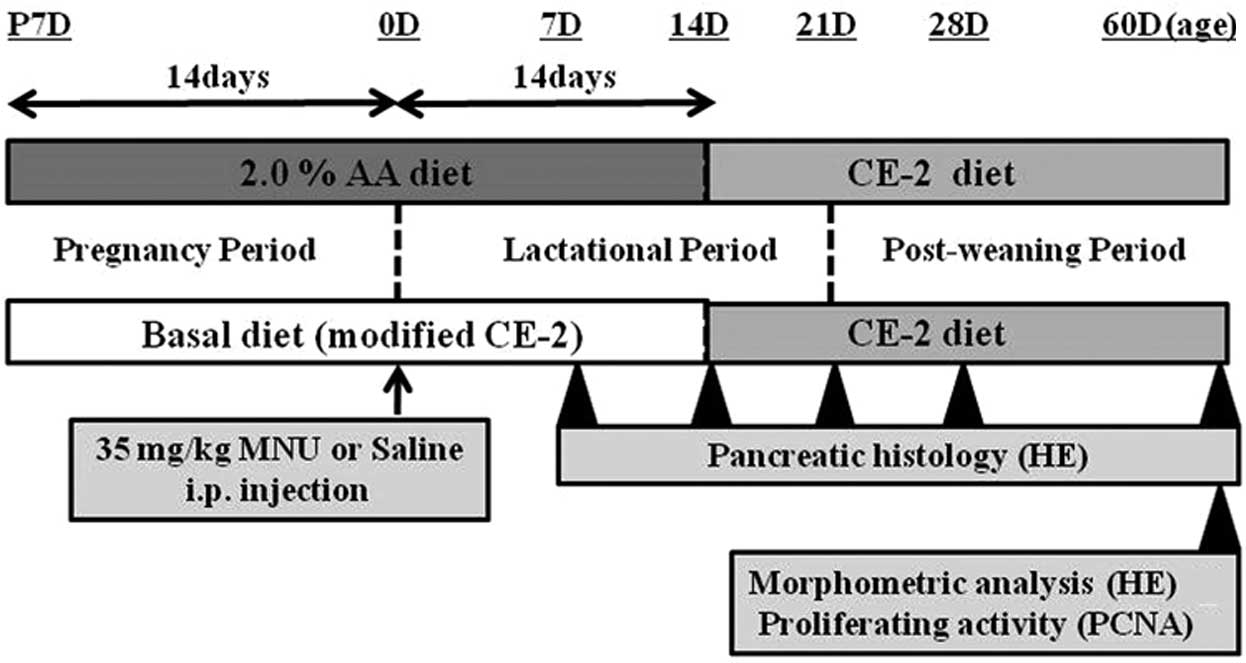
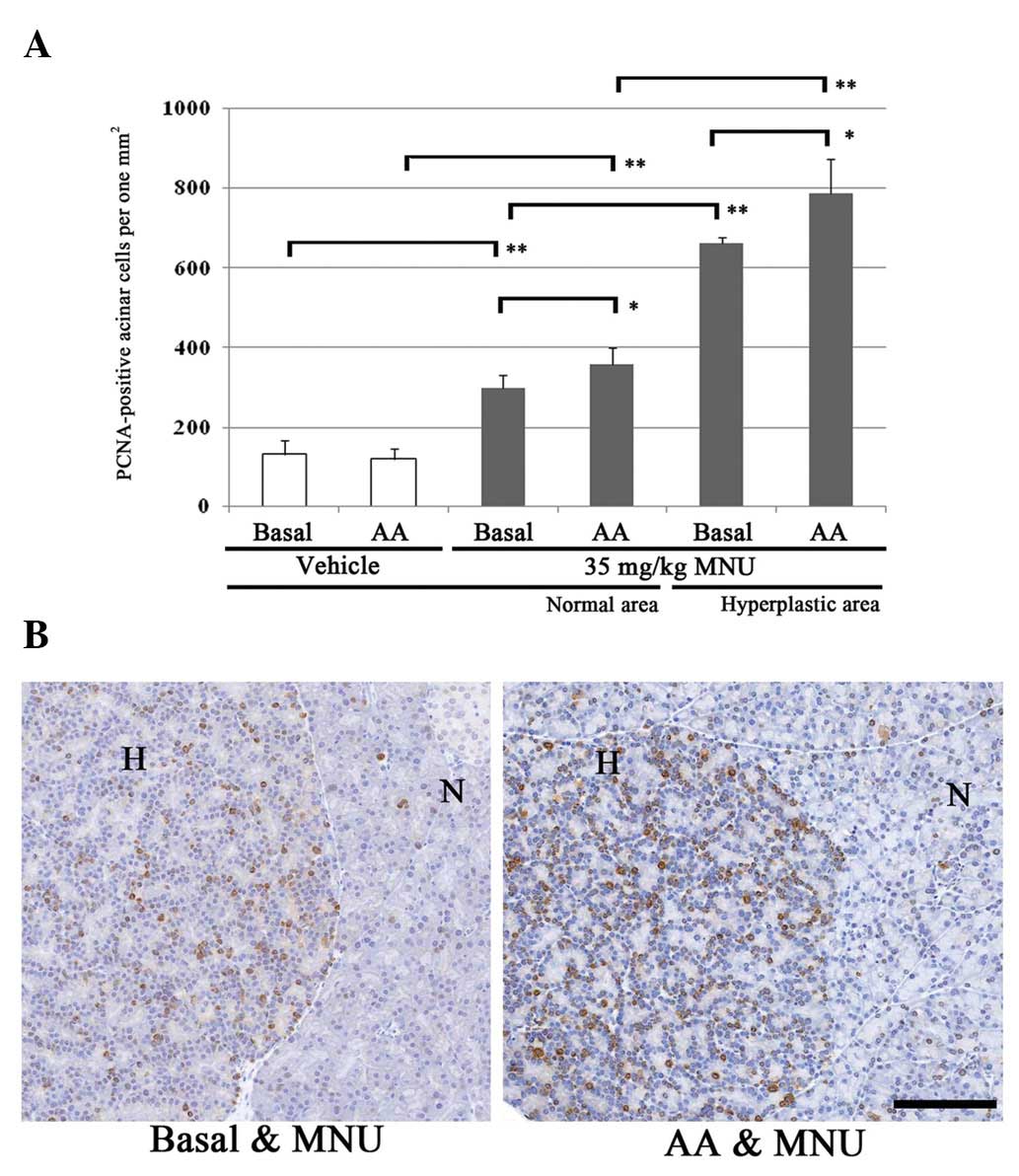
|
1
|
Davis-Bruno K and Tassinari MS: Essential
fatty acid supplementation of DHA and ARA and effects on
neurodevelopment across animal species: a review of the literature.
Birth Defects Res B Dev Reprod Toxicol. 92:240–250. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Uauy R, Hoffman DR, Peirano P, Birch DG
and Birch EE: Essential fatty acids in visual and brain
development. Lipids. 36:885–895. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Le HD, Meisel JA, de Meijer VE, Gura KM
and Puder M: The essentiality of arachidonic acid and
docosahexaenoic acid. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids.
81:165–170. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Codex Alimentarius Commission, Joint
FAO/WHO Food Standards Programme: Report of the 28th Session of the
Codex Committee on Nutrition and Foods for Special Dietary Uses,
2007.
|
|
5
|
Hoffman DR, Boettcher JA and
Diersen-Schade DA: Toward optimizing vision and cognition in term
infants by dietary docosahexaenoic and arachidonic acid
supplementation: a review of randomized controlled trials.
Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 81:151–158. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Anonymous: Final report on the safety
assessment of arachidonic acid. Int J Toxicol. 12:481–559. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Hamazaki T: Reports on “Research on the
toxicity of arachidonic acid supplementation”. The Health and Labor
Sciences Research Grants, Japan (H22-Shokuhin-Ippan-002). 2012.(In
Japanese).
|
|
8
|
Gong Z, Holly EA, Wang F, Chan JM and
Bracci PM: Intake of fatty acids and antioxidants and pancreatic
cancer in a large population-based case-control study in the San
Francisco bay area. Int J Cancer. 127:1893–1904. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Risch HA: Etiology of pancreatic cancer,
with a hypothesis concerning the role of N-nitroso compounds and
excess gastric acidity. J Natl Cancer Inst. 95:948–960. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Rao MS: Animal models of exocrine
pancreatic carcinogenesis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 6:665–676. 1987.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Woutersen RA, van Garderen-Hoetmer A,
Lamers CB and Scherer E: Early indicators of exocrine pancreas
carcinogenesis produced by non-genotoxic agents. Mutat Res.
248:291–302. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kimura A, Yoshizawa K, Sasaki T, Uehara N,
Kinoshita Y, Miki H, Yuri T, Uchida T and Tsubura A:
N-methyl-N-nitrosourea-induced changes in epithelial rests of
Malassez and the development of odontomas in rats. Exp Ther Med.
4:15–20. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tsubura A, Lai YC, Miki H, Sasaki T,
Uehara N, Yuri T and Yoshizawa K: Animal models of
N-methyl-N-nitrosourea-induced mammary cancer and retinal
degeneration with special emphasis on therapeutic trials. In Vivo.
25:11–22. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Reddy JK and Rao MS: Pancreatic
adenocarcinoma in inbred guinea pigs induced by
N-methyl-N-nitrosourea. Cancer Res. 35:2269–2277. 1975.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Furukawa F, Sato H, Imaida K, Toyoda K,
Imazawa T, Takahashi M and Hayashi Y: Induction of pancreatic
tumors in male Syrian golden hamsters by intraperitoneal
N-methyl-N-nitrosourea injection. Pancreas.
7:153–158. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Monis B and Valentich MA: Promoting
effects of mancozeb on pancreas of nitrosomethylurea-treated rats.
Carcinogenesis. 14:929–933. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Valentich MA, Eynard AR, Barotto NN, Diaz
MP and Bongiovanni GA: Effect of the co-administration of
pheno-barbital, quercetin and mancozeb on nitrosomethylurea-induced
pancreatic tumors in rats. Food Chem Toxicol. 44:2101–2105. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Harauma A and Moriguchi T: Dietary n-3
fatty acid deficiency in mice enhances anxiety induced by chronic
mild stress. Lipids. 46:409–416. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Eustis SL, Boorman GA and Hayashi Y:
Exocrine pancreas. Pathology of the Fischer Rat: Reference and
Atlas. Boorman GA, Montgomery CA Jr and MacKenzie WF: Academic
Press; San Diego: pp. 95–108. 1990
|
|
20
|
Longnecker DS and Millar PM: Tumors of the
pancreas. Pathology of Tumors in Laboratory Animals, Vol 1, Tumours
of the Rat. Turusov VS and Mohr U: IARC Scientific Publications No.
99, International Agency for Research in Cancer; Lyon: pp. 241–257.
1990
|
|
21
|
Yoshizawa K, Sasaki T, Kuro M, Miki H,
Kimura A, Uehara N, Yuri T and Tsubura A: Corneal damage induced in
adult mice by a single intraperitoneal injection of
N-ethyl-N-nitrosourea. In Vivo. 25:609–616. 2011.
|
|
22
|
Barotto NN, López CB, Eynard AR, Fernández
Zapico ME and Valentich MA: Quercetin enhances pretumorous lesions
in the NMU model of rat pancreatic carcinogenesis. Cancer Lett.
129:1–6. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Appel MJ, van Garderen-Hoetmer A and
Woutersen RA: Effects of dietary linoleic acid on pancreatic
carcinogenesis in rats and hamsters. Cancer Res. 54:2113–2120.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Boorman GA: Proliferative exocrine
pancreatic lesions in rats. The effect of sample size on the
incidence of lesions. Toxicol Pathol. 15:451–456. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dominick MA, Bobrowski WF and Metz AL:
Proliferative exocrine pancreatic lesions in aged Wistar rats.
Toxicol Pathol. 18:423–426. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Appel MJ and Woutersen RA: Modulation of
growth and cell turnover of preneoplastic lesions and of
prostaglandin levels in rat pancreas by dietary fish oil.
Carcinogenesis. 15:2107–2112. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yoshizawa K, Marsh T, Foley JF, Cai B,
Peddada S, Walker NJ and Nyska A: Mechanisms of exocrine pancreatic
toxicity induced by oral treatment with
2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in female Harlan
Sprague-Dawley rats. Toxicol Sci. 85:594–606. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
McGuiness EE, Morgan RGH and Wormsley KG:
Effects of soybean flour on the pancreas of rats. Environ Health
Perspect. 56:205–212. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Haschek WM, Rousseaux CG and Wallig MA:
Pancreas, Section I, Exocrine pancreas. Fundamentals of Toxicologic
Pathology. 2nd edition. Academic Press; San Diego: pp. 237–251.
2010
|
|
30
|
Hand KV, Bruen CM, O'Halloran F, Giblin L
and Green BD: Acute and chronic effects of dietary fatty acids on
cholecystokinin expression, storage and secretion in
enteroendocrine STC-1 cells. Mol Nutr Food Res. 54:S93–S103. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hou W, Arita Y and Morisset J: Endogenous
arachidonic acid release and pancreatic amylase secretion.
Pancreas. 14:301–308. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kusumoto A, Ishikura Y, Kawashima H, Kiso
Y, Takai S and Miyazaki M: Effects of arachidonate-enriched
triacylglycerol supplementation on serum fatty acids and platelet
aggregation in healthy male subjects with a fish diet. Br J Nutr.
98:626–635. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Nelson GJ, Schmidt PC, Bartolini G, Kelley
DS and Kyle D: The effect of dietary arachidonic acid on platelet
function, platelet fatty acid composition, and blood coagulation in
humans. Lipids. 32:421–425. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Imai N, Kawabe M, Tamano S, Doi Y,
Nakashima H, Suguro M, Numano T, Hara T, Hagiwara A, Furukawa F,
Kaneda Y, et al: Arachidonate-enriched triglyceride oil does not
promote tumor development in a rat medium-term multi-organ
carcinogenesis model. Food Chem Toxicol. 50:2780–2791. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|