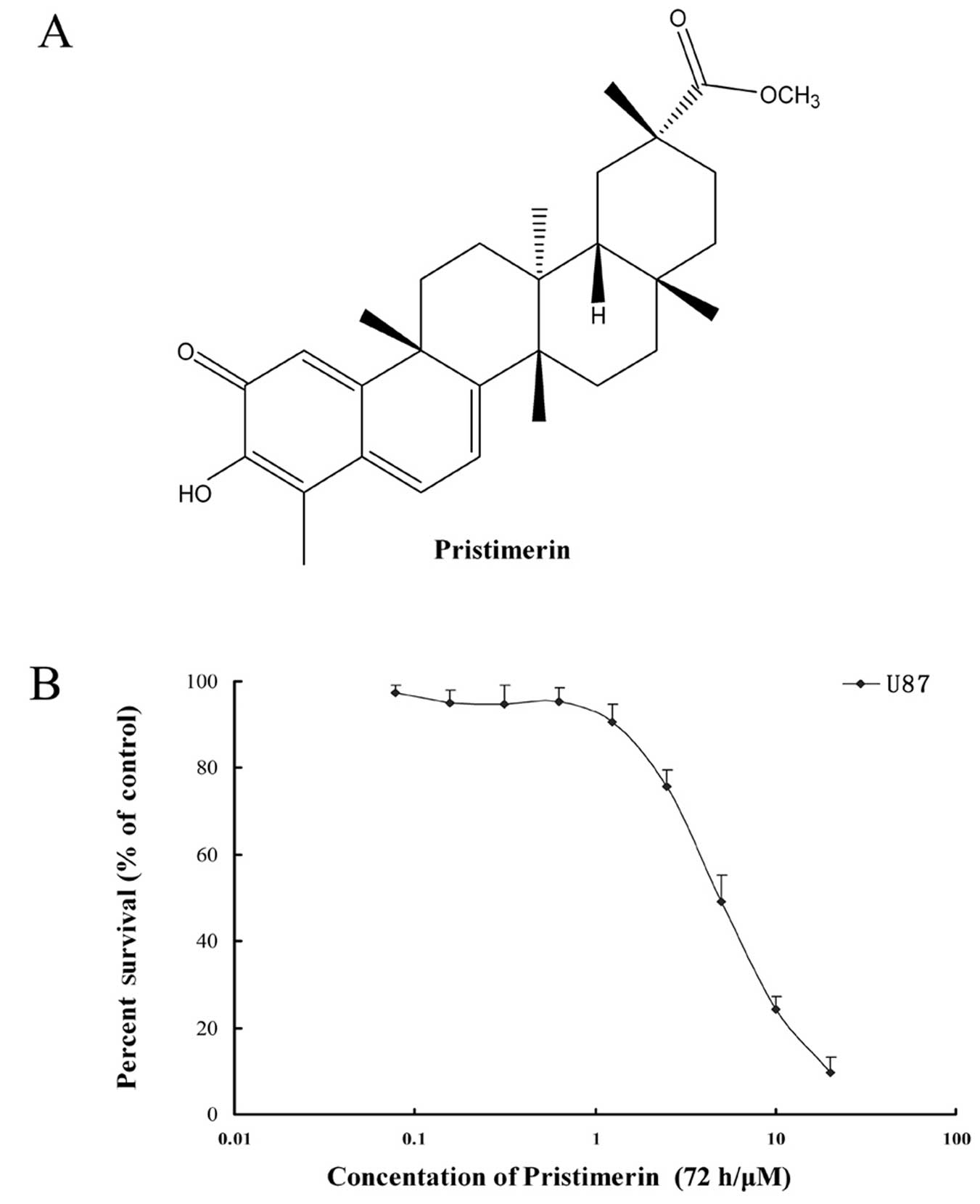
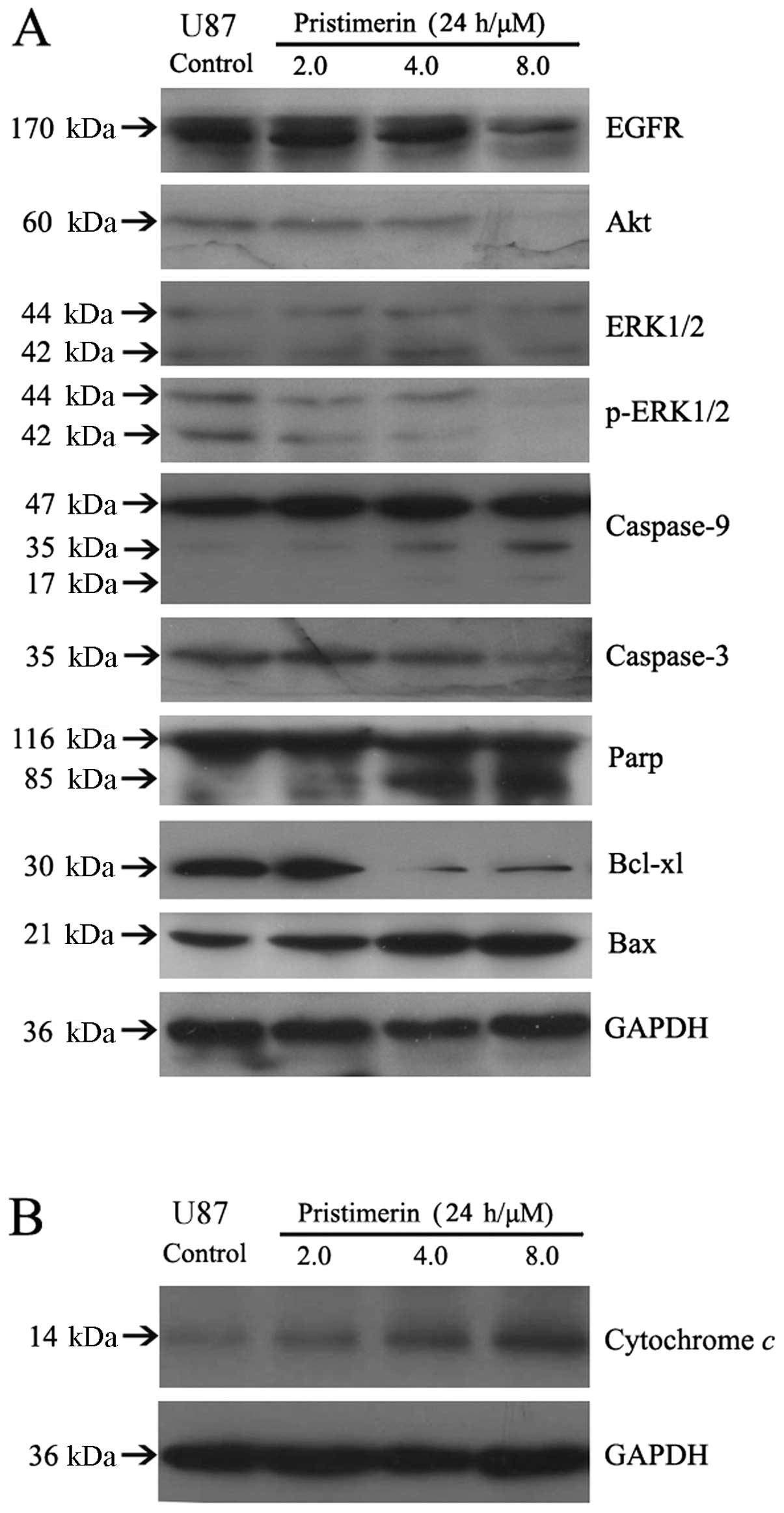
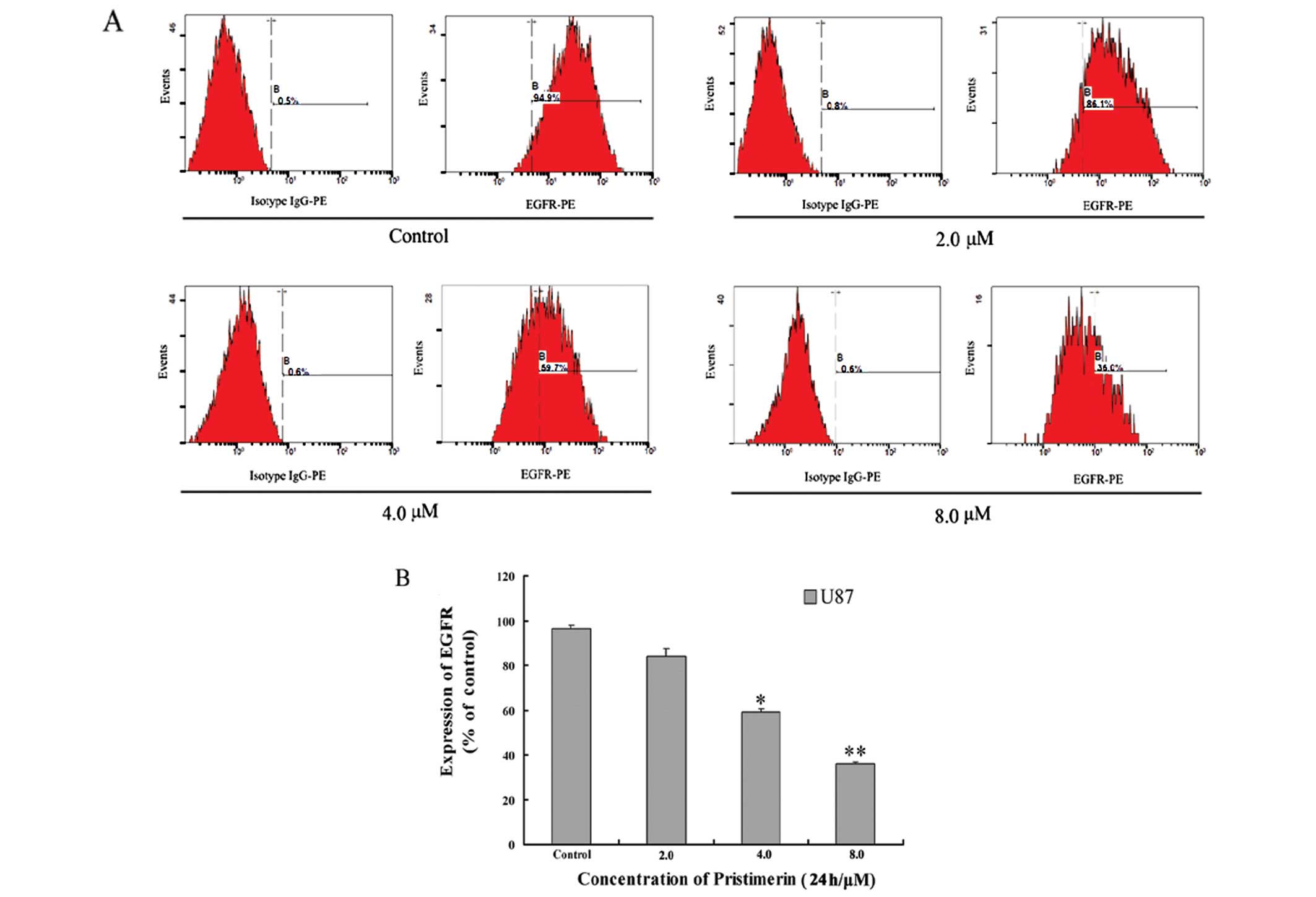
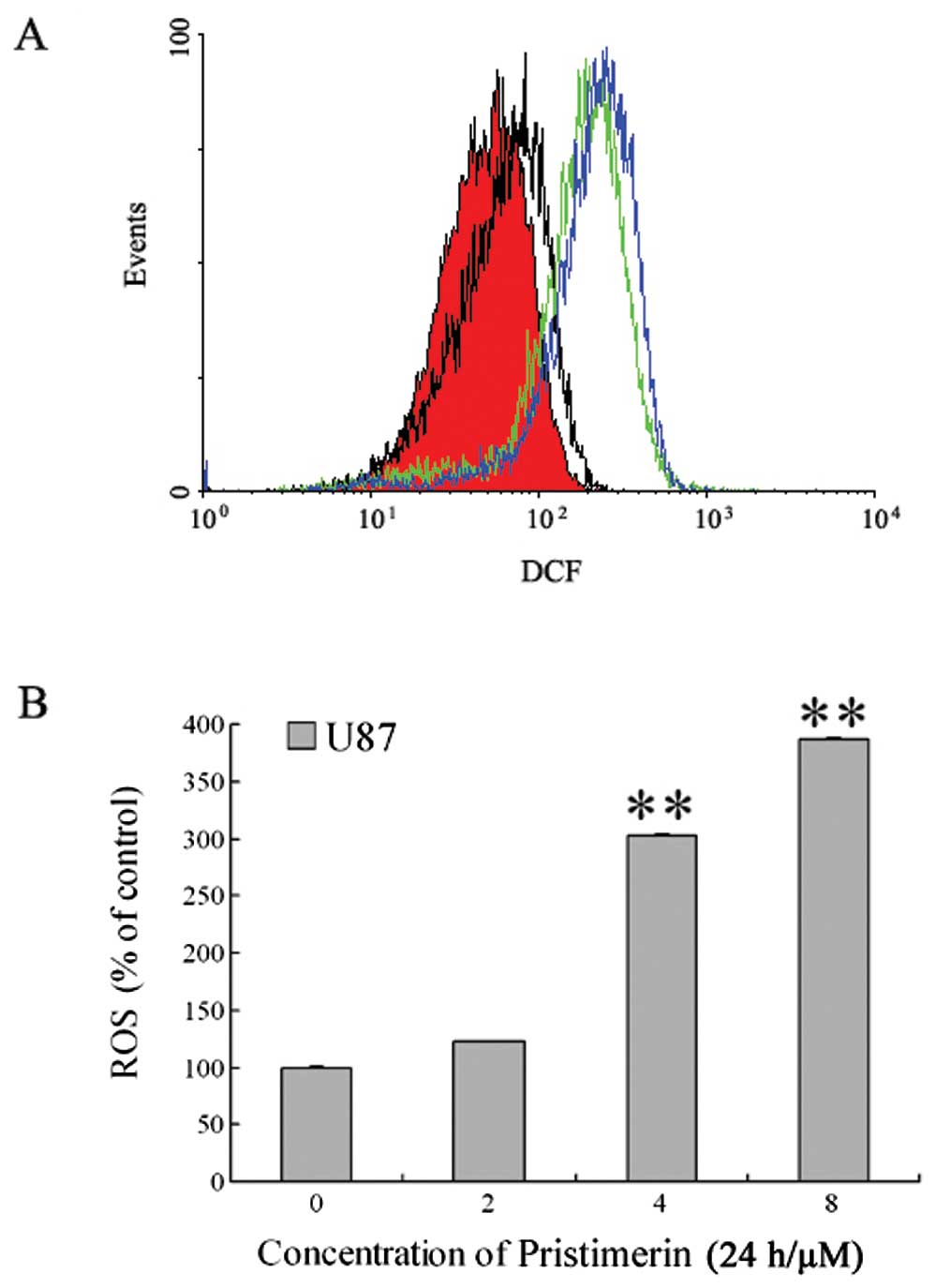
|
1
|
Debatin KM: Activation of apoptosis
pathways by anticancer drugs. Adv Exp Med Biol. 457:237–244. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hengartner MO: The biochemistry of
apoptosis. Nature. 407:770–776. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kroemer G and Reed JC: Mitochondrial
control of cell death. Nat Med. 6:513–519. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Gulbins E, Dreschers S and Bock J: Role of
mitochondria in apoptosis. Exp Physiol. 88:85–90. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Friesen C, Fulda S and Debatin KM:
Cytotoxic drugs and the CD95 pathway. Leukemia. 13:1854–1858. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sharma K, Wang RX, Zhang LY, et al: Death
the Fas way: regulation and pathophysiology of CD95 and its ligand.
Pharmacol Ther. 88:333–347. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gao JM, Wu WJ, Zhang JW and Konishi Y: The
dihydro-beta-agarofuran sesquiterpenoids. Nat Prod Rep.
24:1153–1189. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Brinker AM, Ma J, Lipsky PE and Raskin I:
Medicinal chemistry and pharmacology of genus Tripterygium
(Celastraceae). Phytochemistry. 68:732–766. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Salminen A, Lehtonen M, Suuronen T,
Kaarniranta K and Huuskonen J: Terpenoids: natural inhibitors of
NF-kappaB signaling with anti-inflammatory and anticancer
potential. Cell Mol Life Sci. 65:2979–2999. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wu CC, Chan ML, Chen WY, Tsai CY, Chang FR
and Wu YC: Pristimerin induces caspase-dependent apoptosis in
MDA-MB-231 cells via direct effects on mitochondria. Mol Cancer
Ther. 4:1277–1285. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nagase M, Oto J, Sugiyama S, Yube K,
Takaishi Y and Sakato N: Apoptosis induction in HL-60 cells and
inhibition of topoisomerase II by triterpene celastrol. Biosci
Biotechnol Biochem. 67:1883–1887. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yang H, Landis-Piwowar KR, Lu D, et al:
Pristimerin induces apoptosis by targeting the proteasome in
prostate cancer cells. J Cell Biochem. 103:234–244. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lu Z, Jin Y, Chen C, Li J, Cao Q and Pan
J: Pristimerin induces apoptosis in imatinib-resistant chronic
myelogenous leukemia cells harboring T315I mutation by blocking
NF-kappaB signaling and depleting Bcr-Abl. Mol Cancer. 9:1122010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Tiedemann RE, Schmidt J, Keats JJ, et al:
Identification of a potent natural triterpenoid inhibitor of
proteosome chymotrypsin-like activity and NF-kappaB with
antimyeloma activity in vitro and in vivo. Blood. 113:4027–4037.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shao CJ, Fu J, Shi HL, Mu YG and Chen ZP:
Activities of DNA-PK and Ku86, but not Ku70, may predict
sensitivity to cisplatin in human gliomas. J Neurooncol. 89:27–35.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fu J, Shao CJ, Chen FR, Ng HK and Chen ZP:
Autophagy induced by valproic acid is associated with oxidative
stress in glioma cell lines. Neuro Oncology. 12:328–340. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yan YY, Zheng LS, Zhang X, et al: Blockade
of Her2/neu binding to Hsp90 by emodin azide methyl anthraquinone
derivative induces proteasomal degradation of Her2/neu. Mol Pharm.
8:1687–1697. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yan Y, Su X, Liang Y, et al: Emodin azide
methyl anthraquinone derivative triggers mitochondrial-dependent
cell apoptosis involving in caspase-8-mediated Bid cleavage. Mol
Cancer Ther. 7:1688–1697. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Zhang JY, Wu HY, Xia XK, et al:
Anthracenedione derivative 1403P-3 induces apoptosis in KB and
KBv200 cells via reactive oxygen species-independent mitochondrial
pathway and death receptor pathway. Cancer Biol Ther. 6:1413–1421.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Nakagawa T, Zhu H, Morishima N, et al:
Caspase-12 mediates endoplasmic-reticulum-specific apoptosis and
cytotoxicity by amyloid-beta. Nature. 403:98–103. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Barry M, Heibein JA, Pinkoski MJ, et al:
Granzyme B short-circuits the need for caspase 8 activity during
granule-mediated cytotoxic T-lymphocyte killing by directly
cleaving Bid. Mol Cell Biol. 20:3781–3794. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lavrik IN, Golks A, Baumann S and Krammer
PH: Caspase-2 is activated at the CD95 death-inducing signaling
complex in the course of CD95-induced apoptosis. Blood.
108:559–565. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Vanhaesebroeck B and Alessi DR: The
PI3K-PDK1 connection: more than just a road to PKB. Biochem J 346
Pt. 3:561–576. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Marte BM and Downward J: PKB/Akt:
connecting phosphoinositide 3-kinase to cell survival and beyond.
Trends Biochem Sci. 22:355–358. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Surawicz TS, Davis F, Freels S, Laws ER Jr
and Menck HR: Brain tumor survival: results from the National
Cancer Data Base. J Neurooncol. 40:151–160. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lefranc F, Facchini V and Kiss R:
Proautophagic drugs: a novel means to combat apoptosis-resistant
cancers, with a special emphasis on glioblastomas. Oncologist.
12:1395–1403. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shirota O, Morita H, Takeya K and Itokawa
H: Cytotoxic aromatic triterpenes from Maytenus ilicifolia
and Maytenus chuchuhuasca. J Nat Prod. 57:1675–1681. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chang FR, Hayashi K, Chen IH, et al:
Antitumor agents. 228 five new agarofurans, Reissantins A–E, and
cytotoxic principles from Reissantia buchananii. J Nat Prod.
66:1416–1420. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Li SS, Tang QL, Wang SH, Chen YH, Liu JJ
and Yang XM: Simultaneously targeting Bcl-2 and Akt pathways
reverses resistance of nasopharyngeal carcinoma to TRAIL
synergistically. Tumori. 97:762–770. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yoo NJ, Kim MS, Park SW, et al: Expression
analysis of caspase-6, caspase-9 and BNIP3 in prostate cancer.
Tumori. 96:138–142. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Fleury C, Mignotte B and Vayssiere JL:
Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species in cell death signaling.
Biochimie. 84:131–141. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Xia Z, Lundgren B, Bergstrand A, DePierre
JW and Nassberger L: Changes in the generation of reactive oxygen
species and in mitochondrial membrane potential during apoptosis
induced by the antidepressants imipramine, clomipramine, and
citalopram and the effects on these changes by Bcl-2 and Bcl-X(L).
Biochem Pharmacol. 57:1199–1208. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Chan WH, Wu CC and Yu JS: Curcumin
inhibits UV irradiation-induced oxidative stress and apoptotic
biochemical changes in human epidermoid carcinoma A431 cells. J
Cell Biochem. 90:327–338. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Byun JY, Kim MJ, Eum DY, et al: Reactive
oxygen species-dependent activation of Bax and poly(ADP-ribose)
polymerase-1 is required for mitochondrial cell death induced by
triterpenoid pristimerin in human cervical cancer cells. Mol
Pharmacol. 76:734–744. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Mani A and Gelmann EP: The
ubiquitin-proteasome pathway and its role in cancer. J Clin Oncol.
23:4776–4789. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ciechanover A: The ubiquitin-proteasome
pathway: on protein death and cell life. EMBO J. 17:7151–7160.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|