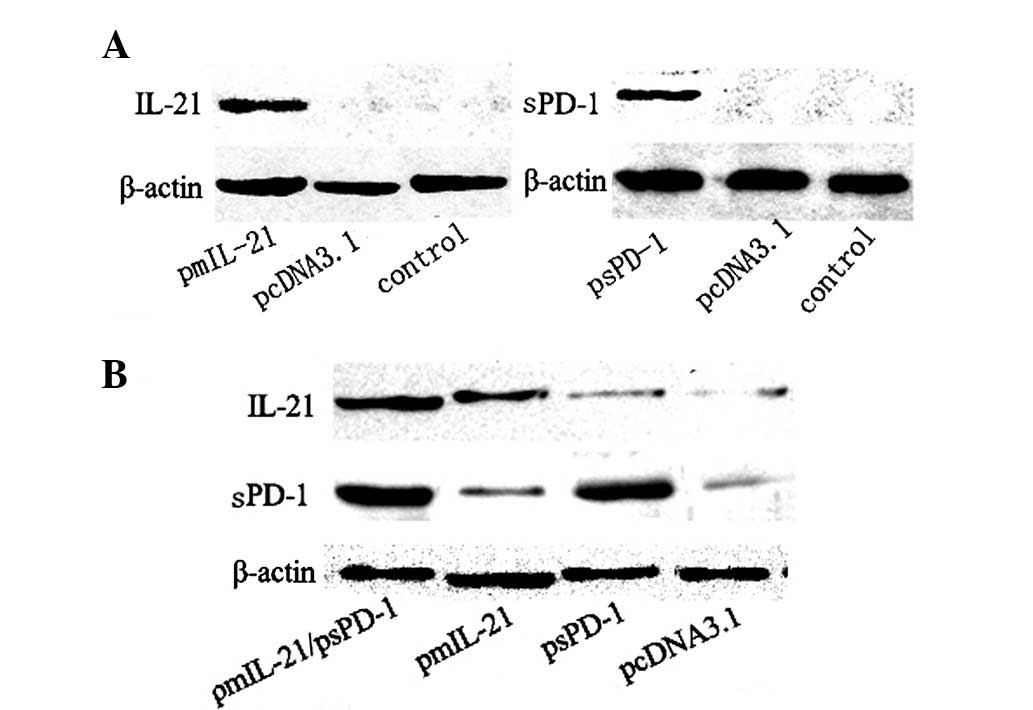
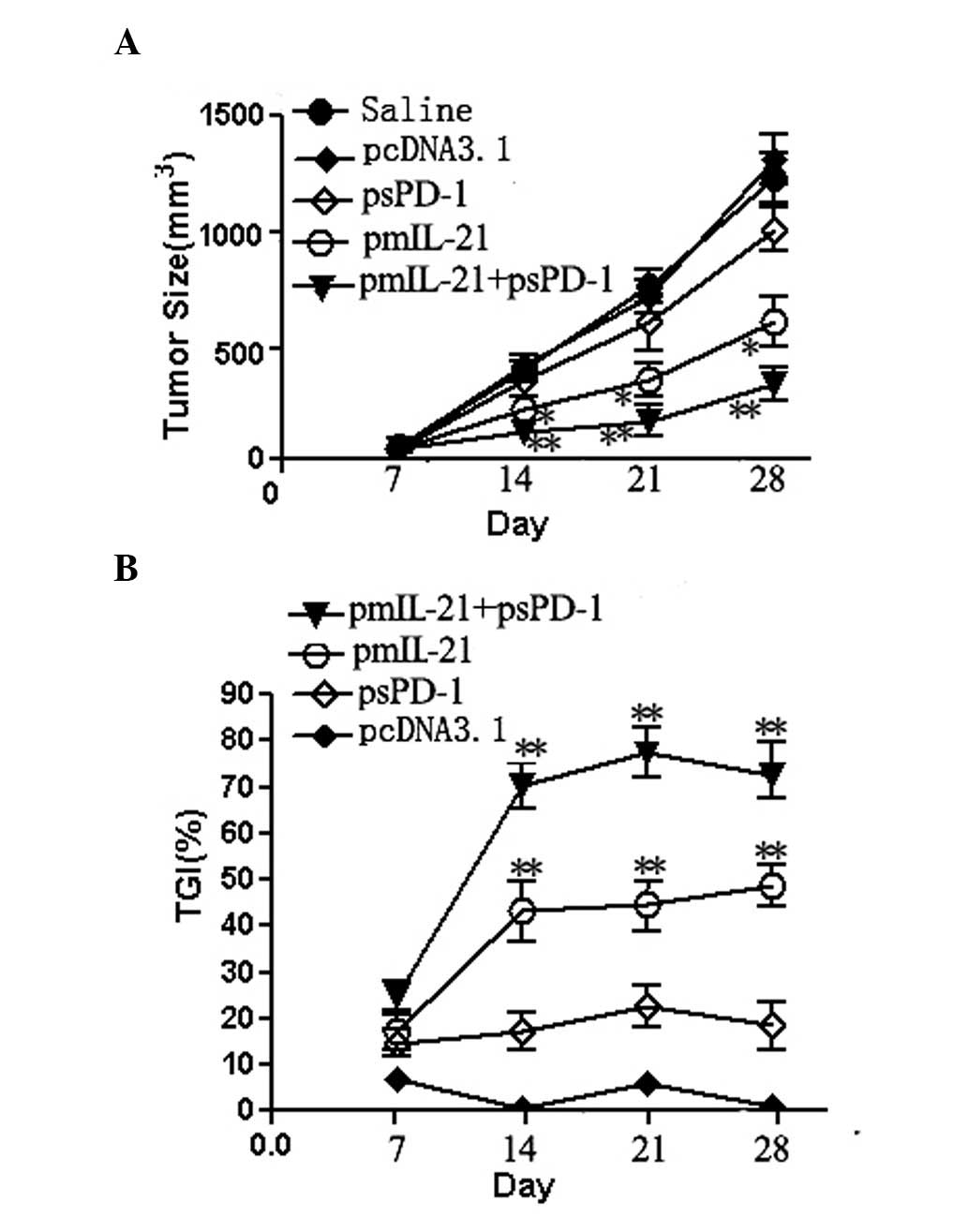
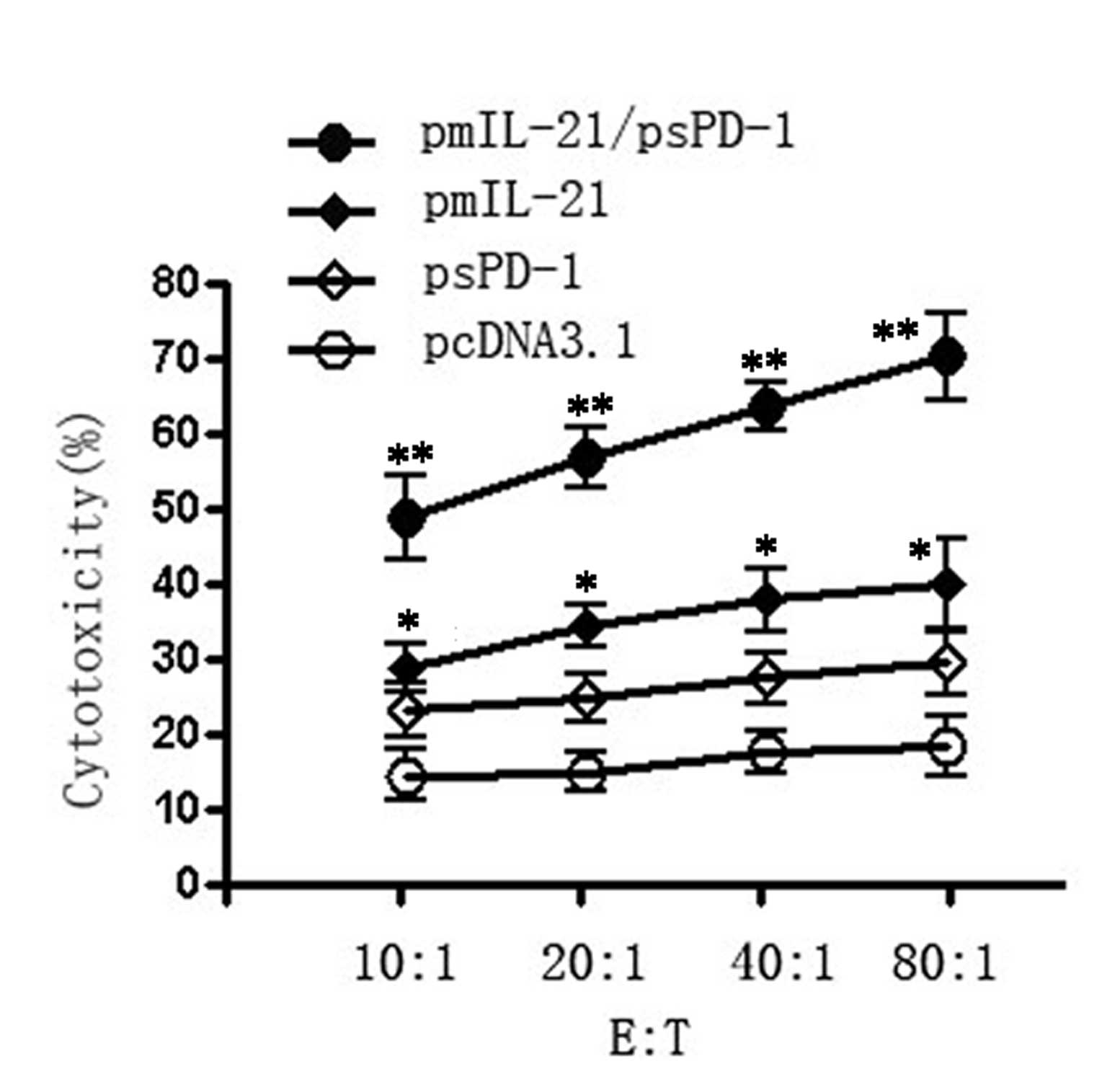
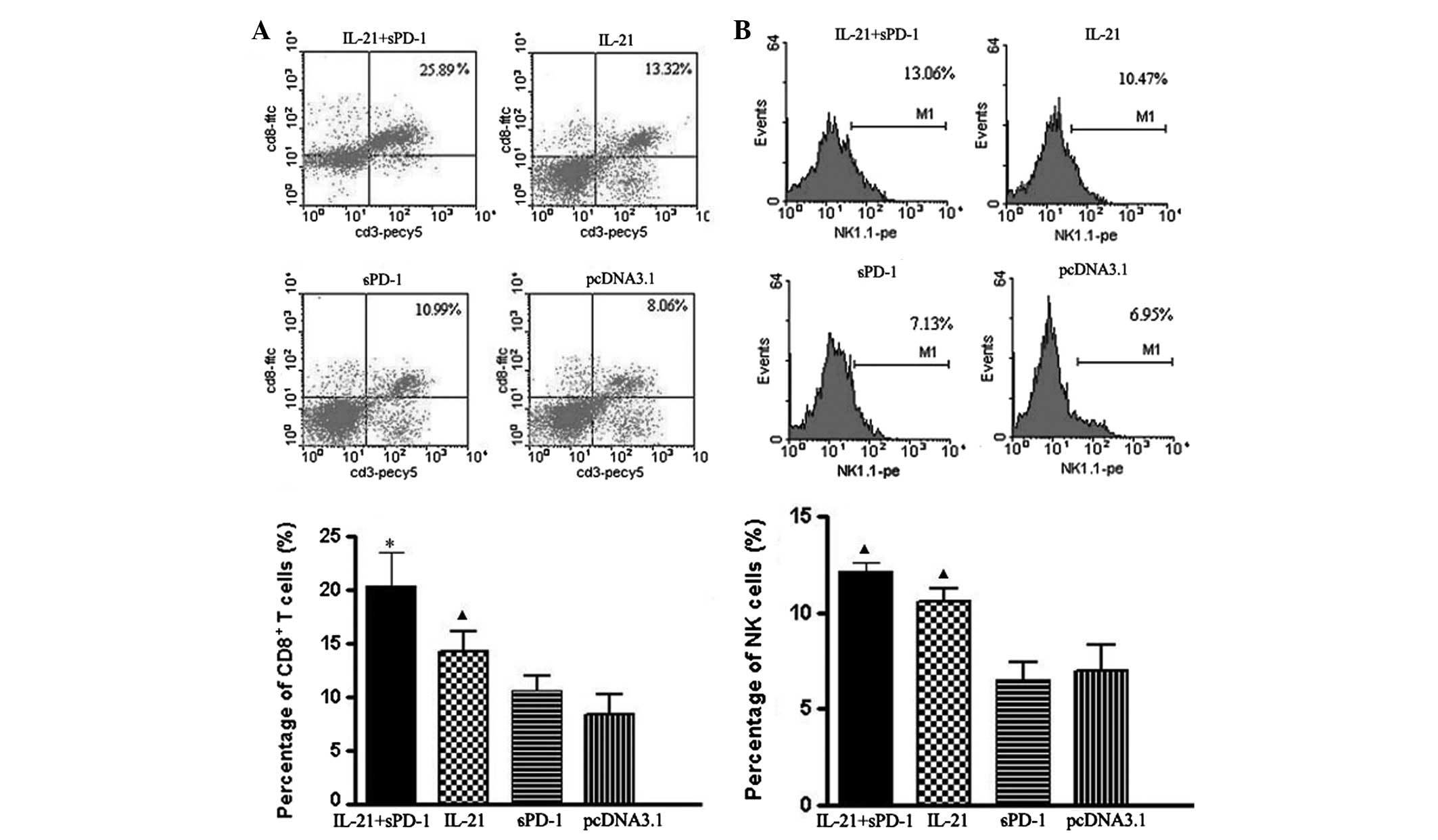
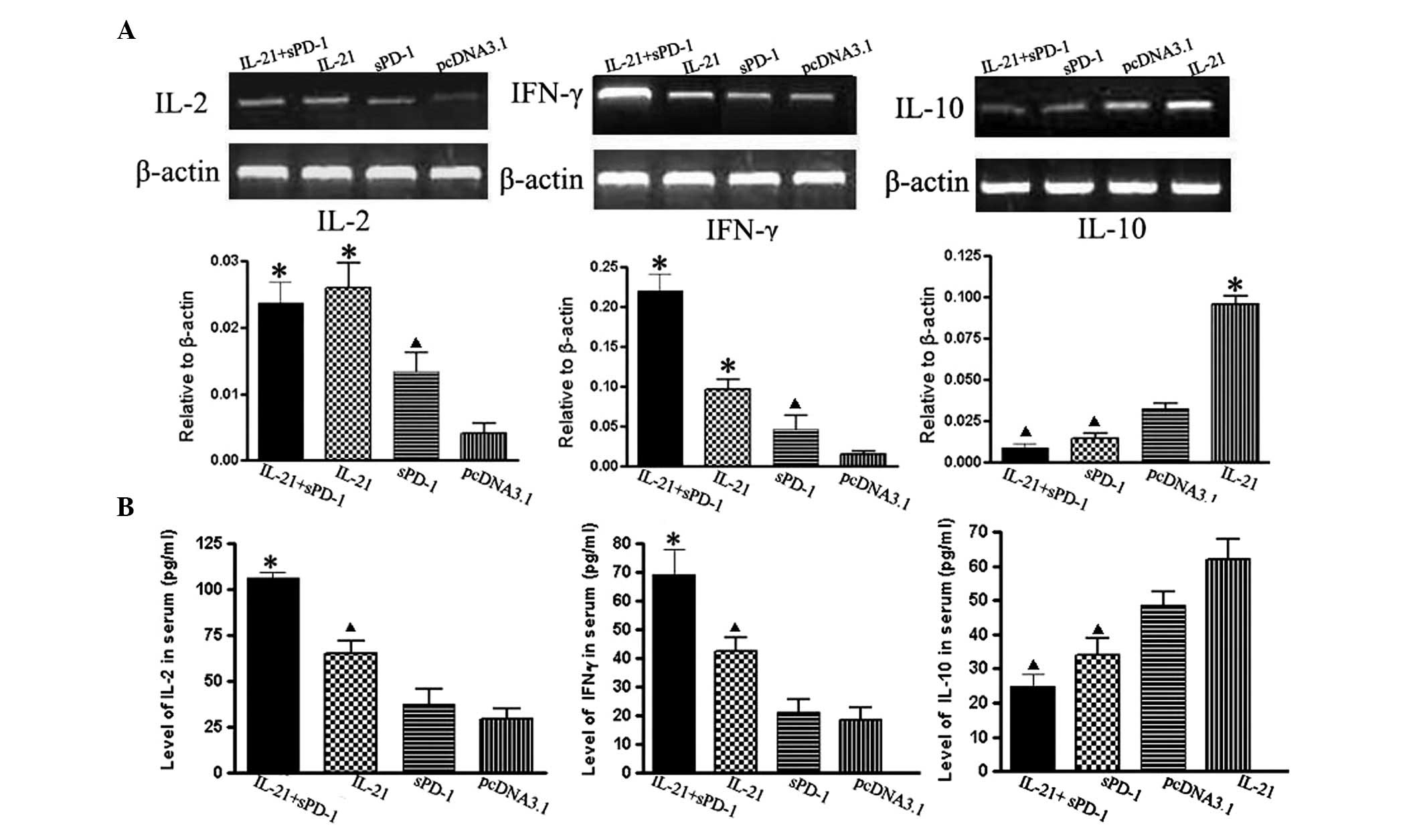
|
1
|
Parrish-Novak J, Dillon SR, Nelson A, et
al: Interleukin 21 and its receptor are involved in NK cell
expansion and regulation of lymphocyte function. Nature. 408:57–63.
2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bryant VL, Ma CS, Avery DT, Li Y, Good KL,
Corcoran LM, de Waal Malefyt R and Tangye SG: Cytokine-mediated
regulation of human B cell differentiation into Ig-secreting cells:
predominant role of IL-21 produced by CXCR5+T follicular
helper cells. J Immunol. 179:8180–8190. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kashiwakuma D, Suto A, Hiramatsu Y, Ikeda
K, Takatori H, Suzuki K, Kaqami S, Hirose K, Watanabe N, Iwamoto I
and Nakajima H: B and T lymphocyte attenuator suppresses IL-21
production from follicular Th cells and subsequent humoral immune
responses. J Immunol. 185:2730–2736. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Coquet JM, Kyparissoudis K, Pellicci DG,
Besra G, Berzins SP, Smyth MJ and Godfrey DI: IL-21 is produced by
NKT cells and modulates NKT cell activation and cytokine
production. J Immunol. 178:2827–2834. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jin H, Carrio R, Yu A and Malek TR:
Distinct activation signals determine whether IL-21 induces B cell
costimulation, growth arrest, or Bim-dependent apoptosis. J
Immunol. 173:657–665. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Brandt K, Bulfone-Paus S, Foster DC and
Rückert R: Interleukin-21 inhibits dendritic cell activation and
maturation. Blood. 102:4090–4098. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Distler JH, Jüngel A, Kowal-Bielecka O, et
al: Expression of interleukin-21 receptor in epidermis from
patients with systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum. 52:856–864.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Caruso R, Fina D, Peluso I, Stolfi C,
Fantini MC, Gioia V, Caprioli F, Del Vecchio Bianco G, Paoluzi OA,
Macdonald TT, et al: A functional role for interleukin-21 in
promoting the synthesis of the T-cell chemoattractant, MIP-3alpha,
by gut epithelial cells. Gastroenterology. 132:166–175. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Pesce J, Kaviratne M, Ramalingam TR,
Thompson RW, Urban JF Jr, Cheever AW, Young DA, Collins M, Grusby
MJ and Wynn TA: The IL-21 receptor augments Th2 effector function
and alternative macrophage activation. J Clin Invest.
116:2044–2055. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Di Carlo E, Comes EA, Orengo AM, Rosso O,
Meazza R, Musiani P, Colombo MP and Ferrini S: IL-21 induces tumor
rejection by specific CTL and IFN-γ-dependent CXC chemokines in
syngeneic mice. J Immunol. 172:1540–1547. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Dou J, Chen GB, Wang J, Zhao FS, Chen JS,
Fang XS, Tang Q and Chu LL: Preliminary study on mouse
interleukin-21 application in tumor gene therapy. Cell Mol Immunol.
1:461–466. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Moroz A, Eppolito C, Li Q, Tao JM, Clegg
CH and Shrikant PA: IL-21 enhances and sustains CD8+ T
cell responses to achieve durable tumor immunity: comparative
evaluation of IL-2, IL-15, and IL-21. J Immunol. 173:900–909.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu S, Lizée G, Lou Y, Liu CW, Overwijk
WW, Wang G and Hwu P: IL-21 synergizes with IL-7 to augment
expansion and anti-tumor function of cytotoxic T cells. Int
Immunol. 19:1213–1221. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Casey KA and Mescher MF: IL-21 promotes
differentiation of naive CD8 T cells to a unique effector
phenotype. J Immunol. 178:7640–7648. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kim-Schulze S, Kim HS, Fan Q, Kim DW and
Kaufman HL: Local IL-21 promotes the therapeutic activity of
effector T cells by decreasing regulatory T cells within the tumor
microenvironment. Mol Ther. 17:380–388. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang G, Tschoi M, Spolski R, Lou YY, Ozaki
K, Feng C, Kim G, Leonard WJ and Hwu P: In vivo antitumor activity
of interleukin 21 mediated by natural killer cells. Cancer Res.
63:9016–9022. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Schmidt H, Brown J, Mouritzen U, Selby P,
Fode K, Svane IM, Cook GP, Mollerup DH and Geertsen PF: Safety and
clinical effect of subcutaneous human interleukin-21 in patients
with metastatic melanoma or renal cell carcinoma: a phase I trial.
Clin Cancer Res. 16:5312–5319. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Grünwald V, Desar IM, Haanen J, Fiedler W,
Mouritzen U, Olsen MW and van Herpen CM: A phase I study of
recombinant human interleukin-21 (rIL-21) in combination with
sunitinib in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma (RCC).
Acta Oncol. 50:121–126. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hashmi MH and Van Veldhuizen PJ:
Interleukin-21: updated review of Phase I and II clinical trials in
metastatic renal cell carcinoma, metastatic melanoma and
relapsed/refractory indolent non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Expert Opin
Biol Ther. 5:807–817. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Dong H, Strome SE and Salomao DR:
Tumor-associated B7-H1 promotes T-cell apoptosis: a potential
mechanism of immune evasion. Nat Med. 8:793–800. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gao Q, Wang XY, Qiu SJ, Yamato I, Sho M,
Nakajima Y, Zhou J, Li BZ, Shi YH, Xiao YS, Xu Y and Fan J:
Overexpression of PD-L1 significantly associates with tumor
aggressiveness and postoperative recurrence in human hepatocellular
carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 15:971–979. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Butte MJ, Keir ME, Phamduy TB, Sharpe AH
and Freeman GJ: Programmed death-1 ligand 1 interacts specifically
with the B7-1 costimulatory molecule to inhibit T cell responses.
Immunity. 27:111–122. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Iwai Y, Terawaki S and Honjo T: PD-1
blockade inhibits hematogenous spread of poorly immunogenic tumor
cells by enhanced recruitment of effector T cells. Int Immunol.
17:133–144. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang W, Lau R, Yu D, Zhu WW, Korman A and
Weber J: PD-1 blockade reverses the suppression of melanoma
antigen-specific CTL by CD4+ CD25 (Hi) regulatory T
cells. Int Immunol. 21:1065–1077. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Onlamoon N, Rogers K, Mayne AE,
Pattanapanyasat K, Mori K, Villinger F and Ansari AA: Soluble PD-1
rescues the proliferative response of simian immunodeficiency
virus-specific CD4 and CD8 T cells during chronic infection.
Immunology. 124:277–293. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang XH, Zhang GM, He YF, Zhang H and Feng
ZH: Soluble PD-1 can augment anti-tumor immunity induced by
HSP70-peptide complex in tumor bearing mice. Chin J Cell Mol
Immunol. 20:655–658. 2004.(In Chinese).
|
|
27
|
He YF, Zhang GM, Wang XH, Zhang H, Yuan Y,
Li D and Feng ZH: Eukaryotic expression and functional
characterization of PD-1 extracellular domain. Chin J Biotechnol.
20:699–703. 2004.(In Chinese).
|
|
28
|
Dou J, Wang Y, Wang J, Zhao F, Li Y, Cao
M, et al: Antitumor efficacy induced by human ovarian cancer cells
secreting IL-21 alone or combination with GM-CSF cytokines in nude
mice model. Immunobiolog. 214:483–492. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jauch D, Martin M, Schiechl G, Kesselring
R, Schlitt HJ, Geissler EK and Fichtner-Feigl S: Interleukin 21
controls tumour growth and tumour immunosurveillance in
colitis-associated tumorigenesis in mice. Gut. 60:1678–1686. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kinter AL, Godbout EJ, McNally JP, Sereti
I, Roby GA, O’Shea MA and Fauci AS: The common γ-chain cytokines
IL-2, IL-7, IL-15, and IL-21 induce the expression of programmed
death-1 and its ligands. J Immunol. 181:6738–6746. 2008.
|
|
31
|
Arens R and Schoenberger SP: Plasticity in
programming of effector and memory CD8 T-cell formation. Immunol
Rev. 235:190–205. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Cerwenka A and Lanier LL: Natural killer
cells, viruses and cancer. Nat Rev Immunol. 1:41–49. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Smyth MJ, Hayakawa Y, Takeda K and Yagita
H: New aspects of natural-killer-cell surveillance and therapy of
cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:850–861. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
O’Garra A and Arai N: The molecular basis
of T helper 1 and T helper 2 cell differentiation. Trends Cell
Biol. 10:542–550. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|