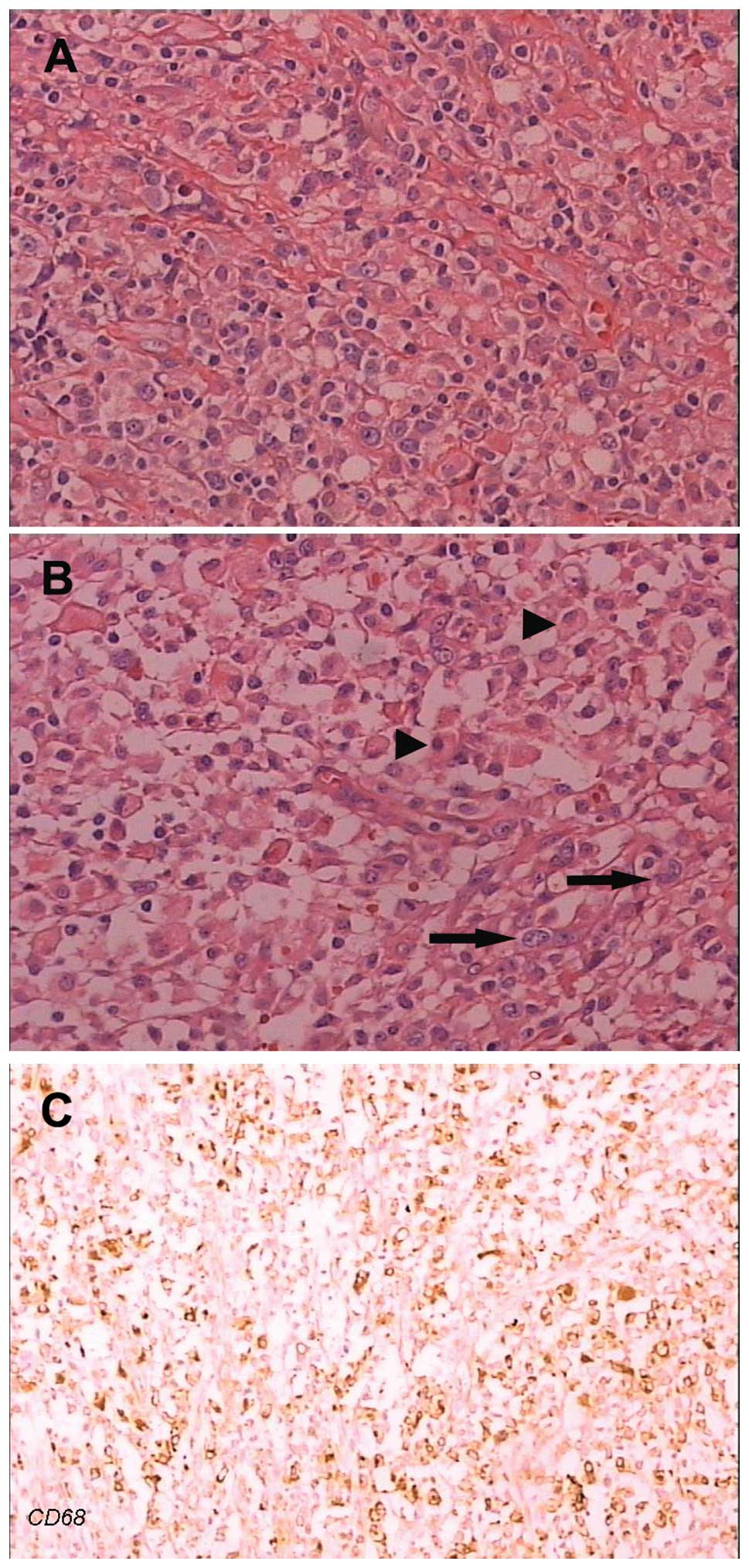
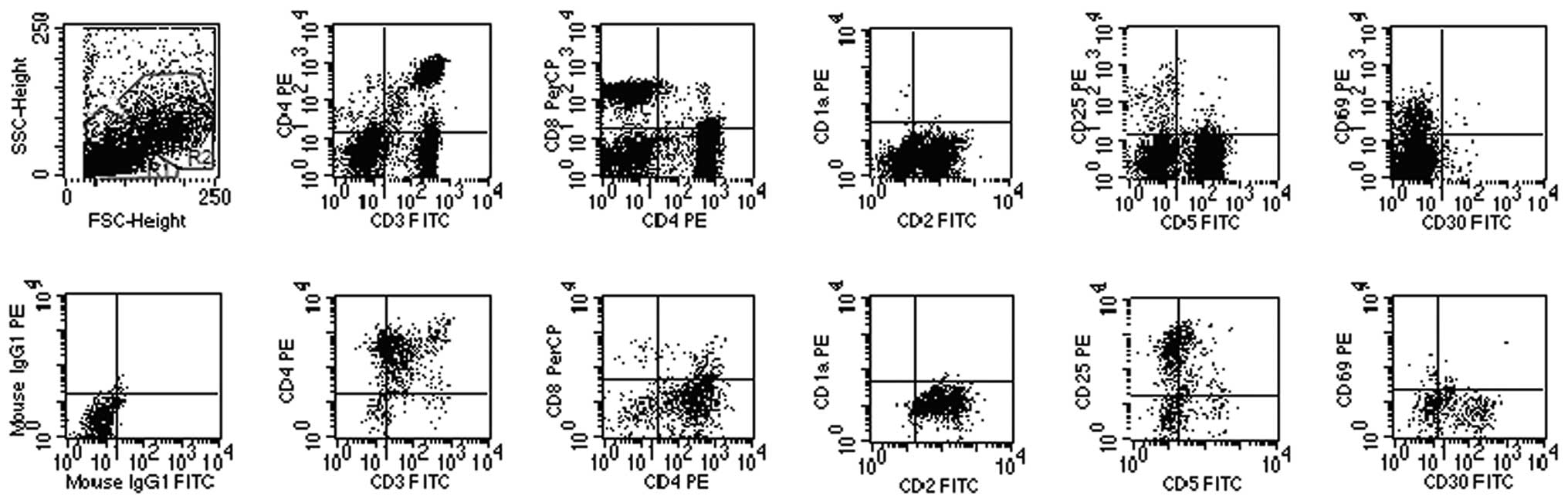
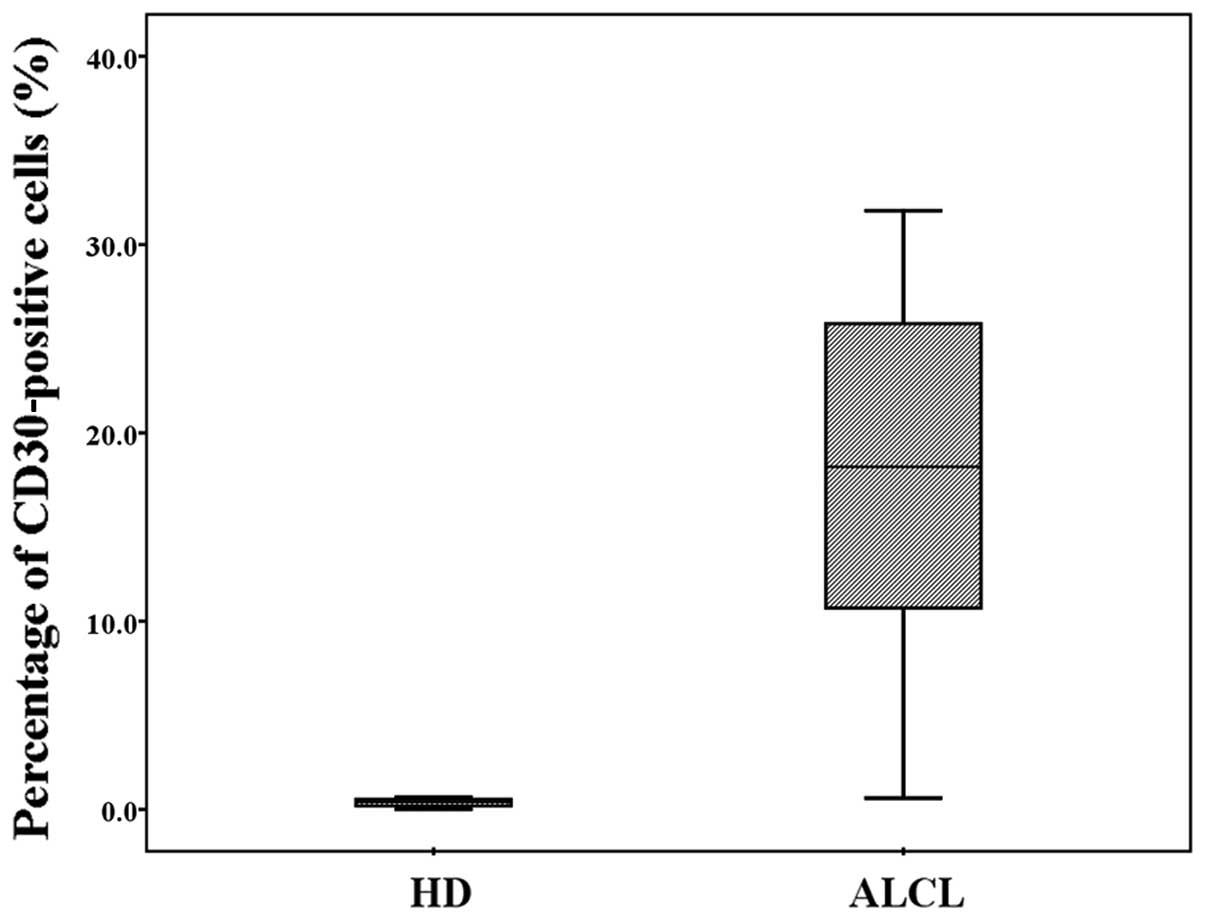
|
1.
|
Campo E, Swerdlow SH, Harris NL, Pileri S,
Stein H and Jaffe ES: The 2008 WHO classification of lymphoid
neoplasms and beyond: evolving concepts and practical applications.
Blood. 117:5019–5032. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Stein H, Mason DY, Gerdes J, et al: The
expression of the Hodgkin’s disease associated antigen Ki-1 in
reactive and neoplastic lymphoid tissue: evidence that
Reed-Sternberg cells and histiocytic malignancies are derived from
activated lymphoid cells. Blood. 66:848–858. 1985.
|
|
3.
|
Falini B: Anaplastic large cell lymphoma:
pathological, molecular and clinical features. Br J Haematol.
114:741–760. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Medeiros LJ and Elenitoba-Johnson KS:
Anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Am J Clin Pathol. 127:707–722.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
ten Berge RL, Oudejans JJ, Ossenkoppele GJ
and Meijer CJ: ALK-negative systemic anaplastic large cell
lymphoma: differential diagnostic and prognostic aspects - a
review. J Pathol. 200:4–15. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Savage KJ, Harris NL, Vose JM, et al:
ALK-anaplastic large-cell lymphoma is clinically and
immunophenotypically different from both ALK+ ALCL and peripheral
T-cell lymphoma, not otherwise specified: report from the
International Peripheral T-Cell Lymphoma Project. Blood.
111:5496–5504. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Sethuraman C, Simmerson M, Vora AJ and
Cohen MC: Flowcytometric immunophenotyping in the diagnosis of
pediatric lymphoma: how reliable is it and how can we optimize its
use? J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 32:298–303. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Barrena S, Almeida J, Del Carmen
Garcia-Macias M, et al: Flow cytometry immunophenotyping of
fine-needle aspiration specimens: utility in the diagnosis and
classification of non-Hodgkin lymphomas. Histopathology.
58:906–918. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Kesler MV, Paranjape GS, Asplund SL,
McKenna RW, Jamal S and Kroft SH: Anaplastic large cell lymphoma: a
flow cytometric analysis of 29 cases. Am J Clin Pathol.
128:314–322. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Muzzafar T, Wei EX, Lin P, Medeiros LJ and
Jorgensen JL: Flow cytometric immunophenotyping of anaplastic large
cell lymphoma. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 133:49–56. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Wright D, McKeever P and Carter R:
Childhood non-Hodgkin lymphomas in the United Kingdom: findings
from the UK Children’s Cancer Study Group. J Clin Pathol.
50:128–134. 1997.
|
|
12.
|
Jacobsen E: Anaplastic large-cell
lymphoma, T-/null-cell type. Oncologist. 11:831–840. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Stein H, Foss HD, Durkop H, et al: CD30(+)
anaplastic large cell lymphoma: a review of its histopathologic,
genetic, and clinical features. Blood. 96:3681–3695. 2000.
|
|
14.
|
Lamant L, McCarthy K, d’Amore E, et al:
Prognostic impact of morphologic and phenotypic features of
childhood ALK-positive anaplastic large-cell lymphoma: Results of
the ALCL99 study. J Clin Oncol. 29:4669–4676. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Kinney MC, Higgins RA and Medina EA:
Anaplastic large cell lymphoma: twenty-five years of discovery.
Arch Pathol Lab Med. 135:19–43. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Creager AJ, Geisinger KR and Bergman S:
Neutrophil-rich Ki-1-positive anaplastic large cell lymphoma: a
study by fine-needle aspiration biopsy. Am J Clin Pathol.
117:709–715. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Deutsch YE, Tadmor T, Podack ER and
Rosenblatt JD: CD30: an important new target in hematologic
malignancies. Leuk Lymphoma. 52:1641–1654. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Costa V, Oliva T and Norton L: Successful
treatment with daclizumab of refractory anaplastic lymphoma.
Pediatr Blood Cancer. 53:1130–1131. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, et al:
WHO Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid
Tissues. IARC Press; Lyon: pp. 326–329. 2008
|
|
20.
|
Craig FE and Foon KA: Flow cytometric
immunophenotyping for hematologic neoplasms. Blood. 111:3941–3967.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
El-Sayed AM, El-Borai MH, Bahnassy AA and
El-Gerzawi SM: Flow cytometric immunophenotyping (FCI) of lymphoma:
correlation with histopathology and immunohistochemistry. Diagn
Pathol. 3:432008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Shen H, Tang Y, Xu X, et al: Rapid
detection of neoplastic cells in serous cavity effusions in
children with flow cytometry immunophenotyping. Leuk Lymphoma.
53:1509–1514. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Damm-Welk C, Schieferstein J, Schwalm S,
Reiter A and Woessmann W: Flow cytometric detection of circulating
tumour cells in nucleophosmin/anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive
anaplastic large cell lymphoma: comparison with quantitative
polymerase chain reaction. Br J Haematol. 138:459–466. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|