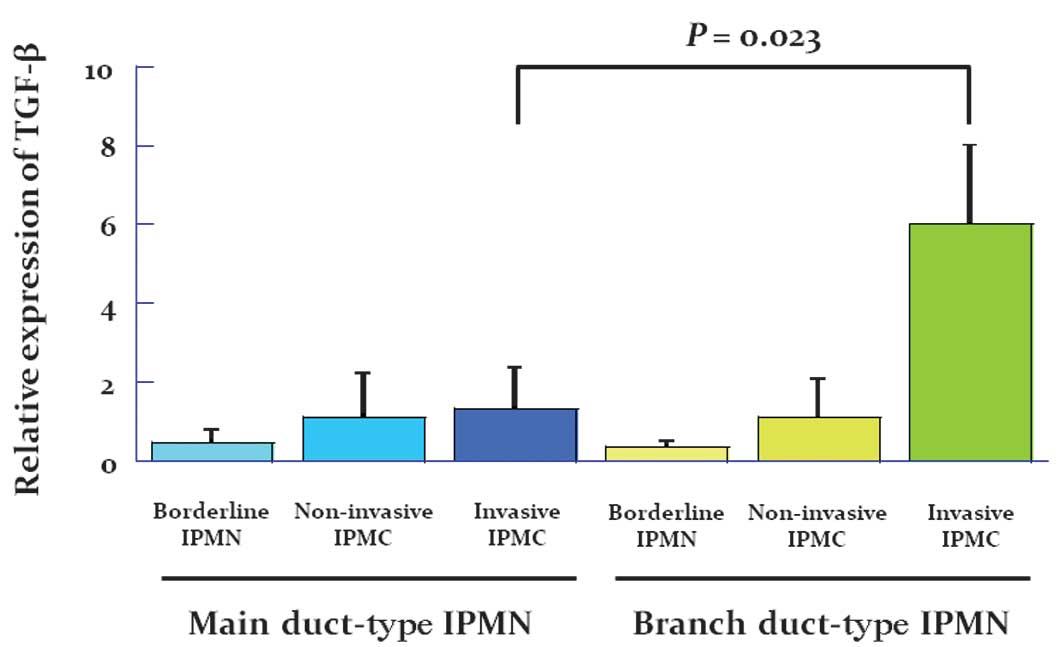
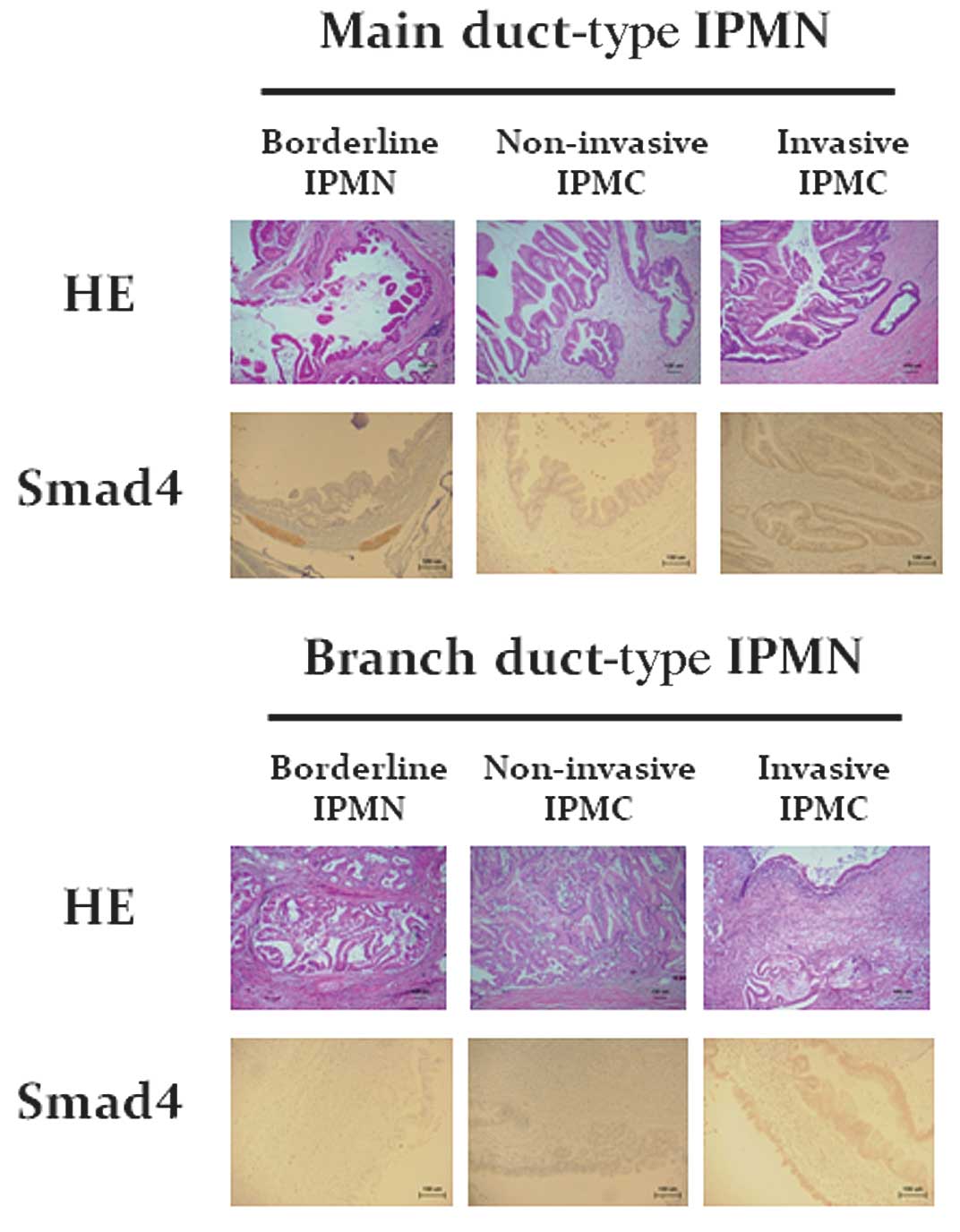
|
1
|
Tanaka M: Controversies in the management
of pancreatic IPMN. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 8:56–60. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mino-Kenudson M, Fernández-del Castillo C,
Baba Y, et al: Prognosis of invasive intraductal papillary mucinous
neoplasm depends on histological and precursor epithelial subtypes.
Gut. 60:1712–1720. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Fernández-del Castillo C and Adsay VN:
Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas.
Gastroenterology. 139:708–713. 2010.
|
|
4
|
Loftus EV Jr, Olivares-Pakzad BA, Batts
KP, et al: Intraductal papillary-mucinous tumors of the pancreas:
clinicopathologic features, outcome, and nomenclature. Members of
the Pancreas Clinic, and Pancreatic Surgeons of Mayo Clinic.
Gastroenterology. 110:1909–1918. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Azar C, Van de Stadt J, Rickaert F, et al:
Intraductal papillary and mucinous tumour of the pancreas. Clinical
and therapeutic issues in 32 patients. Gut. 39:457–464. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tanaka M, Chari S, Adsay V, et al
International Association of Pancreatology: International Consensus
Guidelines for management of intraductal papillary mucinous
neoplasms andmucinous cystic neoplasms of the pancreas.
Pancreatology. 6:17–32. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Salvia R, Fernández-del Castillo C, Bassi
C, et al: Main-duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the
pancreas: clinical predictors of malignancy and long-term survival
following resection. Ann Surg. 239:678–685. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Okabayashi T, Kobayashi M, Nishimori I, et
al: Clinicopathological features and medical management of
intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms. J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
21:462–467. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Uehara H, Ishikawa O, Ikezawa K, et al: A
natural course of main duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm
of the pancreas with lower likelihood of malignancy. Pancreas.
39:653–657. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Arlix A, Bournet B, Otal P, et al:
Long-term clinical and imaging follow-up of nonoperated branch duct
form of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas.
Pancreas. 41:295–301. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Garcea G and Dennison AR: Branch-type
intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms: an update. Pancreatology.
11:336–342. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Okabayashi T, Nishimori I, Maeda H and
Hanazaki K: Incidence of and predictive risk factors for
intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the pancreas with
ordinary pancreatic cancer. J Clin Gastroenterol. 44:75–76. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Matthaei H, Norris AL, Tsiatis AC, et al:
Clinicopathological characteristics and molecular analyses of
multifocal intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the
pancreas. Ann Surg. 255:326–333. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Maguchi H, Tanno S, Mizuno N, et al:
Natural history of branch duct intraductal papillary mucinous
neoplasms of the pancreas: a multicenter study in Japan. Pancreas.
40:364–370. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tanno S, Nakano Y, Nishikawa T, et al:
Natural history of branch duct intraductal papillary-mucinous
neoplasms of the pancreas without mural nodules: long-term
follow-up results. Gut. 57:339–343. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Rautou PE, Lévy P, Vullierme MP, et al:
Morphologic changes in branch duct intraductal papillary mucinous
neoplasms of the pancreas: a midterm follow-up study. Clin
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 6:807–814. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hahn SA, Schutte M, Hoque AT, et al: DPC4,
a candidate tumor suppressor gene at human chromosome 18q21.1.
Science. 271:350–353. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yachida S, Jones S, Bozic I, et al:
Distant metastasis occurs late during the genetic evolution of
pancreatic cancer. Nature. 467:1114–1117. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kang MJ, Jang JY, Kim SJ, et al: Cyst
growth rate predicts malignancy in patients with branch duct
intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms. Clin Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 9:87–93. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Linton K, Hey Y, Dibben S, et al: Methods
comparison for high-resolution transcriptional analysis of archival
material on Affymetrix Plus 2.0 and Exon 1.0 microarrays.
Biotechniques. 47:587–596. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Yang J, Ikezoe T, Nishioka C, et al:
Long-term exposure of gastrointestinal stromal tumor cells to
sunitinib induces epigenetic silencing of the PTEN gene. Int J
Cancer. 130:959–966. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Rodriguez JR, Salvia R, Crippa S, et al:
Branch-duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms: observations
in 145 patients who underwent resection. Gastroenterology.
133:72–79. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Salvia R, Crippa S, Falconi M, et al:
Branch-duct intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the
pancreas: to operate or not to operate? Gut. 56:1086–1090. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Iacobuzio-Donahue CA, Klimstra DS, Adsay
NV, et al: Dpc-4 protein is expressed in virtually all human
intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas:
comparison with conventional ductal adenocarcinomas. Am J Pathol.
157:755–761. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Pedrazzoli S, Sperti C, Pasquali C,
Bissoli S and Chierichetti F: Comparison of International Consensus
Guidelines versus 18-FDG PET in detecting malignancy of intraductal
papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas. Ann Surg.
254:971–976. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Bierie B and Moses HL: Tumour
microenvironment: TGFbeta: the molecular Jekyll and Hyde of cancer.
Nat Rev Cancer. 6:506–520. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zavadil J and Böttinger EP: TGFbeta and
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transitions. Oncogene. 24:5764–5774.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Bardeesy N, Cheng KH, Berger JH, et al:
Smad4 is dispensable for normal pancreas development yet critical
in progression and tumor biology of pancreas cancer. Genes Dev.
20:3130–3146. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Braga M, Capretti G, Pecorelli N, et al: A
prognostic score to predict major complications after
pancreaticoduodenectomy. Ann Surg. 254:702–707. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Poultsides GA, Reddy S, Cameron JL, et al:
Histopathologic basis for the favorable survival after resection of
intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm-associated invasive
adenocarcinoma of the pancreas. Ann Surg. 251:470–476. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|