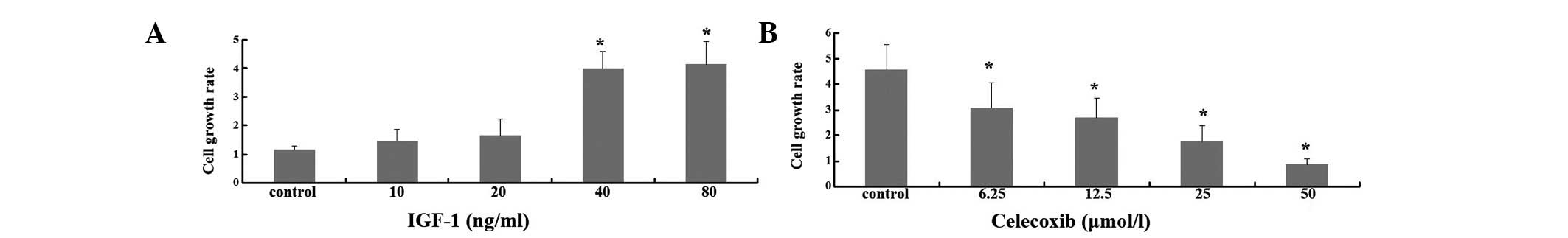
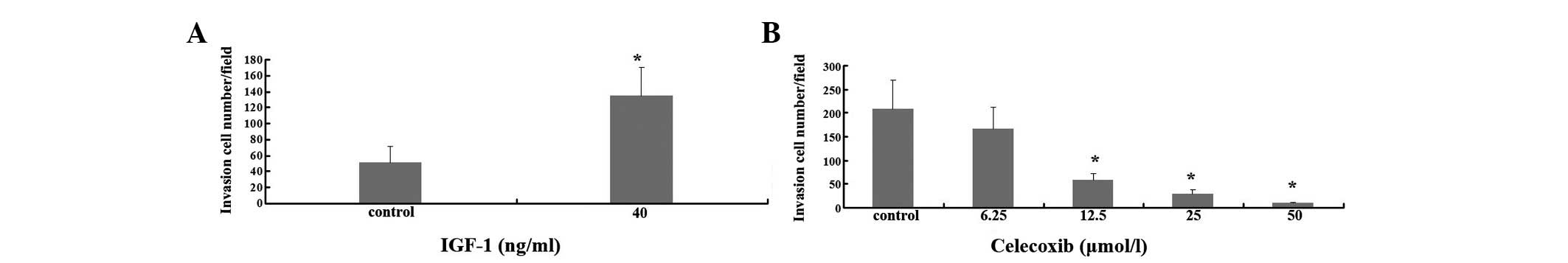
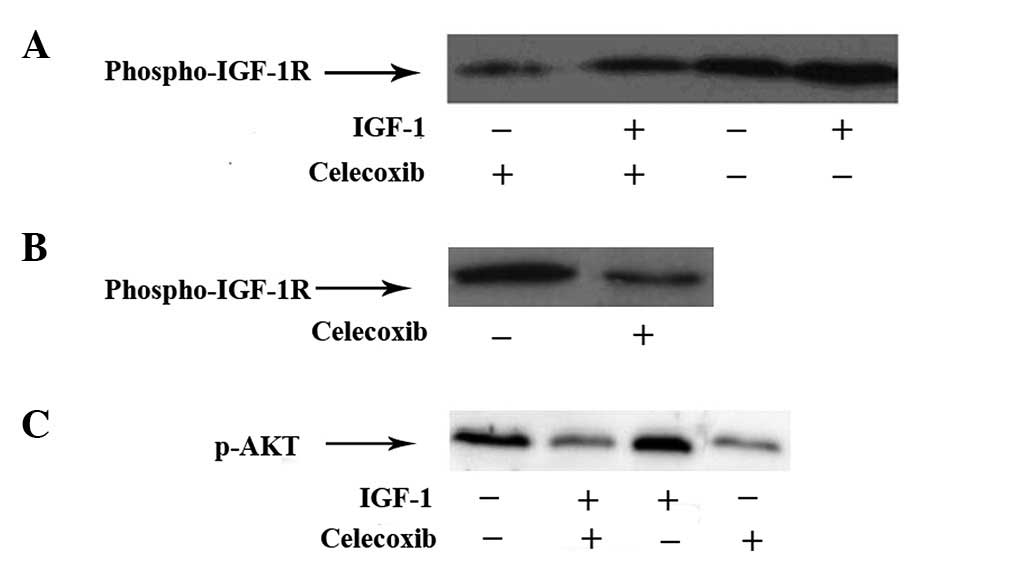
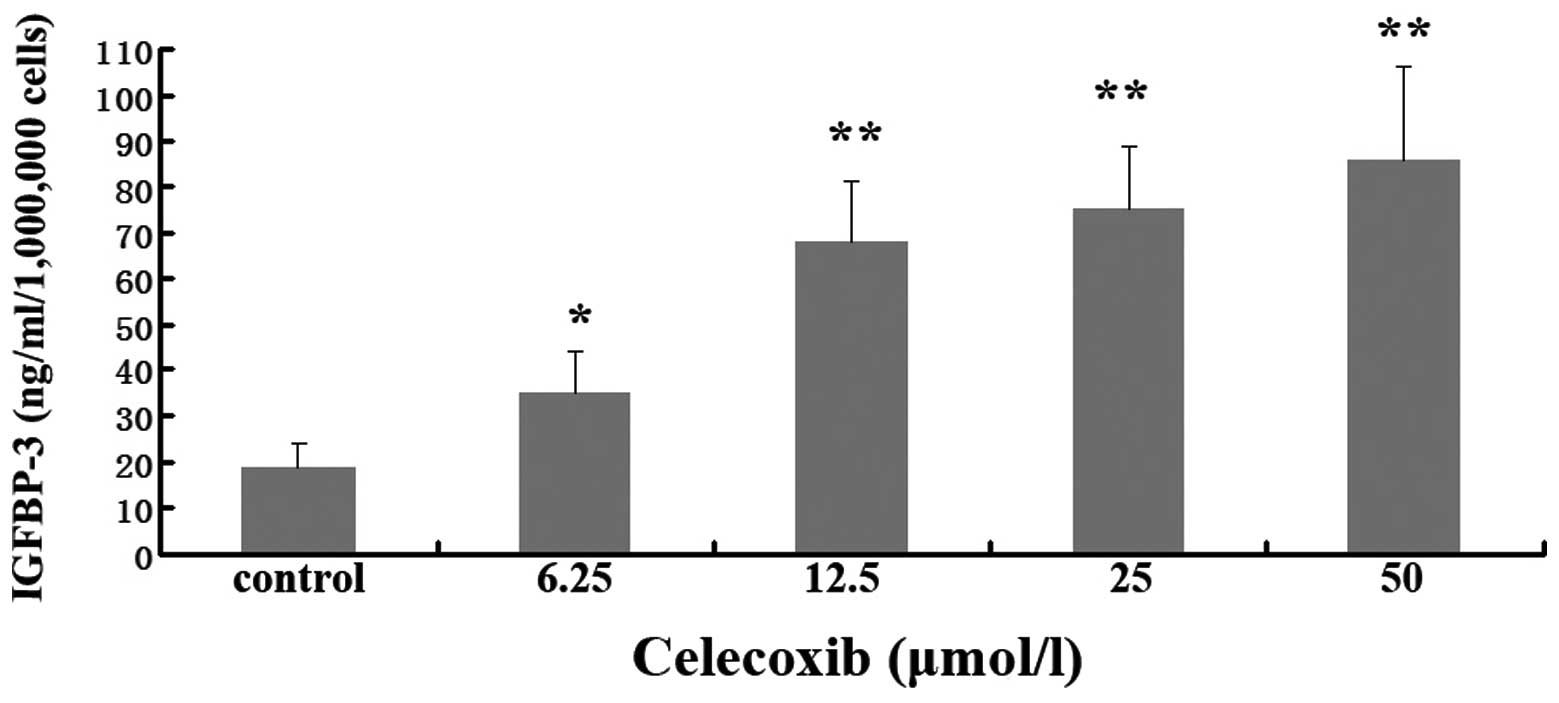
|
1
|
Yasumaru M, Tsuji S, Tsujii M, Irie T,
Komori M, Kimura A, Nishida T, Kakiuchi Y, Kawai N, Murata H,
Horimoto M, Sasaki Y, Hayashi N, Kawano S and Hori M: Inhibition of
angiotensin II activity enhanced the antitumor effect of
cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors via insulin-like growth factor I
receptor pathway. Cancer Res. 63:6726–6734. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mukhopadhyay P, Ali MA, Nandi A, Carreon
P, Choy H and Saha D: The cyclin-dependent kinase 2 inhibitor
down-regulates interleukin-1 beta-mediated induction of
cyclooxygenase-2 expression in human lung carcinoma cells. Cancer
Res. 66:1758–1766. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Põld M, Krysan K, Põld A, Dohadwala M,
Heuze-Vourc’h N, Mao JT, Riedl KL, Sharma S and Dubinett SM:
Cyclooxygenase-2 modulates the insulin-like growth factor axis in
non-small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Res. 64:6549–6555.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Koch A, Bergman B, Holmberg E, Sederholm
C, Ek L, Kosieradzki J, et al: Effect of celecoxib on survival in
patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer: a double blind
randomised clinical phase III trial (CYCLUS study) by the Swedish
Lung Cancer Study Group. Eur J Cancer. 47:1546–1555. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Liu X, Yue P, Zhou Z, Khuri FR and Sun SY:
Death receptor regulation and celecoxib-induced apoptosis in human
lung cancer cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 96:1769–1780. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Liu B, Wen JK, Li BH, Fang XM, Wang JJ,
Zhang YP, Shi CJ, Zhang DQ and Han M: Celecoxib and
acetylbritannilactone interact synergistically to suppress breast
cancer cell growth via COX-2-dependent and -independent mechanisms.
Cell Death Dis. e1852011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jogie-Brahim S, Feldman D and Oh Y:
Unraveling insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 actions in
human disease. Endocr Rev. 30:417–437. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Rodon J, DeSantos V, Ferry RJ Jr and
Kurzrock R: Early drug development of inhibitors of the
insulin-like growth factor-I receptor pathway: lessons from the
first clinical trials. Mol Cancer Ther. 7:2575–2588. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Masago K, Fujita S, Togashi Y, Kim YH,
Hatachi Y, Fukuhara A, Nagai H, Irisa K, Sakamori Y, Mio T and
Mishima M: Clinical significance of epidermal growth factor
receptor mutations and insulin-like growth factor 1 and its binding
protein 3 in advanced non-squamous non-small cell lung cancer.
Oncol Rep. 26:795–803. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gao Y, Katki H, Graubard B, Pollak M,
Martin M, Tao Y, Schoen RE, Church T, Hayes RB, Greene MH and
Berndt SI: Serum IGF1, IGF2 and IGFBP3 and risk of advanced
colorectal adenoma. Int J Cancer. 131:E105–E113. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Teas J, Irhimeh MR, Druker S, Hurley TG,
Hébert JR, Savarese TM and Kurzer MS: Serum IGF-1 concentrations
change with soy and seaweed supplements in healthy postmenopausal
American women. Nutr Cancer. 63:743–748. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Butler AA, Blakesley VA, Poulaki V, Tsokos
M, Wood TL and LeRoith D: Stimulation of tumor growth by
recombinant human insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) is dependent
on the dose and the level of IGF-I receptor expression. Cancer Res.
58:3021–3027. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wu Y, Cui K, Miyoshi K, Hennighausen L,
Green JE, Setser J, LeRoith D and Yakar S: Reduced circulating
insulin-like growth factor I levels delay the onset of chemically
and genetically induced mammary tumors. Cancer Res. 63:4384–4388.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
McCarthy K, Laban C, McVittie CJ,
Ogunkolade W, Khalaf S, Bustin S, Carpenter R and Jenkins PJ: The
expression and function of IGFBP-3 in normal and malignant breast
tissue. Anticancer Res. 29:3785–3790. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Valenciano A, Henríquez-Hernández LA,
Moreno M, Lloret M and Lara PC: Role of IGF-1 receptor in radiation
response. Transl Oncol. 5:1–9. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Yamamoto T, Oshima T, Yoshihara K, Nishi
T, Arai H, Inui K, Kaneko T, Nozawa A, Adachi H, Rino Y, Masuda M
and Imada T: Clinical significance of immunohistochemical
expression of insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor and matrix
metalloproteinase-7 in resected non-small cell lung cancer. Exp
Ther Med. 3:797–802. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wang H, Zhang Q, Zhang L, Little PJ, Xie
X, Meng Q, Ren Y, Zhou L, Gao G, Quirion R and Zheng W:
Insulin-like growth factor-1 induces the phosphorylation of PRAS40
via the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in PC12 cells. Neurosci Lett.
516:105–109. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Qiu R, Chen J, Sima J, Shen X, Liu D and
Shen J: NS398 induces apoptosis in non-small cell lung cancer
cells. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 138:119–124. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shakhar G and Ben-Eliyahu S: Potential
prophylactic measures against postoperative immunosuppression:
could they reduce recurrence rates in oncological patients? Ann
Surg Oncol. 10:972–992. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Ghosh N, Chaki R, Mandal V and Mandal SC:
COX-2 as a target for cancer chemotherapy. Pharmaol Rep.
62:233–244. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Backhus LM, Sievers E, Lin GY, Castanos R,
Bart RD, Starnes VA and Bremner RM: Perioperative cyclooxygenase 2
inhibition to reduce tumor cell adhesion and metastatic potential
of circulating tumor cells in non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac
Cardiovasc Surg. 132:297–303. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Vlachostergios PJ, Gioulbasanis I,
Kamposioras K, Georgoulias P, Baracos VE, Ghosh S, Maragouli E,
Georgoulias V and Papandreou CN: Baseline insulin-like growth
factor-I plasma levels, systemic inflammation, weight loss and
clinical outcome in metastatic non-small cell lung cancer patients.
Oncology. 81:113–118. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Kelly GM, Buckley DA, Kiely PA, Adams DR
and O’Connor R: Serine phosphorylation of the insulin-like growth
factor I (IGF-1) receptor C-terminal tail restrains kinase activity
and cell growth. J Biol Chem. 287:28180–28194. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lee DY, Yi HK, Hwang PH and Oh Y: Enhanced
expression of insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3
sensitizes the growth inhibitory effect of anticancer drugs in
gastric cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 294:480–486.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jones JI and Clemmons DR: Insulin-like
growth factors and their binding proteins: biological actions.
Endocr Rev. 16:3–34. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kozaki K, Koshikawa K, Tatematsu Y,
Miyaishi O, Saito H, Hida T, Osada H and Takahashi T: Multi-faceted
analyses of a highly metastatic human lung cancer cell line
NCI-H460-LNM35 suggest mimicry of inflammatory cells in metastasis.
Oncogene. 20:4228–4234. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Sheppard K, Kinross KM, Solomon B, Pearson
RB and Phillips WA: Targeting PI3 kinase/AKT/mTOR signaling in
cancer. Crit Rev Oncog. 17:69–95. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cappuzzo F, Magrini E, Ceresoli GL,
Bartolini S, Rossi E, Ludovini V, et al: Akt phosphorylation and
gefitinib efficacy in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung
cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 96:1133–1141. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Uddin S, Ahmed M, Hussain A, Assad L,
Al-Dayel F, Bavi P, Al-Kuraya KS and Munkarah A: Cyclooxygenase-2
inhibition inhibits PI3K/AKT kinase activity in epithelial ovarian
cancer. Int J Cancer. 126:382–394
|
|
30
|
Liu B, Qu L, Yang Z and Tao H:
Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors induce anoikis in osteosarcoma via
PI3K/Akt pathway. Med Hypotheses. 79:98–100. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|