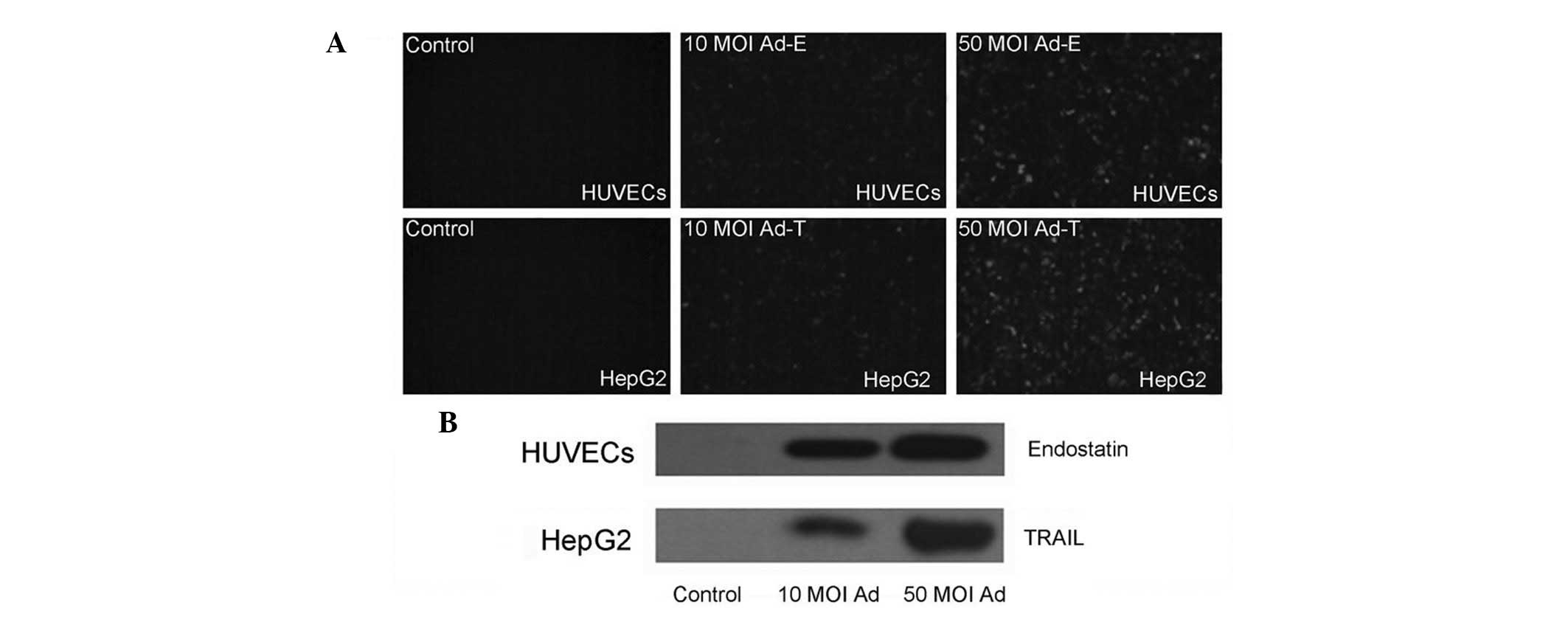
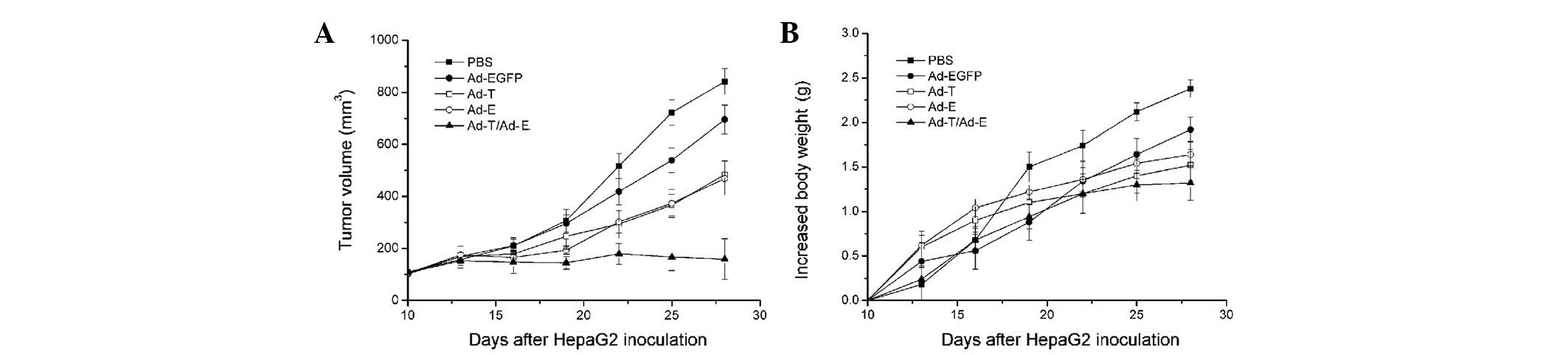
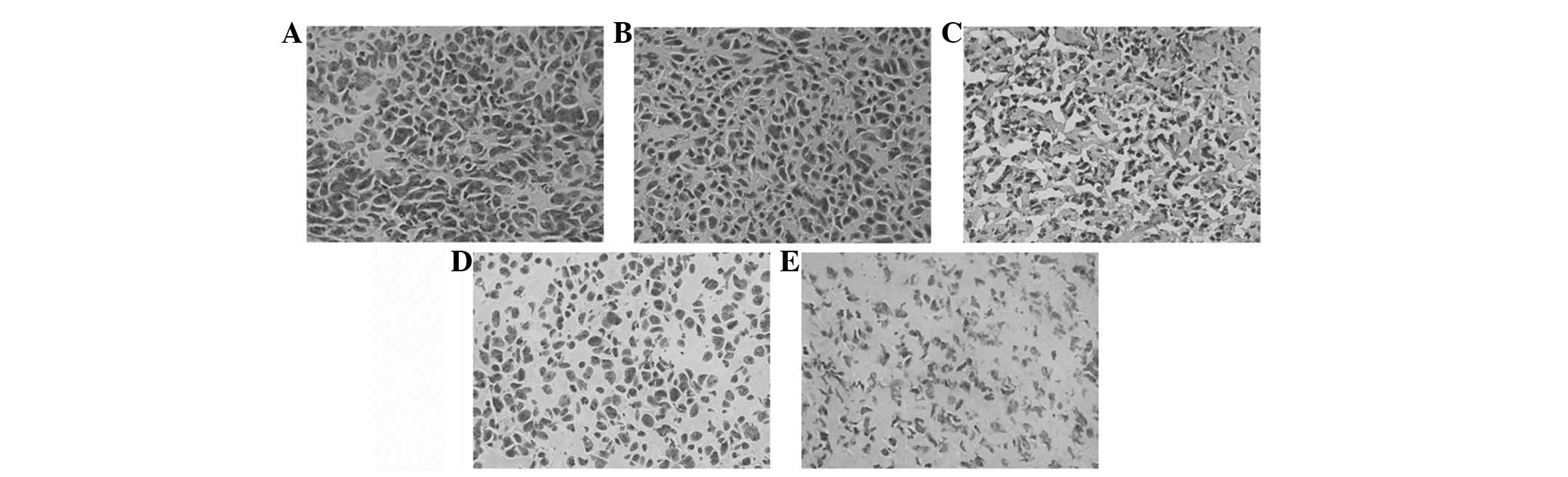
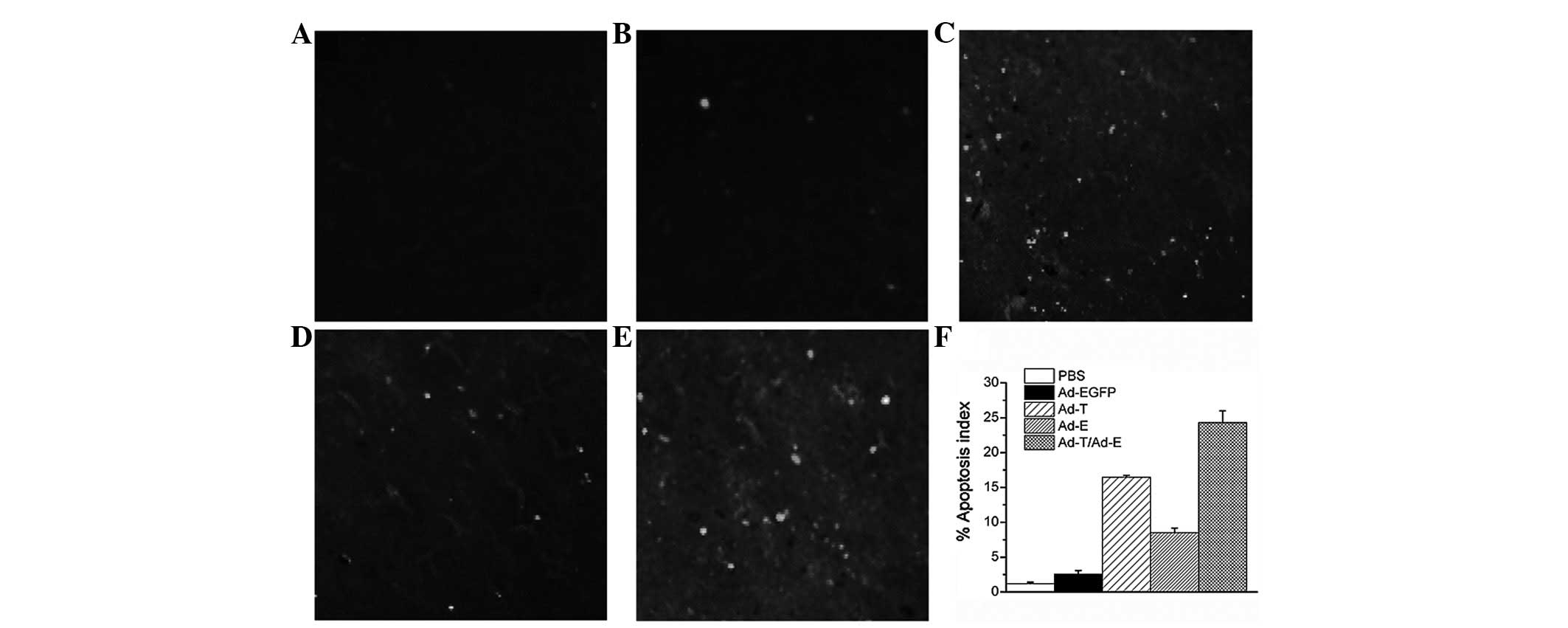
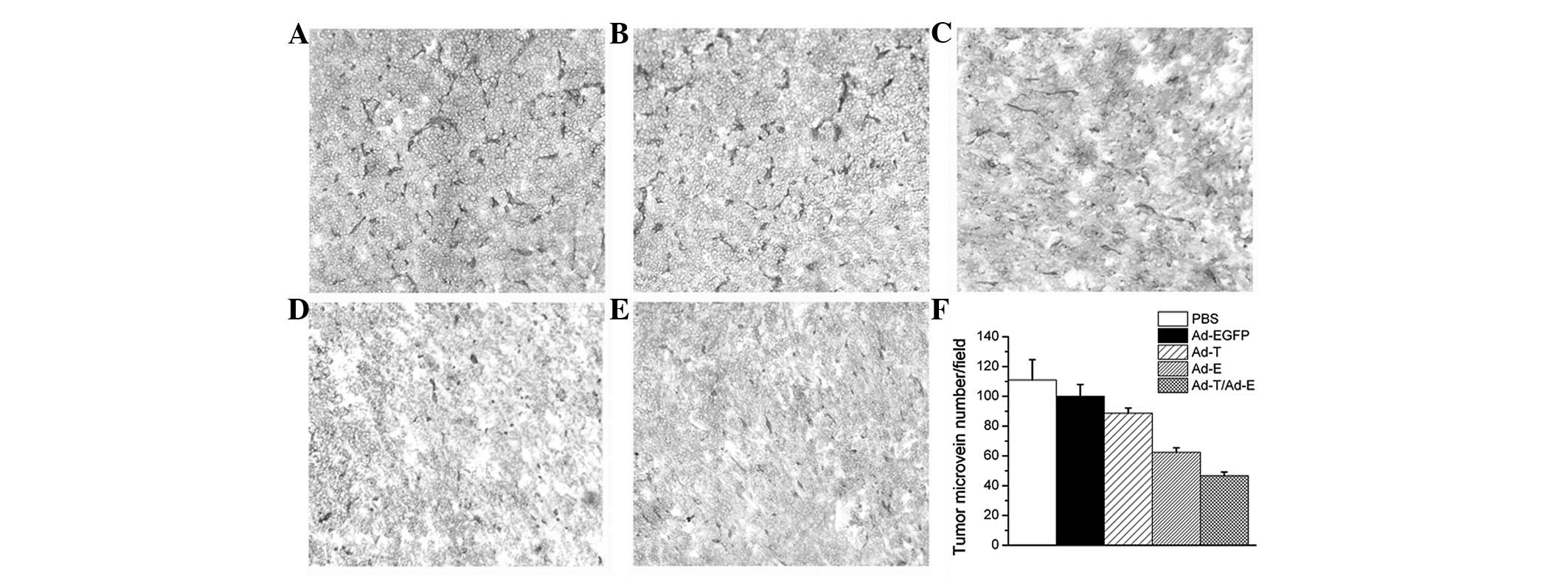
|
1
|
Cha C, DeMatteo RP and Blumgart LH:
Surgery and ablative therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin
Gastroenterol. 35(Suppl 2): S130–S137. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Forner A, Llovet JM and Bruix J:
Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 379:1245–1255. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
El-Serag HB: Hepatocellular carcinoma. N
Engl J Med. 365:1118–1127. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Carr BI: Hepatocellular carcinoma: current
management and future trends. Gastroenterology. 127:S218–S224.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Di Maio M, De Maio E, Perrone F, Pignata S
and Daniele B: Hepatocellular carcinoma; systemic treatments. J
Clin Gastroenterol. 35(Suppl 2): S109–S114. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Prieto J, Qian C, Hernandez-Alcoceba R,
Gonzalez-Aseguinolaza G, Mazzolini G, Sangro B and Kramer MG: Gene
therapy of liver diseases. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 4:1073–1091.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hernández-Alcoceba R, Sangro B and Prieto
J: Gene therapy of liver cancer. Ann Hepatol. 6:5–14. 2007.
|
|
8
|
Cosman D: A family of ligands for TNF
receptor superfamily. Stem Cells. 12:440–445. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ashkenazi A and Dixit VM: Death receptors:
signaling and modulation. Science. 281:1305–1308. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Walczak H, Miller RE, Ariail K, et al:
Tumoricidal activity of tumor necrosis factor-related
apoptosis-inducing ligand in vivo. Nat Med. 5:157–163. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Piras V, Hayashi K, Tomita M and
Selvarajoo K: Enhancing apoptosis in TRAIL-resistant cancer cells
using fundamental response rules. Sci Rep. 1:1442011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yang A, Wilson NS and Ashkenazi A:
Proapoptotic DR4 and DR5 signaling in cancer cells: toward clinical
translation. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 22:837–844. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Nagane M, Huang HJ and Cavenee WK: The
potential of TRAIL for cancer chemotherapy. Apoptosis. 6:191–197.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yamaguchi N: An analysis of the functional
mechanisms of endostatin-the anti-angiogenic activity of endostatin
is mediated by its multiple binding ability. Connect Tissue.
36:171–178. 2004.
|
|
15
|
O’Reilly MS, Boehm T, Shing Y, et al:
Endostatin: an endogenous inhibitor of angiogenesis and tumor
growth. Cell. 88:277–285. 1997.
|
|
16
|
Yamaguchi N, Anand-Apte B, Lee M, et al:
Endostatin inhibits VEGF-induced endothelial cell migration and
tumor growth independently of zinc binding. EMBO J. 18:4414–4423.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Bao Y, Feng WM, Tang CW, Zheng YY, Gong HB
and Hou EG: Endostatin inhibits angiogenesis in hepatocellular
carcinoma after transarterial chemoembolization.
Hepatogastroenterology. 59:1566–1568. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Franceschi RT and Ge C: Gene delivery by
adenoviruses. Methods Mol Biol. 455:137–147. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lee J and Moon C: Current status of
experimental therapeutics for head and neck cancer. Exp Biol Med.
236:375–389. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang Y, Qu ZH, Cui M, Guo C, Zhang XM, Ma
CH and Sun WS: Combined endostatin and TRAIL gene transfer
suppresses human hepatocellular carcinoma growth and angiogenesis
in nude mice. Cancer Biol Ther. 8:466–473. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wei YQ, Wang QR, Zhao X, et al:
Immunotherapy of tumors with xenogeneic endothelial cells as a
vaccine. Nat Med. 6:1160–1166. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wei YQ, Huang MJ, Yang L, et al:
Immunogene therapy of tumors with vaccine based on Xenopus
homologous vascular endothelial growth factor as a model antigen.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:11545–11550. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ingber D, Fujita T, Kishimoto S, Sudo K,
Kanamaru T, Brem H and Folkman J: Synthetic analogues of fumagillin
that inhibit angiogenesis and suppress tumor growth. Nature.
348:555–557. 1990. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
O’Reilly MS, Holmgren L, Shing Y, et al:
Angiostatin: a novel angiogenesis inhibitor that mediates the
suppression of metastases by a Lewis lung carcinoma. Cell.
79:315–328. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sauter BV, Martinet O, Zhang WJ, Mandeli J
and Woo SL: Adenovirus-mediated gene transfer of endostatin in vivo
results in high level of transgene expression and inhibition of
tumor growth and metastases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 97:4802–4807.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lin T, Zhang L, Davis J, et al:
Combination of TRAIL gene therapy and chemotherapy enhances
antitumor and antimetastasis effects in chemosensitive and
chemoresistant breast cancers. Mol Ther. 8:441–448. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wissink EH, Verbrugge I, Vink SR, et al:
TRAIL enhances efficacy of radiotherapy in a p53 mutant, Bcl-2
overexpressing lymphoid malignancy. Radiother Oncol. 80:214–222.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wu DS, Wu CM, Huang TH and Xie QD:
Combined effects of radiotherapy and endostatin gene therapy in
melanoma tumor model. Radiat Environ Biophys. 47:285–291. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhu LP, Xing J, Wang QX, et al:
Therapeutic efficacy of recombinant human endostatin combined with
chemotherapeutics in mice-transplanted tumors. Eur J Pharmacol.
617:23–27. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kim Y: The effects of nutrient depleted
microenvironments and delta-like 1 homologue (DLK1) on apoptosis in
neuroblastoma. Nutr Res Pract. 4:455–461. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Braun F, Bertin-Ciftci J, Gallouet AS,
Millour J and Juin P: Serum-nutrient starvation induces cell death
mediated by Bax and Puma that is counteracted by p21 and unmasked
by Bcl-xL inhibition. PLoS One. 6:e235772011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|