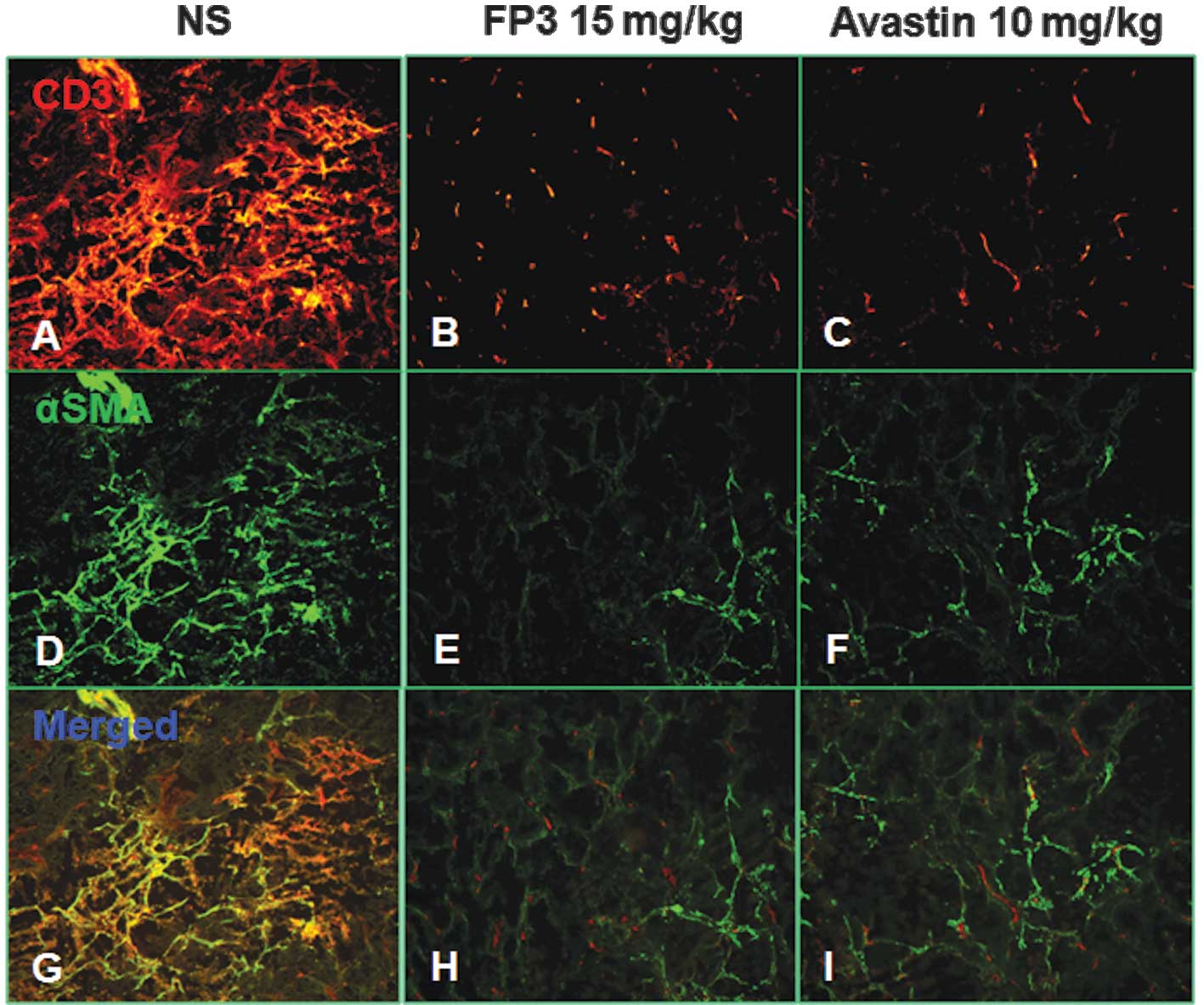
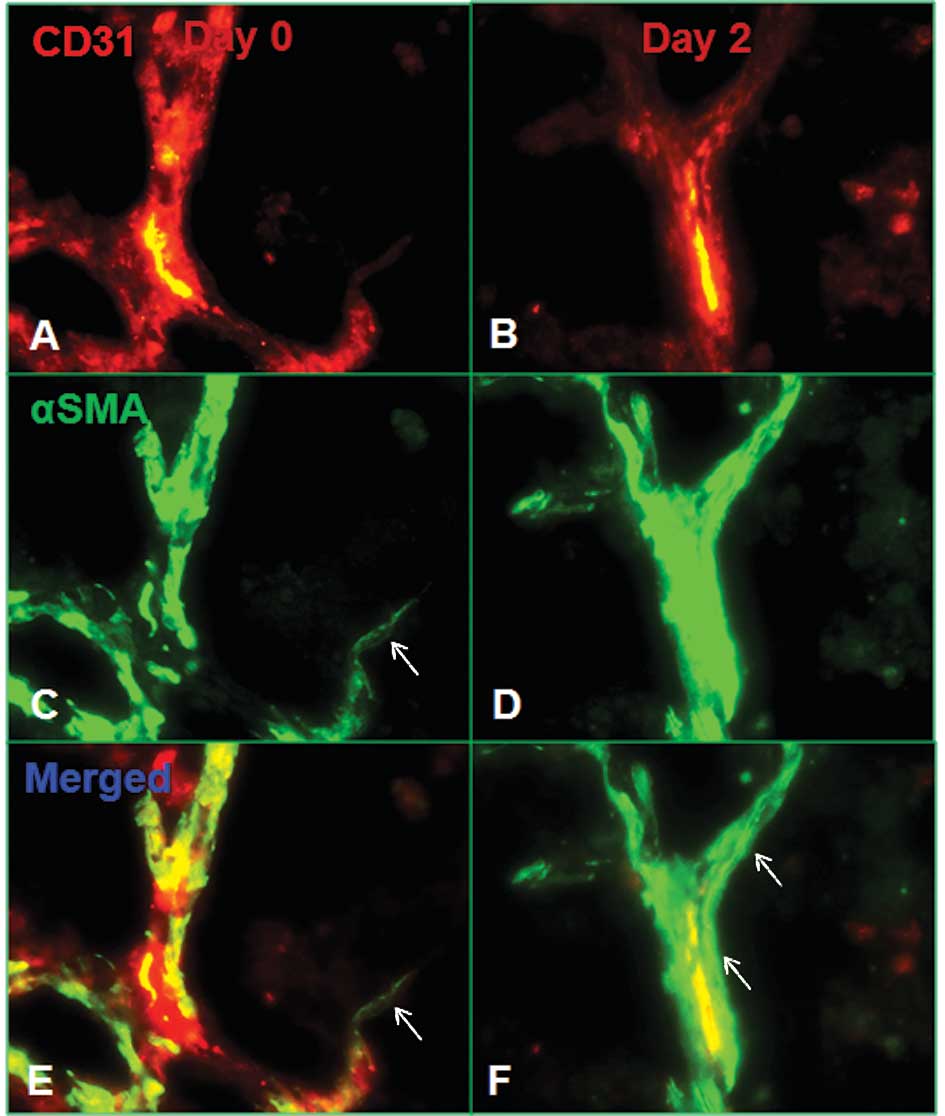
|
1
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: the next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Paku S and Paweletz N: First steps of
tumor-related angiogenesis. Lab Invest. 65:334–346. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Holash J, Maisonpierre PC, Compton D,
Boland P, Alexander CR, Zagzag D, Yancopoulos GD and Wiegand SJ:
Vessel cooption, regression, and growth in tumors mediated by
angiopoietins and VEGF. Science. 284:1994–1998. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Döme B, Paku S, Somlai B and Tímár J:
Vascularization of cutaneous melanoma involves vessel co-option and
has clinical significance. J Pathol. 197:355–362. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Vermeulen PB, Colpaert C, Salgado R,
Royers R, Hellemans H, Van Den Heuvel E, Goovaerts G, Dirix LY and
Van Marck E: Liver metastases from colorectal adenocarcinomas grow
in three patterns with different angiogenesis and desmoplasia. J
Pathol. 195:336–342. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Paku S, Kopper L and Nagy P: Development
of the vasculature in ‘pushing-type’ liver metastases of an
experimental colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer. 115:893–902.
2005.
|
|
7
|
Kurz H, Burri PH and Djonov VG:
Angiogenesis and vascular remodeling by intussusception: from form
to function. News Physiol Sci. 18:65–70. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Osawa M, Masuda M, Kusano K and Fujiwara
K: Evidence for a role of platelet endothelial cell adhesion
molecule-1 in endothelial cell mechanosignal transduction: is it a
mechanoresponsive molecule? J Cell Biol. 158:773–785. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sundberg C, Nagy JA, Brown LF, Feng D,
Eckelhoefer IA, Manseau EJ, Dvorak AM and Dvorak HF: Glomeruloid
microvascular proliferation follows adenoviral vascular
permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor-164 gene
delivery. Am J Pathol. 158:1145–1160. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Asahara T and Kawamoto A: Endothelial
progenitor cells for postnatal vasculogenesis. Am J Physiol Cell
Physiol. 287:572–579. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Maniotis AJ, Folberg R, Hess A, Seftor EA,
Gardner LM, Pe'er J, Trent JM, Meltzer PS and Hendrix MJ: Vascular
channel formation by human melanoma cells in vivo and in
vitro: vasculogenic mimicry. Am J Pathol. 155:739–752. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hendrix MJ, Seftor EA, Hess AR and Seftor
RE: Vasculogenic mimicry and tumour-cell plasticity: lessons from
melanoma. Nat Rev Cancer. 3:411–421. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ferrara N: Vascular endothelial growth
factor: basic science and clinical progress. Endocr Rev.
25:581–611. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hicklin DJ and Ellis LM: Role of the
vascular endothelial growth factor pathway in tumor growth and
angiogenesis. J Clin Oncol. 23:1011–1027. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ferrara N, Gerber HP and LeCouter J: The
biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat Med. 9:669–676. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Teng LS, Jin KT, He KF, Wang HH, Cao J and
Yu DC: Advances in combination of antiangiogenic agents targeting
VEGF-binding and conventional chemotherapy and radiation for cancer
treatment. J Chin Med Assoc. 73:281–288. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Teng LS, Jin KT, He KF, Zhang J, Wang HH
and Cao J: Clinical applications of VEGF-trap (aflibercept) in
cancer treatment. J Chin Med Assoc. 73:449–456. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jin K, He K, Teng F, Li G, Wang H, Han N,
Xu Z, Cao J, Wu J, Yu D and Teng L: FP3: a novel VEGF blocker with
antiangiogenic effects in vitro and antitumour effects in vivo.
Clin Transl Oncol. 13:878–884. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang M, Zhang J, Yan M, Li H, Yang C and
Yu D: Recombinant anti-vascular endothelial growth factor fusion
protein efficiently suppresses choridal neovasularization in
monkeys. Mol Vis. 14:37–49. 2008.
|
|
20
|
Zhang M, Yu D, Yang C, Xia Q, Li W, Liu B
and Li H: The pharmacology study of a new recombinant human VEGF
receptor-fc fusion protein on experimental choroidal
neovascularization. Pharm Res. 26:204–210. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zhang M, Zhang J, Yan M, Luo D, Zhu W,
Kaiser PK and Yu DC; KH902 Phase 1 Study Group. A phase 1 study of
KH902, a vascular endothelial growth factor receptor decoy, for
exudative age-related macular degeneration. Ophthalmology.
118:672–678. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Inai T, Mancuso M, Hashizume H, Baffert F,
Haskell A, Baluk P, Hu-Lowe DD, Shalinsky DR, Thurston G,
Yancopoulos GD and McDonald DM: Inhibition of vascular endothelial
growth factor (VEGF) signaling in cancer causes loss of endothelial
fenestrations, regression of tumor vessels, and appearance of
basement membrane ghosts. Am J Pathol. 165:35–52. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Jin K, Teng L, Shen Y, He K, Xu Z and Li
G: Patient-derived human tumour tissue xenografts in
immunodeficient mice: a systematic review. Clin Transl Oncol.
12:473–480. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jin K, He K, Li G and Teng L: Personalized
cancer therapy using a patient-derived tumor tissue xenograft
model: a translational field worthy of exploring further? Pers Med.
7:597–606. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Jin K, He K, Teng F, Han N, Li G, Xu Z and
Teng L: Heterogeneity in primary tumors and corresponding
metastases: could it provide us with any hints to personalize
cancer therapy? Pers Med. 8:175–182. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Jin K, He K, Han N, Li G, Wang H, Xu Z,
Jiang H, Zhang J and Teng L: Establishment of a PDTT xenograft
model of gastric carcinoma and its application in personalized
therapeutic regimen selection. Hepatogastroenterology.
58:1814–1822. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Mancuso MR, Davis R, Norberg SM, O'Brien
S, Sennino B, Nakahara T, Yao VJ, Inai T, Brooks P, Freimark B,
Shalinsky DR, Hu-Lowe DD and McDonald DM: Rapid vascular regrowth
in tumors after reversal of VEGF inhibition. J Clin Invest.
116:2610–2621. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Morikawa S, Baluk P, Kaidoh T, Haskell A,
Jain RK and McDonald DM: Abnormalities in pericytes on blood
vessels and endothelial sprouts in tumors. Am J Pathol.
160:985–1000. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Baluk P, Morikawa S, Haskell A, Mancuso M
and McDonald DM: Abnormalities of basement membrane on blood
vessels and endothelial sprouts in tumors. Am J Pathol.
163:1801–1815. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Willett CG, Boucher Y, Di Tomaso E, Duda
DG, Munn LL, Tong RT, Chung DC, Sahani DV, Kalva SP, Kozin SV, et
al: Direct evidence that the VEGF-specific antibody bevacizumab has
antivascular effects in human rectal cancer. Nat Med. 10:145–147.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Baffert F, Le T, Sennino B, Thurston G,
Kuo CJ, Hu-Lowe D and McDonald DM: Cellular changes in normal blood
capillaries undergoing regression after inhibition of VEGF
signaling. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 290:H547–559. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Byrne AT, Ross L, Holash J, Nakanishi M,
Hu L, Hofmann JI, Yancopoulos GD and Jaffe RB: Vascular endothelial
growth factor-trap decreases tumor burden, inhibits ascites, and
causes dramatic vascular remodeling in an ovarian cancer model.
Clin Cancer Res. 9:5721–5728. 2003.
|
|
33
|
Jain RK: Normalizing tumor vasculature
with anti-angiogenic therapy: a new paradigm for combination
therapy. Nat Med. 7:987–989. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Jain RK: Normalization of tumor
vasculature: an emerging concept in antiangiogenic therapy.
Science. 307:58–62. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|