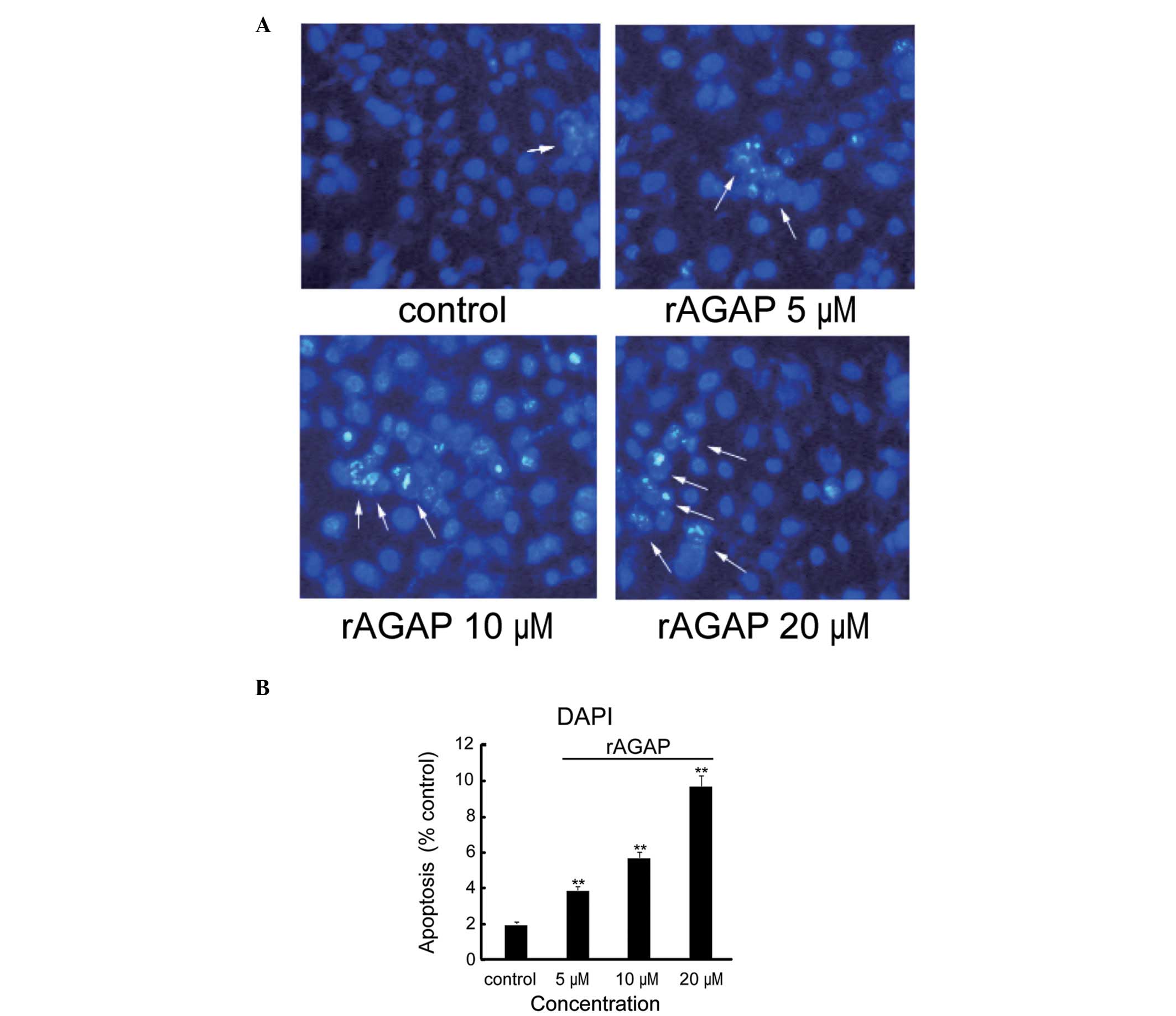
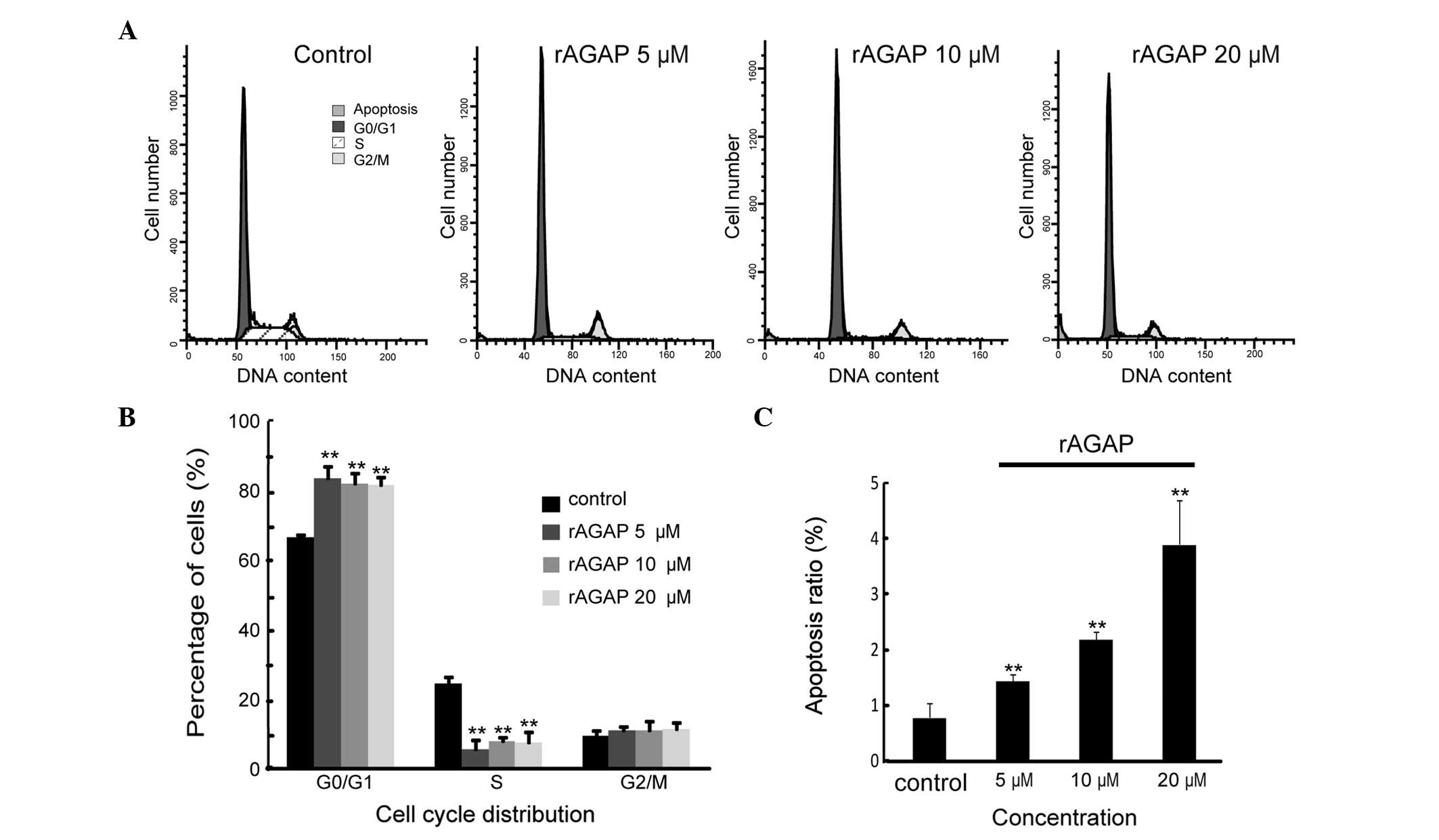
|
1.
|
Center MM, Jemal A, Smith RA and Ward E:
Worldwide variations in colorectal cancer. CA Cancer J Clin.
59:366–378. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D,
Mathers C and Parkin DM: Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in
2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 127:2893–2917. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Weekes J, Lam AK, Sebesan S and Ho YH:
Irinotecan therapy and molecular targets in colorectal cancer: a
systemic review. World J Gastroenterol. 15:3597–3602. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Zhao Y, Cai X, Ye T, et al:
Analgesic-antitumor peptide inhibits proliferation and migration of
SHG-44 human malignant glioma cells. J Cell Biochem. 112:2424–2434.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Cao P, Yu J, Lu W, et al: Expression and
purification of an antitumor-analgesic peptide from the venom of
Mesobuthus martensii Karsch by small ubiquitin-related modifier
fusion in Escherichia coli. Biotechnol Prog. 26:1240–1244.
2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Guo Y, Srinivasula SM, Druilhe A,
Fernandes-Alnemri T and Alnemri ES: Caspase-2 induces apoptosis by
releasing proapoptotic proteins from mitochondria. J Biol Chem.
277:13430–13437. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Amado RG, Wolf M, Peeters M, et al:
Wild-type KRAS is required for panitumumab efficacy in patients
with metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 26:1626–1634.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Karapetis CS, Khambata-Ford S, Jonker DJ,
et al: K-ras mutations and benefit from cetuximab in advanced
colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 359:1757–1765. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Deorukhkar A, Krishnan S, Sethi G and
Aggarwal BB: Back to basics: how natural products can provide the
basis for new therapeutics. Expert Opin Investig Drugs.
16:1753–1773. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Newman DJ and Cragg GM: Natural products
as sources of new drugs over the last 25 years. J Nat Prod.
70:461–477. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
du Plessis LH, Elgar D and du Plessis JL:
Southern African scorpion toxins: an overview. Toxicon. 51:1–9.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Rodriguez de la Vega RC and Possani LD:
Overview of scorpion toxins specific for Na+ channels and related
peptides: biodiversity, structure-function relationships and
evolution. Toxicon. 46:831–844. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Fan S, Sun Z, Jiang D, et al: BmKCT toxin
inhibits glioma proliferation and tumor metastasis. Cancer Lett.
291:158–166. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Das Gupta S, Debnath A, Saha A, et al:
Indian black scorpion (Heterometrus bengalensis Koch) venom
induced antiproliferative and apoptogenic activity against human
leukemic cell lines U937 and K562. Leukemia. 31:817–825. 2007.
|
|
15.
|
Gao R, Zhang Y and Gopalakrishnakone P:
Purification and N-terminal sequence of a serine proteinase-like
protein (BMK-CBP) from the venom of the Chinese scorpion (Buthus
martensii Karsch). Toxicon. 52:348–353. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Chaudhry MA: Base excision repair of
ionizing radiation-induced DNA damage in G1 and G2 cell cycle
phases. Cancer Cell Int. 7:152007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Sitko JC, Yeh B, Kim M, et al: SOCS3
regulates p21 expression and cell cycle arrest in response to DNA
damage. Cell Signal. 20:2221–2230. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Narbonne-Reveau K and Lilly M: The
Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor Dacapo promotes genomic stability
during premeiotic S phase. Mol Biol Cell. 20:1960–1969. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Liu S and Yamauchi H: p27-Associated G1
arrest induced by hinokitiol in human malignant melanoma cells is
mediated via down-regulation of pRb, Skp2 ubiquitin ligase, and
impairment of Cdk2 function. Cancer Lett. 286:240–249. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Connor MK, Kotchetkov R, Cariou S, et al:
CRM1/Ran-mediated nuclear export of p27(Kip1) involves a nuclear
export signal and links p27 export and proteolysis. Mol Biol Cell.
14:201–213. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Yakes FM, Chinratanalab W, Ritter CA, King
W, Seelig S and Arteaga CL: Herceptin-induced inhibition of
phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase and Akt is required for
antibody-mediated effects on p27, cyclin D1, and antitumor action.
Cancer Res. 62:4132–4141. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Kerkhoff E, Simpson JC, Leberfinger CB, et
al: The Spir actin organizers are involved in vesicle transport
processes. Curr Biol. 11:1963–1968. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Jones SM and Kazlauskas A:
Growth-factor-dependent mitogenesis requires two distinct phases of
signalling. Nat Cell Biol. 3:165–172. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Liang J, Zubovitz J, Petrocelli T, et al:
PKB/Akt phosphorylates p27, impairs nuclear import of p27 and
opposes p27-mediated G1 arrest. Nat Med. 8:1153–1160. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Liang J and Slingerland JM: Multiple roles
of the PI3K/PKB (Akt) pathway in cell cycle progression. Cell
Cycle. 2:339–345. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Petros AM, Olejniczak ET and Fesik SW:
Structural biology of the Bcl-2 family of proteins. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1644:83–94. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Chowdhury I, Tharakan B and Bhat GK:
Caspases - an update. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol.
151:10–27. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
D'Amelio M, Tino E and Cecconi F: The
apoptosome: emerging insights and new potential targets for drug
design. Pharm Res. 25:740–751. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Vivanco I and Sawyers CL: The
phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase AKT pathway in human cancer. Nat Rev
Cancer. 2:489–501. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Di Cristofano A and Pandolfi PP: The
multiple roles of PTEN in tumor suppression. Cell. 100:387–390.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Laurent-Puig P, Cayre A, Manceau G, et al:
Analysis of PTEN, BRAF, and EGFR status in determining benefit from
cetuximab therapy in wild-type KRAS metastatic colon cancer. J Clin
Oncol. 27:5924–5930. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Loupakis F, Pollina L, Stasi I, et al:
PTEN expression and KRAS mutations on primary tumors and metastases
in the prediction of benefit from cetuximab plus irinotecan for
patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol.
27:2622–2629. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Frattini M, Saletti P, Romagnani E, et al:
PTEN loss of expression predicts cetuximab efficacy in metastatic
colorectal cancer patients. Br J Cancer. 97:1139–1145. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Vyas S, Juin P, Hancock D, et al:
Differentiation-dependent sensitivity to apoptogenic factors in
PC12 cells. J Biol Chem. 279:30983–30993. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Majewski N, Nogueira V, Robey RB and Hay
N: Akt inhibits apoptosis downstream of BID cleavage via a
glucose-dependent mechanism involving mitochondrial hexokinases.
Mol Cell Biol. 24:730–740. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36.
|
Engelman JA, Luo J and Cantley LC: The
evolution of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases as regulators of growth
and metabolism. Nat Rev Genet. 7:606–619. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37.
|
Carnero A: The PKB/AKT pathway in cancer.
Curr Pharm Des. 16:34–44. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38.
|
Song G, Ouyang G and Bao S: The activation
of Akt/PKB signaling pathway and cell survival. J Cell Mol Med.
9:59–71. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39.
|
Liu J, Yin S, Reddy N, Spencer C and Sheng
S: Bax mediates the apoptosis-sensitizing effect of maspin. Cancer
Res. 64:1703–1711. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40.
|
Maianski NA, Geissler J, Srinivasula SM,
Alnemri ES, Roos D and Kuijpers TW: Functional characterization of
mitochondria in neutrophils: a role restricted to apoptosis. Cell
Death Differ. 11:143–153. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41.
|
Kang MH and Reynolds CP: Bcl-2 inhibitors:
targeting mitochondrial apoptotic pathways in cancer therapy. Clin
Cancer Res. 15:1126–1132. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|