
carcinoma metastasis: rationale for clinical studies in humans.
Semin Thromb Hemost. 28:53–66. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Sobel M, Fish WR, Toma N, Luo S, Bird K,
Mori K, Kusumoto S, Blystone SD and Suda Y: Heparin modulates
integrin function in human platelets. J Vasc Surg. 33:587–594.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wei M, Tai G, Gao Y, Li N, Huang B, Zhou
Y, Hao S and Zeng X: Modified heparin inhibits P-selectin-mediated
cell adhesion of human colon carcinoma cells to immobilized
platelets under dynamic flow conditions. J Biol Chem.
279:29202–29210. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gao Y, Wei M, Zheng S, Ba X, Hao S and
Zeng X: Chemically modified heparin inhibits the in vitro adhesion
of nonsmall cell lung cancer cells to P-selectin. J Cancer Res Clin
Oncol. 132:257–264. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang C, Liu Y, Gao Y, Shen J, Zheng S,
Wei M and Zeng X: Modified heparins inhibit integrin
alpha(IIb)beta(3) mediated adhesion of melanoma cells to platelets
in vitro and in vivo. Int J Cancer. 125:2058–2065. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zheng S, Shen S, Jiao Y, Liu Y, Zhang C,
Wei M, Hao S and Zeng X: Platelets and fibrinogen facilitate each
other in protecting tumor cells from NK cytotoxicity. Cancer Sci.
100:859–865. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Vestweber D and Blanks JE: Mechanisms that
regulate the function of the selectins and their ligands. Physiol
Rev. 79:181–213. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Diamond MS, Alon R, Parkos CA, Quinn MT
and Springer TA: Heparin is an adhesive ligand for the leukocyte
integrin Mac-1 (CD11b/CD1). J Cell Biol. 130:1473–1482. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gunji Y, Lewis J and Gorelik E: Fibrin
formation inhibits the in vitro cytotoxic activity of human natural
and lymphokine- activated killer cells. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis.
6:663–672. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Palumbo JS, Talmage KE, Massari JV, La
Jeunesse CM, Flick MJ, Kombrinck KW, Jirousková M and Degen JL:
Platelets and fibrin (ogen) increase metastatic potential by
impeding natural killer cell-mediated elimination of tumor cells.
Blood. 105:178–185. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Leung L and Nachman R: Molecular
mechanisms of platelet aggregation. Annu Rev Med. 37:179–186. 1986.
View Article : Google Scholar
|