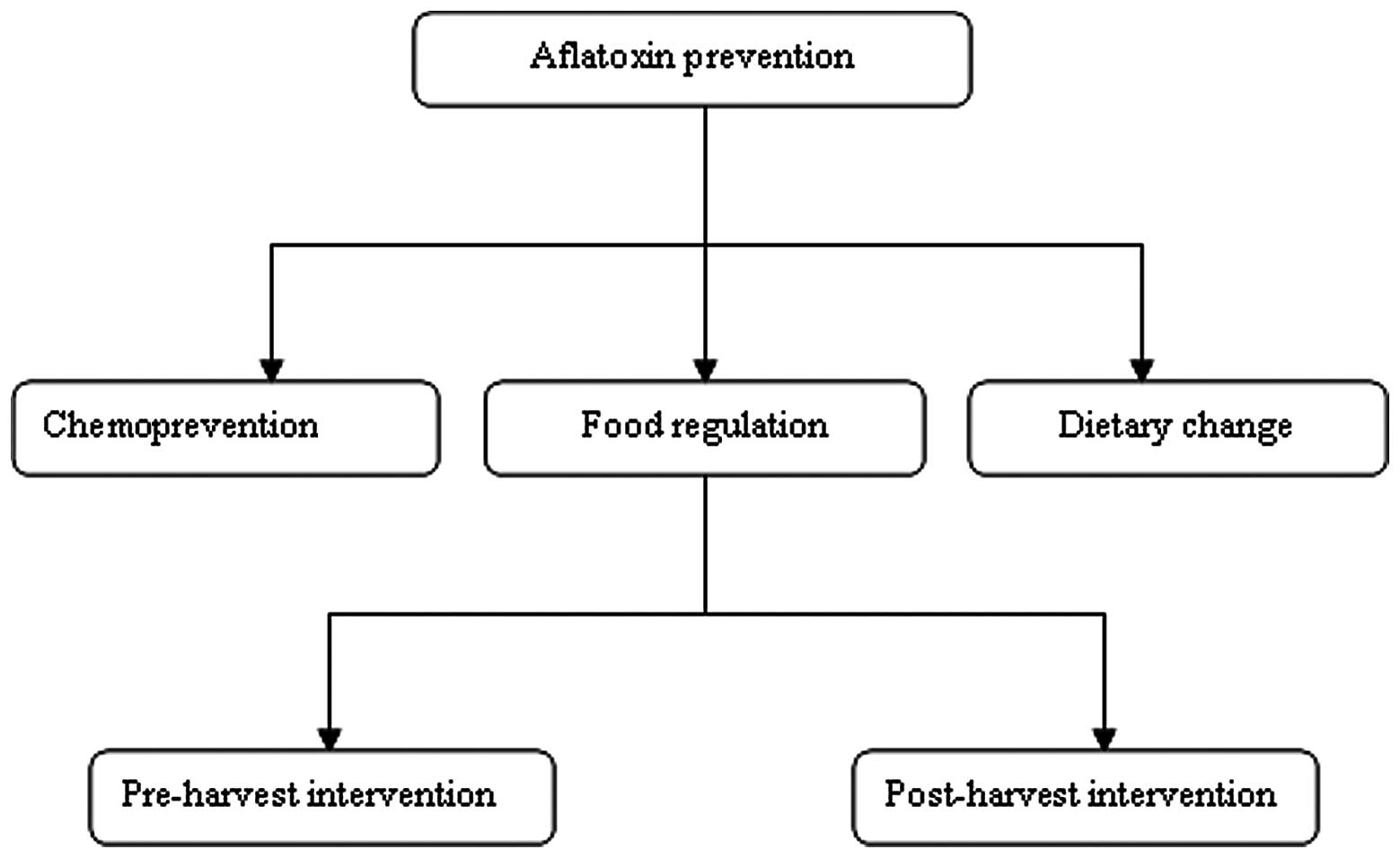
|
1
|
Llovet JM, Burroughs A and Bruix J:
Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 362:1907–1917. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Lord R, Suddle A and Ross PJ: Emerging
strategies in the treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma:
the role of targeted therapies. Int J Clin Pract. 65:182–188. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
El-Serag HB and Rudolph KL: Hepatocellular
carcinoma: epidemiology and molecular carcinogenesis.
Gastroenterology. 132:2557–2576. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D,
Mathers C and Parkin DM: Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in
2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 127:2893–2917. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
El-Serag HB and Mason AC: Rising incidence
of hepatocellular carcinoma in the United States. N Engl J Med.
340:745–750. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Altekruse SF, McGlynn KA and Reichman ME:
Hepatocellular carcinoma incidence, mortality, and survival trends
in the United States from 1975 to 2005. J Clin Oncol. 27:1485–1491.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Nguyen MH, Whittemore AS, Garcia RT, et
al: Role of ethnicity in risk for hepatocellular carcinoma in
patients with chronic hepatitis C and cirrhosis. Clin Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 2:820–824. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Farazi PA and DePinho RA: Hepatocellular
carcinoma pathogenesis: from genes to environment. Nat Rev Cancer.
6:674–687. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ward E, Jemal A, Cokkinides V, et al:
Cancer disparities by race/ethnicity and socioeconomic status. CA
Cancer J Clin. 54:78–93. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
McCracken M, Olsen M, Chen MS Jr, et al:
Cancer incidence, mortality, and associated risk factors among
Asian Americans of Chinese, Filipino, Vietnamese, Korean, and
Japanese ethnicities. CA Cancer J Clin. 57:190–205. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Röcken C and Carl-McGrath S: Pathology and
pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Dig Dis. 19:269–278.
2001.
|
|
12
|
McGlynn KA and London WT: Epidemiology and
natural history of hepatocellular carcinoma. Best Pract Res Clin
Gastroenterol. 19:3–23. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sherman M: Hepatocellular carcinoma:
epidemiology, risk factors, and screening. Semin Liver Dis.
25:143–154. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
London WT, Evans AA, McGlynn K, et al:
Viral, host and environmental risk factors for hepatocellular
carcinoma: a prospective study in Haimen City, China.
Intervirology. 38:155–161. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen CJ, Yu MW and Liaw YF:
Epidemiological characteristics and risk factors of hepatocellular
carcinoma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 12:S294–S308. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Madden CR, Finegold MJ and Slagle BL:
Altered DNA mutation spectrum in aflatoxin b1-treated transgenic
mice that express the hepatitis B virus x protein. J Virol.
76:11770–11774. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Li Y, Su JJ, Qin LL, Yang C, Ban KC and
Yan RQ: Synergistic effect of hepatitis B virus and aflatoxin B1 in
hepatocarcinogenesis in tree shrews. Ann Acad Med Singapore.
28:67–71. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Montalto G, Cervello M, Giannitrapani L,
Dantona F, Terranova A and Castagnetta LA: Epidemiology, risk
factors, and natural history of hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann NY
Acad Sci. 963:13–20. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Groopman JD, Scholl P and Wang JS:
Epidemiology of human aflatoxin exposures and their relationship to
liver cancer. Prog Clin Biol Res. 395:211–222. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Baydar T, Engin AB, Girgin G, Aydin S and
Sahin G: Aflatoxin and ochratoxin in various types of commonly
consumed retail ground samples in Ankara, Turkey. Ann Agric Environ
Med. 12:193–197. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bennett JW and Klich M: Mycotoxins. Clin
Microbiol Rev. 16:497–516. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Fink-Gremmels J: Mycotoxins: their
implications for human and animal health. Vet Q. 21:115–120. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Williams JH, Phillips TD, Jolly PE, Stiles
JK, Jolly CM and Aggarwal D: Human aflatoxicosis in developing
countries: a review of toxicology, exposure, potential health
consequences, and interventions. Am J Clin Nutr. 80:1106–1122.
2004.
|
|
24
|
McLean M and Dutton MF: Cellular
interactions and metabolism of aflatoxin: an update. Pharmacol
Ther. 65:163–192. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang JS, Huang T, Su J, et al:
Hepatocellular carcinoma and aflatoxin exposure in Zhuqing Village,
Fusui County, People’s Republic of China. Cancer Epidemiol
Biomarkers Prev. 10:143–146. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Mardani M, Rezapour S and Rezapour P:
Survey of aflatoxins in Kashkineh: A traditional Iranian food. Iran
J Microbiol. 3:147–151. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Banerjee S, Brown KL, Egli M and Stone MP:
Bypass of aflatoxin B1 adducts by the Sulfolobus solfataricus DNA
polymerase IV. J Am Chem Soc. 133:12556–12568. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Obuseh FA, Jolly PE, Kulczycki A, et al:
Aflatoxin levels, plasma vitamins A and E concentrations, and their
association with HIV and hepatitis B virus infections in Ghanaians:
a cross-sectional study. J Int AIDS Soc. 14:532011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lewis L, Onsongo M, Njapau H, et al:
Aflatoxin contamination of commercial maize products during an
outbreak of acute aflatoxicosis in eastern and central Kenya.
Environ Health Perspect. 113:1763–1767. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Oyelami OA, Maxwell SM and Adeoba E:
Aflatoxins and ochratoxin A in the weaning food of Nigerian
children. Ann Trop Paediatr. 16:137–140. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Egal S, Hounsa A, Gong YY, et al: Dietary
exposure to aflatoxin from maize and groundnut in young children
from Benin and Togo, West Africa. Int J Food Microbiol.
104:215–224. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kpodo K, Thrane U and Hald B: Fusaria and
fumonisins in maize from Ghana and their co-occurrence with
aflatoxins. Int J Food Microbiol. 61:147–157. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Awuah RT and Kpodo KA: High incidence of
Aspergillus flavus and aflatoxins in stored groundnut in
Ghana and the use of a microbial assay to assess the inhibitory
effects of plant extracts on aflatoxin synthesis. Mycopathologia.
134:109–114. 1996.
|
|
34
|
Sugimura T: Nutrition and dietary
carcinogens. Carcinogenesis. 21:387–395. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Sutandyo N: Nutritional carcinogenesis.
Acta Med Indones. 42:36–42. 2010.
|
|
36
|
Sharma RA and Farmer PB: Biological
relevance of adduct detection to the chemoprevention of cancer.
Clin Cancer Res. 10:4901–4912. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Martin J and Dufour JF: Tumor suppressor
and hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 14:1720–1733.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Jackson PE, Kuang SY, Wang JB, et al:
Prospective detection of codon 249 mutations in plasma of
hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Carcinogenesis. 24:1657–1663.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Bressac B, Kew M, Wands J and Ozturk M:
Selective G to T mutations of p53 gene in hepatocellular carcinoma
from southern Africa. Nature. 350:429–431. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Montesano R, Hainaut P and Wild CP:
Hepatocellular carcinoma: from gene to public health. J Natl Cancer
Inst. 89:1844–1851. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Hsu IC, Metcalf RA, Sun T, Welsh JA, Wang
NJ and Harris CC: Mutational hotspot in the p53 gene in human
hepatocellular carcinomas. Nature. 350:427–428. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Ozturk M: p53 mutation in hepatocellular
carcinoma after aflatoxin exposure. Lancet. 338:1356–1359. 1991.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Stern MC, Umbach DM, Yu MC, London SJ,
Zhang ZQ and Taylor JA: Hepatitis B, aflatoxin B(1), and p53 codon
249 mutation in hepatocellular carcinomas from Guangxi, People’s
Republic of China, and a meta-analysis of existing studies. Cancer
Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 10:617–625. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Nogueira JA, Ono-Nita SK, Nita ME, et al:
249 TP53 mutation has high prevalence and is correlated with larger
and poorly differentiated HCC in Brazilian patients. BMC Cancer.
9:2042009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Wang JS and Groopman JD: DNA damage by
mycotoxins. Mutat Res. 424:167–181. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Eaton DL and Gallagher EP: Mechanisms of
aflatoxin carcinogenesis. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 34:135–172.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Gallagher EP, Kunze KL, Stapleton PL and
Eaton DL: The kinetics of aflatoxin B1 oxidation by human
cDNA-expressed and human liver microsomal cytochromes P450 1A2 and
3A4. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 141:595–606. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Ilic Z, Crawford D, Vakharia D, Egner PA
and Sell S: Glutathione-S-transferase A3 knockout mice are
sensitive to acute cytotoxic and genotoxic effects of aflatoxin B1.
Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 242:241–246. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Dash B, Afriyie-Gyawu E, Huebner HJ, et
al: Determinants of the variability of aflatoxin-albumin adduct
levels in Ghanaians. J Toxicol Environ Health A. 70:58–66. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Eaton DL, Bammler TK and Kelly EJ:
Interindividual differences in response to chemoprotection against
aflatoxin-induced hepatocarcinogenesis: implications for human
biotransformation enzyme polymorphisms. Adv Exp Med Biol.
500:559–576. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Kirk GD, Turner PC, Gong Y, et al:
Hepatocellular carcinoma and polymorphisms in
carcinogen-metabolizing and DNA repair enzymes in a population with
aflatoxin exposure and hepatitis B virus endemicity. Cancer
Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 14:373–379. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Smela ME, Currier SS, Bailey EA and
Essigmann JM: The chemistry and biology of aflatoxin B(1): from
mutational spectrometry to carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis.
22:535–545. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Wild CP and Turner PC: The toxicology of
aflatoxins as a basis for public health decisions. Mutagenesis.
17:471–481. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Guengerich FP, Johnson WW, Shimada T, Ueng
YF, Yamazaki H and Langouët S: Activation and detoxication of
aflatoxin B1. Mutat Res. 402:121–128. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Sabbioni G, Skipper PL, Büchi G and
Tannenbaum SR: Isolation and characterization of the major serum
albumin adduct formed by aflatoxin B1 in vivo in rats.
Carcinogenesis. 8:819–824. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Anand P, Kunnumakkara AB, Sundaram C, et
al: Cancer is a preventable disease that requires major lifestyle
changes. Pharm Res. 25:2097–2116. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Wild CP and Hall AJ: Primary prevention of
hepatocellular carcinoma in developing countries. Mutat Res.
462:381–393. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Gescher AJ, Sharma RA and Steward WP:
Cancer chemoprevention by dietary constituents: a tale of failure
and promise. Lancet Oncol. 2:371–379. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Brahmi D, Bouaziz C, Ayed Y, Ben Mansour
H, Zourgui L and Bacha H: Chemopreventive effect of cactus
Opuntia ficus indica on oxidative stress and genotoxicity of
aflatoxin B1. Nutr Metab (Lond). 8:732011.
|
|
60
|
Peterson S, Lampe JW, Bammler TK,
Gross-Steinmeyer K and Eaton DL: Apiaceous vegetable constituents
inhibit human cytochrome P-450 1A2 (hCYP1A2) activity and
hCYP1A2-mediated mutagenicity of aflatoxin B1. Food Chem Toxicol.
44:1474–1484. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Miyata M, Takano H, Guo LQ, Nagata K and
Yamazoe Y: Grapefruit juice intake does not enhance but rather
protects against aflatoxin B1-induced liver DNA damage through a
reduction in hepatic CYP3A activity. Carcinogenesis. 25:203–209.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Cavin C, Marin-Kuan M, Langouët S, et al:
Induction of Nrf2-mediated cellular defenses and alteration of
phase I activities as mechanisms of chemoprotective effects of
coffee in the liver. Food Chem Toxicol. 46:1239–1248. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Gross-Steinmeyer K, Stapleton PL, Tracy
JH, Bammler TK, Strom SC and Eaton DL: Sulforaphane- and phenethyl
isothiocyanate-induced inhibition of aflatoxin B1-mediated
genotoxicity in human hepatocytes: role of GSTM1 genotype and
CYP3A4 gene expression. Toxicol Sci. 116:422–432. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Sotomayor RE, Washington M, Nguyen L,
Nyang’anyi R, Hinton DM and Chou M: Effects of intermittent
exposure to aflatoxin B1 on DNA and RNA adduct formation in rat
liver: dose-response and temporal patterns. Toxicol Sci.
73:329–338. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
McGlynn KA, Hunter K, LeVoyer T, et al:
Susceptibility to aflatoxin B1-related primary hepatocellular
carcinoma in mice and humans. Cancer Res. 63:4594–4601.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Turner PC, Sylla A, Gong YY, et al:
Reduction in exposure to carcinogenic aflatoxins by postharvest
intervention measures in west Africa: a community-based
intervention study. Lancet. 365:1950–1956. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|