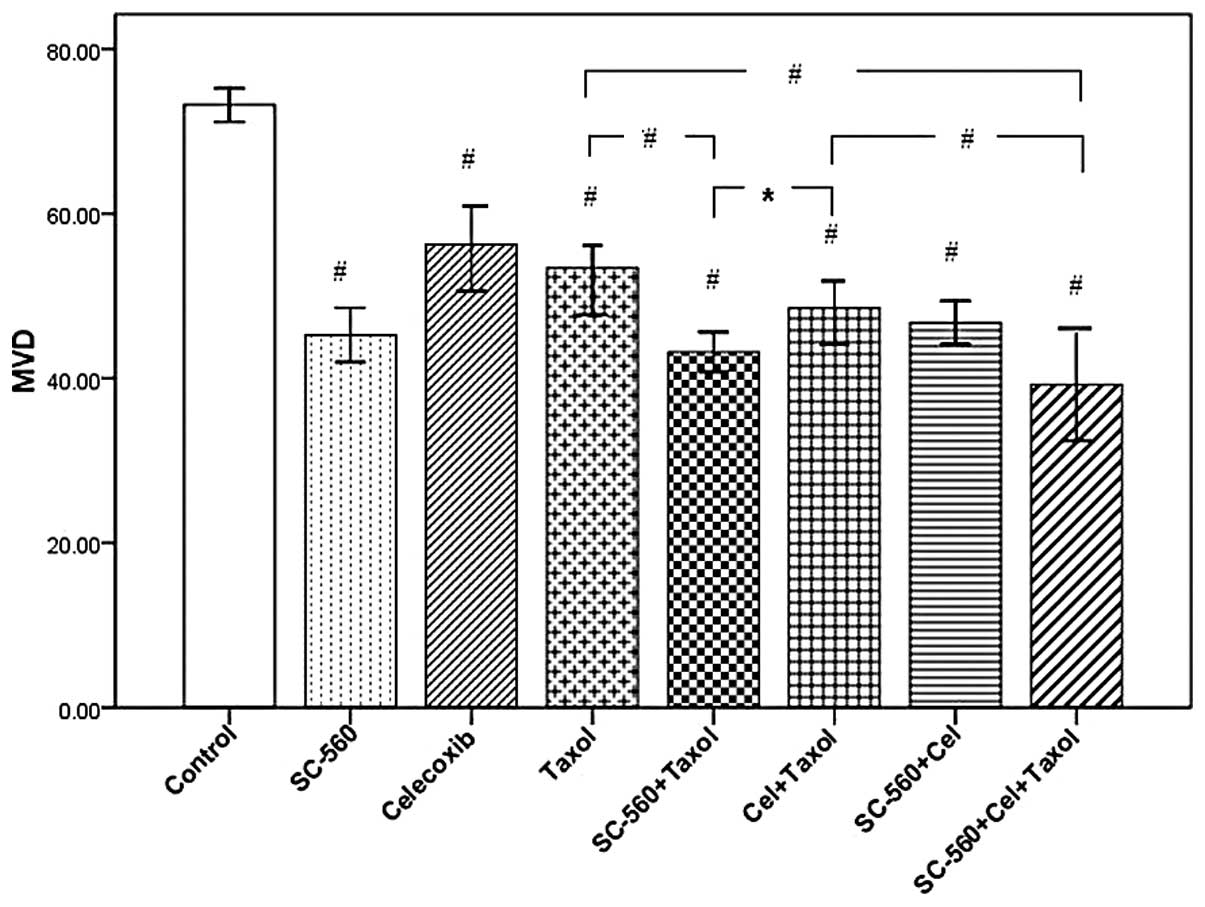
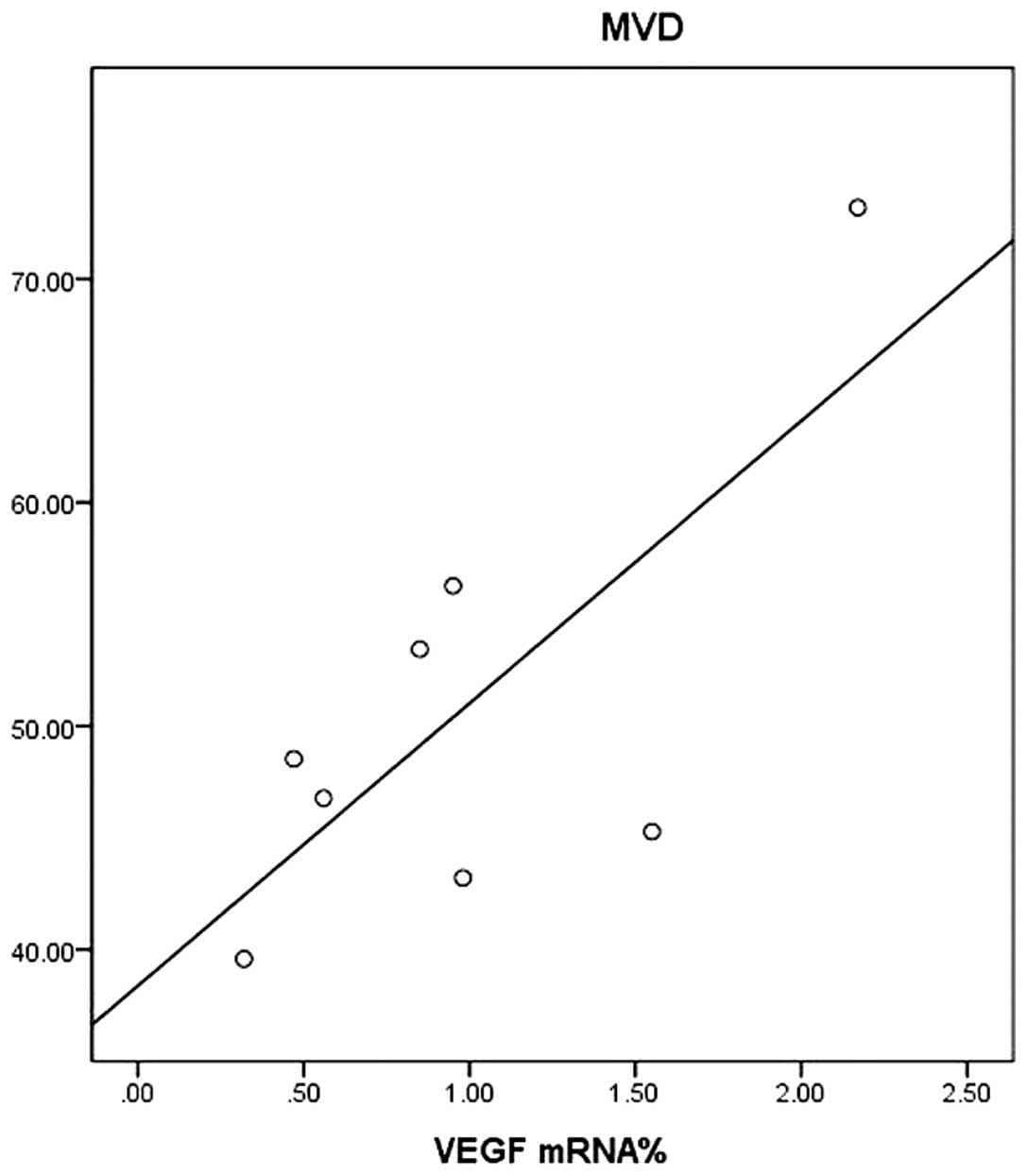
|
1
|
Ozols RF: Future directions in the
treatment of ovarian cancer. Semin Oncol. 29:32–42. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yokoyama Y, Sakamoto T, Sato S and Saito
Y: Evaluation of cytoreductive surgery with pelvic and paraaortic
lymphadenectomy and intermittent cisplatin-based combination
chemotherapy for improvement of long-term survival in ovarian
cancer. Eur J Gynaecol Oncol. 20:361–366. 1999.
|
|
3
|
Ozols RF: Recurrent ovarian cancer:
evidence-based treatment. J Clin Oncol. 20:1161–1163.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kohler DR and Goldspiel BR: Evaluation of
new drugs: Paclitaxel (taxol). Pharmacotherapy. 14:3–34. 1994.
|
|
5
|
Pignata S, Scambia G, Ferrandina G, et al:
Carboplatin plus paclitaxel versus carboplatin plus pegylated
liposomal doxorubicin as first-line treatment for patients with
ovarian cancer: the MITO-2 randomized phase III trial. J Clin
Oncol. 29:3628–3635. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang Y, Qu Y, Niu XL, Sun WJ, Zhang XL and
Li LZ: Autocrine production of interleukin-8 confers cisplatin and
paclitaxel resistance in ovarian cancer cells. Cytokine.
56:365–375. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Subbaramaiah K, Hart JC, Norton L and
Dannenberg AJ: Microtubule-interfering agents stimulate the
transcription of cyclooxygenase-2. Evidence for involvement of
ERK1/2 AND p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways. J Biol
Chem. 275:14838–14845. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Sorokin A: Cyclooxygenase-2: potential
role in regulation of drug efflux and multidrug resistance
phenotype. Curr Pharm Des. 10:647–657. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Uddin S, Ahmed M, Hussain A, Assad L,
Al-Dayel F, Bavi P, Al-Kuraya KS and Munkarah A: Cyclooxygenase-2
inhibitior inhibits PI3-K/AKT kinase activity in epithelial ovarian
cancer. Int J Cancer. 126:382–394. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gu P, Su Y, Guo S, Teng L, Xu Y, Qi J,
Gong H and Cai Y: Over-expression of COX-2 induces human ovarian
cancer cells (CAOV-3) viability, migration and proliferation in
association with PI3-k/Akt activation. Cancer Invest. 26:822–829.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Athanassiadou P, Grapsa D, Athanassiades
P, Gonidi M, Athanassiadou AM, Tsipis A and Patsouris E: The
prognostic significance of COX-2 and survivin expression in ovarian
cancer. Pathol Res Pract. 204:241–249. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ferrandina G, Ranelletti FO, Martinelli E,
Paglia A, Zannoni GF and Scambia G: Cyclooxygenase-2 (Cox-2)
expression and resistance to platinum versus platinum/paclitaxel
containing chemotherapy in advanced ovarian cancer. BMC Cancer.
6:1822006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Masferrer JL, Leahy KM, Koki AT, Zweifel
BS, Settle SL, Woerner BM, Edwards DA, Flickinger AG, Moore RJ and
Seibert K: Antiangiogenic and antitumor activities of
cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors. Cancer Res. 60:1306–1311.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Olsen SR: Taxanes and COX-2 inhibitors
from molecular pathways to clinical practice. Biomed Pharmacother.
59(Suppl 2): S306–S310. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Merchan JR, Jayaram DR, Supko JG, He X,
Bubley GJ and Sukhatme VP: Increased endothelial uptake of
paclitaxel as a potential mechanism for its antiangiogenic effects:
potentiation by COX-2 inhibition. Int J Cancer. 113:490–498. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gupta RA, Tejada LV, Tong BJ, Das SK,
Morrow JD, Dey SK and Dubois RN: Cyclooxygenase-1 is overexpressed
and promotes angiogenic growth factor production in ovarian cancer.
Cancer Res. 63:906–911. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Daikoku T, Wang D, Tranguch S, Morrow JD,
Orsulic S, DuBois RN and Dey SK: Cyclooxygenase-1 is a potential
target for prevention and treatment of ovarian epithelial cancer.
Cancer Res. 65:3735–3744. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Daikoku T, Tranquch S, Trofimova IN,
Dinulescu DM, Jacks T, Nikitin AY, Connolly DC and Dey SK:
Cyclooxygenase-1 is overexpressed in multiple genetically
engineered mouse models of epithelial ovarian cancer. Cancer Res.
66:2527–2531. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li W, Wang J, Jiang HR, Xu XL, Zhang J,
Liu ML and Zhai LY: Combined effects of cyclooxygenase-1 and
cyclooxygenase-2 selective inhibitors on ovarian carcinoma in vivo.
Int J Mol Sci. 12:668–681. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Williams CS, Watson AJ, Sheng H, Helou R,
Shao J and DuBois RN: Celecoxib prevents tumor growth in vivo
without toxicity to normal gut: lack of correlation between in
vitro and in vivo models. Cancer Res. 60:6045–6051. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gerdes J, Lemke H, Baisch H, Wacker HH,
Schwab U and Stein H: Cell cycle analysis of a cell proliferation
associated human nuclear antigen defined by the monoclonal antibody
Ki-67. J Immunol. 133:1710–1715. 1984.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Weidner N, Folkman J, Pozza F, Bevilacqua
P, Allred EN, Moore DH, Meli S and Gasparini G: Tumor angiogenesis:
a new significant and independent prognostic indicator in
early-stage breast carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 84:1875–1887.
1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
del Vecchio MT, Leoncini L, Buerki K,
Kraft R, Megha T, Barbini P, Tosi P and Cottier H: Diffuse
controcytic and/or centroblastic malignant non-Hodgkins lymphomas:
comparison of mitotic and pyknotic (apoptotic) indices. Int J
Cancer. 47:38–43. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ratnasinghe D, Daschner PJ, Anver MR,
Kasprzak BH, Taylor PR, Yeh GC and Tangrea JA: Cyclooxygenase-2,
P-glycoprotein-170 and drug resistance; is chemoprevention against
multidrug resistance possible? Anticancer Res. 21:2141–2147.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Altorki NK, Keresztes RS, Port JL, Libby
DM, Korst RJ, Flieder DB, Ferrara CA, Yankelevitz DF, Subbaramaiah
K, Pasmantier MW and Dannenberg AJ: Celecoxib, a selective
cyclo-Oxygenase-2 inhibitor, enhances the response to preoperative
paclitaxel and carboplatin in early-stage non-small-cell lung
cancer. J Clin Oncol. 21(14): 2645–2650. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Gasparini G, Meo S, Comella G, Stani SC,
Mariani L, Gamucci T, Avallone A, LoVullo S, Mansueto G, Bonginelli
P, Gattuso D and Gion M: The combination of the selective
cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor celecoxib with weekly paclitaxel is a
safe and active second-line therapy for non-small cell lung cancer
a phase II study with biological correlates. Cancer J. 11:209–216.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Altorki NK, Christos P, Port JL, Lee PC,
Mirza F, Spinelli C, Keresztes RS, Beneck D, Paul S, Stiles BM,
Zhang Y and Schrump DS: Preoperative taxane-based chemotherapy and
celecoxib for carcinoma of the esophagus and gastroesophageal
junction: results of a phase 2 trial. J Thorac Oncol. 6:1121–1127.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bhatt RS, Merchan J, Parker R, Wu HK,
Zhang L, Seery V, Heymach JV, Atkins MB, McDermott D and Sukhatme
VP: A phase 2 pilot trial of low-dose, continuous infusion, or
“metronomic” paclitaxel and oral celecoxib in patients with
metastatic melanoma. Cancer. 116:1751–1756. 2010.
|
|
29
|
Mutter R, Lu B, Carbone DP, Csiki I,
Moretti L, Johnson DH, Morrow JD, Sandler AB, Shyr Y, Ye F and Choy
H: A phase II study of celecoxib in combination with paclitaxel,
carboplatin, and radiotherapy for patients with inoperable stage
IIIA/B non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 15:2158–2165.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kitamura T, Itoh M, Noda T, Matsuura M and
Wakabayashi K: Combined effects of cyclooxygenase-1 and
cyclooxygenase-2 selective inhibitors on intestinal tumorigenesis
in adenomatous polyposis coli gene knockout mice. Int J Cancer.
109:576–580. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yamamoto S, Konishi I, Mandai M, Kuroda H,
Komatsu T, Nanbu K, Sakahara H and Mori T: Expression of vascular
endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in epithelia ovarian neoplasms:
correlation with clinicopathology and patient survival and analysis
of serum VEGF levels. Br J Cancer. 76:1221–1227. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Carmeliet P and Jain RK: Angiogenesis in
cancer and other diseases. Nature. 407:249–257. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Folkman J: Angiogenesis: an organizing
principle for drug discovery? Nat Rev Drug Discov. 6:273–286. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Weidner N, Semple JP, Welch WR and Folkman
J: Tumor angiogenesis and metastasis - correlation in invasive
breast carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 324:1–8. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Li W, Xu RJ, Lin ZY, Zhuo GC and Zhang HH:
Effects of a cyclooxygenase-1-selective inhibitor in a mouse model
of ovarian cancer, administered alone or in combination with
ibuprofen, a nonselective cyclooxygenase inhibitor. Med Oncol.
26:170–177. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Dore M, Cote LC, Mitchell A and Sirois J:
Expression of prostaglandin G/H synthase type 1, but not type 2, in
human ovarian adenocarcinomas. J Histochem Cytochem. 46:77–84.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Gastman BR: Apoptosis and its clinical
impact. Head Neck. 23:409–425. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Foa R, Norton L and Seidman AD: Taxol
(paclitaxel): A novel antimicrotubule agent with remarkable
anti-neoplastic activity. Int J Clin Lab Res. 24:6–14. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Leahy KM, Ornberg RL, Wang Y, Zweifel BS,
Koki AT and Masferrer JL: Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibition by celecoxib
reduces proliferation and induces apoptosis in angiogenic
endothelial cells in vivo. Cancer Res. 62:625–631. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Daikoku T, Tranguch S, Chakrabarty A, Wang
D, Khabele D, Orsulic S, Morrow JD, Dubois RN and Dey SK:
Extracellular signal-regulated kinase is a target of
cyclooxygenase-1-peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-delta
signaling in epithelial ovarian cancer. Cancer Res. 67:5285–5292.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Bottone FG Jr, Martinez JM, Alston-Mills B
and Eling TE: Gene modulation by Cox-1 and Cox-2 specific
inhibitors in human colorectal carcinoma cancer cells.
Carcinogenesis. 25:349–357. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zhu J, Song X, Lin HP, Young DC, Yan S,
Marquez VE and Chen CS: Using cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors as
molecular platforms to develop a new class of apoptosis-inducing
agents. J Natl Cancer Inst. 94:1745–1757. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|