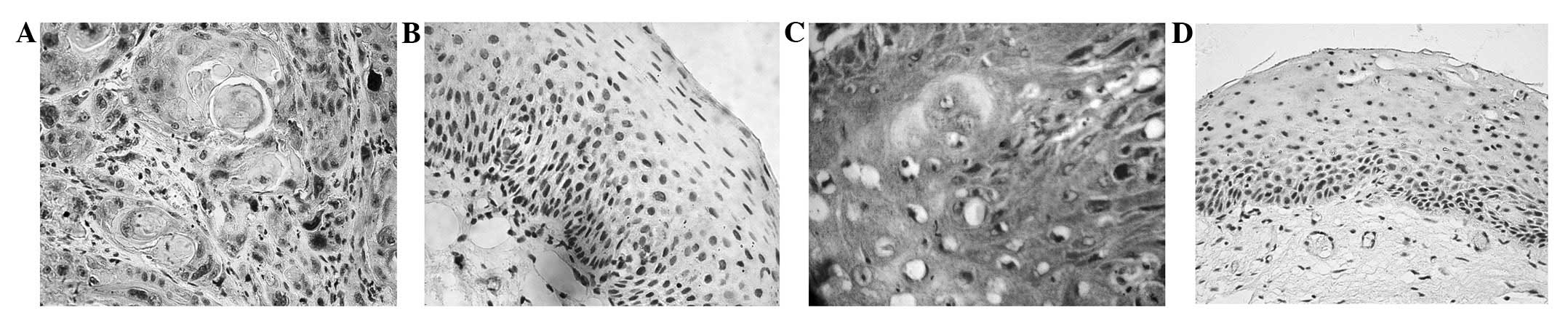
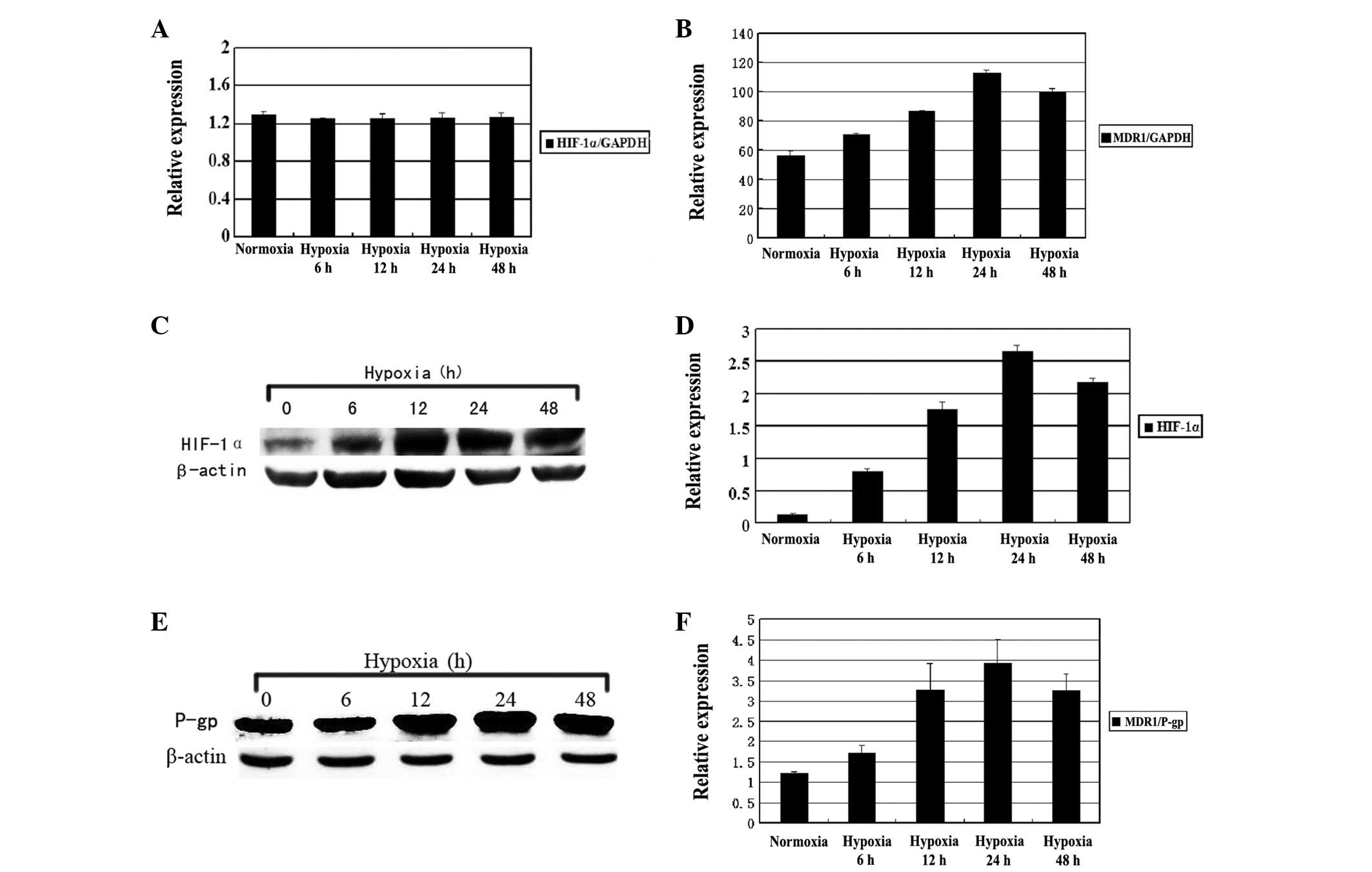
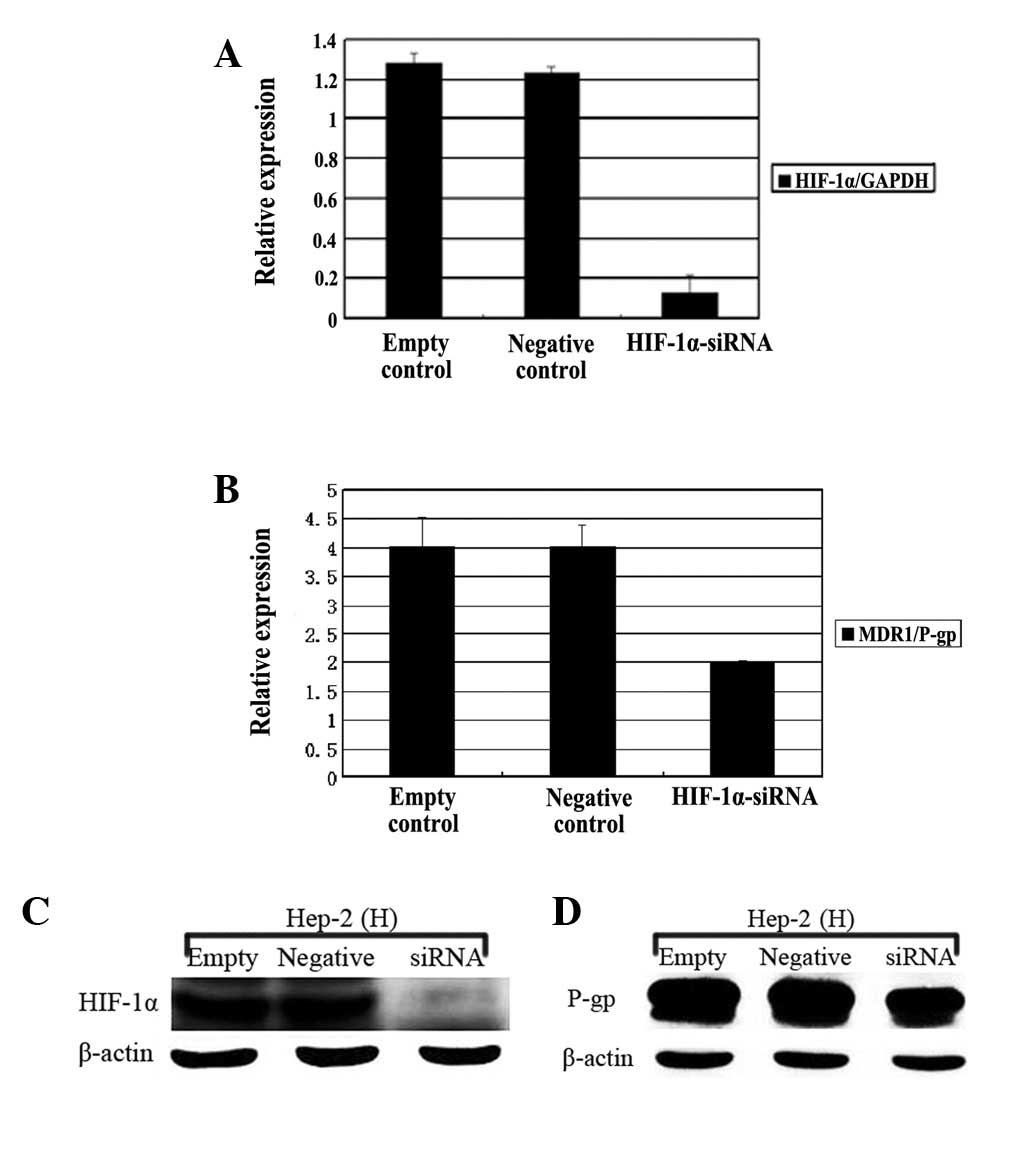
|
1.
|
Wilson WR and Hay MP: Targeting hypoxia in
cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 11:393–410. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2.
|
Li Y and Ye D: Cancer-therapy by targeting
hypoxia-inducible factor-1. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 10:782–796.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
O’Donnell JL, Joyce MR, Shannon AM, Harmey
J, Geraghty J and Bouchier-Hayes D: Oncological implications of
hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha (HIF-1alpha) expression. Cancer
Treat Rev. 32:407–416. 2006.
|
|
4.
|
Liu LZ, Li C, Chen Q, et al: MiR-21
induced angiogenesis through AKT and ERK activation and HIF-1α
expression. PLoS One. 6:e191392011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Park SY, Jang WJ, Yi EY, Jang JY, Jung Y,
Jeong JW and Kim YJ: Melatonin suppresses tumor angiogenesis by
inhibiting HIF-1alpha stabilization under hypoxia. J Pineal Res.
48:178–184. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Jing SW, Wang YD, Kuroda M, et al: HIF-1α
contributes to hypoxia-induced invasion and metastasis of
esophageal carcinoma via inhibiting E-cadherin and promoting MMP-2
expression. Acta Med Okayama. 66:399–407. 2012.
|
|
7.
|
Song G, Ouyang G, Mao Y, Ming Y, Bao S and
Hu T: Osteopontin promotes gastric cancer metastasis by augmenting
cell survival and invasion through Akt-mediated HIF-1alpha
upregulation and MMP9 activation. J Cell Mol Med. 13:1706–1718.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Huang L, Zhang Z, Zhang S, et al:
Inhibitory action of Celastrol on hypoxia-mediated angiogenesis and
metastasis via the HIF-1α pathway. Int J Mol Med. 27:407–415.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Rho JK, Choi YJ, Lee JK, et al: Gefitinib
circumvents hypoxia-induced drug resistance by the modulation of
HIF-1alpha. Oncol Rep. 21:801–807. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Huang C, Xu D, Xia Q, Wang P, Rong C and
Su Y: Reversal of P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance of
human hepatic cancer cells by Astragaloside II. J Pharm Pharmacol.
64:1741–1750. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Wu XH, Lu YF, Hu XD, Mao JY, Ji XX, Yao HT
and Zhou SH: Expression of hypoxia inducible factor-1α and its
significance in laryngeal carcinoma. J Int Med Res. 38:2040–2046.
2010.
|
|
12.
|
Cabanillas R, Rodrigo JP, Secades P,
Astudillo A, Nieto CS and Chiara MD: The relation between
hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1alpha expression with p53
expression and outcome in surgically treated supraglottic laryngeal
cancer. J Surg Oncol. 99:373–378. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13.
|
Hao YX, He ZW, Zhu JH, Shen Q, Sun JZ, Du
N and Xiao WH: Reversal of multidrug resistance in renal cell
carcinoma by short hairpin RNA targeting MDR1 gene. Chin Med J
(Engl). 125:2741–2745. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Li L, Jiang AC, Dong P, Wan Y and Yu ZW:
The characteristics of Hep-2 cell with multiple drug resistance
induced by Taxol. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 137:659–664. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Zhigang H, Qi Z, Jugao F, et al: Reverse
multidrug resistance in laryngeal cancer cells by knockdown MDR1
gene expression. J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 38:440–448.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Ding Z, Yang L, Xie X, et al: Expression
and significance of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha and
MDR1/P-glycoprotein in human colon carcinoma tissue and cells. J
Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 136:1697–1707. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Zhu H, Luo SF, Wang J, et al: Effect of
environmental factors on chemoresistance of HepG2 cells by
regulating hypoxia-inducible factor-1α. Chin Med J (Engl).
125:1095–1103. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Psychogios G, Waldfahrer F, Bozzato A and
Iro H: Evaluation of the revised TNM classification in advanced
laryngeal cancer. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 267:117–121. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Batmunkh E, Shimada M, Morine Y, et al:
Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha (HIF-1alpha) in
patients with the gallbladder carcinoma. Int J Clin Oncol.
15:59–64. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Ng IO, Liu CL, Fan ST and Ng M: Expression
of P-glycoprotein in hepatocellular carcinoma. A determinant of
chemotherapy response. Am J Clin Pathol. 113:355–363. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Sowter HM, Raval RR, Moore JW, Ratcliffe
PJ and Harris AL: Predominant role of hypoxia-inducible
transcription factor (Hif)-1alpha versus Hif-2alpha in regulation
of the transcriptional response to hypoxia. Cancer Res.
63:6130–6134. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2[-Delta Delta C(T)] Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
|
|
23.
|
Li L, Jiang AC, Dong P, Wang H, Xu W and
Xu C: MDR1/P-gp and VEGF synergistically enhance the invasion of
Hep-2 cells with multidrug resistance induced by taxol. Ann Surg
Oncol. 16:1421–1428. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Miletti-González KE, Chen S, Muthukumaran
N, et al: The CD44 receptor interacts with P-glycoprotein to
promote cell migration and invasion in cancer. Cancer Res.
65:6660–6667. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Tokunaga Y, Hosogi H, Hoppou T, Nakagami
M, Tokuka A and Ohsumi K: Effects of MDR1/P-glycoprotein expression
on prognosis in advanced colorectal cancer after surgery. Oncol
Rep. 8:815–819. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Sagol O, Yavuzsen T, Oztop I, et al: The
effect of apoptotic activity, survivin, Ki-67, and P-glycoprotein
expression on prognosis in pancreatic carcinoma. Pancreas.
30:343–348. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Wartenberg M, Ling FC, Müschen M, et al:
Regulation of the multidrug resistance transporter P-glycoprotein
in multicellular tumor spheroids by hypoxia-inducible factor
(HIF-1) and reactive oxygen species. FASEB J. 17:503–505.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Xia S, Yu SY, Yuan XL and Xu SP: Effects
of hypoxia on expression of P-glycoprotein and multidrug resistance
protein in human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cell line. Zhonghua Yi
Xue Za Zhi. 84:663–666. 2004.(In Chinese).
|
|
29.
|
Song X, Liu X, Chi W, Liu Y, Wei L, Wang X
and Yu J: Hypoxia-induced resistance to cisplatin and doxorubicin
in non-small cell lung cancer is inhibited by silencing of
HIF-1alpha gene. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 58:776–784. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Liu L, Ning X, Sun L, et al:
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha contributes to hypoxia-induced
chemoresistance in gastric cancer. Cancer Sci. 99:121–128.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31.
|
Min L, Chen Q, He S, Liu S and Ma Y:
Hypoxia-induced increases in A549/CDDP cell drug resistance are
reversed by RNA interference of HIF-1α expression. Mol Med Report.
5:228–232. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|