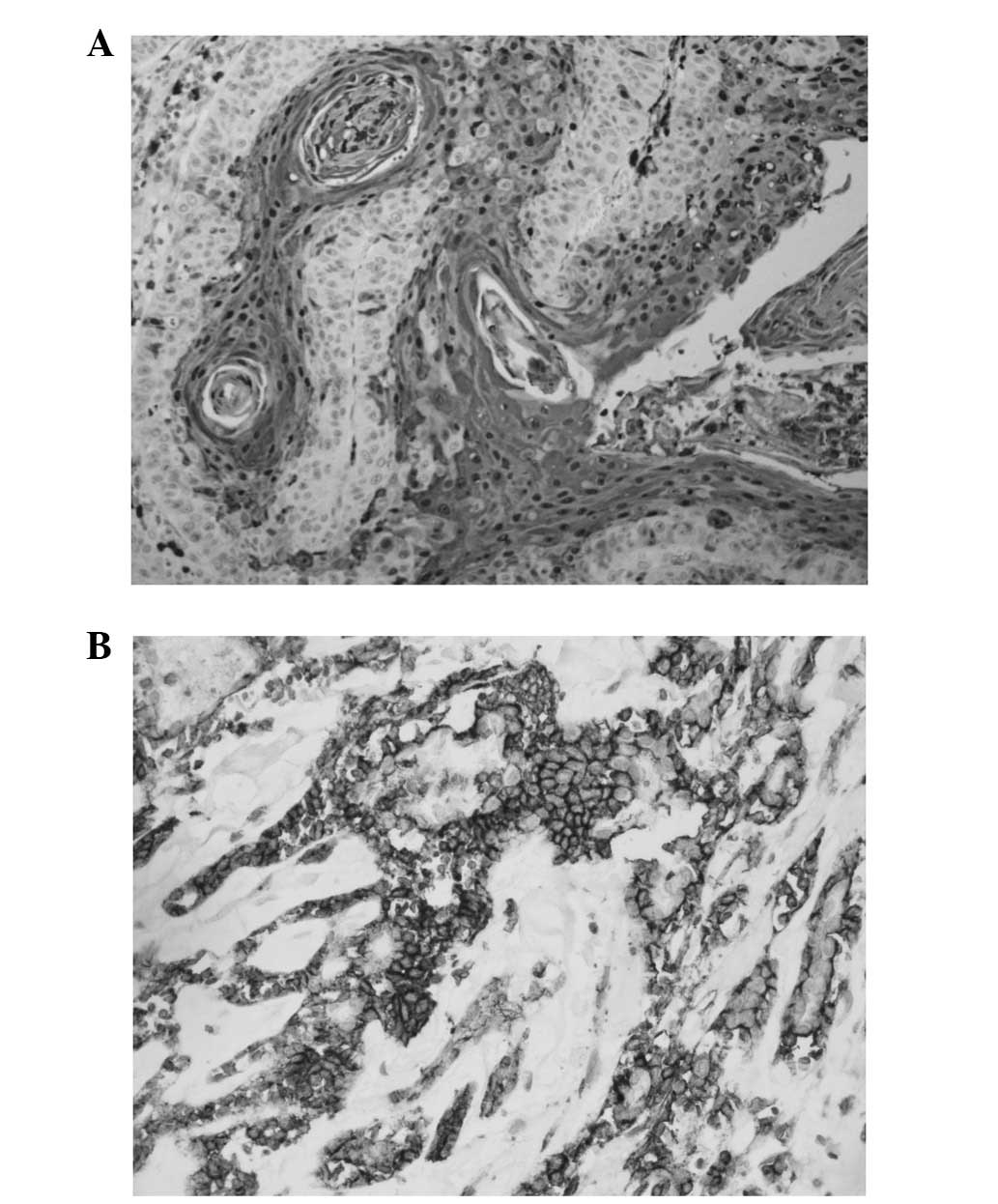
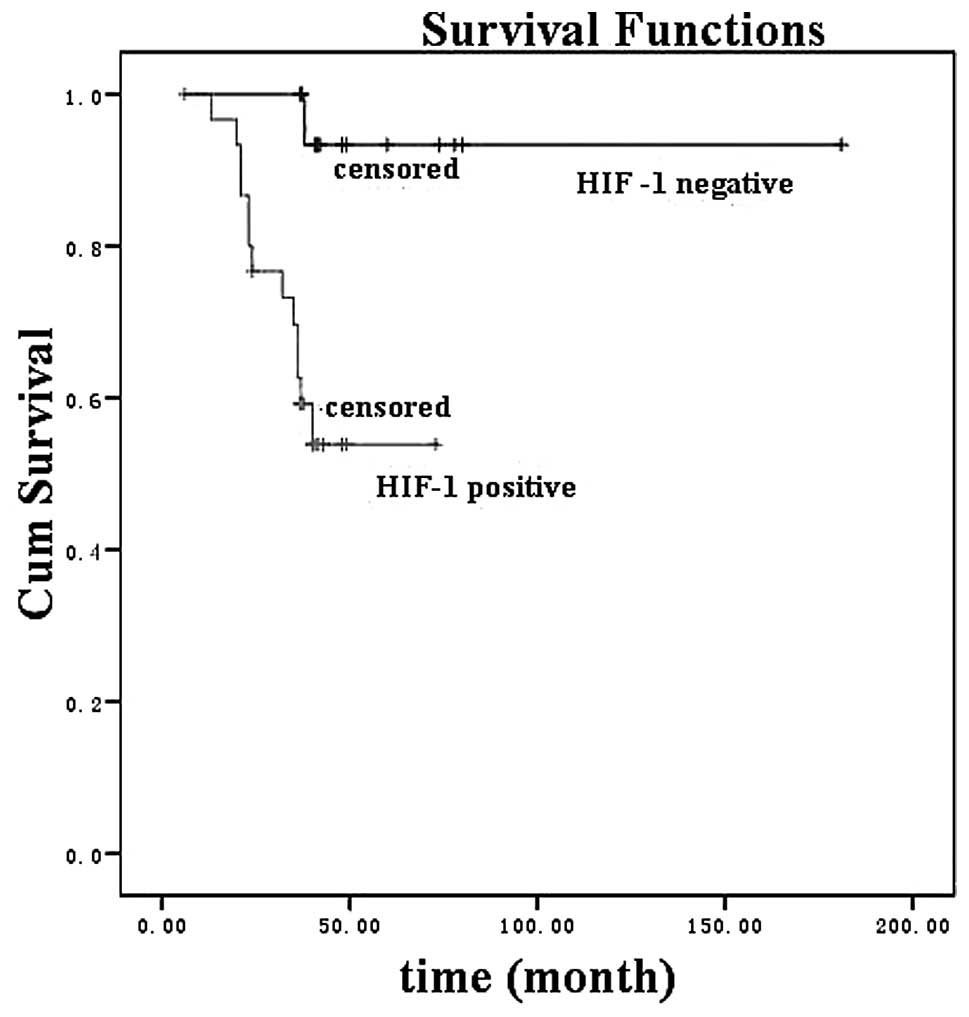
|
1
|
Yasuda M, Miyazawa M, Fujita M, et al:
Expression of hypoxia inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) and glucose
transporter-1 (GLUT-1) in ovarian adenocarcinomas: difference in
hypoxic status depending on histological character. Oncol Rep.
19:111–116. 2008.
|
|
2
|
Havelund BM, Sørensen FB, Lindebjerg J,
Spindler KL and Jakobsen A: Pretreatment HIF-1α and GLUT-1
expressions do not correlate with outcome after preoperative
chemoradiotherapy in rectal cancer. Anticancer Res. 31:1559–1565.
2011.
|
|
3
|
Gu J, Yamamoto H, Fukunaga H, et al:
Correlation of GLUT-1 overexpression, tumor size, and depth of
invasion with 18F-2-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose uptake by positron
emission tomography in colorectal cancer. Dig Dis Sci. 51:198–205.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Merrall NW, Plevin R and Gould GW: Growth
factors, mitogens, oncogenes and the regulation of glucose
transport. Cell Signal. 5:667–675. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhou S, Wang S, Wu Q, Fan J and Wang Q:
Expression of glucose transporter-1 and -3 in the head and neck
carcinoma - the correlation of the expression with the biological
behaviors. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec. 70:189–194. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Eckert AW, Lautner MH, Taubert H, Schubert
J and Bilkenroth U: Expression of Glut-1 is a prognostic marker for
oral squamous cell carcinoma patients. Oncol Rep. 20:1381–1385.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Deron P, Vermeersch H, Mees G, Vangestel
C, Pauwels P and Van de Wiele C: Expression and prognostic value of
glucose transporters and hexokinases in tonsil and mobile tongue
squamous cell carcinoma. Histol Histopathol. 26:1165–1172.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nakajo M, Nakajo M, Tani A, et al:
Clinical significance of primary lesion FDG uptake for choice
between oesophagectomy and endoscopic submucosal dissection for
resectable oesophageal squamous cell carcinomas. Eur Radiol.
21:2396–2407. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Kondo Y, Yoshikawa K, Omura Y, et al:
Clinicopathological significance of carbonic anhydrase 9, glucose
transporter-1, Ki-67 and p53 expression in oral squamous cell
carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 25:1227–1233. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Deron P, Vangestel C, Goethals I, et al:
FDG uptake in primary squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck.
The relationship between overexpression of glucose transporters and
hexokinases, tumour proliferation and apoptosis. Nuklearmedizin.
50:15–21. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ayala FR, Rocha RM, Carvalho KC, et al:
GLUT1 and GLUT3 as potential prognostic markers for oral squamous
cell carcinoma. Molecules. 15:2374–2387. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pez F, Dayan F, Durivault J, et al: The
HIF-1-inducible lysyl oxidase activates HIF-1 via the Akt pathway
in a positive regulation loop and synergizes with HIF-1 in
promoting tumor cell growth. Cancer Res. 71:1647–1657. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Eckert AW, Lautner MH, Schütze A, Taubert
H, Schubert J and Bilkenroth U: Coexpression of hypoxia-inducible
factor-1α and glucose transporter-1 is associated with poor
prognosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma patients. Histopathology.
58:1136–1147. 2011.
|
|
14
|
Ogane N, Yasuda M, Shimizu M, et al:
Clinicopathological implications of expressions of hypoxia-related
molecules in esophageal superficial squamous cell carcinoma. Ann
Diagn Pathol. 14:23–29. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sulkowska M, Wincewicz A, Sulkowski S,
Koda M and Kanczuga-Koda L: Relations of TGF-beta1 with HIF-1alpha,
GLUT-1 and longer survival of colorectal cancer patients.
Pathology. 41:254–260. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Iida T, Yasuda M, Miyazawa M, et al:
Hypoxic status in ovarian serous and mucinous tumors: relationship
between histological characteristics and HIF-1α/GLUT-1 expression.
Arch Gynecol Obstet. 277:539–546. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lidgren A, Bergh A, Grankvist K, Rasmuson
T and Ljungberg B: Glucose transporter-1 expression in renal cell
carcinoma and its correlation with hypoxia inducible factor-1
alpha. BJU Int. 101:480–484. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Palit V, Phillips RM, Puri R, Shah T and
Bibby MC: Expression of HIF-1α and Glut-1 in human bladder cancer.
Oncol Rep. 14:909–913. 2005.
|
|
19
|
Koukourakis MI, Giatromanolaki A, Harris
AL and Sivridis E: Comparison of metabolic pathways between cancer
cells and stromal cells in colorectal carcinomas: a metabolic
survival role for tumor-associated stroma. Cancer Res. 66:632–637.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Wincewicz A, Sulkowska M, Koda M and
Sulkowski S: Clinicopathological significance and linkage of the
distribution of HIF-1α and GLUT-1 in human primary colorectal
cancer. Pathol Oncol Res. 13:15–20. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Schrijvers ML, van der Laan BF, de Bock
GH, et al: Overexpression of intrinsic hypoxia markers HIF1α and
CA-IX predict for local recurrence in stage T1-T2 glottic laryngeal
carcinoma treated with radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys.
72:161–169. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wu XH, Lu YF, Hu XD, et al: Expression of
hypoxia inducible factor-1α and its significance in laryngeal
carcinoma. J Int Med Res. 38:2040–2046. 2010.
|
|
23
|
Yu L, Liu Y and Cui Y: Expression of
hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha and its relationship to apoptosis
and proliferation in human laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. J
Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 24:636–638. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Luo XM, Zhou SH and Fan J: Glucose
transporter-1 as a new therapeutic target in laryngeal carcinoma. J
Int Med Res. 38:1885–1892. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhou SH, Fan J, Chen XM, Cheng KJ and Wang
SQ: Inhibition of cell proliferation and glucose uptake in human
laryngeal carcinoma cells by antisense oligonucleotides against
glucose transporter-1. Head Neck. 31:1624–1633. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Weljie AM and Jirik FR: Hypoxia-induced
metabolic shifts in cancer cells: moving beyond the Warburg effect.
Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 43:981–989. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wan J, Chai H, Yu Z, et al: HIF-1α effects
on angiogenic potential in human small cell lung carcinoma. J Exp
Clin Cancer Res. 30:772011.
|
|
28
|
Cabanillas R, Rodrigo JP, Secades P, et
al: The relation between hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α
expression with p53 expression and outcome in surgically treated
supraglottic laryngeal cancer. J Surg Oncol. 99:373–378. 2009.
|
|
29
|
Wildeman MA, Gibcus JH, Hauptmann M, et
al: Radiotherapy in laryngeal carcinoma: can a panel of 13 markers
predict response? Laryngoscope. 119:316–322. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|