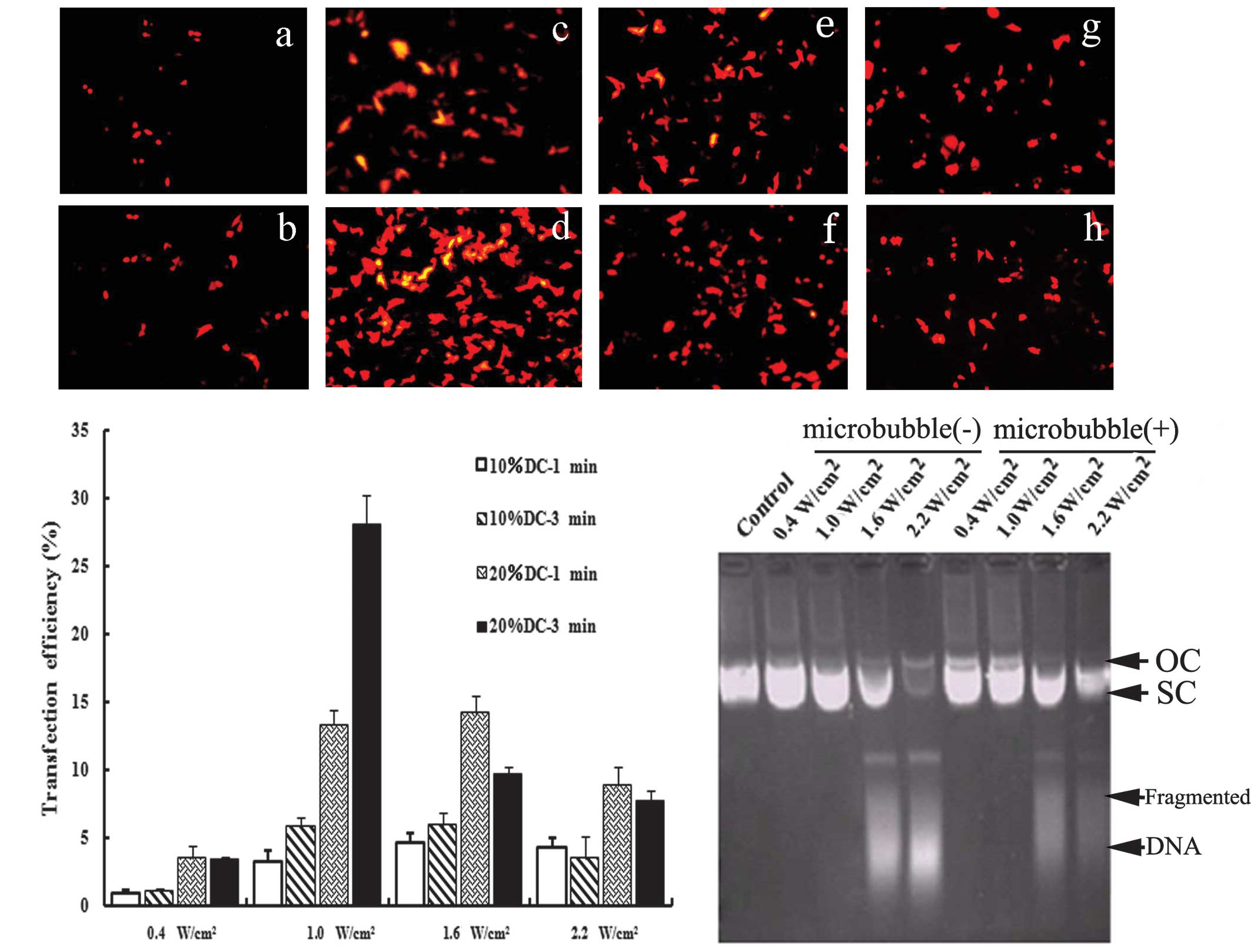
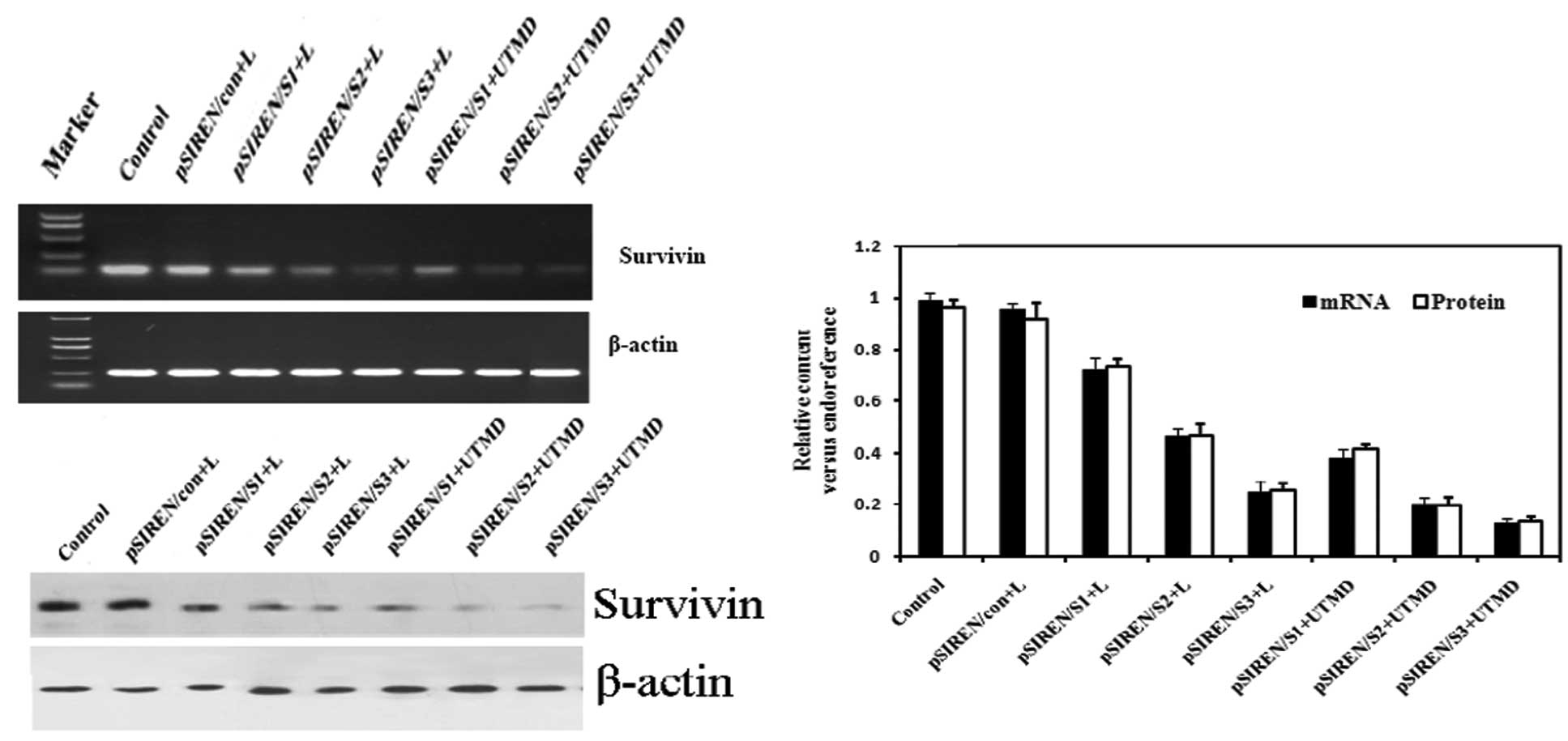
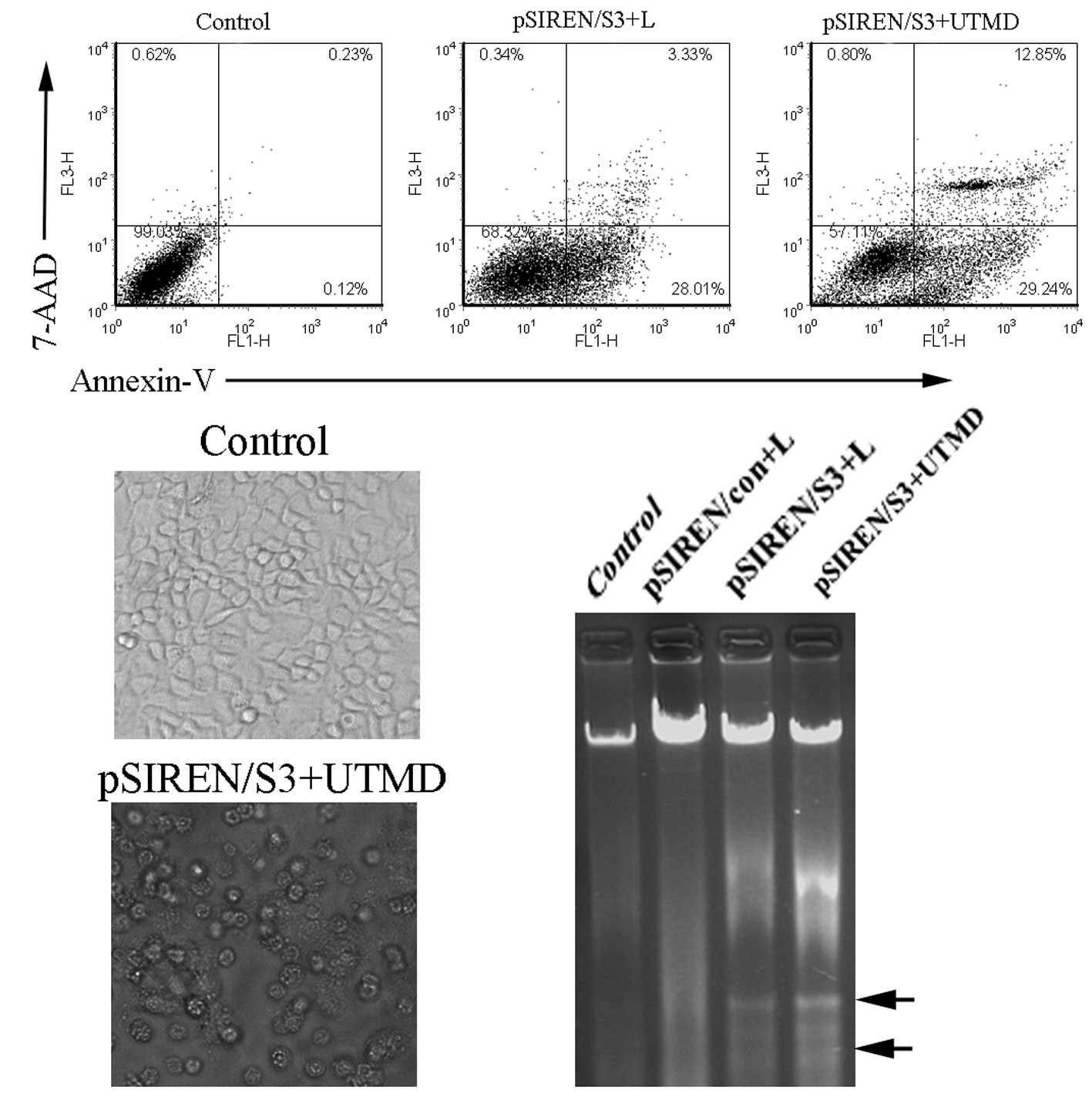
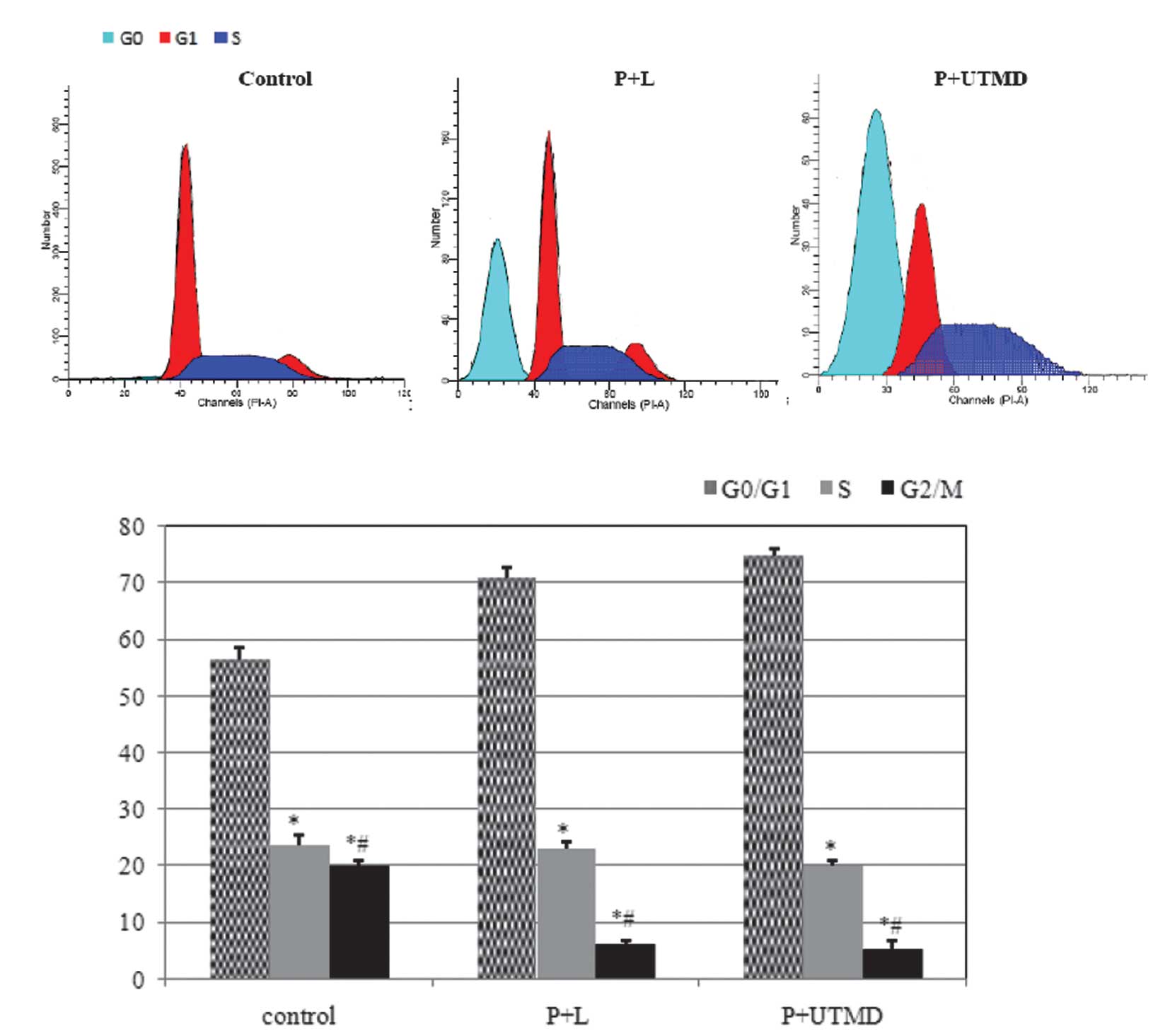
|
1
|
Evan GI and Vousden KH: Proliferation,
cell cycle and apoptosis in cancer. Nature. 411:342–348. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lakhani SA, Masud A, Kuida K, Porter GA
Jr, Booth CJ, Mehal WZ, Inayat I and Flavell RA: Caspases 3 and 7:
key mediators of mitochondrial events of apoptosis. Science.
311:847–851. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chipuk JE, Kuwana T, Bouchier-Hayes L,
Droin NM, Newmeyer DD, Schuler M and Green DR: Direct activation of
Bax by p53 mediates mitochondrial membrane permeabilization and
apoptosis. Science. 303:1010–1014. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Knauer SK, Krämer OH, Knösel T, Engels K,
Rödel F, Kovács AF, Dietmaier W, Klein-Hitpass L, Habtemichael N,
Schweitzer A, Brieger J, Rödel C, Mann W, Petersen I, Heinzel T and
Stauber RH: Nuclear export is essential for the tumor-promoting
activity of survivin. FASEB J. 21:207–216. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Carvalho A, Carmena M, Sambade C, Earnshaw
WC and Wheatley SP: Survivin is required for stable checkpoint
activation in taxol-treated HeLa cells. J Cell Sci. 116:2987–2998.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Caldas H, Holloway MP, Hall BM, Qualman SJ
and Altura RA: Survivin-directed RNA interference cocktail is a
potent suppressor of tumour growth in vivo. J Med Genet.
43:119–128. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kappler M, Bache M, Bartel F, Kotzsch M,
Panian M, Würl P, Blümke K, Schmidt H, Meye A and Taubert H:
Knockdown of survivin expression by small interfering RNA reduces
the clonogenic survival of human sarcoma cell lines independently
of p53. Cancer Gene Ther. 11:186–193. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liu Q, Fu H, Xing R, Tie Y, Zhu J, Sun Z
and Zheng X: Survivin knockdown combined with apoptin
overexpression inhibits cell growth significantly. Cancer Biol
Ther. 7:1053–1060. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Vlassov AV, Korba B, Farrar K, Mukerjee S,
Seyhan AA, Ilves H, Kaspar RL, Leake D, Kazakov SA and Johnston BH:
shRNAs targeting hepatitis C: effects of sequence and structural
features, and comparision with siRNA. Oligonucleotides. 17:223–236.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sui G, Soohoo C, Affar el B, Gay F and Shi
Y, Forrester WC and Shi Y: A DNA vector-based RNAi technology to
suppress gene expression in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 99:5515–5520. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
McAnuff MA, Rettig GR and Rice KG: Potency
of siRNA versus shRNA mediated knockdown in vivo. J Pharm Sci.
96:2922–2930. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Boudreau RL, Monteys AM and Davidson BL:
Minimizing variables among hairpin-based RNAi vectors reveals the
potency of shRNAs. RNA. 14:1834–1844. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Pardridge WM: shRNA and siRNA delivery to
the brain. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 59:141–152. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Guo DP, Li XY, Sun P, Tang YB, Chen XY,
Chen Q, Fan LM, Zang B, Shao LZ and Li XR: Utrasound-targeted
microbubble destruction improves the low density lipoprotein
receptor gene expression in HepG2 cells. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 343:470–474. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen ZY, Xie MX, Wang XF, Lü Q and Ding
SW: Efficient gene delivery to myocardium with ultrasound targeted
microbubble destruction and polyethylenimine. J Huazhong Univ Sci
Technolog Med Sci. 28:613–617. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen ZY, Xie MX, Wang XF and Lü Q: Effects
of lipid shell microbubble on ultrasound mediated EGFP gene
delivery to transplanted tumors: initial experience. Chin-Ger J
Clin Oncol. 7:424–428. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Kinoshita M and Hynynen K: A novel method
for the intracellular delivery of siRNA using microbubble-enhanced
focused ultrasound. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 335:393–399. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Saito M, Mazda O, Takahashi KA, Arai Y,
Kishida T, Shin-Ya M, Inoue A, Tonomura H, Sakao K, Morihara T,
Imanishi J, Kawata M and Kubo T: Sonoporation mediated transduction
of pDNA/siRNA into joint synovium in vivo. J Orthop Res.
25:1308–1316. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tran MA, Gowda R, Sharma A, Park EJ, Adair
J, Kester M, Smith NB and Robertson GP: Targeting V600EB-Raf and
Akt3 using nanoliposomal-small interfering RNA inhibits cutaneous
melanocytic lesion development. Cancer Res. 68:7638–7649. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Vandenbroucke RE, Lentacker I, Demeester
J, De Smedt SC and Sanders NN: Ultrasound assisted siRNA delivery
using PEG-siPlex loaded microbubbles. J Control Release.
126:265–273. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang J, Zheng Y, Yang F, Zhao P and Li H:
Survivin small interfering RNA transfected with a microbubble and
ultrasound exposure inducing apoptosis in ovarian carcinoma cells.
Int J Gynecol Cancer. 20:500–506. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen ZY, Liang K, Xie MX, Wang XF, Lü Q
and Zhang J: Novel ultrasound-targeted microbubble destruction
mediated short hairpin RNA plasmid transfection targeting survivin
inhibits gene expression and induces apoptosis of HeLa cells. Mol
Biol Rep. 36:2059–2067. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Chen ZY, Liang K, Liu JH, Xie MX, Wang XF,
Lü Q, Zhang J and Fang LY: Enhancement of survivin gene
downregulation and cell apoptosis by a novel combination: liposome
microbubbles and ultrasound exposure. Med Oncol. 26:491–500. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ling X and Li F: Silencing of
antiapoptotic survivin gene by multiple approaches of RNA
interference technology. Biotechniques. 36:450–454. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mehier-Humbert S, Bettinger T, Yan F and
Guy RH: Ultrasound- mediated gene delivery: kinetics of plasmid
internalization and gene expression. J Control Release.
104:203–211. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zarnitsyn VG and Prausnitz MR: Physical
parameters influencing optimization of ultrasound-mediated DNA
transfection. Ultrasound Med Biol. 30:527–538. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kodama T, Tomita Y, Koshiyama K and
Blomley MJ: Transfection effect of microbubbles on cells in
superposed ultrasound waves and behavior of cavitation bubble.
Ultrasound Med Biol. 32:905–914. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li H, Wang S, Zhu T, Zhou J, Xu Q, Lu Y
and Ma D: Pin1 contributes to cervical tumorigenesis by regulating
cyclin D1 expression. Oncol Rep. 16:491–496. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ochiai N, Uchida R, Fuchida S, Okano A,
Okamoto M, Ashihara E, Inaba T, Fujita N, Matsubara H and Shimazaki
C: Effect of farnesyl transferase inhibitor R115777 on the growth
of fresh and cloned myeloma cells in vitro. Blood. 102:3349–3353.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Liang HD, Lu QL, Xue SA, Halliwell M,
Kodama T, Cosgrove DO, Stauss HJ, Partridge TA and Blomley MJ:
Optimisation of ultrasound-mediated gene transfer (sonoporation) in
skeletal muscle cells. Ultrasound Med Biol. 30:1523–1529. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kuo JH, Jan MS and Sung KC: Evaluation of
the stability of polymer-based plasmid DNA delivery systems after
ultrasound exposure. Int J Pharm. 257:75–84. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang R, Ma L, Zheng M, Ren J, Wang T,
Meng Y, Zhao J, Jia L, Yao L, Han H, Li K and Yang A: Survivin
knockdown by short hairpin RNA abrogates the growth of human
hepatocellular carcinoma xenografts in nude mice. Cancer Gene Ther.
17:275–288. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|