|
1
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J and Ward E: Cancer
statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 60:277–300. 2010.
|
|
2
|
Mandel JS, Bond JH, Church TR, et al:
Reducing mortality from colorectal cancer by screening for fecal
occult blood. Minnesota Colon Cancer Control Study. N Engl J Med.
328:1365–1371. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jeon CH, Lee HI, Shin IH and Park JW:
Genetic alterations of APC, K-ras, p53, MSI, and MAGE in Korean
colorectal cancer patients. Int J Colorectal Dis. 23:29–35. 2008.
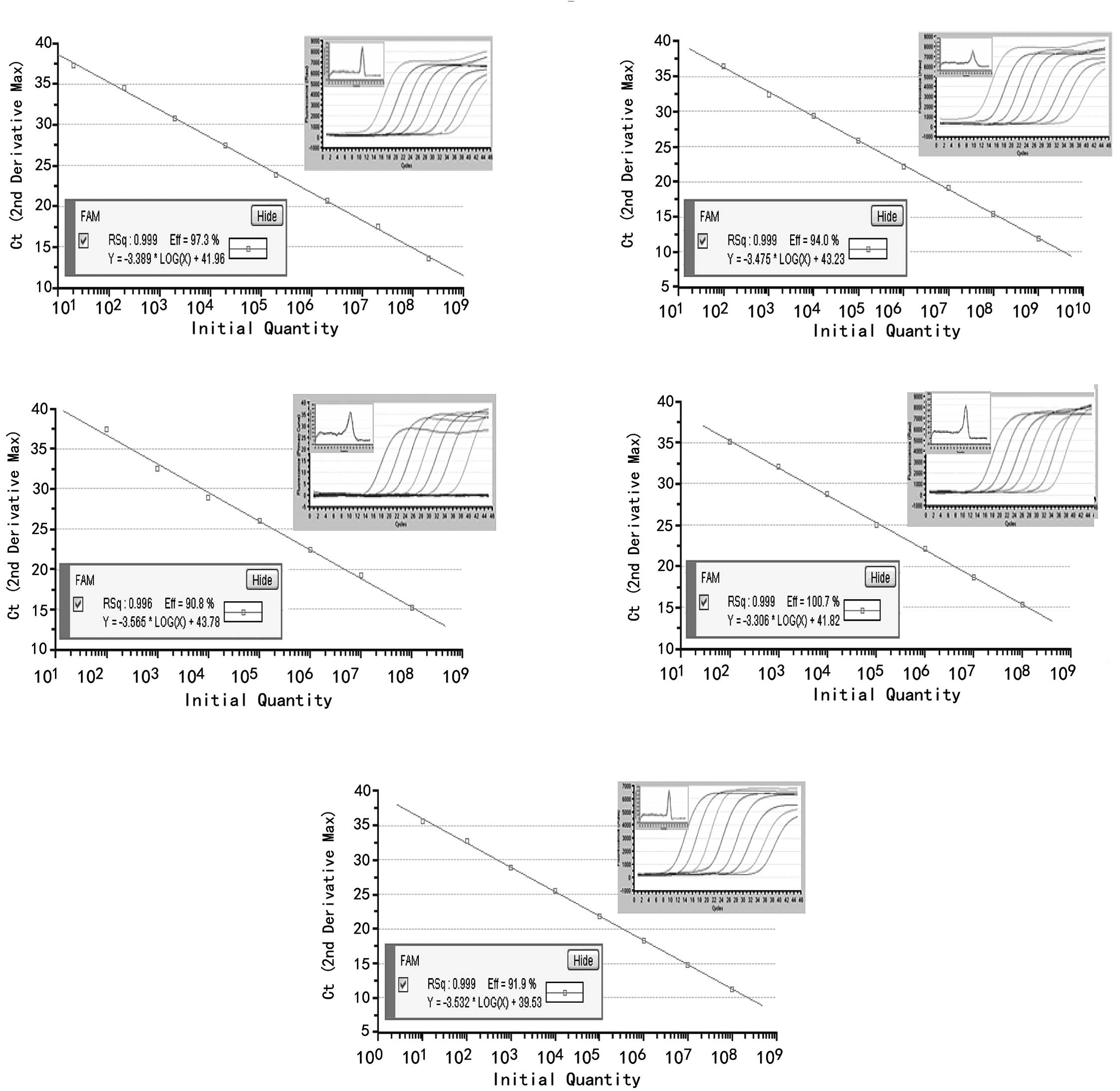
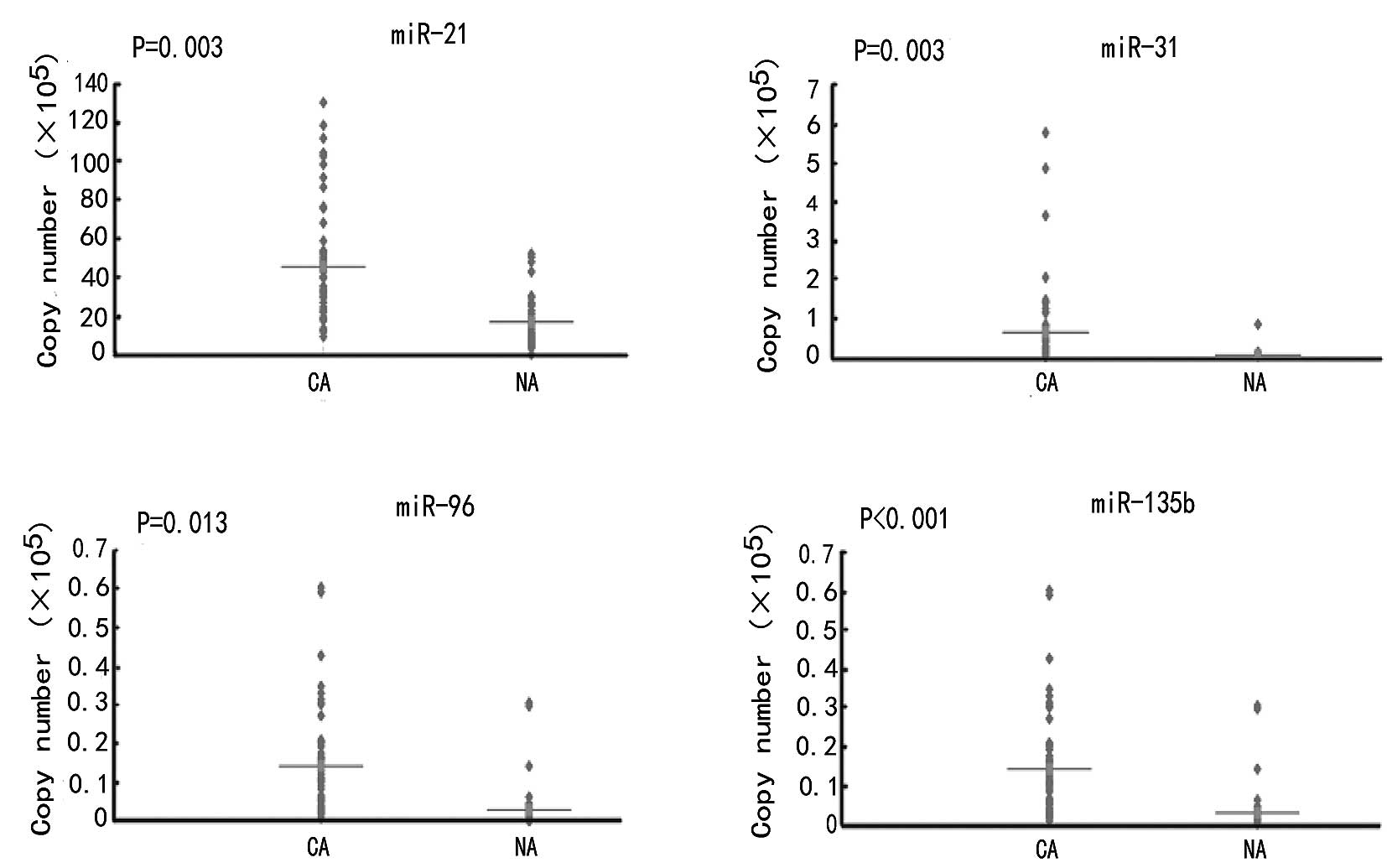
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Slack FJ and Weidhaas JB: MicroRNA in
cancer prognosis. N Engl J Med. 359:2720–2722. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Huang GL, Zhang XH, Guo GL, et al:
Clinical significance of miR-21 expression in breast cancer:
SYBR-Green I-based real-time RT-PCR study of invasive ductal
carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 21:673–679. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Schaefer A, Jung M, Mollenkopf HJ, et al:
Diagnostic and prognostic implications of microRNA profiling in
prostate carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 126:1166–1176. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Meng F, Henson R, Wehbe-Janek H, et al:
MicroRNA-21 regulates expression of the PTEN tumor suppressor gene
in human hepatocellular cancer. Gastroenterology. 133:647–658.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Filipowicz W, Bhattacharyya SN and
Sonenberg N: Mechanisms of post-transcriptional regulation by
microRNAs: are the answers in sight? Nat Rev Genet. 9:102–114.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Slaby O, Svoboda M, Fabian P, et al:
Altered expression of miR-21, miR-31, miR-143 and miR-145 is
related to clinicopathologic features of colorectal cancer.
Oncology. 72:397–402. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu CJ, Kao SY, Tu HF, et al: Increase of
microRNA miR-31 level in plasma could be a potential marker of oral
cancer. Oral Dis. 16:360–364. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Borkhardt A, Fuchs U and Tuschl T:
MicroRNA in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med.
354:524–525. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Han Y, Chen J, Zhao X, et al: MicroRNA
expression signatures of bladder cancer revealed by deep
sequencing. PLoS One. 6:e182862011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Aslam MI, Taylor K, Pringle JH and Jameson
JS: MicroRNAs are novel biomarkers of colorectal cancer. Br J Surg.
96:702–710. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bandrés E, Cubedo E, Agirre X, et al:
Identification by Real-time PCR of 13 mature microRNAs
differentially expressed in colorectal cancer and non-tumoral
tissues. Mol Cancer. 5:292006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhu S, Si ML, Wu H and Mo YY: MicroRNA-21
targets the tumor suppressor gene tropomyosin 1 (TPM1). J Biol
Chem. 282:14328–14336. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Frankel LB, Christoffersen NR, Jacobsen A,
et al: Programmed cell death 4 (PDCD4) is an important functional
target of the microRNA miR-21 in breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem.
283:1026–1033. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cottonham CL, Kaneko S and Xu L: miR-21
and miR-31 converge on TIAM1 to regulate migration and invasion of
colon carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem. 285:35293–35302. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nagel R, le Sage C, Diosdado B, et al:
Regulation of the adenomatous polyposis coli gene by the miR-135
family in colorectal cancer. Cancer Res. 68:5795–5802. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Dhanasekaran S, Doherty TM and Kenneth J:
Comparison of different standards for real-time PCR-based absolute
quantification. J Immunol Methods. 354:34–39. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Whelan JA, Russell NB and Whelan MA: A
method for the absolute quantification of cDNA using real-time PCR.
J Immunol Methods. 278:261–269. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lee C, Kim J, Shin SG and Hwang S:
Absolute and relative QPCR quantification of plasmid copy number in
Escherichia coli. J Biotechnol. 123:273–280. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chen C, Ridzon DA, Broomer AJ, et al:
Real-time quantification of microRNAs by stem-loop RT-PCR. Nucleic
Acids Res. 33:e1792005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Aprelikova O, Yu X, Palla J, et al: The
role of miR-31 and its target gene SATB2 in cancer-associated
fibroblasts. Cell Cycle. 9:4387–4398. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Michael MZ, SM OC, van Holst Pellekaan NG,
et al: Reduced accumulation of specific microRNAs in colorectal
neoplasia. Mol Cancer Res. 1:882–891. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yu S, Lu Z, Liu C, et al: miRNA-96
suppresses KRAS and functions as a tumor suppressor gene in
pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res. 70:6015–6025. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, et al: MicroRNA
expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature. 435:834–838.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Allawi HT, Dahlberg JE, Olson S, et al:
Quantitation of microRNAs using a modified Invader assay. RNA.
10:1153–1161. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wang CJ, Zhou ZG, Wang L, et al:
Clinicopathological significance of microRNA-31, -143 and -145
expression in colorectal cancer. Dis Markers. 26:27–34. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lu Z, Liu M, Stribinskis V, et al:
MicroRNA-21 promotes cell transformation by targeting the
programmed cell death 4 gene. Oncogene. 27:4373–4379. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Huang Q, Gumireddy K, Schrier M, et al:
The microRNAs miR-373 and miR-520c promote tumour invasion and
metastasis. Nat Cell Biol. 10:202–210. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lee EJ, Gusev Y, Jiang J, et al:
Expression profiling identifies microRNA signature in pancreatic
cancer. Int J Cancer. 120:1046–1054. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Tong AW, Fulgham P, Jay C, et al: MicroRNA
profile analysis of human prostate cancers. Cancer Gene Ther.
16:206–216. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|